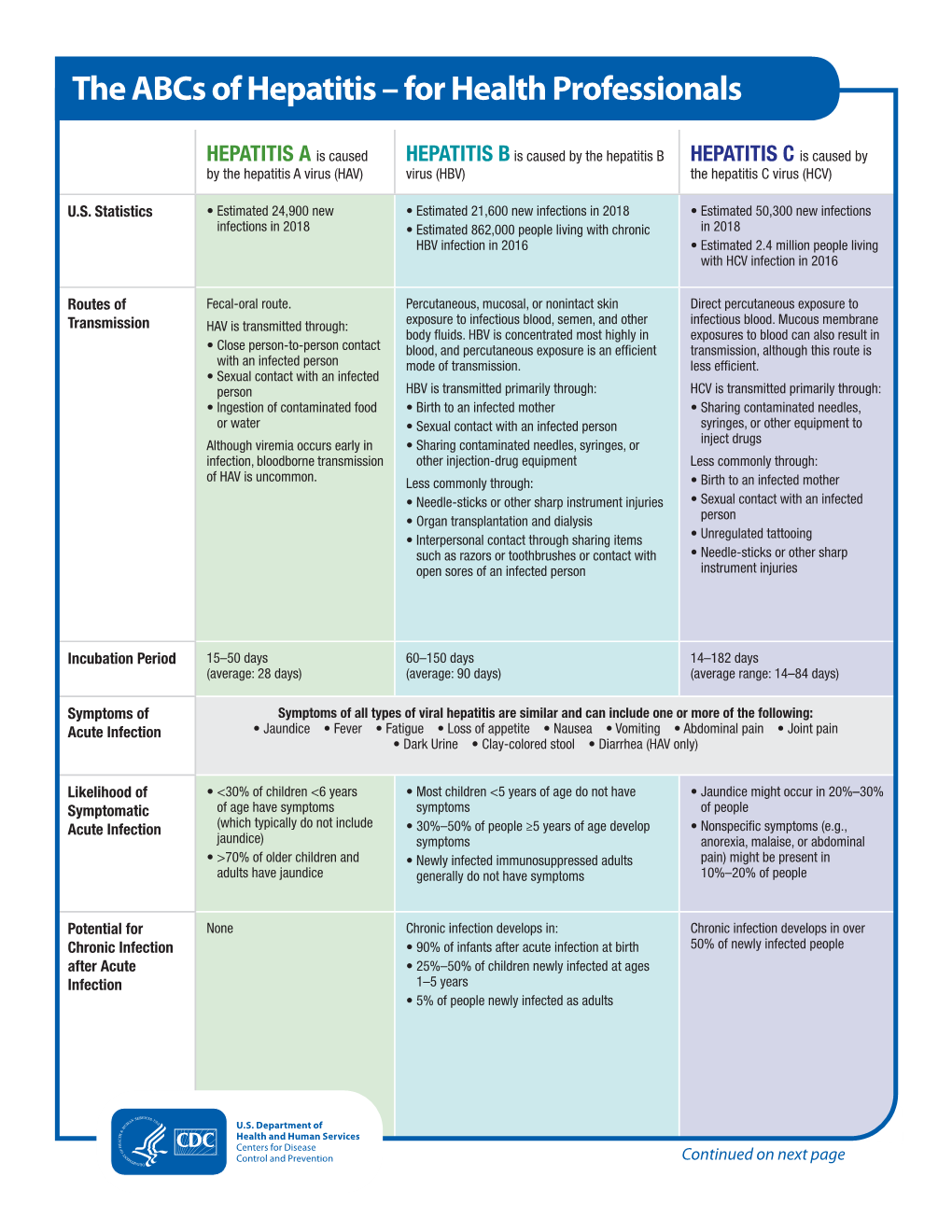
The Abcs of Hepatitis – for Health Professionals
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Food Handler Exclusion Guidelines
Food Handler Exclusion Guidelines A guide for determining suitable exclusion periods for ill food handlers November 2017 Food handler exclusion guidelines Published by the State of Queensland (Queensland Health), November 2017 This document is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Australia licence. To view a copy of this licence, visit creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/au © State of Queensland (Queensland Health) 2017 You are free to copy, communicate and adapt the work, as long as you attribute the State of Queensland (Queensland Health). For more information contact: Food Safety Standards and Regulation, Department of Health, GPO Box 48, Brisbane QLD 4001, email [email protected], phone 07 3328 9310. An electronic version of this document is available at www.health.qld.gov.au. Disclaimer: The content presented in this publication is distributed by the Queensland Government as an information source only. The State of Queensland makes no statements, representations or warranties about the accuracy, completeness or reliability of any information contained in this publication. The State of Queensland disclaims all responsibility and all liability (including without limitation for liability in negligence) for all expenses, losses, damages and costs you might incur as a result of the information being inaccurate or incomplete in any way, and for any reason reliance was placed on such information. Food Handler Exclusion Guidelines - ii - Contents 1. Introduction ............................................................................................... -

PEDIARIX Is a Vaccine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION • If Guillain-Barré syndrome occurs within 6 weeks of receipt of a prior These highlights do not include all the information needed to use vaccine containing tetanus toxoid, the decision to give PEDIARIX should PEDIARIX safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for be based on potential benefits and risks. (5.2) PEDIARIX. • The tip caps of the prefilled syringes contain natural rubber latex which may cause allergic reactions. (5.3) PEDIARIX [Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Acellular Pertussis • Syncope (fainting) can occur in association with administration of Adsorbed, Hepatitis B (Recombinant) and Inactivated Poliovirus injectable vaccines, including PEDIARIX. Procedures should be in place Vaccine], Suspension for Intramuscular Injection to avoid falling injury and to restore cerebral perfusion following Initial U.S. Approval: 2002 syncope. (5.4) • If temperature ≥105°F, collapse or shock-like state, or persistent, ----------------------------- INDICATIONS AND USAGE ---------------------------- PEDIARIX is a vaccine indicated for active immunization against diphtheria, inconsolable crying lasting ≥3 hours have occurred within 48 hours after tetanus, pertussis, infection caused by all known subtypes of hepatitis B virus, receipt of a pertussis-containing vaccine, or if seizures have occurred and poliomyelitis. PEDIARIX is approved for use as a 3-dose series in infants within 3 days after receipt of a pertussis-containing vaccine, the decision born of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-negative mothers. PEDIARIX to give PEDIARIX should be based on potential benefits and risks. (5.5) may be given as early as 6 weeks of age through 6 years of age (prior to the • For children at higher risk for seizures, an antipyretic may be 7th birthday). -

Viral Hepatitis Testing Effective Date: January 1, 2012
Viral Hepatitis Testing Effective Date: January 1, 2012 Scope This guideline provides guidance for the use of laboratory tests to diagnose acute and chronic viral hepatitis in adults (> 19 years) in the primary care setting. General Considerations for Ordering Laboratory Tests Prior to ordering tests for hepatitis, consider the patient’s history, age, risk factors (see below), hepatitis vaccination status, and any available previous hepatitis test results. Risk Factors for Viral Hepatitis include: • Substance use (includes sharing drug snorting, smoking or injection equipment) • High-risk sexual activity or sexual partner with viral hepatitis • Travel to or from high-risk hepatitis endemic areas or exposure during a local outbreak • Immigration from hepatitis B and/or C endemic countries • Household contact with an infected person especially if personal items (e.g., razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers) are shared • Recipient of unscreened blood products* • Needle-stick injury or other occupational exposure (e.g., healthcare workers) • Children born to mothers with chronic hepatitis B or C infection • Attendance at daycare • Contaminated food or water (hepatitis A only) • Tattoos and body piercing • History of incarceration • HIV or other sexually transmitted infection • Hemodialysis *screening of donated blood products for hepatitis C (anti-HCV) began in 1990 in Canada.1 Types of Viral Hepatitis Hepatitis A: causes acute but not chronic hepatitis Hepatitis B: causes acute and chronic hepatitis Hepatitis C: causes chronic hepatitis but rarely manifests as acute hepatitis Hepatitis D: rare and only occurs in patients infected with hepatitis B Hepatitis E: clinically similar to hepatitis A, mostly restricted to endemic areas and occasionally causes chronic infection in immunosuppressed people Others: e.g. -

Autoimmune Hepatitis
Page 1 of 5 Autoimmune Hepatitis Autoimmune hepatitis is an uncommon cause of chronic hepatitis (persistent liver inflammation). The cause is not known. If left untreated, the inflammation causes cirrhosis (scarring of the liver). However, with treatment, the outlook for people with this condition is very good. Treatment is usually with steroids and other medicines which suppress inflammation. What does the liver do? The liver is in the upper right part of the abdomen. It has many functions which include: Storing glycogen (fuel for the body) which is made from sugars. When required, glycogen is broken down into glucose which is released into the bloodstream. Helping to process fats and proteins from digested food. Making proteins that are essential for blood to clot (clotting factors). Processing many medicines which you may take. Helping to remove or process alcohol, poisons and toxins from the body. Making bile which passes from the liver to the gut down the bile duct. Bile breaks down the fats in food so that they can be absorbed from the bowel. What is autoimmune hepatitis? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. There are many causes of hepatitis. For example, alcohol excess and infections with various viruses are the common causes of hepatitis. Autoimmune hepatitis is an uncommon cause of chronic hepatitis. Chronic means that the inflammation is persistent or long-term. The chronic inflammation gradually damages the liver cells, which can result in serious problems. What causes autoimmune hepatitis? Page 2 of 5 The cause is not clear. It is thought to be an autoimmune disease. Our immune system normally defends us against infection from bacteria, viruses and other germs. -

Prevention & Control of Viral Hepatitis Infection
Prevention & Control of Viral Hepatitis Infection: A Strategy for Global Action © World Health Organization 2011. All rights reserved. The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the World Health Organization concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Dotted lines on maps represent approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement. The mention of specific companies or of certain manufacturers’ products does not imply that they are endorsed or recommended by the World Health Organization in preference to others of a similar nature that are not mentioned. Errors and omissions excepted, the names of proprietary products are distinguished by initial capital letters. All reasonable precautions have been taken by WHO to verify the information contained in this publication. However, the published material is being distributed without warranty of any kind, either express or implied. The responsibility for the interpretation and use of the material lies with the reader. In no event shall the World Health Organization be liable for damages arising from its use. Table of contents Disease burden 02 What is viral hepatitis? 05 Prevention & control: a tailored approach 06 Global Achievements 08 Remaining challenges 10 World Health Assembly: a mandate for comprehensive prevention & control 13 WHO goals and strategy -

The Role of Hepatitis C Virus in Hepatocellular Carcinoma U
Viruses in cancer cell plasticity: the role of hepatitis C virus in hepatocellular carcinoma U. Hibner, D. Gregoire To cite this version: U. Hibner, D. Gregoire. Viruses in cancer cell plasticity: the role of hepatitis C virus in hepato- cellular carcinoma. Contemporary Oncology, Termedia Publishing House, 2015, 19 (1A), pp.A62–7. 10.5114/wo.2014.47132. hal-02187396 HAL Id: hal-02187396 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02187396 Submitted on 2 Jun 2021 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution - NonCommercial - ShareAlike| 4.0 International License Review Viruses are considered as causative agents of a significant proportion of human cancers. While the very Viruses in cancer cell plasticity: stringent criteria used for their clas- sification probably lead to an under- estimation, only six human viruses the role of hepatitis C virus are currently classified as oncogenic. In this review we give a brief histor- in hepatocellular carcinoma ical account of the discovery of on- cogenic viruses and then analyse the mechanisms underlying the infectious causes of cancer. We discuss viral strategies that evolved to ensure vi- Urszula Hibner1,2,3, Damien Grégoire1,2,3 rus propagation and spread can alter cellular homeostasis in a way that increases the probability of oncogen- 1Institut de Génétique Moléculaire de Montpellier, CNRS, UMR 5535, Montpellier, France ic transformation and acquisition of 2Université Montpellier 2, Montpellier, France stem cell phenotype. -

The Use of Non-Human Primates in Research in Primates Non-Human of Use The
The use of non-human primates in research The use of non-human primates in research A working group report chaired by Sir David Weatherall FRS FMedSci Report sponsored by: Academy of Medical Sciences Medical Research Council The Royal Society Wellcome Trust 10 Carlton House Terrace 20 Park Crescent 6-9 Carlton House Terrace 215 Euston Road London, SW1Y 5AH London, W1B 1AL London, SW1Y 5AG London, NW1 2BE December 2006 December Tel: +44(0)20 7969 5288 Tel: +44(0)20 7636 5422 Tel: +44(0)20 7451 2590 Tel: +44(0)20 7611 8888 Fax: +44(0)20 7969 5298 Fax: +44(0)20 7436 6179 Fax: +44(0)20 7451 2692 Fax: +44(0)20 7611 8545 Email: E-mail: E-mail: E-mail: [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] Web: www.acmedsci.ac.uk Web: www.mrc.ac.uk Web: www.royalsoc.ac.uk Web: www.wellcome.ac.uk December 2006 The use of non-human primates in research A working group report chaired by Sir David Weatheall FRS FMedSci December 2006 Sponsors’ statement The use of non-human primates continues to be one the most contentious areas of biological and medical research. The publication of this independent report into the scientific basis for the past, current and future role of non-human primates in research is both a necessary and timely contribution to the debate. We emphasise that members of the working group have worked independently of the four sponsoring organisations. Our organisations did not provide input into the report’s content, conclusions or recommendations. -

EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Autoimmune Hepatitisq
Clinical Practice Guidelines EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Autoimmune hepatitisq ⇑ European Association for the Study of the Liver striking progress, and now patients in specialised centres have an Introduction excellent prognosis, both in respect to survival and to quality of life. Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) was the first liver disease for which The aim of the present Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) is to an effective therapeutic intervention, corticosteroid treatment, provide guidance to hepatologists and general physicians in the was convincingly demonstrated in controlled clinical trials. diagnosis and treatment of AIH in order to improve care for However, 50 years later AIH still remains a major diagnostic affected patients. In view of the limited data from large con- and therapeutic challenge. There are two major reasons for this trolled studies and trials, many recommendations are based on apparent contradiction: Firstly, AIH is a relatively rare disease. expert consensus. This is to some extent a limitation of this Secondly, AIH is a very heterogeneous disease. EASL-CPG, but at the same time it is its special strength: consen- Like other rare diseases, clinical studies are hampered by the sus in this guideline is based on intensive discussions of experts limited number of patients that can be included in trials. Possibly from large treatment centres. The core consensus group has and more importantly, the interest of the pharmaceutical indus- experience of over one thousand AIH patients managed person- try to develop effective specific therapies for rare diseases is lim- ally, and the recommendations have been reviewed by both the ited due to the very restricted market for such products. -

Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea: Candidate Organisms Other Than Clostridium Difficile
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine : 23:9-15, 2008 Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea: Candidate Organisms other than Clostridium Difficile Hyun Joo Song, M.D.1, Ki-Nam Shim, M.D.1, Sung-Ae Jung, M.D.1, Hee Jung Choi, M.D.1, Mi Ae Lee, M.D.2, Kum Hei Ryu, M.D.1, Seong-Eun Kim, M.D.1 and Kwon Yoo, M.D.1 Department of Internal Medicine1 and Laboratory Medicine2, Ewha Medical Research Institute, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea Background/Aims : The direct toxic effects of antibiotics on the intestine can alter digestive functions and cause pathogenic bacterial overgrowth leading to antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD). Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) is widely known to be responsible for 10~20% of AAD cases. However, Klebsiella oxytoca, Clostridium perfringens, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida species might also contribute to AAD. Methods : We prospectively analyzed the organisms in stool and colon tissue cultures with a C. difficile toxin A assay in patients with AAD between May and December 2005. In addition, we performed the C. difficile toxin A assays using an enzyme-linked fluorescent assay technique. Patients were enrolled who had diarrhea with more than three stools per day for at least 2 days after the initiation of antibiotic treatment for up to 6~8 weeks after antibiotic discontinuation. Results : Among 38 patients (mean age 59±18 years, M:F=18:20), the organism isolation rates were 28.9% (11/38) for stool culture, 18.4% (7/38) for colon tissue cultures and 13.2% (5/38) for the C. -

Chronic Viral Hepatitis in a Cohort of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
pathogens Article Chronic Viral Hepatitis in a Cohort of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients from Southern Italy: A Case-Control Study Giuseppe Losurdo 1,2 , Andrea Iannone 1, Antonella Contaldo 1, Michele Barone 1 , Enzo Ierardi 1 , Alfredo Di Leo 1,* and Mariabeatrice Principi 1 1 Section of Gastroenterology, Department of Emergency and Organ Transplantation, University “Aldo Moro” of Bari, 70124 Bari, Italy; [email protected] (G.L.); [email protected] (A.I.); [email protected] (A.C.); [email protected] (M.B.); [email protected] (E.I.); [email protected] (M.P.) 2 Ph.D. Course in Organs and Tissues Transplantation and Cellular Therapies, Department of Emergency and Organ Transplantation, University “Aldo Moro” of Bari, 70124 Bari, Italy * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +39-080-559-2925 Received: 14 September 2020; Accepted: 21 October 2020; Published: 23 October 2020 Abstract: We performed an epidemiologic study to assess the prevalence of chronic viral hepatitis in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and to detect their possible relationships. Methods: It was a single centre cohort cross-sectional study, during October 2016 and October 2017. Consecutive IBD adult patients and a control group of non-IBD subjects were recruited. All patients underwent laboratory investigations to detect chronic hepatitis B (HBV) and C (HCV) infection. Parameters of liver function, elastography and IBD features were collected. Univariate analysis was performed by Student’s t or chi-square test. Multivariate analysis was performed by binomial logistic regression and odds ratios (ORs) were calculated. We enrolled 807 IBD patients and 189 controls. Thirty-five (4.3%) had chronic viral hepatitis: 28 HCV (3.4%, versus 5.3% in controls, p = 0.24) and 7 HBV (0.9% versus 0.5% in controls, p = 0.64). -

Does Your Patient Have Bile Acid Malabsorption?
NUTRITION ISSUES IN GASTROENTEROLOGY, SERIES #198 NUTRITION ISSUES IN GASTROENTEROLOGY, SERIES #198 Carol Rees Parrish, MS, RDN, Series Editor Does Your Patient Have Bile Acid Malabsorption? John K. DiBaise Bile acid malabsorption is a common but underrecognized cause of chronic watery diarrhea, resulting in an incorrect diagnosis in many patients and interfering and delaying proper treatment. In this review, the synthesis, enterohepatic circulation, and function of bile acids are briefly reviewed followed by a discussion of bile acid malabsorption. Diagnostic and treatment options are also provided. INTRODUCTION n 1967, diarrhea caused by bile acids was We will first describe bile acid synthesis and first recognized and described as cholerhetic enterohepatic circulation, followed by a discussion (‘promoting bile secretion by the liver’) of disorders causing bile acid malabsorption I 1 enteropathy. Despite more than 50 years since (BAM) including their diagnosis and treatment. the initial report, bile acid diarrhea remains an underrecognized and underappreciated cause of Bile Acid Synthesis chronic diarrhea. One report found that only 6% Bile acids are produced in the liver as end products of of British gastroenterologists investigate for bile cholesterol metabolism. Bile acid synthesis occurs acid malabsorption (BAM) as part of the first-line by two pathways: the classical (neutral) pathway testing in patients with chronic diarrhea, while 61% via microsomal cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase consider the diagnosis only in selected patients (CYP7A1), or the alternative (acidic) pathway via or not at all.2 As a consequence, many patients mitochondrial sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1). are diagnosed with other causes of diarrhea or The classical pathway, which is responsible for are considered to have irritable bowel syndrome 90-95% of bile acid synthesis in humans, begins (IBS) or functional diarrhea by exclusion, thereby with 7α-hydroxylation of cholesterol catalyzed interfering with and delaying proper treatment. -

Zoonotic Diseases Fact Sheet
ZOONOTIC DISEASES FACT SHEET s e ion ecie s n t n p is ms n e e s tio s g s m to a a o u t Rang s p t tme to e th n s n m c a s a ra y a re ho Di P Ge Ho T S Incub F T P Brucella (B. Infected animals Skin or mucous membrane High and protracted (extended) fever. 1-15 weeks Most commonly Antibiotic melitensis, B. (swine, cattle, goats, contact with infected Infection affects bone, heart, reported U.S. combination: abortus, B. suis, B. sheep, dogs) animals, their blood, tissue, gallbladder, kidney, spleen, and laboratory-associated streptomycina, Brucellosis* Bacteria canis ) and other body fluids causes highly disseminated lesions bacterial infection in tetracycline, and and abscess man sulfonamides Salmonella (S. Domestic (dogs, cats, Direct contact as well as Mild gastroenteritiis (diarrhea) to high 6 hours to 3 Fatality rate of 5-10% Antibiotic cholera-suis, S. monkeys, rodents, indirect consumption fever, severe headache, and spleen days combination: enteriditis, S. labor-atory rodents, (eggs, food vehicles using enlargement. May lead to focal chloramphenicol, typhymurium, S. rep-tiles [especially eggs, etc.). Human to infection in any organ or tissue of the neomycin, ampicillin Salmonellosis Bacteria typhi) turtles], chickens and human transmission also body) fish) and herd animals possible (cattle, chickens, pigs) All Shigella species Captive non-human Oral-fecal route Ranges from asymptomatic carrier to Varies by Highly infective. Low Intravenous fluids primates severe bacillary dysentery with high species. 16 number of organisms and electrolytes, fevers, weakness, severe abdominal hours to 7 capable of causing Antibiotics: ampicillin, cramps, prostration, edema of the days.