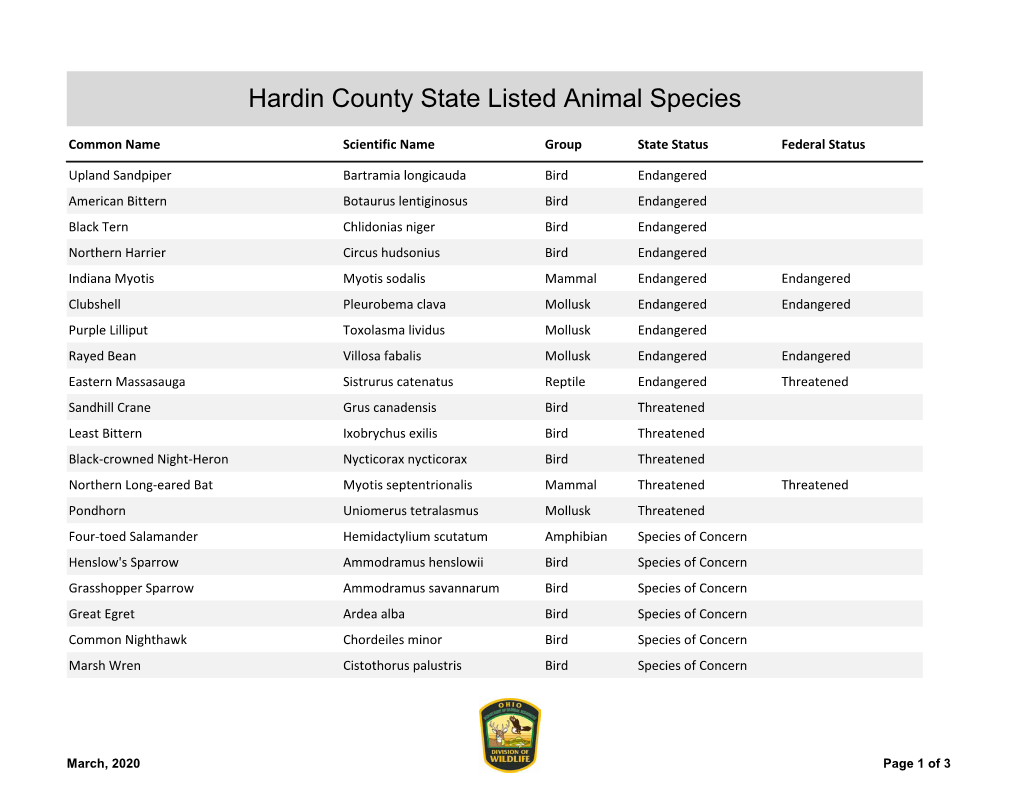
Hardin County State Listed Animal Species
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

OBSERVATIONS on a GREAT EGRET Ardea Alba and NANKEEN NIGHT HERON Nycticorax Caledonicus COLONY at the PERTH ZOO, WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Corella, 2004, 28(3): 82-86 OBSERVATIONS ON A GREAT EGRET Ardea alba AND NANKEEN NIGHT HERON Nycticorax caledonicus COLONY AT THE PERTH ZOO, WESTERN AUSTRALIA ROBYN L. PHILLIMORE' and HARRY F. RECHER2 'School of Natural Sciences, Edith Cowan University, Joondalup, Western Australia, Australia 6027 email: [email protected]: [email protected] 'Corresponding author. Present address: P.O. Box 154, Brooklyn, New South Wales, Australia 2083 Received: I I Augusr 2003 A colony of Great Egrets Ardea alba and Nankeen Night Herons Nycticorax caledonicus has existed at the Perth Zoo, Western Australia for over 25 years. The colony of egrets is one of very few in the region and hence is significant for the conservation and management of Great Egrets in Western Australia. From 1996 to 1998, surveys were conducted to determine the number of breeding pairs, clutch size, breeding success, and nest site selection of birds in the colony. Most observations were ground based, but a 30-metre cherry picker was used to inspect nests and determine clutch size. One hundred and thirty night heron and 49 egret nests were found in 1996; 92 night heron and 41 egret nests in 1997; and, 153 night heron and 36 egret nests in 1998. Nesting commenced in September, with peak numbers in early November. Both species nested in tall trees well above zoo visitors and animals. Egrets nested only in pines, whereas night herons nested mainly in figs. Great Egrets had an average clutch size of 2.6-2.7 by early November compared with a clutch of 1.6-1.8 for Nankeen Night Herons. -

The Birds (Aves) of Oromia, Ethiopia – an Annotated Checklist
European Journal of Taxonomy 306: 1–69 ISSN 2118-9773 https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2017.306 www.europeanjournaloftaxonomy.eu 2017 · Gedeon K. et al. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Monograph urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A32EAE51-9051-458A-81DD-8EA921901CDC The birds (Aves) of Oromia, Ethiopia – an annotated checklist Kai GEDEON 1,*, Chemere ZEWDIE 2 & Till TÖPFER 3 1 Saxon Ornithologists’ Society, P.O. Box 1129, 09331 Hohenstein-Ernstthal, Germany. 2 Oromia Forest and Wildlife Enterprise, P.O. Box 1075, Debre Zeit, Ethiopia. 3 Zoological Research Museum Alexander Koenig, Centre for Taxonomy and Evolutionary Research, Adenauerallee 160, 53113 Bonn, Germany. * Corresponding author: [email protected] 2 Email: [email protected] 3 Email: [email protected] 1 urn:lsid:zoobank.org:author:F46B3F50-41E2-4629-9951-778F69A5BBA2 2 urn:lsid:zoobank.org:author:F59FEDB3-627A-4D52-A6CB-4F26846C0FC5 3 urn:lsid:zoobank.org:author:A87BE9B4-8FC6-4E11-8DB4-BDBB3CFBBEAA Abstract. Oromia is the largest National Regional State of Ethiopia. Here we present the first comprehensive checklist of its birds. A total of 804 bird species has been recorded, 601 of them confirmed (443) or assumed (158) to be breeding birds. At least 561 are all-year residents (and 31 more potentially so), at least 73 are Afrotropical migrants and visitors (and 44 more potentially so), and 184 are Palaearctic migrants and visitors (and eight more potentially so). Three species are endemic to Oromia, 18 to Ethiopia and 43 to the Horn of Africa. 170 Oromia bird species are biome restricted: 57 to the Afrotropical Highlands biome, 95 to the Somali-Masai biome, and 18 to the Sudan-Guinea Savanna biome. -

First Documented Observation of Sedge Wren in Arizona Accepted
Arizona Birds - Journal of Arizona Field Ornithologists Volume 2011 FIRST DOCUMENTED OBSERVATION OF SEDGE WREN (Cistothorus platensis) IN ARIZONA Alan Schmierer, PO Box 626, Patagonia, AZ 85624 ([email protected]) Photos by the author. On 27 November 2010 the author discovered and photographed a Sedge Wren (Cistothorus platensis) on the shores of Peña Blanca Lake, Santa Cruz County, Arizona. This sighting was the first documented record of this species for Arizona. INITIAL DISCOVERY AND CONTINUED SIGHTINGS The initial discovery of this bird was a very brief encounter. At about mid-morning I was birding the south shore of the cove (informally called Thumb Rock Cove; see Figure 2) that is just north of the Upper Thumb Rock Picnic Area parking lot. Several double-chip notes, some- what reminiscent of those of the Pacific and Winter Wrens (Troglodytes pacificus and heimalis) alerted me to a potentially interesting bird be- ing present, followed by a 15 second look at the bird with binoculars (at about a two meter dis- tance), two quick photos (a lesson for photogra- phers to keep their cameras handy for such “bird emergencies”) and then the bird was gone. The wren was seen while it was about 1.5 m up in bare branches close to the trunk of a small deciduous tree at the water’s edge, and it then flew across the cove to a grassy edge of the op- posite shore. That brief view was enough for me to identify it as a Sedge Wren. Even as a new- comer to Arizona I knew that it was likely a very Figure 1: SEDGE WREN (27 November 2010) at initial sighting. -

California Red-Legged Frog (Rana Aurora Draytonii)
AMPHIBIANS California Red-Legged Frog (Rana aurora draytonii) California Red-Legged Frog (Rana aurora draytonii) Status State: Meets requirements as a “rare, threatened or endangered species” under CEQA Federal: Threatened Critical Habitat: Designated in 2001 (USFWS 2001) but rescinded in 2002 by court order except for one unit in the Sierra Nevada; proposed again in 2004 (USFWS 2004) Population Trend Global: State endemic; declining State: Declining Within Inventory Area: Apparently stable in some areas Data Characterization The location database for the California red-legged frog (Rana aurora draytonii) within its known range in California includes 419 data records dated from 1919 to 2001. Of these records, 344 were documented within the past 10 years; of these, 203 are of high precision and may be accurately located within the inventory area. Approximately 81 of these high-precision records are located within or near the inventory area. These records occur within non-native grassland, riparian forest, riparian woodland, riparian scrub, freshwater marsh, and wetland. A moderate amount of literature is available regarding the California red-legged frog because of its threatened status and the recent trend in global decline in amphibians. Most of the literature pertains to habitat requirements, population trends, ecological relationships, threats, and conservation efforts. A final recovery plan for the California red-legged frog has been published by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (2002). Range The historical range of the California red-legged frog extended along the coast from the vicinity of Point Reyes National Seashore, Marin County, California and inland from Redding, Shasta County southward to northwestern Baja California, Mexico (Jennings and Hayes 1985, Hayes and Krempels 1986). -

Black-Crowned Night-Heron (Nycticorax Nycticorax) William C
Black-crowned Night-Heron (Nycticorax nycticorax) William C. Scharf Status: Special Concern (MNFI) Detroit Zoo, MI. 6/11/2008 © Joan Tisdale (Click to view a comparison of Atlas I to II) Known by the elegant black and white of its Distribution Black-crowned Night-Herons in Michigan adult plumage and its red-eyed stare, the Black- historically have had their colonies along the crowned Night-Heron is a voracious and shores and islands of Lake Erie, the Detroit stealthy predator of fish, frogs, mice, and River, Lake St. Clair and Lake Huron with new especially young gulls, terns and other birds. colonies since Scharf (1998) expanding into Many potential prey animals should heed its northern Lake Michigan, Lake Huron, the St. “quawk” call in the night. A widespread species, Marys River and eastern Lake Superior. They it is found nesting on every continent except seek nesting on islands or other similar insulated Australia and Antarctica (Davis 1993). They are spots protected from predators. Twelve breeding colonial breeders, and are often found breeding colonies were documented on the Great Lakes and foraging with other species of herons as islands or along the shoreline of the NLP and well as other species of colonial nesting UP during MBBA II. This seems to indicate an waterbirds. increase in northward nesting for this species. A noteworthy coincident change has been that new Suitable wetland habitat for nesting and colonies established in Ontario are northward of foraging influences Black-crowned Night Heron the traditional nesting areas by 72 km (48 mi) distribution. Sites of Black-crowned Night (Cadman 2007). -

La Brea and Beyond: the Paleontology of Asphalt-Preserved Biotas
La Brea and Beyond: The Paleontology of Asphalt-Preserved Biotas Edited by John M. Harris Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County Science Series 42 September 15, 2015 Cover Illustration: Pit 91 in 1915 An asphaltic bone mass in Pit 91 was discovered and exposed by the Los Angeles County Museum of History, Science and Art in the summer of 1915. The Los Angeles County Museum of Natural History resumed excavation at this site in 1969. Retrieval of the “microfossils” from the asphaltic matrix has yielded a wealth of insect, mollusk, and plant remains, more than doubling the number of species recovered by earlier excavations. Today, the current excavation site is 900 square feet in extent, yielding fossils that range in age from about 15,000 to about 42,000 radiocarbon years. Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County Archives, RLB 347. LA BREA AND BEYOND: THE PALEONTOLOGY OF ASPHALT-PRESERVED BIOTAS Edited By John M. Harris NO. 42 SCIENCE SERIES NATURAL HISTORY MUSEUM OF LOS ANGELES COUNTY SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS COMMITTEE Luis M. Chiappe, Vice President for Research and Collections John M. Harris, Committee Chairman Joel W. Martin Gregory Pauly Christine Thacker Xiaoming Wang K. Victoria Brown, Managing Editor Go Online to www.nhm.org/scholarlypublications for open access to volumes of Science Series and Contributions in Science. Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County Los Angeles, California 90007 ISSN 1-891276-27-1 Published on September 15, 2015 Printed at Allen Press, Inc., Lawrence, Kansas PREFACE Rancho La Brea was a Mexican land grant Basin during the Late Pleistocene—sagebrush located to the west of El Pueblo de Nuestra scrub dotted with groves of oak and juniper with Sen˜ora la Reina de los A´ ngeles del Rı´ode riparian woodland along the major stream courses Porciu´ncula, now better known as downtown and with chaparral vegetation on the surrounding Los Angeles. -

House Wren Nest-Destroying Behavior’
The Condor 88:190-193 0 The Cooper Ornithological Society 1986 HOUSE WREN NEST-DESTROYING BEHAVIOR’ JEAN-CLAUDE BELLES-ISLES AND JAROSLAV PICMAN Department of Biology, Universityof Ottawa, Ottawa KIN 6N5, Canada Abstract. House Wren (Troglodytesaedon) nest-destroying behavior was studied by experi- mentally offering 38 wrens nestswith eggs(or nestlings)throughout the nesting season.Individuals of both sexespecked all six types of eggspresented, regardless of the nest type and location. House Wrens also attacked conspecificyoung. Older nestlings(nine days old) were less vulnerable than three-day-old young. Our resultssuggest that nest-destroyingbehavior is inherent in all adult House Wrens but is inhibited in mated males and breeding females. It is suggestedthat nest destruction may have evolved as an interference mechanism reducing intra- and interspecific competition. Key words: House Wren; Troglodytes aedon; infanticide;nest destruction; competition. INTRODUCTION specificnestlings? (3) Is this behavior exhibited Destruction of eggs by small passerinesis a throughout the breeding season?(4) Do indi- relatively rare phenomenon which has been vidual House Wrens destroy neststhroughout observed mainly in members of two families, their breeding cycle? (5) How widespread is the Troglodytidae and Mimidae. Species this behavior among individuals from a pop- known to destroy eggsinclude the Marsh Wren ulation? (6) Is this behavior a local phenom- (Cistothoruspalustris; Allen 19 14); House enon or is it characteristic of all House Wren Wren (Troglodytesaedon; Sherman 1925, populations?(7) What is the adaptive value of Kendeigh 194 1); Cactus Wren (Campylorhyn- this behavior? thusbrunneicapillus; Anderson and Anderson METHODS 1973); SedgeWren (Cistothorusplatensis; Pic- man and Picman 1980); Bewick’s Wren This study was conducted at Presqu’ile Pro- (Thryomanesbewickii; J. -

Sora Rail in Stilly and the Identification of Immature Small Crakes D
Sora Rail in Stilly and the identification of immature small crakes D. I. M. Wallace The immature Sora Rail Porzana Carolina present on St Agnes, Isles of Scilly, from 26th September to 9th October 1973 (Brit. Birds, 67: 320; Scilly Bird Report for IQ73'- 19-21) was the first to be recorded in Europe since 1920. The record was accepted by both the Rarities Committee and the Records Committee of the British Ornithologists' Union, and the species was once again listed in category A of the British and Irish list (Ibis, 116: 578). This short paper, which stems from the decision to publish in this journal the details of records that result in category promotion, also includes some comparative notes on immature small crake identification. DETAILS OF THE SORA RAIL IN SCILLY The bird was first seen in the rushes of the Big Pool by D. Smallshire, but early opinions on its identity were hopelessly divided. DS, A. R. Dean and B. R. Dean persisted in seeing slight but distinct differences from the closely related Spotted Crake P. porzana, the species to which others ascribed the bird on the basis of its noticeably buff under tail. The literature available at the time implied that this was a character only of the Spotted Crake and the controversy might have remained unresolved but for the arrival of fresh, open- minded observers, some already familiar with Sora Rails. A phone call from DS to DIMW on 7th produced redoubled efforts at identification. Close attention had already been paid to the bird by B. -

Reproductive Success, Growth and Survival of Black-Crowned Night-Heron (Nycticorax Nycticorax) and Snowy Egret (Egretta Thula) Chicks in Coastal Virginia
The Auk 113(1):119-130, 1996 REPRODUCTIVE SUCCESS, GROWTH AND SURVIVAL OF BLACK-CROWNED NIGHT-HERON (NYCTICORAX NYCTICORAX) AND SNOWY EGRET (EGRETTA THULA) CHICKS IN COASTAL VIRGINIA R. MICHAEL ERWIN, JOHN G. HAIG, DANIEL B. $TOTTS,AND JEFF$. HATFIELD NationalBiological Service, Patuxent Environmental Science Center, 11410American Holly Drive, Laurel,Maryland 20708, USA ABSTRACT.--Westudied reproductive success, growth, and survivalof Black-crownedNight- Heron (Nycticoraxnycticorax) and Snowy Egret (Egrettathula) chicksin two mixed-species heronries on marsh islands in ChincoteagueBay, AccomackCounty, Virginia in 1992 and 1993. We attachedradio transmitterswith mortality sensorsto the oldest chicks (A-chicks) in 11 to 22 nestsof both speciesto monitor survival during the mid- to late nestlingperiod and into the postnestingdispersal period. For both species,we found significantdifferences between 1992and 1993in growth ratesand survival. Massgrowth ratesof chickswere higher in 1993 than in 1992for both species.Culmen-length growth ratesvaried significantlydue to year-colonyeffects for night-herons,but only for hatching order for egrets.Differences in survival rates due to hatching order were found for the egrets in both years, but were found only in 1992for night-herons.As with massgrowth rates, survival of chickswas higher in 1993 than 1992.Survival of radio-markedA-chicks did not differ between speciesor years for the period from hatchingto fledging or from fledging through the end of the study (ca. two monthspostfledging). Survival ranged from 0.80 to 1.00from the time radio transmitters were attached(ca. two weeksof age) until dispersalage (53-55 daysfor egrets;55-60 days for night-herons).After birds left the colony,survival rateswere lower during the next 40 to 55 days,ranging from 0.25 to 0.60. -

Heron, Black-Crowned Night
142 Herons and Bitterns — Family Ardeidae Black-crowned Night-Heron Nycticorax nycticorax The Black-crowned Night-Heron spends much of the day resting quietly in marshes or trees, then at dusk flies off to forage, broadcasting a startlingly loud “quock!” In San Diego County it is locally common year round, both along the coast and at lakes and marshes inland. From 1997 to 2001 there were seven substantial colonies in the county, most mixed with other species of herons. Isolated pairs or small colo- nies also contribute to the population, to an unknown degree. Breeding distribution: Like the Great Blue, the Black- crowned Night-Heron nests mainly in colonies, often in mixed heronies. Seven sites appear to account for most Photo by Anthony Mercieca of San Diego County’s population. At the Wild Animal Park (J12), in the multispecies heronry in the Heart of Scripps Institution of Oceanography (O7) were a colony Africa exhibit, counts of the birds (fledglings included) site for many years, until some heavy construction at ranged up to 150 on 15 June 1998 (D. and D. Bylin); our the campus in 2002. At least three, possibly seven, nests best count of nests was at least 20 on 8 May 1999 (K. L. were active on 4 June 1998 (S. E. Smith). In 1999, Black- Weaver). At Sierra Avenue and Plaza Street in Solana crowned Night-Herons founded the mixed heronry at Beach (M7), Black-crowned Night-Herons nest in com- Lindo Lake (P14; M. B. Stowe). By 9 July 2001, there were pany with Snowy Egrets. -

Atoll Research Bulletin No. 252 Bird and Denis Islands
ATOLL RESEARCH BULLETIN NO. 252 BIRD AND DENIS ISLANDS, SEYCHELLES by D. R. Stoddart and F. R. Fosberg Issued by THE SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION Washington, D. C., U.S.A. ~ul~'l981 Contents 1. Geography and ecology of Bird Island, Seychelles Introduction Morphology and structure Climate Vegetation Flora Invertebrates Reptiles Mammals Birds History 2. Plants recorded from Bird Island 3. Geography and ecology of Denis Island, Seychelles Introduction Morphology and structure Climate Vegetation Flora Invertebrates Reptiles Mammals Birds History 4. Plants recorded from Denis Island 5. References Manuscript received May 1980 --Eds. List of Figures 1. The Seychelles Bank following page 11 2. Bird Island in 1976 following page 11 3. Beach sediment at Bird Island following page 11 4. Denis Island in 1977 following page 50 5. Monthly rainfall at Denis Island, 19 71-1962 following page 50 List of Tables 1. Scientific studies at Bird Island 2. Characteristics of Bird Island beach sands 3. Monthly rainfall at Bird Island, 1951-1962 4. Key to the literature on insects collected at Bird Island 5. Scientific studies at Denis Island 6. Monthly and annual rainfall records at Denis Island iii List of Plates Bird Island: Suriana zone on the northeast shore following page 11 Bird Island: Pisonia and Cordia woodland with Suriana on the northeast shore Bird Island: Tournefortia parkland in the northeast Bird Island: tree-like Tournefortia in the northeast Bird Island: pioneer sedges and Scaevola on the east shore Bird Island: pioneer Ipomoea pes-caprae on the east shore Bird Island: pioneer sedges, Scaevola and Tournefortia on the northeast shore Bird Island: airstrip from the southeast Denis Island: phosphate cliffs with Casuarina woodland, southwest shore following page 50 10. -

Harrison County State Listed Animal Species
Harrison County State Listed Animal Species Common Name Scientific Name Group State Status Federal Status Upland Sandpiper Bartramia longicauda Bird Endangered Northern Harrier Circus hudsonius Bird Endangered Black Bear Ursus americanus Mammal Endangered Northern Long-eared Bat Myotis septentrionalis Mammal Threatened Threatened Sharp-shinned Hawk Accipiter striatus Bird Species of Concern Henslow's Sparrow Ammodramus henslowii Bird Species of Concern Grasshopper Sparrow Ammodramus savannarum Bird Species of Concern Eastern Whip-poor-will Antrostomus vociferus Bird Species of Concern Great Egret Ardea alba Bird Species of Concern Black-billed Cuckoo Coccyzus erythropthalmus Bird Species of Concern Bobolink Dolichonyx oryzivorus Bird Species of Concern American Coot Fulica americana Bird Species of Concern Red-headed Woodpecker Melanerpes erythrocephalus Bird Species of Concern Vesper Sparrow Pooecetes gramineus Bird Species of Concern Sora Rail Porzana carolina Bird Species of Concern Prothonotary Warbler Protonotaria citrea Bird Species of Concern Virginia Rail Rallus limicola Bird Species of Concern Cerulean Warbler Setophaga cerulea Bird Species of Concern Tiger Spiketail Cordulegaster erronea Dragonfly Species of Concern Muskellunge Esox masquinongy Fish Species of Concern March, 2020 Page 1 of 2 Common Name Scientific Name Group State Status Federal Status Blue Catfish Ictalurus furcatus Fish Species of Concern Star-nosed Mole Condylura cristata Mammal Species of Concern Big Brown Bat Eptesicus fuscus Mammal Species of Concern Silver-haired