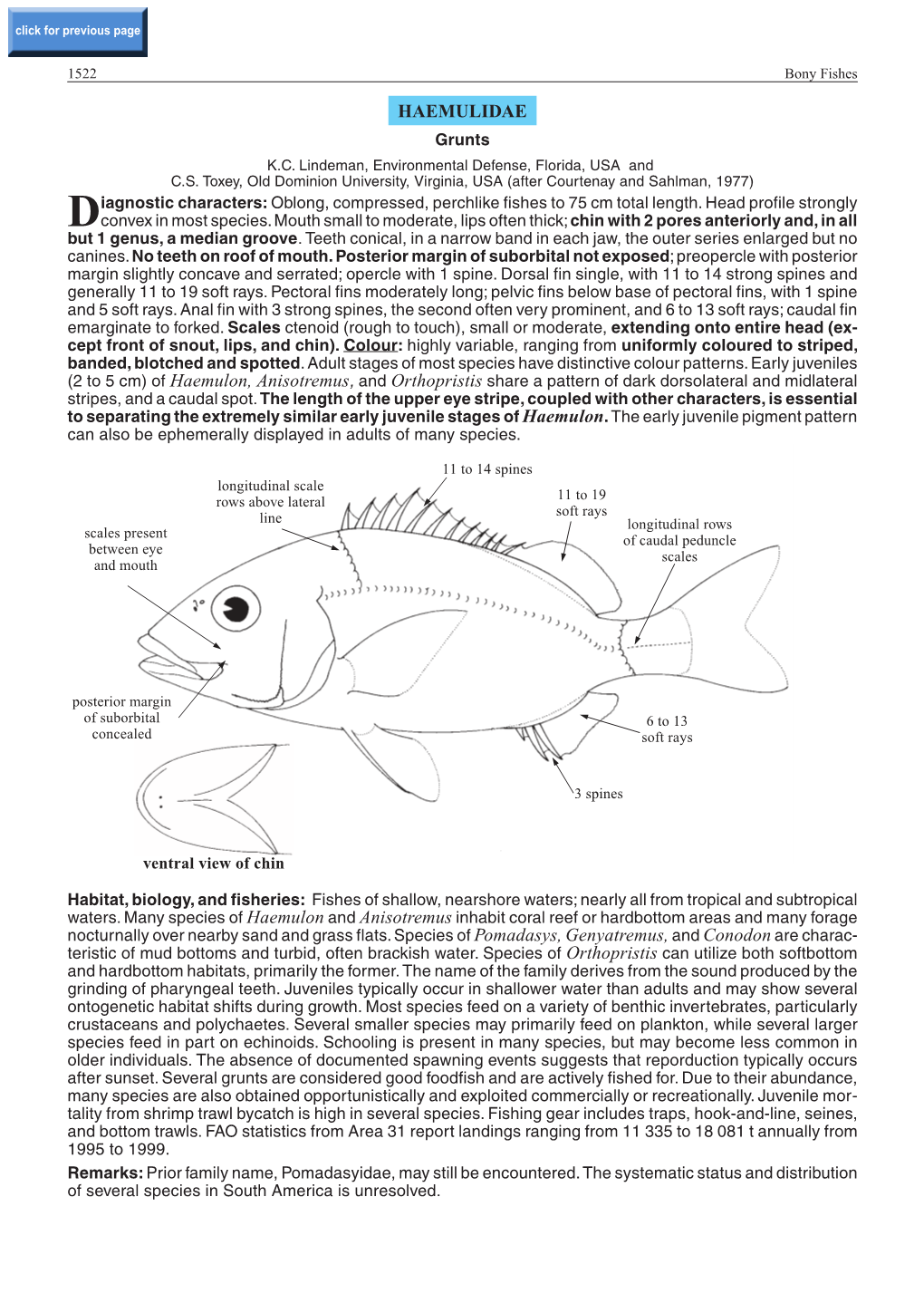
HAEMULIDAE Grunts K.C
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Reef Fish Biodiversity in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Megan E
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School November 2017 Reef Fish Biodiversity in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Megan E. Hepner University of South Florida, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarcommons.usf.edu/etd Part of the Biology Commons, Ecology and Evolutionary Biology Commons, and the Other Oceanography and Atmospheric Sciences and Meteorology Commons Scholar Commons Citation Hepner, Megan E., "Reef Fish Biodiversity in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary" (2017). Graduate Theses and Dissertations. https://scholarcommons.usf.edu/etd/7408 This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Graduate School at Scholar Commons. It has been accepted for inclusion in Graduate Theses and Dissertations by an authorized administrator of Scholar Commons. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Reef Fish Biodiversity in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary by Megan E. Hepner A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Marine Science with a concentration in Marine Resource Assessment College of Marine Science University of South Florida Major Professor: Frank Muller-Karger, Ph.D. Christopher Stallings, Ph.D. Steve Gittings, Ph.D. Date of Approval: October 31st, 2017 Keywords: Species richness, biodiversity, functional diversity, species traits Copyright © 2017, Megan E. Hepner ACKNOWLEDGMENTS I am indebted to my major advisor, Dr. Frank Muller-Karger, who provided opportunities for me to strengthen my skills as a researcher on research cruises, dive surveys, and in the laboratory, and as a communicator through oral and presentations at conferences, and for encouraging my participation as a full team member in various meetings of the Marine Biodiversity Observation Network (MBON) and other science meetings. -

CAT Vertebradosgt CDC CECON USAC 2019
Catálogo de Autoridades Taxonómicas de vertebrados de Guatemala CDC-CECON-USAC 2019 Centro de Datos para la Conservación (CDC) Centro de Estudios Conservacionistas (Cecon) Facultad de Ciencias Químicas y Farmacia Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala Este documento fue elaborado por el Centro de Datos para la Conservación (CDC) del Centro de Estudios Conservacionistas (Cecon) de la Facultad de Ciencias Químicas y Farmacia de la Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala. Guatemala, 2019 Textos y edición: Manolo J. García. Zoólogo CDC Primera edición, 2019 Centro de Estudios Conservacionistas (Cecon) de la Facultad de Ciencias Químicas y Farmacia de la Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala ISBN: 978-9929-570-19-1 Cita sugerida: Centro de Estudios Conservacionistas [Cecon]. (2019). Catálogo de autoridades taxonómicas de vertebrados de Guatemala (Documento técnico). Guatemala: Centro de Datos para la Conservación [CDC], Centro de Estudios Conservacionistas [Cecon], Facultad de Ciencias Químicas y Farmacia, Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala [Usac]. Índice 1. Presentación ............................................................................................ 4 2. Directrices generales para uso del CAT .............................................. 5 2.1 El grupo objetivo ..................................................................... 5 2.2 Categorías taxonómicas ......................................................... 5 2.3 Nombre de autoridades .......................................................... 5 2.4 Estatus taxonómico -

Diagramma Pictum (Thunberg. 1792)
Diagramma pictum (Thunberg. 1792) English Name: Painted sweetlips Family: HAEMULIDAE Local Name: Kilanbu guruva Order: Perciformes Size: Max. 90 cm Specimen: MRS/P048 1/97 Distinctive Characters: Dorsal fin with 9-10 spines and 17-20 rays. Anal fin with 3 spines and 7 rays. Pectoral fin with 16-17 rays. Second dorsal spine much longer than the first. 20 to 25 scales between lateral line and dorsal fin origin. Scales small and ctenoid. Mouth small, lips thick. Colour: Adults light grey with scattered large blackish blotches on sides, white on belly. Juveniles with conspicuous alternating black and white stripes, and yellowish on headand belly. Stripes eventually break up into spots that disappear in adults. Habitat and Biology: Found on shallow coastal areas and coral reefs down to a depth of 80 rn. Most common on silty areas. Feeds on bottom invertebrates and fish. Distribution: Indo-West Pacific. Remarks: Di gramma picluni can easily be distinguished from other sweetlips by its short. first dorsal spine and second (with the third) abruptly the longest. 172 Plectorhinchus albovittatus (Ruppell, 1838) English Name: Giant sweetlips Family: HAEMULIDAE Local Name: Maa guruva Order: Perciformes Size: Max. 1 m Specimen: MRS/P030l/88 Distinctive Characters: Dorsal fin with 13 spines and 18-19 rays. Anal fin with 3 spines and 7 rays. Pectoral fin 17 rays. Lips greatly enlarged. Caudal fin slightly emarginate. Colour: Adults dark grey with numerous pale spots and short irregular lines. Usually a broad diffused pale bar just behind pectoral fins, extending onto abdomen. Soft portion of dorsal fin and lobes of caudal fin with large black areas. -

Fish Assemblage of the Mamanguape Environmental Protection Area, NE Brazil: Abundance, Composition and Microhabitat Availability Along the Mangrove-Reef Gradient
Neotropical Ichthyology, 10(1): 109-122, 2012 Copyright © 2012 Sociedade Brasileira de Ictiologia Fish assemblage of the Mamanguape Environmental Protection Area, NE Brazil: abundance, composition and microhabitat availability along the mangrove-reef gradient Josias Henrique de Amorim Xavier1, Cesar Augusto Marcelino Mendes Cordeiro2, Gabrielle Dantas Tenório1, Aline de Farias Diniz1, Eugenio Pacelli Nunes Paulo Júnior1, Ricardo S. Rosa1 and Ierecê Lucena Rosa1 Reefs, mangroves and seagrass biotopes often occur in close association, forming a complex and highly productive ecosystem that provide significant ecologic and economic goods and services. Different anthropogenic disturbances are increasingly affecting these tropical coastal habitats leading to growing conservation concern. In this field-based study, we used a visual census technique (belt transects 50 m x 2 m) to investigate the interactions between fishes and microhabitats at the Mamanguape Mangrove-Reef system, NE Brazil. Overall, 144 belt transects were performed from October 2007 to September 2008 to assess the structure of the fish assemblage. Fish trophic groups and life stage (juveniles and adults) were recorded according to literature, the percent cover of the substrate was estimated using the point contact method. Our results revealed that fish composition gradually changed from the Estuarine to the Reef zone, and that fish assemblage was strongly related to the microhabitat availability, as suggested by the predominance of carnivores at the Estuarine zone and presence of herbivores at the Reef zone. Fish abundance and diversity were higher in the Reef zone and estuary margins, highlighting the importance of structural complexity. A pattern of nursery area utilization, with larger specimens at the Transition and Reef Zone and smaller individuals at the Estuarine zone, was recorded for Abudefduf saxatilis, Anisotremus surinamensis, Lutjanus alexandrei, and Lutjanus jocu. -

Dedication Donald Perrin De Sylva
Dedication The Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Mangroves as Fish Habitat are dedicated to the memory of University of Miami Professors Samuel C. Snedaker and Donald Perrin de Sylva. Samuel C. Snedaker Donald Perrin de Sylva (1938–2005) (1929–2004) Professor Samuel Curry Snedaker Our longtime collaborator and dear passed away on March 21, 2005 in friend, University of Miami Professor Yakima, Washington, after an eminent Donald P. de Sylva, passed away in career on the faculty of the University Brooksville, Florida on January 28, of Florida and the University of Miami. 2004. Over the course of his diverse A world authority on mangrove eco- and productive career, he worked systems, he authored numerous books closely with mangrove expert and and publications on topics as diverse colleague Professor Samuel Snedaker as tropical ecology, global climate on relationships between mangrove change, and wetlands and fish communities. Don pollutants made major scientific contributions in marine to this area of research close to home organisms in south and sedi- Florida ments. One and as far of his most afield as enduring Southeast contributions Asia. He to marine sci- was the ences was the world’s publication leading authority on one of the most in 1974 of ecologically important inhabitants of “The ecology coastal mangrove habitats—the great of mangroves” (coauthored with Ariel barracuda. His 1963 book Systematics Lugo), a paper that set the high stan- and Life History of the Great Barracuda dard by which contemporary mangrove continues to be an essential reference ecology continues to be measured. for those interested in the taxonomy, Sam’s studies laid the scientific bases biology, and ecology of this species. -

(<I>Anisotremus Virginicus,</I> Haemulidae) And
BULLETIN OF MARINE SCIENCE, 34(1): 21-59,1984 DESCRIPTION OF PORKFISH LARVAE (ANISOTREMUS VIRGINICUS, HAEMULIDAE) AND THEIR OSTEOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT Thomas Potthoff, Sharon Kelley, Martin Moe and Forrest Young ABSTRACT Wild-caught adult porkfish (Anisotremus virginicus, Haemulidae) were spawned in the laboratory and their larvae reared. A series of 35 larvae 2.4 mm NL to 21.5 mm SL from 2 to 30 days old or older (larvae of unknown age) was studied for pigmentation characteristics. Cleared and stained specimens were examined for meristic and osteological development. Cartilaginous neural and haemal arches develop first anteriorly, at the center, and posteriorly, above and below the notochord, but ossification of the vertebral column is from anterior in a posterior direction. Epipleural rib pairs develop from bone, but pleural rib pairs develop from cartilage first and then ossify. The second dorsal, anal and caudal fins develop rays first and simultaneously, followed by first dorsal fin spine development. The pectoral and pelvic fins are the last of all fins to develop rays. All bones basic to a perciform pectoral girdle develop with cartilaginous radials present between the pectoral fin ray bases. Development and structure of pre dorsal bones and dorsal and anal fin pterygiophores were studied. All bones basic to a perciform caudal complex developed and no fusion of any of these bones was observed in the adults. Radial cartilages developed ventrad in the hypural complex. The hyoid arches originated from cartilage but the branchiostegal rays formed from bone. The development and anatomy of the branchial skeleton were studied. Spines develop on the four bones of the opercular series in larvae and juveniles but are absent in the adults. -

Morphological and Karyotypic Differentiation in Caranx Lugubris (Perciformes: Carangidae) in the St. Peter and St. Paul Archipelago, Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Helgol Mar Res (2014) 68:17–25 DOI 10.1007/s10152-013-0365-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Morphological and karyotypic differentiation in Caranx lugubris (Perciformes: Carangidae) in the St. Peter and St. Paul Archipelago, mid-Atlantic Ridge Uedson Pereira Jacobina • Pablo Ariel Martinez • Marcelo de Bello Cioffi • Jose´ Garcia Jr. • Luiz Antonio Carlos Bertollo • Wagner Franco Molina Received: 21 December 2012 / Revised: 16 June 2013 / Accepted: 5 July 2013 / Published online: 24 July 2013 Ó Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg and AWI 2013 Abstract Isolated oceanic islands constitute interesting Introduction model systems for the study of colonization processes, as several climatic and oceanographic phenomena have played Ichthyofauna on the St. Peter and St. Paul Archipelago an important role in the history of the marine ichthyofauna. (SPSPA) is of great biological interest, due to its degree The present study describes the presence of two morpho- of geographic isolation. The region is a remote point, far types of Caranx lugubris, in the St. Peter and St. Paul from the South American (&1,100 km) and African Archipelago located in the mid-Atlantic. Morphotypes were (&1,824 km) continents, with a high level of endemic fish compared in regard to their morphological and cytogenetic species (Edwards and Lubbock 1983). This small archi- patterns, using C-banding, Ag-NORs, staining with CMA3/ pelago is made up of four larger islands (Belmonte, St. DAPI fluorochromes and chromosome mapping by dual- Paul, St. Peter and Bara˜o de Teffe´), in addition to 11 color FISH analysis with 5S rDNA and 18S rDNA probes. smaller rocky points. The combined action of the South We found differences in chromosome patterns and marked Equatorial Current and Pacific Equatorial Undercurrent divergence in body patterns which suggest that different provides a highly complex hydrological pattern that sig- populations of the Atlantic or other provinces can be found nificantly influences the insular ecosystem (Becker 2001). -

Sharkcam Fishes
SharkCam Fishes A Guide to Nekton at Frying Pan Tower By Erin J. Burge, Christopher E. O’Brien, and jon-newbie 1 Table of Contents Identification Images Species Profiles Additional Info Index Trevor Mendelow, designer of SharkCam, on August 31, 2014, the day of the original SharkCam installation. SharkCam Fishes. A Guide to Nekton at Frying Pan Tower. 5th edition by Erin J. Burge, Christopher E. O’Brien, and jon-newbie is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/. For questions related to this guide or its usage contact Erin Burge. The suggested citation for this guide is: Burge EJ, CE O’Brien and jon-newbie. 2020. SharkCam Fishes. A Guide to Nekton at Frying Pan Tower. 5th edition. Los Angeles: Explore.org Ocean Frontiers. 201 pp. Available online http://explore.org/live-cams/player/shark-cam. Guide version 5.0. 24 February 2020. 2 Table of Contents Identification Images Species Profiles Additional Info Index TABLE OF CONTENTS SILVERY FISHES (23) ........................... 47 African Pompano ......................................... 48 FOREWORD AND INTRODUCTION .............. 6 Crevalle Jack ................................................. 49 IDENTIFICATION IMAGES ...................... 10 Permit .......................................................... 50 Sharks and Rays ........................................ 10 Almaco Jack ................................................. 51 Illustrations of SharkCam -

Mapping Ontogenetic Habitat Shifts of Coral Reef Fish at Mona Island, Puerto Rico Cartografía De Las Mudanzas De Habitáculos D
Mapping ontogenetic habitat shifts of coral reef fish at Mona Island, Puerto Rico Item Type conference_item Authors Schärer, M.T.; Nemeth, M.I.; Appeldoorn, R.S. Download date 02/10/2021 07:32:38 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/1834/31272 Mapping Ontogenetic Habitat Shifts of Coral Reef Fish at Mona Island, Puerto Rico MICHELLE T. SCHÄRER, MICHAEL I. NEMETH, and RICHARD S. APPELDOORN Department of Marine Sciences, University of Puerto Rico, Mayagüez, Puerto Rico 00681 ABSTRACT Coral reef fishes use a variety of habitats throughout daily, ontogenetic, and spawning migrations, therefore requiring a suite of habitats to complete their life cycle. The use of multiple habitats by grunts (Haemulidae) and snappers (Lutjanidae) was investigated at Mona Island, a remote island off western Puerto Rico. The objective of this study was to determine if the distribution of three different life stages was random in relation to benthic habitat types. Coral reef fish were sampled throughout all habitat types randomly over a period of six months. For seven species of grunts and snappers median fork length was significantly different by habitat type identifying critical habitats for juveniles distinct from adult habitats. Within a life stage significant differences were observed in fish density by habitat type. Early juvenile grunts and snappers were more abundant in habitats of depths less than 5 m, mainly in rocky shores and seagrass areas with patches of coral or other hard structures. Larger juveniles were significantly more abundant in depths less than 5m in coral dominated habitats. Adults were abundant throughout the habitats of all depth ranges, except for two species Haemulon chrysargyreum and Lutjanus mahogoni, which were limited to shallower habitats. -

<I>Haemulon Sciurus
BULLETIN OF MARINE SCIENCE, 80(3): 473–495, 2007 nearsHore Habitat use BY GraY snaPPer (LUTJANUS GRISEUS) anD bluestriPED Grunt (HAEMULON SCIURUS): enVironmental GraDients anD ontoGenetic SHifts Craig H. Faunce and Joseph E. Serafy ABSTRACT Fringing mangrove forests and seagrass beds harbor high densities of juvenile snappers and grunts compared to bare substrates, but their occupancy of these habitats is not homogeneous at ecologically meaningful scales, thus limiting our ability to compare habitat value. Here, density and size information were used to de- termine how gray snapper, Lutjanus griseus (Linnaeus, 1758) and bluestriped grunt, Haemulon sciurus (Shaw, 1803), use vegetated habitats during their ontogeny, and how their use of mangrove forests varied with season across broad spatial scales and physicochemical conditions. Both species exhibited a three-stage ontogenetic strategy: (1) settlement and grow-out (8–10 mo) within seagrass beds, (2) expan- sion to mangrove habitats at 10–12 cm total length, and (3) increasing utilization of inland mangroves during the dry season and with increasing body size. For fishes inhabiting mangroves, multivariate tests revealed that the factors distance from oceanic inlet and water depth were stronger predictors of reef fish utilization than the factors latitude, temperature, or habitat width. These findings highlight that the nursery function of mangrove shorelines is likely limited to the area of immediately accessible habitat, and that more expansive forests may contain a substantial num- ber of larger adult individuals. The importance of coastal vegetated seascapes to the early life history stages of diadromous nekton has been well documented, and has led to the conclusion that many temperate and warm-water marine fishes are “estuarine dependent” G( unter, 1967; McHugh 1967; Day Jr. -

Taverampe2018.Pdf
Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 121 (2018) 212–223 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ympev Multilocus phylogeny, divergence times, and a major role for the benthic-to- T pelagic axis in the diversification of grunts (Haemulidae) ⁎ Jose Taveraa,b, , Arturo Acero P.c, Peter C. Wainwrightb a Departamento de Biología, Universidad del Valle, Cali, Colombia b Department of Evolution and Ecology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616, United States c Instituto de Estudios en Ciencias del Mar, CECIMAR, Universidad Nacional de Colombia sede Caribe, El Rodadero, Santa Marta, Colombia ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT Keywords: We present a phylogenetic analysis with divergence time estimates, and an ecomorphological assessment of the Percomorpharia role of the benthic-to-pelagic axis of diversification in the history of haemulid fishes. Phylogenetic analyses were Fish performed on 97 grunt species based on sequence data collected from seven loci. Divergence time estimation Functional traits indicates that Haemulidae originated during the mid Eocene (54.7–42.3 Ma) but that the major lineages were Morphospace formed during the mid-Oligocene 30–25 Ma. We propose a new classification that reflects the phylogenetic Macroevolution history of grunts. Overall the pattern of morphological and functional diversification in grunts appears to be Zooplanktivore strongly linked with feeding ecology. Feeding traits and the first principal component of body shape strongly separate species that feed in benthic and pelagic habitats. The benthic-to-pelagic axis has been the major axis of ecomorphological diversification in this important group of tropical shoreline fishes, with about 13 transitions between feeding habitats that have had major consequences for head and body morphology. -

Proceedings of the United States National Museum
A REVIEW OF THE SPARID^ AND RELATED FAMILIES OF PERCH-LIKE FISHES FOUND IN THE WATERS OF JAPAN. By David Starr Jordan and William Francis Thompson, Of Stanford University, California. In the present paper is given a review of the species of fishes belonging to those percomorphoiis famihes alUed to the Sparoid fishes, or fishes related to the tai or porgy of the waters of Japan, which have not been hitherto discussed in these pages by the senior author and his associates. The families of Kuldiidse, Priacanthidse, Theraponidse, Banjosidae, Hsemulidae, Sparidse, Kyphosidse, and Ery- thrichthyidse are thus included. The paper is based on material collected in Japan in 1900 by Pro- fessors Jordan and Snyder and now divided between the United States National Museum and the museum of Stanford University. Most of the cuts are from drawings by Mr. Sekko Shimada. The families here named are adopted provisionally only. The dis- tinctions between Sparidse, Haemulidse, Lutianidae, and their relatives are of doubtful value, while at present no definite boundaries can be assigned to the Serranidse. L Family KUHLIID.^. Body oblong, strongly compressed; scales large, cihated. Lateral line complete, the tubes straight and occupying the half or more of the exposed surface of the scale. Mouth rather large, protractile; maxillary exposed, without supplemental bone; teeth in jaws in villi- form bands; teeth on vomer, palatines, entopterygoids, and ecto- pterygoids; tongue smooth; head partly naked; preorbital and pre- opercle denticulate; opercle with 2 spines. Gill membranes separate; 6 branchiostegals; pseudobranchise large; gill-rakers long and slender. Dorsal fms connected at the base, with X, 9 to 13 rays, the spinous portion longer than the soft.