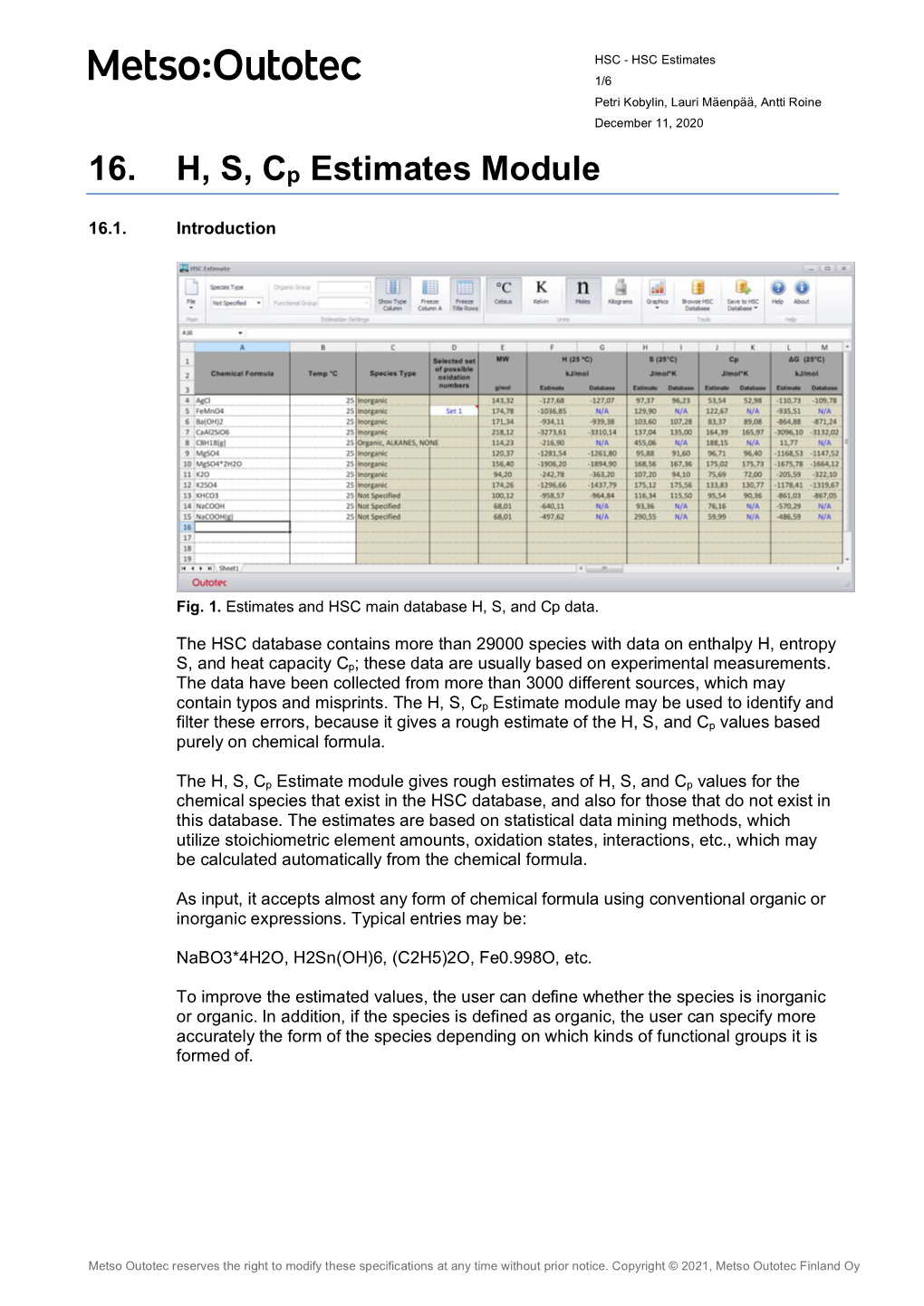
16. H, S, Cp Estimates Module
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Impurity Control in Copper Metallurgical Plants with Special Focus on Arsenic Oct 2018 17
Impurity Control in Copper Metallurgical Plants with Special Focus on Arsenic Oct 2018 17, George P. Demopoulos* Department of Mining and Materials Engineering, McGill University *[email protected] https://www.mcgill.ca/materials/people/faculty/george-p- Seminar Impurity JOGMEC demopoulos P1resented at the Int’l Seminar on Impurities in Copper 1 Raw Materials, Tokyo, Japan, October 2018 Towards Sustainable Metallurgical Processes • Impurity control- a must in making the Copper metallurgical industry sustainable! • Development of sustainable processes means Oct Oct 2018 17, innovation • Meet economic and environmental goals simultaneously • Innovation needs research collaborations Seminar Impurity JOGMEC • This series of seminars is an excellent initiative… 2 Sustainability Aspects of Impurity Control Technologies-1 • Consider deportment of impurities throughout the whole process flowsheet for best intervention strategy Oct Oct 2018 17, • Work towards clean impurity-specific separation approaches to minimize valuable metal loss, reagent usage, or intro of new pollutants: SX (residual organics?), IX, Molecular Recognition Technology (MRT), magnetic resins, selective precipitation, Sorption/Adsorption etc. Seminar Impurity JOGMEC • Equally important to get enrichment-concentration to 3 facilitate economic recovery and/or disposal Sustainability Aspects of Impurity Control Technologies-2 • Consider recovery if there is demand of the impurity as by-product; Oct 2018 17, Example: Se, Te, Sb, Bi in Cu industry: Can be sold as feedstock -

Ore Processing in Fluidized Bed Technologies Overview • Fundamentals in Fluidized Bed Technology
Ore processing in fluidized bed technologies Overview • Fundamentals in fluidized bed technology. • Outotec‘s experience in fluidized bed technologies. • CFB/FB applications for iron containing ores. • CFB aplications for alumina calcination. • Technology and project development. © Outotec – All rights reserved Fluidized bed systems - fundamentals Bubbling Circulating Transport or flash fluidized bed fluidized bed reactor (FR) (FB) (CFB) • In a fluidized bed particles are held suspended by the upward. • Increasing gas velocities will create different flow regimes. • The highest slip velocity is reached in CFB, leading to high mass & heat transfer rates. • Outotec has applied CFB, FB, AFB and FR for treatment of different fine ores. Annular fluidized bed (AFB) © Outotec – All rights reserved Circulating fluidized bed advantages • High mass & heat transfer CFB Uniform temperature, low energy consumption. • Direct processing of fines Fuel NG Minimum fines losses and accretions. • High productivity GasAir Minimum plant downtime & low GasAir specific investment costs. • No heavy rotating equipment Easy and flexible control, low operation & maintenance costs. • Easy and exact control of temperature and retention time. • Direct combustion of natural gas in the CFB furnace. Circulating fluidized bed © Outotec – All rights reserved Outotec‘s experience in fluidized bed technologies CFB applications Rio Tinto Alcan Gove 3 CFB calciners. HBI Circored plant Trinidad. Capacity 0.5 million t/a 6 © Outotec – All rights reserved CFB applications Outotec‘s fluidized bed applications 7 © Outotec – All rights reserved CFB applications – iron ore processing • Outotec has built CFB plants for preheating, roasting and hydrogen based reduction of iron ores. • In the case of iron ore preheating & calcination, the target is to remove LOI and to preheat the ore for down stream processes (e.g. -

Investor Presentation
Investor presentation September 2020 Forward looking statements It should be noted that certain statements herein which are not historical facts, including, without limitation, those regarding expectations for general economic development and the market situation, expectations for customer industry profitability and investment willingness, expectations for company growth, development and profitability and the realization of synergy benefits and cost savings, and statements preceded by ”expects”, ”estimates”, ”forecasts” or similar expressions, are forward looking statements. These statements are based on current decisions and plans and currently known factors. They involve risks and uncertainties which may cause the actual results to materially differ from the results currently expected by the company. Such factors include, but are not limited to: 1) general economic conditions, including fluctuations in exchange rates and interest levels which influence the operating environment and profitability of customers and thereby the orders received by the company and their margins 2) the competitive situation, especially significant technological solutions developed by competitors 3) the company’s own operating conditions, such as the success of production, product development and project management and their continuous development and improvement 4) the success of pending and future acquisitions and restructuring. August 5, 2020 2 Metso Outotec in brief Metso Outotec is a frontrunner in sustainable technologies, end-to- end solutions and services for the aggregates, minerals processing, 4.2 50+ metals refining and recycling billion euro countries with industries globally. sales* presence By improving our customers’ energy and water efficiency, increasing their productivity and reducing environmental risks with our process 15,000+ 150 years of and product expertise, we are the employees, 80+ expertise in mining partner for positive change. -

Metso Outotec's Magazine for Mining & Aggregates Customers >> Issue 1, 2021
resultsMetso Outotec’s magazine for mining & aggregates customers >> Issue 1, 2021 Partner for positive change 1 results - mining + aggregates In this issue Metso Outotec in brief............................................................................................................... 4 Our businesses............................................................................................................................. 5 Our offerings - Aggregates / Mining / Metals refining.............................................. 6 Our strengths................................................................................................................................ 9 Our services................................................................................................................................... 10 Our customers : Our references............................................................................................. 12 Products / solutions.................................................................................................................... 26 Dear Customers, News updates............................................................................................................................... 44 I hope that you and your families are keeping safe and business is also improving. In these uncertain times, we need sharper focus on delivery & service capabilities to ensure business continuity for our customers. Therefore, we have ensured that our operations continue to deliver despite current challenges, -

Hydrometallurgical Precious Metals Process
Hydrometallurgical Precious Metals Process The Metso Outotec Hydrometallurgical Precious Metals Benefits Process is the result of decades of experience and • High direct recovery and high end-product continuous development in precious metals processing quality with low inventories technology. It offers high direct recoveries with low • Short processing time • Highly automated process enables stable inventories. The cost-effective, modular approach end-product quality and smooth operation comprises leaching, filtration, and precipitation steps, • Modular approach is both flexible and and can be adapted for a variety of applications, cost-efficient including processing of anode slimes or other residues • Recovered impurities can be sold as by-products instead of disposed of containing precious metals. • Low environmental impact with no flue dust or slag generation The Metso Outotec Hydrometallurgical Precious Metals Process Production of precious metals from anode TROF or Kaldo Furnace. The modular approach makes it A flexible, safe, and cost-effective process slimes or secondary raw materials possible to integrate the Metso Outotec process with your In the Metso Outotec Hydrometallurgical Precious Metals Originally developed for the treatment of copper existing process equipment. Process, slime is first leached in three sequential sulfuric acid electrorefining anode slime, the Metso Outotec leaching steps. The soluble copper and excess chlorides Hydrometallurgical Precious Metals Process can also be used The process ensures effective separation of impurities with are removed in copper recovery. The remaining copper and to process other raw materials containing precious metals, high recovery. Impurities can be converted into saleable most of the selenium, silver, and impurities are dissolved in including some secondary raw materials or lead anode products such as selenium, copper telluride, and lead sulfate pressure leaching. -

Secure Fuels from Domestic Resources ______Profiles of Companies Engaged in Domestic Oil Shale and Tar Sands Resource and Technology Development
5th Edition Secure Fuels from Domestic Resources ______________________________________________________________________________ Profiles of Companies Engaged in Domestic Oil Shale and Tar Sands Resource and Technology Development Prepared by INTEK, Inc. For the U.S. Department of Energy • Office of Petroleum Reserves Naval Petroleum and Oil Shale Reserves Fifth Edition: September 2011 Note to Readers Regarding the Revised Edition (September 2011) This report was originally prepared for the U.S. Department of Energy in June 2007. The report and its contents have since been revised and updated to reflect changes and progress that have occurred in the domestic oil shale and tar sands industries since the first release and to include profiles of additional companies engaged in oil shale and tar sands resource and technology development. Each of the companies profiled in the original report has been extended the opportunity to update its profile to reflect progress, current activities and future plans. Acknowledgements This report was prepared by INTEK, Inc. for the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Petroleum Reserves, Naval Petroleum and Oil Shale Reserves (DOE/NPOSR) as a part of the AOC Petroleum Support Services, LLC (AOC- PSS) Contract Number DE-FE0000175 (Task 30). Mr. Khosrow Biglarbigi of INTEK, Inc. served as the Project Manager. AOC-PSS and INTEK, Inc. wish to acknowledge the efforts of representatives of the companies that provided information, drafted revised or reviewed company profiles, or addressed technical issues associated with their companies, technologies, and project efforts. Special recognition is also due to those who directly performed the work on this report. Mr. Peter M. Crawford, Director at INTEK, Inc., served as the principal author of the report. -

Outotec Casestudy
OUTOTEC’S FEEDGUARD PRODUCT APPLIES ROCSOLE’S TOMOGRAPHIC PLATFORM OUTOTEC FEEDGUARD OUTOTEC FEEDGUARD, BASED ON THE ELECTRICAL CAPACITANCE TOMOGRAPHY (ECT) IS CAPABLE OF DETECTING EVEN THE SMALLEST VARIATIONS IN THE FEED MIXTURE. OUTOTEC FEEDGUARD The Outotec® FeedGuard provides easy and quick detection of uneven feed or feed blockages. It has low maintenance requirements (non-intrusive sensors) and it is based on a very accurate and reliable ECT measurement. An online measurement of feed distribution and ensuring that it is even and without blockages improves the oxygen efficiency of the process, decreases weak acid production and reduces the slag losses of Cu or Ni. The total mass flow of FeedGuard is very close to the total mass flow of the individual feeds, normally within 1 % error calculated over a fill cycle of the loss-in-weight feeder. THE FEEDGUARD SENSOR SPECIALLY DEVELOPED FOR THE FLASH SMELTING OR FLASH CONVERTING PROCESS IT IS INTEGRATED TO THE CONCENTRATE OR MATTE BURNER FEED INLET PORT AND PROVIDES THE MEASUREMENT RESULT TO THE CONTROL ROOM ONLINE ROCSOLE’S TOMOGRAPHIC PLATFORM STATEMENTS PETER BJÖRKLUND TECHNOLOGY MANAGER, OUTOTEC FINLAND OY ”Our aim was to increase the productivity of the concentrate burner and to provide an accurate mass flow measurement. As a base for our product we have been applying Rocsole’s tomographic platform to do the mass flow measurement. A measurement accuracy of 1% has been observed during the pilot project. This FeedGuard solution brings clear benefits to our customers like spotting disturbances and blockages during feeding. In addition to that a non-uniform feed is detected and can be corrected fast.” PASI LAAKKONEN CEO OF ROCSOLE +358 40 147 8797 [email protected] www.rocsole.com “We are glad Outotec has been innovative and applying Rocsole’s Tomographic Platform. -

Alumina and Aluminium Technologies
Alumina and aluminium technologies Outotec's aluminium expertise is a powerful combination of innovative proven technologies. Cooperation and having a team approach enable us to provide you with the best possible service and vast expertise in alumina refining, paste plant and rodding shop as well as casthouse machinery – tailored to meet your specific needs. 002 Alumina and aluminium technologies Proven technologies for the aluminium Alumina refinery Aluminum smelting Steam Grinding Boiler industry Bauxite Tube digestion Clarification Residue washing Evaporation Liquor filtration Red mud storage Coal tar pitch Calcined coke Heat Precipitation Heat exchange exchange Hydrate wash & filtration Alumina Calcination Green anode plant Fume treatment plant Anode baking plant Bath treatment Fume treatment plant Electrolysis/Potline(s) Load/unload I Bath removal Butt crushing plant SPL treatment plant ALUMINIUM Rodding shop Casthouse Rod Billet Slab Ingot Sow Experience in aluminium processing and production One partner for the plant's life cycle A global leader in the development of minerals Early choice of a single technology partner, who can processing and metallurgical technologies, Outotec manage production processes and design throughout has a distinguished history of achievement going back the entire operation, saves time and money. more than a hundred years. Outotec has a long tradition Without bottlenecks, plant operation is smooth, of developing metallurgical processes, which are and profits accrue quickly. Outotec is committed to environmentally sustainable. The company's aluminium continuously developing processes and equipment expertise is based on former Lurgi Metallurgie, KHD for customers' production plants. Outotec helps you and AISCO technologies, now united under the common enhance your production process – and will take care of Outotec brand. -

Outotec® Steel Belt Sintering
Outotec® Steel Belt Sintering The Outotec® Steel Belt Sintering (SBS) process brings smelting furnace efficiency to a whole new level. Benefits The use of sintered pellets makes smelting furnace Strict environmental limits can be achieved operations more stable and profitable. with small gas cleaning units and the Pelletizing and sintering play a crucial role in effective recycling of cooling gases modifying the smelting behavior of ore since good Low operational costs charge uniformity results in consistent smelting Good and consistent pellet quality furnace performance, lower power costs and higher Pellets can be sold for other users as the recovery yields. pellets are strong enough to withstand Outotec Steel Belt Sintering is currently the most long transport distances efficient and profitable solution available for chromite ore and niobium ore pelletizing. It can also be adapted to handle iron ore, manganese ore, nickel ore and steel plant dust. Outotec Steel Belt Sintering Furnace energy consumption is very low. The efficient utilization of CO-rich off-gas from the smelting furnace further The Outotec Steel Belt Sintering Furnace is an increases total savings. effective, multi-compartment oven through which pellets are conveyed on a perforated steel belt. This Solve your fines problem by sintering them treatment gives the pellets a strong structure that can into profitable pellets withstand mechanical and thermal treatment. Since the cooling gases are efficiently utilized in the front- The primary raw materials in the steel belt sintering end compartments for drying, heating and sintering process are ore fines and/or concentrates, as well as purposes, the steel belt sintering furnace's external fine coke. -

PRESS RELEASE Public Joint Stock Company «Mining and Metallurgical Company «NORILSK NICKEL» (PJSC “MMC “Norilsk Nickel”, “Nornickel” Or the “Company”)
PRESS RELEASE Public Joint Stock Company «Mining and Metallurgical Company «NORILSK NICKEL» (PJSC “MMC “Norilsk Nickel”, “Nornickel” or the “Company”) NORNICKEL AWARDS MAJOR CONTRACT FOR PROCESSING EQUIPMENT SUPPLY TO METSO OUTOTEC Moscow, August 10, 2021 - Nornickel, the world’s largest producer of palladium and high- grade nickel and a major producer of platinum and copper, has awarded a major contract for the supply of some of the key industry-leading equipment used in mining operations to Metso Outotec, further extending the partnership with Finland’s technology solutions provider. Nornickel and Metso Outotec have signed an agreement to deliver industry-leading dewatering, flotation and automation equipment for Nornickel’s Talnakh concentrator expansion project in Russia’s Arctic city of Norilsk. The contract value is a commercially sensitive matter and therefore may not be disclosed publicly. Metso Outotec’s delivery scope consists of modernization of three existing thickeners and delivery of over 100 TankCell® flotation machines and an automation system for the new Talnakh concentrator Line 3 flotation area. In addition, the contract covers the supply of spare parts and consumables. Metso Outotec will also provide a metallurgical performance guarantee as well as advisory services for the installation and commissioning of the equipment. The delivery is scheduled for 2022-23. Sergey Dubovitsky, Nornickel Senior Vice President Strategy, Strategic Projects, Logistics & Procurement, commented: “The new contract further develops the collaboration with our longstanding partner Metso Outotec, which has supplied technology to us for many years. We have an excellent track record of using the Metso Outotec machinery across the entire geography of our operations. -

Outotec Electrochemical Water Treatment
OUTOTEC ELECTROCHEMICAL WATER TREATMENT Outotec EWT combines our unique understanding of water treatment, process BENEFITS design, electrolysis, and hydrometallurgy • Fast, effi cient water treatment and in an easy-to-use solution that delivers lower residual impurities compared to efficient performance with minimal manual conventional processes • Modular design supports easy intervention and maintenance. The system relocation and expansion can process wastewater containing a diverse • Highly automated process minimizes personnel requirements and enables range of impurities using only electricity remote operation and monitoring and a combination of electrode materials. • No need to procure or handle chemicals Furthermore, the modular design makes it both easy to transport and easily scalable. COST-EFFICIENT, SUSTAINABLE WASTEWATER TREATMENT Preventing water contamination is an important issue conventional precipitation treatment. While it features for companies in the mining and minerals processing standardized, prefabricated components that support industry as they increasingly focus on finding ways to ‘plug-and-play’ operation, each solution is customized minimize the environmental impact of their operations. according to the individual water treatment requirements Drainage from surface and underground mines, of your site. wastewaters from beneficiation, surface run-off, and acid mine drainage (AMD) are all potential sources The system is designed to be easy to operate, with a high of contamination. level of automation. This makes it possible for personnel who are not experts in water treatment to run the These different types of wastewaters can contain a diverse process. Remote operation is also possible – a significant range of impurities, including oxyanions like arsenic, advantage at sites that are difficult to access. selenium, and antimony; trace metals like copper, cadmium, nickel, and zinc; as well as sulfates, The modular EWT concept can be scaled to suit various nitrates, and cyanides. -

Public Version
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 13.5.2020 C(2020) 3254 final PUBLIC VERSION In the published version of this decision, some information has been omitted pursuant to Article 17(2) of Council Regulation (EC) No 139/2004 concerning non-disclosure of business secrets and other confidential information. The omissions are shown thus […]. Where possible the information omitted has been replaced by ranges of figures or a general description. Outotec Oyj Rauhalanpuisto 9 FI-02230 Espoo Finland Subject: Case M.9585 - OUTOTEC / METSO (MINERALS BUSINESS) Commission decision pursuant to Article 6(1)(b) of Council Regulation No 139/20041 and Article 57 of the Agreement on the European Economic Area2 Dear Sir or Madam, (1) On 2 April 2020, the European Commission received notification of a proposed concentration pursuant to Article 4 of the Merger Regulation by which Outotec Oyj (‘Outotec’, Finland) acquires within the meaning of Article 3(1)(b) of the Merger Regulation sole control of the minerals business of Metso Oyj (Finland) (the “Transaction”).3 Outotec is designated hereinafter as the “Notifying Party”. 1 OJ L 24, 29.1.2004, p. 1 (the “Merger Regulation”). With effect from 1 December 2009, the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (the “TFEU”) has introduced certain changes, such as the replacement of “Community” by “Union” and “common market” by “internal market”. The terminology of the TFEU will be used throughout this decision. 2 OJ L 1, 3.1.1994, p. 3 (the “EEA Agreement”). 3 Publication in the Official Journal of the European Union No C 123, 16.4.2020, p.