Of Duroplast and Technopolymer Plastics.Indd
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Metalized Plastic Articles and Methods Thereof Metallisierte Kunststoffartikel Und Verfahren Dafür Articles Plastiques Métallisés Et Procédés Associés
(19) TZZ Z¥_T (11) EP 2 420 593 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention (51) Int Cl.: of the grant of the patent: C23C 18/20 (2006.01) H05K 3/42 (2006.01) 03.04.2013 Bulletin 2013/14 C23C 18/32 (2006.01) C23C 18/38 (2006.01) H05K 3/38 (2006.01) H05K 3/46 (2006.01) (2006.01) (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11173897.7 C25D 5/12 C25D 5/56 H05K 3/18 (2006.01) (22) Date of filing: 14.07.2011 (54) Metalized Plastic Articles and Methods Thereof Metallisierte Kunststoffartikel und Verfahren dafür Articles plastiques métallisés et procédés associés (84) Designated Contracting States: •ZHOU,Liang AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB 518118 Shenzhen (CN) GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO • MIAO, Weifeng PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR 518118 Shenzhen (CN) • ZHANG, Xiong (30) Priority: 19.08.2010 CN 201010260236 518118 Shenzhen (CN) (43) Date of publication of application: (74) Representative: Gulde Hengelhaupt Ziebig & 22.02.2012 Bulletin 2012/08 Schneider Patentanwälte - Rechtsanwälte (73) Proprietor: BYD Company Limited Wallstrasse 58/59 Shenzhen 518118 (CN) 10179 Berlin (DE) (72) Inventors: (56) References cited: • GONG, Qing EP-A1- 1 650 249 US-A- 3 546 011 518118 Shenzhen, (CN) US-A- 4 767 665 US-A- 5 162 144 Note: Within nine months of the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent in the European Patent Bulletin, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to that patent, in accordance with the Implementing Regulations. -

Marabu Pad Printing Ink Chart
MARABU PAD PRINTING INK CHART PAD PAD PAD PAD PAD-SCREEN PAD-SCREEN PAD PAD PAD-SCREEN PAD-SCREEN PAD-SCREEN PAD-SCREEN PAD-SCREEN SCREEN-PAD TAMPAFLEX TAMPAGRAPH TAMPASTAR TAMPAPLUS TAMPAPOL TAMPAPUR TAMPATECH TAMPACURE GLASS INK LIBRASTAR MARAFLEX MARALOX MARAPROP MARAPUR PRODUCT TPF TPGR TPR TPL TPY TPU TPT TPC (UV) GL HF FX LX PP PU INFORMATION DEGREE OF HIGH GLOSS GLOSSY GLOSSY GLOSSY GLOSSY HIGH GLOSS HIGH GLOSS HIGH GLOSS SATIN GLOSS GLOSSY SATIN GLOSS HIGH GLOSS SATIN GLOSS HIGH GLOSS GLOSS DRYING FAST FAST VERY FAST VERY FAST FAST MEDIUM MEDIUM FAST MEDIUM FAST FAST SLOW FAST SLOW TYPE OF DRYING REACTIVE PHYSICAL PHYSICAL PHYSICAL PHYSICAL REACTIVE REACTIVE REACTIVE REACTIVE PHYSICAL PHYSICAL PHYSICAL PHYSICAL REACTIVE INK SYSTEM - 2C 1C or 2C 1C OR 2C 1C or 2C 1C or 2C 2C 2C 1C or 2C 2C 1C or 2C 1C 1C 1C 2C COMPONENTS RUB AND INTERIOR AND CHEMICAL CHEMICAL GASOLINE GASOLINE GASOLINE DISHWASHER SCRATCH, OUTDOOR RESISTANCE CHEMICALS MECHANICAL CHEMICALS CHEMICALS ALCOHOL MEDIUM OUTDOOR HIGH FLEXIBILITY ALCOHOL ALCOHOL ALCOHOL ALCOHOL PROOF DOMESTIC USECHEMICAL RESISTANT CLEANERS AND MECHANICAL THERMOPLASTIC UNIVERSAL USE, GOOD HALOGEN FREE, EXCELLENT GOOD GOOD FADE AND ELASTOMERS, GOOD DISHWASHER NON PRE- QUALITIES UNIVERSAL USE UNIVERSAL USE GOOD HIGH RESISTANCE PRINTABILITY, HIGH RESISTANCE CANADIAN LAMINATING PRINTABILITY, WEATHER SOFT-TOUCH RESISTANCE PROOF TREATED PP PRINTABILITY LONG POT LIFE STANDARDS ABILITY VERY MILD RESISTANCE VARNISHES AUXILLIARIES TPF TPGR TPR TPL TPY TPU TPT TPC (UV) GL HF FX LX PP PU TPV,TPV2,TPV3 -

Planning Aids and Basic Knowledge Connection and Fastening Systems
VBS Planning aids and basic knowledge Connection and fastening systems Building Connections Contact Customer Service +49 23 73 89 - 17 00 Service times Monday to Friday 09.00 to 18.00 +49 (0)2371 7899-2500 [email protected] www.obo.de 01_VBS / en / 2019/02/21 09:33:37 09:33:37 (LLExport_02514) / 2019/02/21 09:34:05 09:34:05 2 01_VBS / en / 2019/02/21 09:33:37 09:33:37 (LLExport_02514) / 2019/02/21 09:34:05 09:34:05 3 VBS – Connection and fastening systems VBS is one of a total of name from one of the most that it can be fitted seven OBO product units, successful ever products “Ohne BOhren”, that is, but of those it is one of the from the VBS product unit without the need for any longest-standing and most – the OBO anchor, a metal drilling. extensive. Indeed, OBO anchor invented in 1952 Bettermann takes part of its that offers the advantage 01_VBS / en / 2019/02/21 09:33:37 09:33:37 (LLExport_02514) / 2019/02/21 09:34:05 09:34:05 4 VBS – Connection and fastening systems Distribution • Junction box systems • Concealed and cavity wall systems • Terminal systems • Cable gland systems Fastening • Beam clamp systems • Rail systems • Clamp clip systems • Screw-in and knock-in systems 01_VBS / en / 2019/02/21 09:33:37 09:33:37 (LLExport_02514) / 2019/02/21 09:34:05 09:34:05 5 Routing • Cable and pipe fastening systems • Pipe systems 01_VBS / en / 2019/02/21 09:33:37 09:33:37 (LLExport_02514) / 2019/02/21 09:34:05 09:34:05 6 Plastic: materials and properties Essentially plastics can be of one of three types: ther- Elastomers moplastics, elastomers and Duroplast. -

Trade Marks Journal No: 1933 , 23/12/2019 Class 14 3004906 09
Trade Marks Journal No: 1933 , 23/12/2019 Class 14 3004906 09/07/2015 VIKAS CHAIN AND JEWELLERY PVT. LTD. 1157/1124, 2nd floor, Kucha Mahajani, Chandni Chowk, Delhi - 110006, India. SERVICE PROVIDERS A COMPANY INCORPORATED UNDER THE COMPANIES ACT, 1956 Proposed to be Used To be associated with: 3004880 DELHI JEWELLERY, GEMSTONES^ PEARLS, PRECIOUS METALS & THEIR ALLOYS, GOODS IN PRECIOUS METALS OR COATED THEREWITH, IMITATIONS THEREOF; STATUES, FIGURINES & OTHER ARTICLES OF PRECIOUS METALS, PRECIOUS STONES, IMITATIONS THEREOF MADE OF OR COATED WITH PRECIOUS OR SEMI-PRECIOUS METALS OR STONES; ORNAMENTS MADE OF OR COATED WITH PRECIOUS OR SEMI-PRECIOUS METALS OR STONES, OR IMITATIONS THEREOF; COINS AND TOKENS; WORKS OF ART OF PRECIOUS METALS, KEY RINGS, TRINKETS OR FOBS; JEWELLERY BOXES, WATCH BOXES; HOROLC^ICAL & OTHER CHRONOMETRIC INSTRUMENTS; THIS IS SUBJECT TO ASSOCIATION WITH REGISTERED/PENDING REGISTRATION NO..3004880. 2647 Trade Marks Journal No: 1933 , 23/12/2019 Class 14 3018537 27/07/2015 SMT. SUNITA SHARMA W/O. SH. KAILASH SHARMA trading as ;RIYO GEMS 50, MAHAVEER NAGAR, TONK ROAD, JAIPUR-302018 Rajasthan Manufacturer and merchants trading as PROPRIETORSHIP FIRM Address for service in India/Agents address: G. D. BANSAL & ASSOCIATES. M-118-B, MAHESH COLONY, LAXMI MANDIR PHATAK, JAIPUR - 302 015. (RAJASTHAN) Used Since :24/05/1994 AHMEDABAD Gems & Jewellery, Precious Stones, Precious metals and their alloys and goods in precious metals or coated therewith. 2648 Trade Marks Journal No: 1933 , 23/12/2019 Class 14 PINKCITY CRAFT 3195492 25/02/2016 MANISH KHATRI trading as ;PINKCITY CRAFT 87, ARPIT NAGAR, GANDHI PATH, VAISHALI NAGAR, JAIPUR (RAJ) MANUFACTURER & MERCHANT PROPRIETOR Address for service in India/Attorney address: ROHIT JAIN, ADVOCATE F1/163, GANDHI PATH, CHITRAKOOT, VAISHALI NAGAR, JAIPUR - RAJASTHAN - 302021 Used Since :05/11/2015 AHMEDABAD ARTIFICIAL JEWELLERY, JEWELLERY, PRECIOUS AND SEMI PRECIOUS STONES, WATCHES UNDER CLASS 14. -

Product Range Technical Rubber Products Edition 2010-10
Product Range Technical Rubber Products Edition 2010-10 Fluoroelastomers (FKM) Chloroprene rubber (CR) Hydrogenated acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (HNBR) Ethylene-vinyl acetate rubber (EVM) Ethylene-vinyl acetate rubber (EVM) Ethylene-vinyl acetate rubber (EVM) Ethylene-propylene rubber (EPM/EPDM) Butadiene/butadiene-styrene based nanoadditives (SBR) Acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR) Powdered acrylonitrile-butadiene Acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR) rubber (NBR) Synthetic rubber from LANXESS has versatility and peak performance in its genes - making your projects work and speeding up your business. www.lanxess.com LANXESS Technical Rubber Products LANXESS is a globally operating supplier of specialty elastomers for the rub- ber-processing industry with a broad product range, tailored to meet the requirements of a wide variety of applications: in automotive engineering, electronics, construction, mechanical engineering, industrial plants, oil exploration, aviation, domestic goods and many other industries. Resistance to abrasion, heat and aggressive environmental influences are just a few of the excellent properties which make our products so attractive to our international customers. This brochure gives information on our portfolio of Technical Rubber Products. The rubber grades belonging to one category are listed in the same table. The tables give data on the chemical composition, supply form, standard packaging, the most important characteristic data, the basic properties and the main fields of application for each product. For further or more detailed information please do not hesitate to contact our local experts. You will find their addresses at the end of this brochure. For information on food contact applications, please contact the Health, Safety, Environment and Quality Department (HSEQ) of LANXESS Germany or, for business in the USA, the LANXESS Product Safety and Regulatory Affairs Department in Pittsburgh, PA. -

Capacitive Sensors
CONTENTS Capacitive Sensors General Information 62 Calibration 65 Miniature Caps 66 Mini Cap Discs 67 Sensor Amplifiers 68 DC Sensors 69 AC Sensors 71 DC Level 73 AC Level 74 High Temp Level 75 61 CAPACITIVE SENSORS GENERAL INFORMATION Application Repeat accuracy Material correction factor Capacitive proximity switches may be used to The repeat accuracy parameter describes the If the material of the object in question is not metal detect non-metallic and metallic materials. They maximum deviation from the sensing distance or water, the rated sensing distance (Sn) is can be utilised as contact or non-contact sensors when the object in question is approached several reduced. The reduction factors for the different depending upon the application and the sensing times. materials are given in the table below. medium concerned. Capacitive sensors may be used for controlling and monitoring machine Rated sensing distance (Sn) Material Thickness 3 r Reduction processes or as primary detectors for product The rated sensing distance is the usable sensing d/mm factor counting. Level indication for liquids or granular distance of a sensor when directed at a metal Steel ST-37 1.5 1.0 substances can be achieved either through the plate. In accordance with DIN VDE 0660 Part 208, Brass Ms 1.5 1.0 outer container or with direct contact with the it is a 1-mm-thick square metal plate, consisting of Water approx. 81 1.0 medium itself. We distinguish between two areas carbon steel Type FE 360 (definition to ISO Mikanit 132 2 4.5 0.44 of application for capacative sensors: 630:1980). -

Technical Data Index
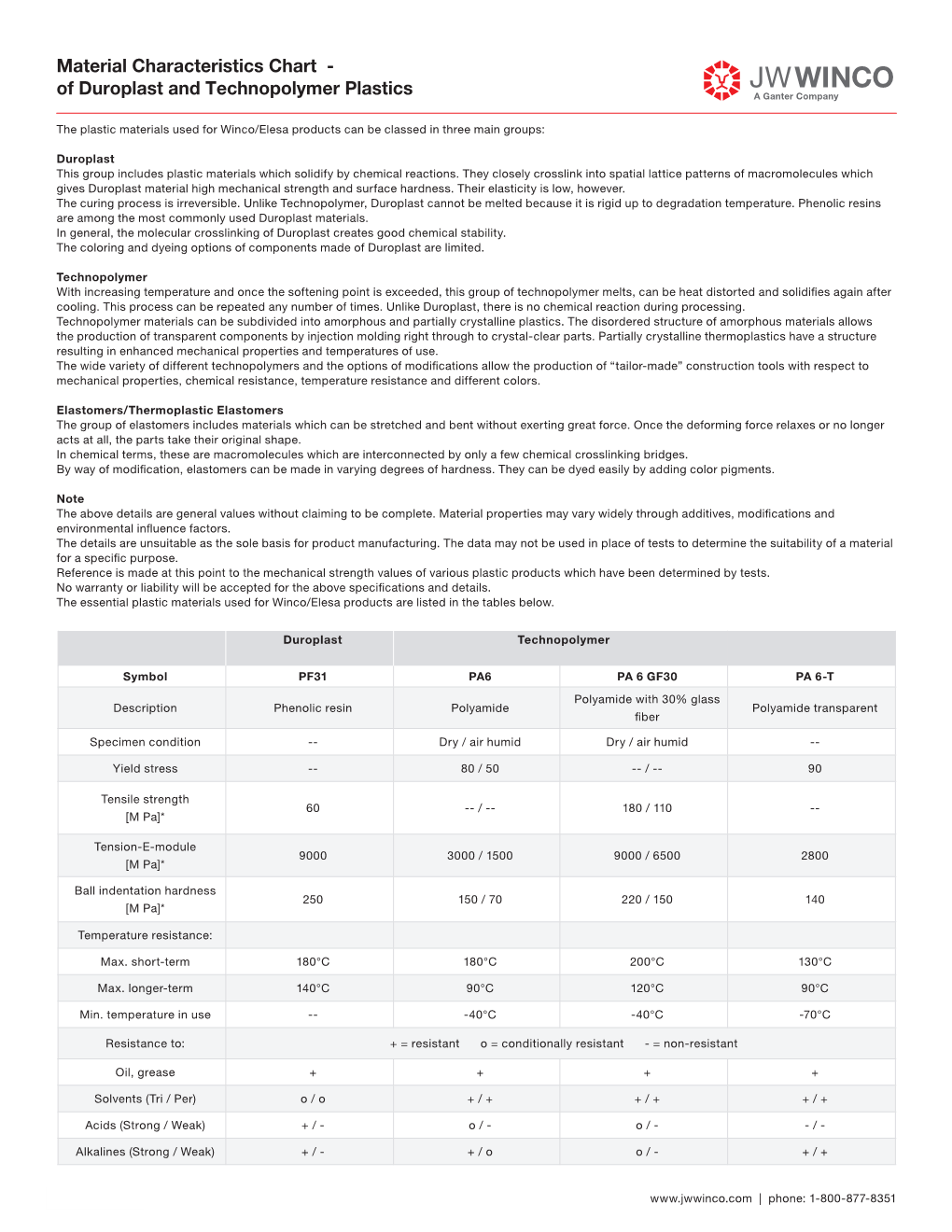
TECHNICAL DATA INDEX 1. Plastic materials A2 1.1 Mechanical strength A2 1.2 Thermal resistance A3 1.3 Strength and surface hardness A4 1.4 Resistance to chemical agents A4 1.5 Resistance to atmospheric agents and UV rays A4 1.6 Flame resistance A5 1.7 Electrical properties A6 1.8 Surface finish and cleanability A6 1.9 Compliance with international standards A7 1.10 Competence of ELESA+GANTER Technical Department A9 2. Metal materials A9 2.1 Properties of metal inserts A10 2.2 Clamping knobs with threaded inserts A10 2.3 Pass-through holes A11 2.4 End of threaded studs A11 2.5 Seizure risk with stainless steel threaded couplings A11 3. Other materials A11 4. Machine tolerances A12 5. Fixed handles A13 6. Assembly measures A14 7. Special executions A14 8. Colours A14 9. Test values A15 10. Technical tables A15 10.1 Conversion tables A15 10.2 DIN 79 Squareholes and shafts A16 10.3 DIN 6885 Keyways A16 10.4 GN 110 and GN 110.1 Transversal holes A17 10.5 DIN 13 ISO Metric threads A19 10.6 DIN 228 Cylindrical GAS-BSP threads A20 A B C 10.7 DIN EN ISO 898-1 | DIN EN 20898-2 Strength values A20 10.8 DIN ISO 286 ISO Fundamental tolerances A21 10.9 IP Protection classification A23 10.10 Thread lockings (PFB, PRB, MVK, GPC) A24 10.11 Stainless Steel characteristics A26 10.12 Surface treatments A29 10.13 Carbon steel, zinc alloys, aluminium, brass characteristics A31 10.14 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics A32 Technical Data Technical 10.15 Load ratings U-Handles A35 10.16 Load ratings metal hinges A40 10.17 Strength of indexing plungers A42 10.18 Assembly sets GN 965 and GN 968 A44 11. -

US5194334.Pdf
|||||||||||| US005194334A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,194,334 Uerdingen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 1993 (54) PROCESS FOR THE PRODUCTION OF 52 U.S.C. .................................... 428/416; 156/196; SHEET METAL/ DUROPLAST COMPOSTE 156/245; 156/315; 264/135; 525/31 ELEMENTS (56) References Cited 75) Inventors: Walter Uerdingen, Leverkusen; Bert U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS Brassat, Krefeld; Karl-Ludwig Noble, 2,384,269 9/1945 Bake................ ... 56/315 Cologne; Bernhard Hess, Moers; 3,508,951 4/1970 Shimp et al. ... ... 525/31 Heino Miller, Leverkusen; Heinz 3,551,517 12/1970 Dowbenko et al. ... 428/416 Eichner, Moenchen-Gladbach, all of 3,844,030 i0/1974 Wilkinson ........... ... 264/135 Fed. Rep. of Germany 4,673,706 6/1987 Atkins ................................... 525/31 73) Assignee: DSM. N.V., Heerlen FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 0182642 10/1986 European Pat. Off. 21 Appl. No.: 603,264 55-117653 9/1980 Japan ................................... 428/416 Primary Examiner-John J. Gallagher (22) Filed: Oct. 25, 1990 Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Connolly & Hutz Related U.S. Application Data (57) ABSTRACT 63) Continuation of Ser. No. 208,675, Jun. 20, 1988, aban The use of molding compositions based on unsaturated doned. polyester resins containing specific reactive groups and of sheet metals with a specially selected coating results (30) Foreign Application Priority Data in sheet metal/duroplast composite elements having Jul. 2, 1987 (DE) Fed. Rep. of Germany ....... 3721849 excellent adhesion. 51) int. Cl........................... B32B 15/08; C09J 5/04 12 Claims, No Drawings 5,194,334 1. 2 cured without shrinking so that they are free from inter PROCESS FOR THE PRODUCTION OF SHEET naq stresses, sink marks and wavyness after cooling. -

Kunststoff - Brennprobe
Kunststoff - Brennprobe Bestimmen von 12 thermoplastischen Kunststoffen mit Hilfe von: Feuerzeug und unseren 5 Sinnen • Polyethylen LDPE • Polyethylen HDPE • Polypropylen PP • Polystyrol PS • Polyoximethylen POM • Acrylnitril-Butadien-Styrol-Copolymer ABS • Polymetylmethacrylat PMMA • Polyvinylchlorid PVC • Polyamid PA • Polyester PET • Polycarbonat PC • Polyurethane TPU Magic Science Urs Gfeller Thunstrasse 80 CH-3400 Burgdorf 079 315 40 45 www.magicscience.ch [email protected] In Zusammenarbeit mit: Prof. Dr. Kramer Leiter MAS Kunststofftechnik Entwicklungspartner: Produktionspartner: Weitere Unterstützung durch: • Aareplast AG • Pfister Werkzeugbau AG • Bützer AG • Röhm Schweiz AG • Eastman AG • Säntis Packaging AG • Fischer Söhne AG • Semadeni AG • Jansen AG • Wild & Küpfer AG • Lambrecht AG Auflage 2 / Oktober / 2017 0 Inhalte 1 Was sind Kunststoffe? ........................................................... 1 2 Strukturen .............................................................................. 2 3 Zusatzstoffe ........................................................................... 3 4 Eigenschaften ........................................................................ 4 5 Verarbeitungsverfahren ......................................................... 5 6 Low Density Polyethylen LDPE ............................................. 8 7 High Density Polyethlen HDPE ............................................. 9 8 Polypropylen PP ..................................................................10 9 Polystyrol PS .......................................................................11 -
Rethinking Plastic a Credible, Dynamic Label for Pioneers in Plastic Reduction
2 rethinking plastic A credible, dynamic label for pioneers in plastic reduction. Welcome! 4 Shining a spotlight on plastic-free “After shopping for my family of five, I usually end up with at least one rubbish bag full of plastic that I’ve only used once. More than half of this bag’s contents gets burned – delicately termed ‘thermal recycling’. It doesn’t feel right, especially not when I think about my children and the generations to come. The idea for Flustix was born out of my wish to change things: it is a certification label that indi- cates the sustainable use of plastics in products. We provide a solution to the plastic problem with this initiative. And it’s a solution that is easy to integrate into daily life. Our label for consumers provides cle- ar guidance which enables everybody to contribute to environmental conservation. Avoiding plastics is an issue that concerns us all. If nature does not re- main intact, we will cause lasting damage to our- selves. With Flustix, we are starting something that every single person can participate in and effect change with.” Malte Biss, FLUSTIX Founder Large areas of ocean already contain six times more plastic than plankton. 7 8 rethink plastics Content Flustix: the plastic-free label, definition...................................................12 Requirements, licensing and labelling options.........................................14 Research into plastic....................................................................................16 Communicating sustainability.....................................................................18 -
WIAC Draft V2.Indd
What are composites? A short guide to fibre reinforced polymer composites, why they are useful and how they are made COMPOSITES Composites LEADERSHIP Trade Association FORUM Who are we? What is a composite? Composites UK is the trade association for the A composite material is composed of at least two materials, which combine UK composites industry. It acts to encourage to give properties superior to those of the individual constituents. Composites continuous growth and development of the Trade Association industry, promoting good practice. Its role is to This guide refers to fibre reinforced polymer (FRP) composites, usually with bring companies throughout the supply chain carbon, glass, aramid, polymer or natural fibres embedded in a polymer together, creating partnerships, as well as being a unified voice to drive the matrix. Other matrix materials can be used and composites may also industry forward. contain fillers or nano-materials such as graphene. compositesuk.co.uk The many component materials and different processes that can be used make composites extremely versatile and efficient. They typically result in The National Composites Centre (NCC) is a lighter, stronger, more durable solutions compared to traditional materials. research and development centre and is part of the High Value Manufacturing Catapult. The NCC mission is to accelerate the growth of UK industrial output by enabling design and manufacturing Growth in the composites industry enterprises to deliver winning solutions in the application of composites. nccuk.com The composites industry is an exciting industry to work in because new materials, processes and applications are being developed all the time – The Composites Leadership Forum is working like using hybrid virgin and recycled fibres, faster and more automated to influence the government and other bodies COMPOSITES manufacturing. -

OC-Kapitel 17 : Kunststoffe
OC-Kapitel: 17 Kunststoffe 1 OC-Kapitel 1 7 : Kunststoffe Freies Lehrbuch der organischen Chemie von H. Hoffmeister und C. Ziegler (unter GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 (GPL)). Die jeweils aktuellste Fassung finden Sie unter: https://hoffmeister.it/index.php/chemiebuch-organik https://hoffmeister.it - 27.06.21 OC-Kapitel: 17 Kunststoffe 2 Inhalt OC-Kapitel 17: Kunststoffe.............................................................................................................................1 Inhalt.......................................................................................................................................................... 2 Mögliche Referate.....................................................................................................................................3 Was sind Kunststoffe?...............................................................................................................................4 Untersuchung von Kunststoffen.................................................................................................................5 Unterscheidung von Kunststoffen..............................................................................................................6 Allgemeines zu Kunststoffen: Was sind Kunststoffe?................................................................................7 Gemeinsame Eigenschaften von Kunststoffen:.....................................................................................7 Grundsätzlicher Aufbau von Kunststoffen.............................................................................................7