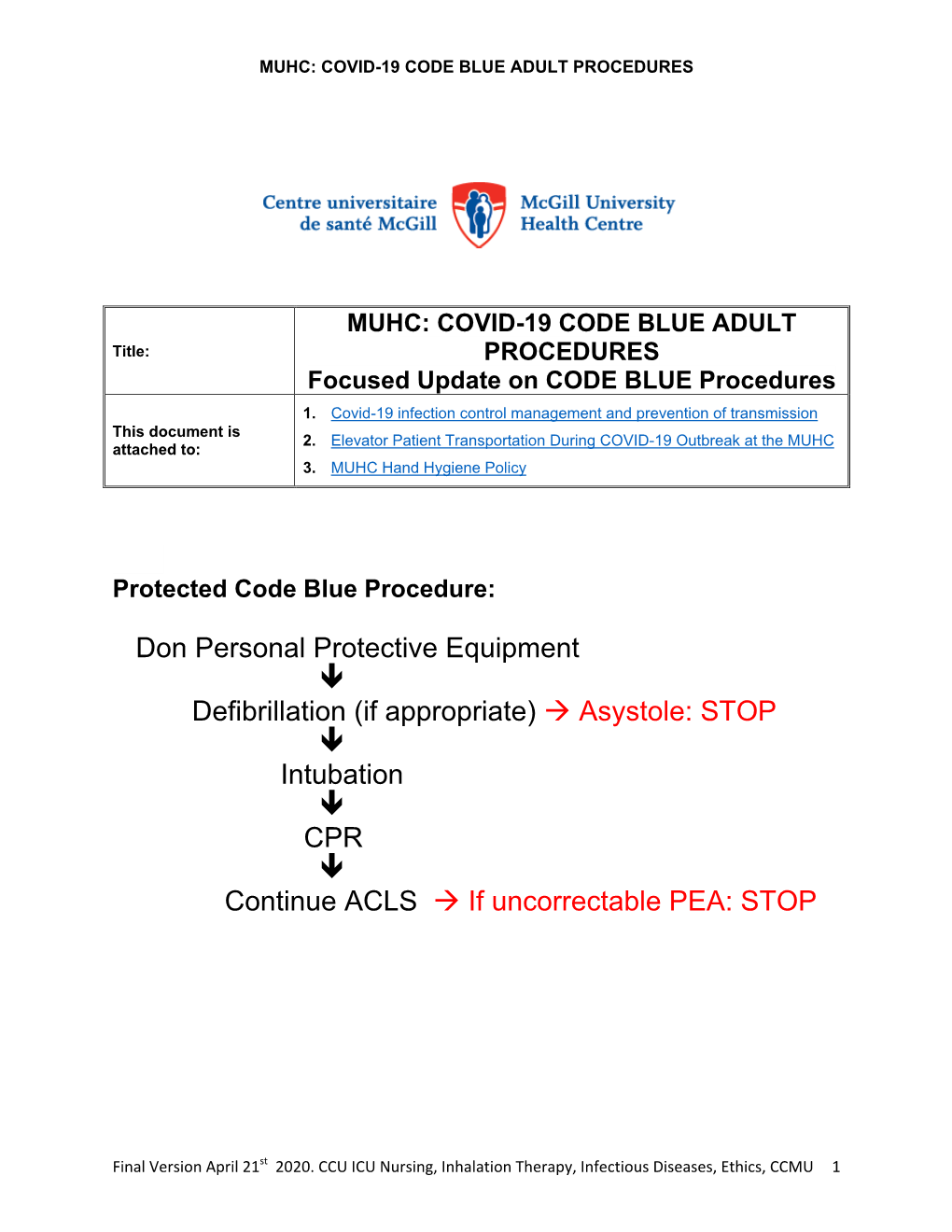
Code Blue Protocol Applies
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

ABCDE Approach
The ABCDE and SAMPLE History Approach Basic Emergency Care Course Objectives • List the hazards that must be considered when approaching an ill or injured person • List the elements to approaching an ill or injured person safely • List the components of the systematic ABCDE approach to emergency patients • Assess an airway • Explain when to use airway devices • Explain when advanced airway management is needed • Assess breathing • Explain when to assist breathing • Assess fluid status (circulation) • Provide appropriate fluid resuscitation • Describe the critical ABCDE actions • List the elements of a SAMPLE history • Perform a relevant SAMPLE history. Essential skills • Assessing ABCDE • Needle-decompression for tension • Cervical spine immobilization pneumothorax • • Full spine immobilization Three-sided dressing for chest wound • • Head-tilt and chin-life/jaw thrust Intravenous (IV) line placement • • Airway suctioning IV fluid resuscitation • • Management of choking Direct pressure/ deep wound packing for haemorrhage control • Recovery position • Tourniquet for haemorrhage control • Nasopharyngeal (NPA) and oropharyngeal • airway (OPA) placement Pelvic binding • • Bag-valve-mask ventilation Wound management • • Skin pinch test Fracture immobilization • • AVPU (alert, voice, pain, unresponsive) Snake bite management assessment • Glucose administration Why the ABCDE approach? • Approach every patient in a systematic way • Recognize life-threatening conditions early • DO most critical interventions first - fix problems before moving on -

Tracheal Intubation Following Traumatic Injury)
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT UPDATE The Journal of TRAUMA Injury, Infection, and Critical Care Guidelines for Emergency Tracheal Intubation Immediately after Traumatic Injury C. Michael Dunham, MD, Robert D. Barraco, MD, David E. Clark, MD, Brian J. Daley, MD, Frank E. Davis III, MD, Michael A. Gibbs, MD, Thomas Knuth, MD, Peter B. Letarte, MD, Fred A. Luchette, MD, Laurel Omert, MD, Leonard J. Weireter, MD, and Charles E. Wiles III, MD for the EAST Practice Management Guidelines Work Group J Trauma. 2003;55:162–179. REFERRALS TO THE EAST WEB SITE and impaired laryngeal reflexes are nonhypercarbic hypox- Because of the large size of the guidelines, specific emia and aspiration, respectively. Airway obstruction can sections have been deleted from this article, but are available occur with cervical spine injury, severe cognitive impairment on the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma (EAST) (Glasgow Coma Scale [GCS] score Յ 8), severe neck injury, Web site (www.east.org/trauma practice guidelines/Emergency severe maxillofacial injury, or smoke inhalation. Hypoventi- Tracheal Intubation Following Traumatic Injury). lation can be found with airway obstruction, cardiac arrest, severe cognitive impairment, or cervical spinal cord injury. I. STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM Aspiration is likely to occur with cardiac arrest, severe cog- ypoxia and obstruction of the airway are linked to nitive impairment, or severe maxillofacial injury. A major preventable and potentially preventable acute trauma clinical concern with thoracic injury is the development of Hdeaths.1–4 There is substantial documentation that hyp- nonhypercarbic hypoxemia. Lung injury and nonhypercarbic oxia is common in severe brain injury and worsens neuro- hypoxemia are also potential sequelae of aspiration. -

Crash Cart Drawers
15MS3130 ASC Guide_Layout 1 4/7/15 8:54 PM Page 97 Emergency Crash Cart Essentials for Physician Office and Healthcare Facilities THIRD DRAWER-Circulation: CC Qty. Inventory Component Order# crash cart 2 Lasix 40mg/10mL – CC Drugs 1 Magnesium Sulfate 5 Gm./10mL CC Drugs drawers FOURTH DRAWER-Circulation (IV): CC Qty. Inventory Component Order# 3 Gloves- Nitratex® Small Sterile PF 100 /Box 685-5866 3 Gloves- Nitratex® Med Sterile PF 100/Box 685-7913 3 Gloves- Nitratex® Large Sterile PF 100/Box 685-4461 Each Tape-Hypafix 2" x 2 Yds. Roll 925-4928 2 Introcan® Safety IV Catheter 22 Ga. x 1” Each 507-5531 2 Introcan® Safety IV Catheter 20 Ga. x 1” Each 507-5995 1 Arterial Blood Gas Kit 25 Ga. x ⅝" 100/Case 245-2041 1 Tourniquet Latex-Free, 18” x 1” 25/Box 270-3884 5 Alcohol Swabs- BD Swabsticks 100/Box 987-5706 2 Syringes 60mL 50/Box 112-6152 2 Syringes 20mL 50/Box 112-6151 5 Syringes 10mL 100/Box 900-4476 5 Syringes 5mL 100/Box 900-4477 5 Syringes 3mL 100/Box 900-4475 10 Needles 18 Ga. x 1” 100/Box 900-4469 2 Injectable Saline 30mL CC Drugs Each Conductivity Gel-Spectra™ 360 8.5 oz. 727-6353 FIRST DRAWER-Medications: CC Qty. Inventory Component Order# FIFTH DRAWER–Intubation: CC Qty. Inventory Component Order# 2 Adenosine 3mg 2mL CC Drugs 1 Amiodarone HCl 50mg 3mL CC Drugs 36 Dantrium 20mg – Each CC Drugs 1 Atropine Sulfate 10mL CC Drugs 1 Laryngoscope – Welch-Allyn Handle Each 566-6530 1 Calcium Gluconate 10% 10mL CC Drugs 1 Miller Blade #2 – Disposable Each 857-5266 1 Dobutamine 250mg 20mL CC Drugs 1 Miller Blade #3 – Disposable Each 857-3605 -

Emergency Department Resuscitation of the Critically Ill Review by Stephen C
BOOK AND MEDIA REVIEW Emergency Department Resuscitation of the Critically Ill Review by Stephen C. Morris, MD, MPH 0196-0644/$-see front matter Copyright © 2018 by the American College of Emergency Physicians. Emergency Department Resuscitation of the crashing morbidly obese patient reviews some of the nuanced Critically Ill management we should be striving for as more of our patients become obese, such as specific airway and ventilation Winters ME, Bond MC, Marcolini EG, et al management and use of ideal versus total body weight American College of Emergency Physicians calculations for critical-care-specific medications. Consider It was with great pleasure that I agreed to review the another example from the chapter on left ventricular assist second edition of Emergency Department Resuscitation of the devices. Although these patients have long been the domain Critically Ill, by Michael E. Winters. I had read and relied of specialty centers, with complex physiology and on the first edition posttraining. Like most who work in complications, the longevity now offered by the devices will emergency medicine, I practice a great deal of critical care; ultimately make them the domain of the community however, I have not completed a fellowship in critical care, emergency department. Additionally, at the cutting edge of nor do I review critical care literature with the level of our practice, the text contains a chapter on extracorporeal scrutiny that I would like. For those of us who want to membrane oxygenation, with a discussion of the practical ensure that we are up to date to guarantee clinical and clinical aspects of implementation. -

Strategies to Support the COVID-19 Response in Lmics a Virtual Seminar Series Screening, Triage and Patient Flow
Strategies to support the COVID-19 response in LMICs A virtual seminar series Screening, Triage and Patient Flow Bhakti Hansoti, MBChB, MPH, PhD - Associate Professor in Emergency Medicine, Johns Hopkins University OBJECTIVES 1. Clinical Features 2. Preparing the Department 3. Initial Management 4. Other Management Considerations 5. Summary Clinical Features Severity • Most people with COVID-19 develop mild or uncomplicated illness • Approximately 14% develop severe disease requiring hospitalization and oxygen support • 5% require admission to an intensive care unit • In severe cases, COVID-19 can be complicated by • Acute respiratory disease syndrome (ARDS) • Sepsis and septic shock • Multiorgan failure, including acute kidney injury and cardiac injury. Preparing the Department Elements to be assessed have been divided into the following areas: • Establishment of a core team and key internal and external contact points • Human, material and facility capacity • Communication and data protection • Hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE), and waste management • Triage, first contact and prioritization • Patient placement, moving of the patients in the facility, and visitor access • Environmental cleaning https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/checklist- hospitals-preparing-reception-and-care-coronavirus-2019-covid-19 Split flow Protecting Yourself These videos can help with PPE donning and doffing technique: • Donning and doffing PPE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I94l IH8xXg8 • Recommended PPE during care https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oPL -

ACLS: Crash Course in Crash Carts
ACLS: Crash course in crash carts By Andrew Herman, MS, RN How proficient would you really be if a code situa- the setting at 2 mA above that capture point. The tion occurred? Even while keeping your skills up to patient should now be ready for immediate transfer date with advanced cardiovascular life support for more definitive care, such as internal pacing. (ACLS) recertification, it’s possible for nurses to find themselves out-of-practice. This article outlines Tachycardia the magic numbers associated with ACLS, the tools At the other extreme, tachycardia can cause the and medications you’ll find in the crash cart, and patient’s cardiac perfusion to drop because the treatment guidelines to follow in a code situation. heart is beating faster than it’s designed to do. This brings us to our next ACLS magic number: Bradycardia 150. A heart rate above 150 beats/minute is the Let’s begin with a bradycardia situation. Here, we point at which electrical therapy should be consid- encounter one of our ACLS magic numbers: 90. As ered. Supraventricular tachycardia, rapid atrial a rule, a patient with a dysrhythmia who still flutter, or rapid atrial fibrillation will show a maintains a systolic BP of 90 mm Hg or higher can narrow QRS complex on the ECG of less than receive treatment with medications. But, if the sys- 0.12 seconds, which equals three of the small tolic BP decreases to below 90, we have to set up 0.04-second squares on the ECG graph. Ventricular for electrical therapy. tachycardia will have a very wide QRS complex of Ideally, crash carts are standardized. -

High Performance CPR Update
High Performance CPR Update Page | 1 Final Revision 8/8/2012 As part of our ongoing Quality Assurance in Cardiac Arrest incidents, Skagit County EMS under the direction of Dr. Don Slack, MPD is making changes to the way that ALS and BLS providers perform CPR. Overview: CPR quality has a dramatic impact on pt survival when done according to these guidelines. Minimal breaks in compressions, full chest recoil, adequate compression depth and adequate compression rate are all components of CPR that an increase survival from sudden cardiac arrest. Together these components go together to create High Performance CPR (HP CPR). Roles: As a rule for the unconscious, unresponsive, pulseless patient the FIRST person to the patient starts compressions. SECOND person does defibrillation (If there are only 2 responders to begin with, ventilations should begin after the rhythm analysis and shock if indicated). THIRD person should start ventilating the patient, placing a King Airway as soon as is practical. A timekeeper needs to be assigned to ensure high quality CPR, minimal interruption and help track the ALS interventions. Principles of HP CPR 1. EMT’s own CPR!! 2. Minimize interruption in CPR at all times, use a timekeeper 3. Ensure proper depth of compressions (>2 inches) 4. Ensure full chest recoil/decompression 5. Ensure proper chest compression rate (100-120/min) 6. Rotate compressors at least every 2 minutes 7. Do not interrupt compressions to ventilate patient, even if an advanced airway is not placed 8. Hands off the chest only during analysis and shock delivery, hover hands over chest during shock delivery and be ready to resume compressions 9. -

The Nebraska Office of Emergency Health Systems Trauma Program Is Pleased That You Wish to Participate in the Statewide Trauma System
Revised July 2019 INSTRUCTIONS FOR FILLING OUT PRE-REVIEW QUESTIONNAIRE (PRQ) The Nebraska Office of Emergency Health Systems Trauma Program is pleased that you wish to participate in the statewide trauma system. The Nebraska Statewide Trauma System is comprised of hospitals and clinics striving to improve trauma patient care. Through this system all facilities offering trauma care may become centers of excellence. Thank you for participating in this process. In order to prepare for your on-site review, please complete this questionnaire. All answers should directly follow the questions. The entire questionnaire is available on the web in a downloadable format @ http://dhhs.ne.gov/Pages/EHS-Statewide-Trauma-System-of-Care.aspx. The PRQ should be completed electronically if possible otherwise, you may submit a hard copy. Note: If a hard copy is printed a color printer should be used so that information and questions printed in blue appear on the page to the applicant. Return the completed questionnaire to: Sherri Wren EHS Trauma Program Manager Office of Emergency Health Systems P.O. Box 95026 Lincoln, NE 68509-5026 Phone: (402) 471-0539 E-mail: [email protected] If you have questions or concerns while filling out the PRQ, please contact: State of Nebraska Trauma Nurse Specialist OR your Regional Trauma Program Manager (please reference website list of Designated Trauma Centers on the website cited above for names and contact information). I. PURPOSE: A. The purpose of this questionnaire for Consultation Visits is: 1. To provide your institution with an outline of what site visitors will be discussing with you. -

Small Adult CPR-2 Bag with Litesaver Manometer Brochure
ORDERING INFORMATION Your Need ... Our Innovation® O Manometer 2 Detector 2 AerosolTubing Reservoir Infant Cushion Mask Expandable Large Bore Color-Coded Mask PEEP w/Filter StatCO Manometer LiteSaverTiming Light with CPR (Synthetic Rubber) CPR-2 (PVC) Light Blue Oxygen Bag Reservoir (22mm) Adult Cushion Mask SmallAdult Cushion Mask with Flange #3 Pediatric Cushion Mask Child Cushion Mask PEEP Valve Pop-Off Dark Blue Oxygen Reservoir 0-60 cm H PART # OTHER #10-56402 X X X X X X #10-56403 X X X X #10-56404 X X X X X #10-56411 X X X X #10-56412 X X X X X #10-56423 X X X X X X #10-56424 X X X X X X CPR-2 Small Adult Bag with Manometer #10-56432 X X X X X #10-56435 X X X X X X X #10-56437 X X X X #10-56438 X X X X X #10-56440 X X X X #10-58500 X X X X #10-58501 X X X X X #10-58502 X X X X X #10-58503 X X X X X X #10-58506 X X X X X X #10-58507 X X X X X #10-58509 X X X X X #10-58512 X X X X X X X #10-55901 X X X #10-55904 X X X #10-55907 X X X #10-55909 X X X X #10-55910 X X X X #10-55912 X X X #10-55913 X X X X X X No lock clip #10-55915 X X X X X #10-55916 X X X #10-55917 X X X X X #10-55918 X X X X X X #10-55922 X X X X X X X #10-55923 X X X X #10-55924 X X X X X #10-55928 X X X #10-58400 X X X X #10-55365 LiteSaver Manometer Assy 20/Box 0-60 cm H2O, Adult Frequency 10 BPM #10-55366 LiteSaver Manometer Assy 20/Box Assembly 0-60 cm H2O In-Line Tee Right Orientation, Adult Frequency 10 BPM #10-55367 LiteSaver Manometer Assy 20/Box Assembly 0-60 cm H2O In-Line Tee Left Orientation, Adult Frequency 10 BPM = CPR-2 Small Adult Bags *References Can EMS Providers Provide Appropriate Tidal Volumes in a Simulated Adult-sized Patient with a Pediatric-sized Bag-Valve-Mask? Journal Pre-hospital Emergency Care, Volume 21, 2017, Issue 1, Jeffery Siegler, MD, EMT-P, Melissa Kroll, MD, Susan Wojcik, PhD, ATC & Hawnwan Philip May, MD Avoid Airway Catastrophes on the Extremes of Minute Ventilation, Acepnow.com, January 20, 2015, Richard M. -

Capnography (ILS/ALS)
Capnography (ILS/ALS) Clinical Indications: 1. Capnography shall be used as soon as possible in conjunction with any airway management adjunct, including endotracheal, Blind Insertion Airway Devices (BIAD) or Bag Valve Mask (BVM). 2. Capnography should also be used on all patients treated with CPAP or epinephrine for respiratory distress. 3. Acute respiratory distress. 4. Assisted ventilations. 5. Sustained altered mental status. Procedure: 1. Attach capnography sensor to the BIAD, endotracheal tube, or oxygen delivery device. 2. Note CO2 level and waveform changes. These will be documented on each respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, or respiratory distress patient. 3. The capnometer shall remain in place with the airway and be monitored throughout the prehospital care and transport. 4. Any loss of CO2 detection or waveform indicates an airway problem and should be documented. 5. The capnogram should be monitored as procedures are performed to verify or correct the airway problem. 6. Document the procedure and results on/with the Patient Care Report (PCR) and the Airway Evaluation Form. 7. In all patients with a pulse, an ETCO2 >20 is anticipated. In the post-resuscitation patient, no effort should be made to lower ETCO2 by modification of the ventilatory rate. Further, in post- resuscitation patients without evidence of ongoing, severe bronchospasm, ventilatory rate should never be < 6 breaths per minute. 8. In the pulseless patient, and ETCO2 waveform with an ETCO2 value >10 may be utilized to confirm the adequacy of an airway to include BVM and advanced devices when Sp02 will not register. Critical Comment: • When CO2 is NOT detected, three factors must be quickly assessed : 1. -

Advances in the Acute Management of Cardiac Arrest
September 2008 Advances In The Acute Volume 10, Number 9 Management Of Cardiac Arrest Authors Bakhtiar Ali, MD Atlanta Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Decatur, GA A 47-year-old man presents with nonspecific chest discomfort intermittently over the past 3 days. Episodes are not related to exertion and last 10 to 30 A. Maziar Zafari, MD, PhD, FACC, FAHA minutes. He has a history of hypertension and smokes 1 pack per day. In the Atlanta Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Decatur, Georgia; Emory University School of Medicine, Division of ED, he is pain free and has an ECG with evidence of left ventricular hypertro- Cardiology, Atlanta, GA phy and j-point elevation. You doubt that he has an acute cardiac syndrome but Peer Reviewers decide to err on the conservative side and admit him to your observation unit. The patient looks well, his first troponin is negative, and the monitor continues Bentley J. Bobrow, MD, FACEP Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine, Department to show a normal sinus rhythm. Two hours later you go to check on the patient of Emergency Medicine, College of Medicine, Mayo and find him disconnected from his monitor, unresponsive, and with no pulse Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ; Medical Director, Bureau of Emergency Medical Services and Trauma System, Arizona (no wonder there was so much beeping coming from the obs unit). The nurse Department of Health Services, Phoenix, AZ has been on break for the past 30 minutes, and due to “sick calls” there was no cross coverage. You call for help which doesn’t immediately come, and you Barbara K. -

Information on Defibrillation and Ventilation with the LUCAS® Chest Compression System
® LUCAS CHEST COMPRESSION SYSTEM Information on Defibrillation and Ventilation with the LUCAS® Chest Compression System The goal when using the LUCAS device is to provide effective, After Defibrillation consistent, and uninterrupted chest compressions. When an After the shock is delivered it is important to verify the position of the interruption to chest compressions occurs, the patient’s coronary suction cup to see it has not moved out of place. This is easier to do perfusion pressure (CPP) drops rapidly. CPP is the measure of the if an ink marker line was marked where the suction cup was originally pressure that drives blood flow through the coronary arteries to the positioned on the patient. Readjust as necessary. heart muscle. The heart normally maintains a CPP of 60 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or more. During cardiac arrest, the CPP drops dramatically, threatening the heart muscle’s blood supply. As it can take Oxygenation with Ventilation some time to build up CPP again, interruptions to chest compressions should be minimized. To supply adequate concentrations of oxygen in the blood, ensure the patient is properly ventilated. Ventilations should be provided in The current American Heart Association Guidelines emphasize conjunction with mechanical chest compressions. Interruptions to 1 minimizing interruptions when delivering high quality CPR: chest compressions should be minimized to maintain the level of • Minimize pre- and post-shock pauses (class I), oxygen delivered to tissues. During the first few minutes of sudden cardiac arrest, chest compressions to improve blood flow have been • Pause compressions for less than 10 seconds when delivering two shown to be more important than ventilations because oxygen blood breaths (class IIa), levels remain high initially.4 • Maximize the time with chest compressions (class IIb).