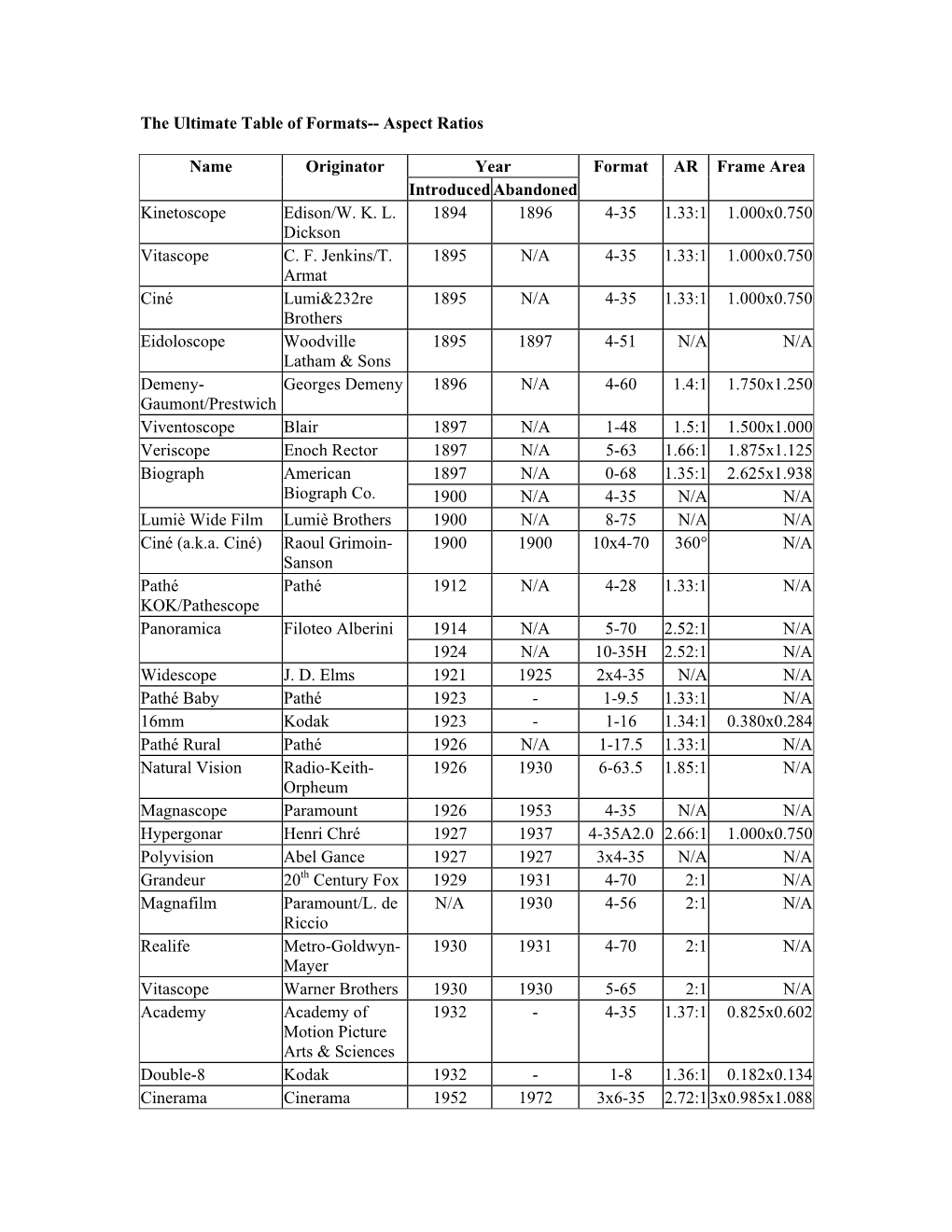
The Ultimate Table of Formats-- Aspect Ratios
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

CINERAMA: the First Really Big Show
CCINEN RRAMAM : The First Really Big Show DIVING HEAD FIRST INTO THE 1950s:: AN OVERVIEW by Nick Zegarac Above left: eager audience line ups like this one for the “Seven Wonders of the World” debut at the Cinerama Theater in New York were short lived by the end of the 1950s. All in all, only seven feature films were actually produced in 3-strip Cinerama, though scores more were advertised as being shot in the process. Above right: corrected three frame reproduction of the Cypress Water Skiers in ‘This is Cinerama’. Left: Fred Waller, Cinerama’s chief architect. Below: Lowell Thomas; “ladies and gentlemen, this is Cinerama!” Arguably, Cinerama was the most engaging widescreen presentation format put forth during the 1950s. From a visual standpoint it was the most enveloping. The cumbersome three camera set up and three projector system had been conceptualized, designed and patented by Fred Waller and his associates at Paramount as early as the 1930s. However, Hollywood was not quite ready, and certainly not eager, to “revolutionize” motion picture projection during the financially strapped depression and war years…and who could blame them? The standardized 1:33:1(almost square) aspect ratio had sufficed since the invention of 35mm celluloid film stock. Even more to the point, the studios saw little reason to invest heavily in yet another technology. The induction of sound recording in 1929 and mounting costs for producing films in the newly patented 3-strip Technicolor process had both proved expensive and crippling adjuncts to the fluidity that silent B&W nitrate filming had perfected. -

Square Vs Non-Square Pixels
Square vs non-square pixels Adapted from: Flash + After Effects By Chris Jackson Square vs non square pixels can cause problems when exporting flash for TV and video if you get it wrong. Here Chris Jackson explains how best to avoid these mistakes... Before you adjust the Stage width and height, you need to be aware of the pixel aspect ratio. This refers to the width and height of each pixel that makes up an image. Computer screens display square pixels. Every pixel has an aspect ratio of 1:1. Video uses non-square rectangular pixels, actually scan lines. To make matters even more complicated, the pixel aspect ratio is not consistent between video formats. NTSC video uses a non-square pixel that is taller than it is wide. It has a pixel aspect ratio of 1:0.906. PAL is just the opposite. Its pixels are wider than they are tall with a pixel aspect ratio of 1:1.06. Figure 1: The pixel aspect ratio can produce undesirable image distortion if you do not compensate for the difference between square and non-square pixels. Flash only works in square pixels on your computer screen. As the Flash file migrates to video, the pixel aspect ratio changes from square to non-square. The end result will produce a slightly stretched image on your television screen. On NTSC, round objects will appear flattened. PAL stretches objects making them appear skinny. The solution is to adjust the dimensions of the Flash Stage. A common Flash Stage size used for NTSC video is 720 x 540 which is slightly taller than its video size of 720 x 486 (D1). -

History of Widescreen Aspect Ratios
HISTORY OF WIDESCREEN ASPECT RATIOS ACADEMY FRAME In 1889 Thomas Edison developed an early type of projector called a Kinetograph, which used 35mm film with four perforations on each side. The frame area was an inch wide and three quarters of an inch high, producing a ratio of 1.37:1. 1932 the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences made the Academy Ratio the standard Ratio, and was used in cinemas until 1953 when Paramount Pictures released Shane, produced with a Ratio of 1.66:1 on 35mm film. TELEVISION FRAME The standard analogue television screen ratio today is 1.33:1. The Aspect Ratio is the relationship between the width and height. A Ratio of 1.33:1 or 4:3 means that for every 4 units wide it is 3 units high (4 / 3 = 1.33). In the 1950s, Hollywood's attempt to lure people away from their television sets and back into cinemas led to a battle of screen sizes. Fred CINERAMA Waller of Paramount's Special Effects Department developed a large screen system called Cinerama, which utilised three cameras to record a single image. Three electronically synchronised projectors were used to project an image on a huge screen curved at an angle of 165 degrees, producing an aspect ratio of 2.8:1. This Is Cinerama was the first Cinerama film released in 1952 and was a thrilling travelogue which featured a roller-coaster ride. See Film Formats. In 1956 Metro Goldwyn Mayer was planning a CAMERA 65 ULTRA PANAVISION massive remake of their 1926 silent classic Ben Hur. -

A Brief Intro to Photoshop. Four by Three (4:3): That's For
A brief intro to Photoshop. Although many other image manipulation tools are cheaper and a bit more user friendly, Photoshop is the leading tool for digital image manipulation. As you will see, our uses of Photoshop are basic, but for the introductory student they do require a little bit of work. Please don’t become bogged down in Photoshop. Complete these simple tasks and move on. Four by three (4:3): that’s for me! The industry standard for video and digital video production is an aspect ratio of 4:3. That means the measurements of the screen on which you will see your story finished is 4:3 and we must make all the images you scan fit into that size. The standard measurement for a computer is 640 pixels by 480 pixels (640 x 480 is 4:3!) If an image is scanned or cropped to be a different ratio, then in the end your image will be stretched and distorted to fit the screen, whether you like it or not. Example: You have to put your image through a sizing operation if you want to avoid this distortion. These are your options: 1 Option 1: The Black Bars 1. Open the picture you are working on. Go to FILE > OPEN. Select your file. 2. First make sure that the background is set to black. At the bottom of the tool bar are two little boxes, one on the top left, and one on the bottom right. Click on the bottom left corner box of the COLOR PICKER and choose black in the color picker window. -

Lærebok I Digital Kinoteknikk
Rolv Gjestland LÆREBOK I DIGITAL KINOTEKNIKK BOKEN ER LAGET I ET SAMARBEID MELLOM FILM & KINO OG FAGFORBUNDET Versjon: 11.12.16 17:36 © 2014 Rolv Gjestland Forsidebilde: Fra premiere på Law Abiding Citizen, Saga Kino i Oslo FOTO: JOHN BERGE, KINOMAGASINET © Illustrasjonene i boken er hentet fra tidligere lærebøker i kinoteknikk (Rolv Gjestland), materiell fra utstyrsfabrikanter, organisasjoner, DCI og fra kilder på internett (Wikipedia mm) Boken er gratis tilgjengelig på web. Det må ikke kopieres fra denne bok utover det som er tillatt etter "Lov om opphavsrett til åndsverk". side 2 Takk Det er mange som har bidratt til denne boken. Først og fremst vil jeg takke Fagforbundet Seksjon kirke, kultur og oppvekst, som har bidratt til finansiering av boken, og rådgiver Ellen Ovenstad, som har vært den viktigste pådriveren og har fulgt bokprosjektet hele veien. Uten denne støtten hadde det ikke blitt noen bok. Fagforbundet har også satt ned en gruppe som har kommet med gode innspill og råd. Gruppen har bestått av Stein Ivar Johansen, Oslo Kino, Per Georg Andersen, Oslo Kino og Hege Lochner, Kristiansand/Vennesla Kino. Stein Ivar har i tillegg vært behjelpelig med mye fagkunnskap og hjelp til illustrasjoner. Takk også til Ronny Bekken Larsen i Folldal, som var en av initiativtakerne til samarbeidet mellom Film & Kino og Fagforbundet om boken. Kinotekniske leverandører og utstyrsfabrikanter har generøst delt av sin kunnskap, og bidratt med informasjon og illustrasjoner om ulike produkter og bruken av disse. Jeg har fått gode råd og mange tips fra teknisk personale på kinoene. Spesielt vil jeg nevne Einar Jacobsen (Bergen), Kurt Laumann (Trondheim), Thor Vidar Hjelmervik (Haugesund) og personalet ved Kristiansand Kino hvor jeg hadde noen dagers praktisk opplæring. -

Widescreen Weekend 2008 Brochure (PDF)
A5 Booklet_08:Layout 1 28/1/08 15:56 Page 41 THIS IS CINERAMA Friday 7 March Dirs. Merian C. Cooper, Michael Todd, Fred Rickey USA 1952 120 mins (U) The first 3-strip film made. This is the original Cinerama feature The Widescreen Weekend continues to welcome all which launched the widescreen those fans of large format and widescreen films – era, and is about as fun a piece of CinemaScope, VistaVision, 70mm, Cinerama and IMAX – Americana as you are ever likely and presents an array of past classics from the vaults of to see. More than a technological curio, it's a document of its era. the National Media Museum. A weekend to wallow in the nostalgic best of cinema. HAMLET (70mm) Sunday 9 March Widescreen Passes £70 / £45 Dir. Kenneth Branagh GB/USA 1996 242 mins (PG) Available from the box office 0870 70 10 200 Kenneth Branagh, Julie Christie, Derek Jacobi, Kate Winslet, Judi Patrons should note that tickets for 2001: A Space Odyssey are priced Dench, Charlton Heston at £10 or £7.50 concessions Anyone who has seen this Hamlet in 70mm knows there is no better-looking version in colour. The greatest of Kenneth Branagh’s many achievements so 61 far, he boldly presents the full text of Hamlet with an amazing cast of actors. STAR! (70mm) Saturday 8 March Dir. Robert Wise USA 1968 174 mins (U) Julie Andrews, Daniel Massey, Richard Crenna, Jenny Agutter Robert Wise followed his box office hits West Side Story and The Sound of Music with Star! Julie 62 63 Andrews returned to the screen as Gertrude Lawrence and the film charts her rise from the music hall to Broadway stardom. -

SCMS 2011 MEDIA CITIZENSHIP • Conference Program and Screening Synopses
SCMS 2011 MEDIA CITIZENSHIP • Conference Program and Screening Synopses The Ritz-Carlton, New Orleans • March 10–13, 2011 • SCMS 2011 Letter from the President Welcome to New Orleans and the fabulous Ritz-Carlton Hotel! On behalf of the Board of Directors, I would like to extend my sincere thanks to our members, professional staff, and volunteers who have put enormous time and energy into making this conference a reality. This is my final conference as SCMS President, a position I have held for the past four years. Prior to my presidency, I served two years as President-Elect, and before that, three years as Treasurer. As I look forward to my new role as Past-President, I have begun to reflect on my near decade-long involvement with the administration of the Society. Needless to say, these years have been challenging, inspiring, and expansive. We have traveled to and met in numerous cities, including Atlanta, London, Minneapolis, Vancouver, Chicago, Philadelphia, and Los Angeles. We celebrated our 50th anniversary as a scholarly association. We planned but unfortunately were unable to hold our 2009 conference at Josai University in Tokyo. We mourned the untimely death of our colleague and President-Elect Anne Friedberg while honoring her distinguished contributions to our field. We planned, developed, and launched our new website and have undertaken an ambitious and wide-ranging strategic planning process so as to better position SCMS to serve its members and our discipline today and in the future. At one of our first strategic planning sessions, Justin Wyatt, our gifted and hardworking consultant, asked me to explain to the Board why I had become involved with the work of the Society in the first place. -

Cinerama to Digital Cinema: from the Zenith to the Decline Written by Enric Mas ( ) January 11, 2016
Enric Mas nitsenblanc.cat Cinerama to digital cinema: from the zenith to the decline Written by Enric Mas ( http://nitsenblanc.cat ) January 11, 2016 I try to imagine what the audience felt when they first saw a movie in Cinerama... but I cannot. I wonder, did they feel the same as I did when I saw a projection in 70 mm IMAX for the first time? Some clues tell me the answer is no. Howard Rust, of the International Cinerama Society, gave me an initial clue: “I was talking to a chap the other day who’d just been to see IMAX. ‘Sensational’, he said. ‘But, you know… it still doesn’t give you the same pins and needles up and down the back of your spin that Cinerama does’ ”. 1 What is its secret? Why is every film seen in Cinerama a unique event that is remembered for decades? We have another clue in a man who had worked with D.W. Griffith in That Royle Girl (1925), who produced and directed technically innovative short films, where black performers appeared, a rarity at the time, including the first appearance of Billie Holiday (Symphony in Black: A Rhapsody of Negro Life , 1935). He created a new imaging system (Vitarama) for the World’s Fair in New York (1939), joining 11 projectors of 16 mm, which reached a vertical image of 75 degrees high and 130 degrees wide, 2,3 developments which led to the most advanced artillery simulator in the world, which was used to train future aircraft gunners in World War II. -

Widescreen Weekend 2010 Brochure (PDF)
52 widescreen weekend widescreen weekend 53 2001: A SPACE ODYSSEY (70MM) REMASTERING A WIDESCREEN CLASSIC: Saturday 27 March, Pictureville Cinema WINDJAMMER GETS A MAJOR FACELIFT Dir. Stanley Kubrick GB/USA 1968 149 mins plus intermission (U) Saturday 27 March, Pictureville Cinema WIDESCREEN Keir Dullea, Gary Lockwood, William Sylvester, Leonard Rossiter, Ed Presented by David Strohmaier and Randy Gitsch Bishop and Douglas Rain as Hal The producer and director team behind Cinerama Adventure offer WEEKEND During the stone age, a mysterious black monolith of alien origination a fascinating behind-the-scenes look at how the Cinemiracle epic, influences the birth of intelligence amongst mankind. Thousands Now in its 17th year, the Widescreen Weekend Windjammer, was restored for High Definition. Several new and of years later scientists discover the monolith hidden on the moon continues to welcome all those fans of large format and innovative software restoration techniques were employed and the re- which subsequently lures them on a dangerous mission to Mars... widescreen films – CinemaScope, VistaVision, 70mm, mastering and preservation process has been documented in HD video. Regarded as one of the milestones in science-fiction filmmaking, Cinerama and IMAX – and presents an array of past A brief question and answer session will follow this event. Stanley Kubrick’s 2001: A Space Odyssey not only fascinated audiences classics from the vaults of the National Media Museum. This event is enerously sponsored by Cinerama, Inc., all around the world but also left many puzzled during its initial A weekend to wallow in the nostalgic best of cinema. release. More than four decades later it has lost none of its impact. -

Film Printing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 Film Technology in Post Production 4 5 6 7 8 9 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 30 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 40 1 2 3111 This Page Intentionally Left Blank 1 2 3 Film Technology 4 5 6 in Post Production 7 8 9 10 1 2 Second edition 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 20 1 Dominic Case 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 30 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 40 1 2 3111 4 5 6 7 8 Focal Press 9 OXFORD AUCKLAND BOSTON JOHANNESBURG MELBOURNE NEW DELHI 1 Focal Press An imprint of Butterworth-Heinemann Linacre House, Jordan Hill, Oxford OX2 8DP 225 Wildwood Avenue, Woburn, MA 01801-2041 A division of Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd A member of the Reed Elsevier plc group First published 1997 Reprinted 1998, 1999 Second edition 2001 © Dominic Case 2001 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any material form (including photocopying or storing in any medium by electronic means and whether or not transiently or incidentally to some other use of this publication) without the written permission of the copyright holder except in accordance with the provisions of the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988 or under the terms of a licence issued by the Copyright Licensing Agency Ltd, 90 Tottenham Court Road, London, England W1P 0LP. Applications for the copyright holder’s written permission to reproduce any part of this publication should be addressed to the publishers British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library Library of Congress Cataloging in Publication Data A catalogue record -

History-Of-The-Moving-Image-LIB-Pd
tEl:T. n83 MASTERPIECES OF MOVINGIMAGE TECI{NOLOGY SEPTEMBER 10, 1988 _ MARCH 19, 1989 Descri ption! gf_fhq Objects in the Exhibition American Museum of the Moving lmage Edison KinetograPh Camera 1891 ln 1888, Thomas Edison set out to create "an instrument that does for the Eye what the phono- graph does for the Ear...." He assigned the project to one of his engineers, W.K.L. Dickson, who, after a series of false starts, completed the Kinetograph in 1891. The Kinetograph was the first motion picture camera to use the Eastman celluloid f ilm; this was a key breakthrough which made modern motion pic- tures possible. The camera photographed circular images one-half inch in diameter on perforated, f lexible strips of film which moved horizontally through a mechanized sprocket system' The prototype was cannibalized for laboratory use soon after completion, but was partially reconstructed in '1895-96 as evidence in a patent dispute. (Lent by the Edison National Historic Site) <Technician Charles H. Kayser posing with the Kinetograph in Edison's West Orange, New .lersey laboratory, c. 1891 . Edison KinetoscoPe 1894 To exploit his moving pictures commercially, Edison introduced the Kinetoscope, a "peep-show" viewer capable of presenting half-minute film shows. The machines were sold on a territory basis to showmen who installed them in arcades and Kinetoscope Parlors in all the major cities of America and Europe' Commercially, the Kinetoscope was a short-lived novelty, but its appearance directly inspired other inventors to find a way of projecting moving images onto a screen. (Reproduction made by A. -

Escape, Cinerama & the Triptych
58 WIDESCREEN WEEKEND Three steps to heaven Escape, Cinerama & The Triptych Mark Trompeteler reports on the evolving Widescreen Weekend festival of big screen technology at the National Science & Media Museum ust as cinema changes and heaven almost no other venue can emulate. central screen. An additional pair of evolves, so the festivals and Barco’s Stefan Vandemaele and acoustically transparent, and retractable institutions around it change too. Frederick Lanoy referred to the company’s screens, with additional curtaining, are A more diverse demographic of development and launch of the three-wall added to the two sides of the existing screen. delegates than usual descended on Escape system as almost part of another It is DCI-compliant and versions of movies Jthe newly renamed National Science and repeat of cinema history. They asserted that will be available with DCPs encoded so that Media Museum in Bradford to attend the recently, whilst box office takings were either the movie can be run with just one 21st Widescreen Weekend for four days in remaining steady, due to the utilisation of central screen, or in a version that has the mid-October. It billed itself as “the unique higher prices for PLF and an improved and two added screens available to project. They festival of big screen technology, past, wider range of offer and other sales factors, argue that, due to digital projection, Escape present and future”. Incorporating its there will always be a concern about falling is deliverable far more easily and reliably IMAX auditorium alongside the analogue, attendances in auditoria. As in previous than was Cinerama.