North & Akkar Governorates Profile
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Cretaceous Transition in Mount Lebanon
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by I-Revues Carnets Geol. 16 (8) Some steps toward a new story for the Jurassic - Cretaceous transition in Mount Lebanon Bruno GRANIER 1 Christopher TOLAND 2 Raymond GÈZE 3 Dany AZAR 3, 4 Sibelle MAKSOUD 3 Abstract: The stratigraphic framework of the Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous strata of Lebanon that dates back to DUBERTRET's publications required either consolidation or full revision. The preliminary results of our investigations in the Mount Lebanon region are presented here. We provide new micro- paleontological and sedimentological information on the Salima Oolitic Limestones, which is probably an unconformity-bounded unit (possibly Early Valanginian in age), and the "Grès du Liban" (Barremian in age). Our revised bio- and holostratigraphic interpretations and the new age assignations lead us to em- phasize the importance of the two hiatuses in the sedimentary record below and above the Salima, i.e., at the transition from the Jurassic to the Cretaceous. Key Words: Tithonian; Valanginian; Barremian; hiatus; unconformity; Salima Oolitic Limestones; "Grès du Liban"; amber; Balkhania. Citation: GRANIER B., TOLAND C., GÈZE R., AZAR D. & MAKSOUD S. (2016).- Some steps toward a new story for the Jurassic - Cretaceous transition in Mount Lebanon.- Carnets Geol., Madrid, vol. 16, no. 8, p. 247- 269. Résumé : Avancées dans une réécriture de l'histoire de la transition du Jurassique au Crétacé dans le Mont Liban.- Le canevas stratigraphique du Jurassique supérieur et du Crétacé inférieur du Liban date des publications anciennes de DUBERTRET et aurait donc besoin d'être soit toiletté et consolidé, soit révisé de fond en comble. -

Impact of the Syrian Crisis on the Lebanese Agriculture
© 2018 International Center for Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) and Caritas Switzerland. All rights reserved. ICARDA and Caritas Switzerland encourage fair use of this material for non-commercial purposes with proper citation. Suggested Citation Aw-Hassan, A., Abou Arrage, J., Duqmaq, N., Voborsky, L., Rekik, M. 2018. Linking Refugees and Host Communities to Agricultural Value Chains in the Bekaa Plain, Lebanon “Potatoes, Tomatoes, and Dairy products”. International Centre for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) and Caritas Switzerland (CACH), Amman, Jordan. ISBN13: 978-9291275250 Key words livelihoods – resilience – agricultural value chains – hosting communities – Syrian refugees ICARDA’s Address Dalia Building, Second Floor, Bashir El Kasser St, Verdun, Beirut, Lebanon 1108-2010. www. icarda.org Caritas Switzerland’s Address Adligenswilerstrasse 15, 6006 Luzern, Switzerland. www.caritas.ch All responsibility for the information in this publication remains with ICARDA. The use of trade names does not imply endorsement of, or discrimination against, any product by the Center. Maps have been used to support research data, and are not intended to show political boundaries. List of Abbreviations CA Cultivated Area CDR Council for Development and Reconstruction CCIABML Chamber of Commerce Industry and Agriculture in Beirut and Mount Lebanon CCIAS Chamber of Commerce Industry and Agriculture in Saida and the South CCIAT Chamber of Commerce Industry and Agriculture in Tripoli and the North CCIAZ Chamber of Commerce -

Potable Water Supply
CDR November 2013 Social Infrastructure 111 Potable Water Supply General overview of the sector technologies of water purification. By the end of the Lebanese war, potable water installations were To put up with such a difficult limited to half completed networks reality, the Lebanese government in main cities and smaller started in 1992 to act in several networks in the rest of the regions. fields: The inadequacy of this service 1) Execution of urgent began to show accompanied by the rehabilitation activities for aggravation of the underground existing equipments relative to and surface water pollution water sources and other problem as a result of random networks and pumping and wastewater infrastructure, thus purification stations, and threatening the environment and solving all existing or citizen’s health. upcoming problems. 2) Completion, expansion and The insufficient service of potable rehabilitation of networks water has many reasons, mainly: according to needs. 1) An increased demand of water 3) Development and increase in and the incapacity of existing water sources and limiting the networks water comedown and thus 2) Increase in water loss as a result increase nutrition average. of network deterioration 3) Absence of means to protect In other words, this sectoral action water from pollution (random plan aims at completing wastewater infrastructure, rehabilitation and expansion of industrial and agricultural potable water in all Lebanese pollutants…) regions and increase water sources 4) Insufficiency of consumption in to put an end to the deficit both water and wastewater expected and that through large sectors, i.e. scant investment projects like building dams and necessary to improve and mountain lakes. -

Informing Targeted Host Community Programming in Lebanon
INFORMING TARGETED HOST COMMUNITY PROGRAMMING IN LEBANON SECONDARY DATA REVIEW SEPTEMBER 2014 Host Community Vulnerabilities in Lebanon: Secondary Data Review – September 2014 SUMMARY As the Syria conflict enters its fourth year, the number of refugees settling in neighbouring countries continues to rise. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), an estimated 1,055,393 registered refugees from Syria reside in Lebanon.1 The influx of refugees from Syria, which constitutes 20 per cent of the total population living in Lebanon, has had a tremendous impact on the demographic, socioeconomic and security situation in the country. The 2014 Syria Regional Response Plan (RRP6) reported that 86 per cent of refugees have relocated to communities hosting 66 per cent of the most vulnerable Lebanese populations.2 The presence of refugees has affected the resilience of host communities, particularly in terms of accessing basic services and public infrastructure, as well as social cohesion within communities already affected by sectarian divisions. This secondary data review report was conducted during the inception phase of an assessment carried out by REACH Initiative in partnership with the United Nations Office for Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) in 2014. This larger study aims to inform host community programming in Lebanon through the participatory identification of vulnerabilities and factors that undermine community resilience and social cohesion. In terms of information management, this assessment hopes to fill a major information gap in regards to community vulnerabilities as they pertain to refugee and host community populations. This report provides a review of secondary data and information available on the social, economic and political impact of the refugee influx on host communities with a specific focus on the principal vectors of tension within these communities in the context of the Syria crisis. -

Akkar Governorate Profile
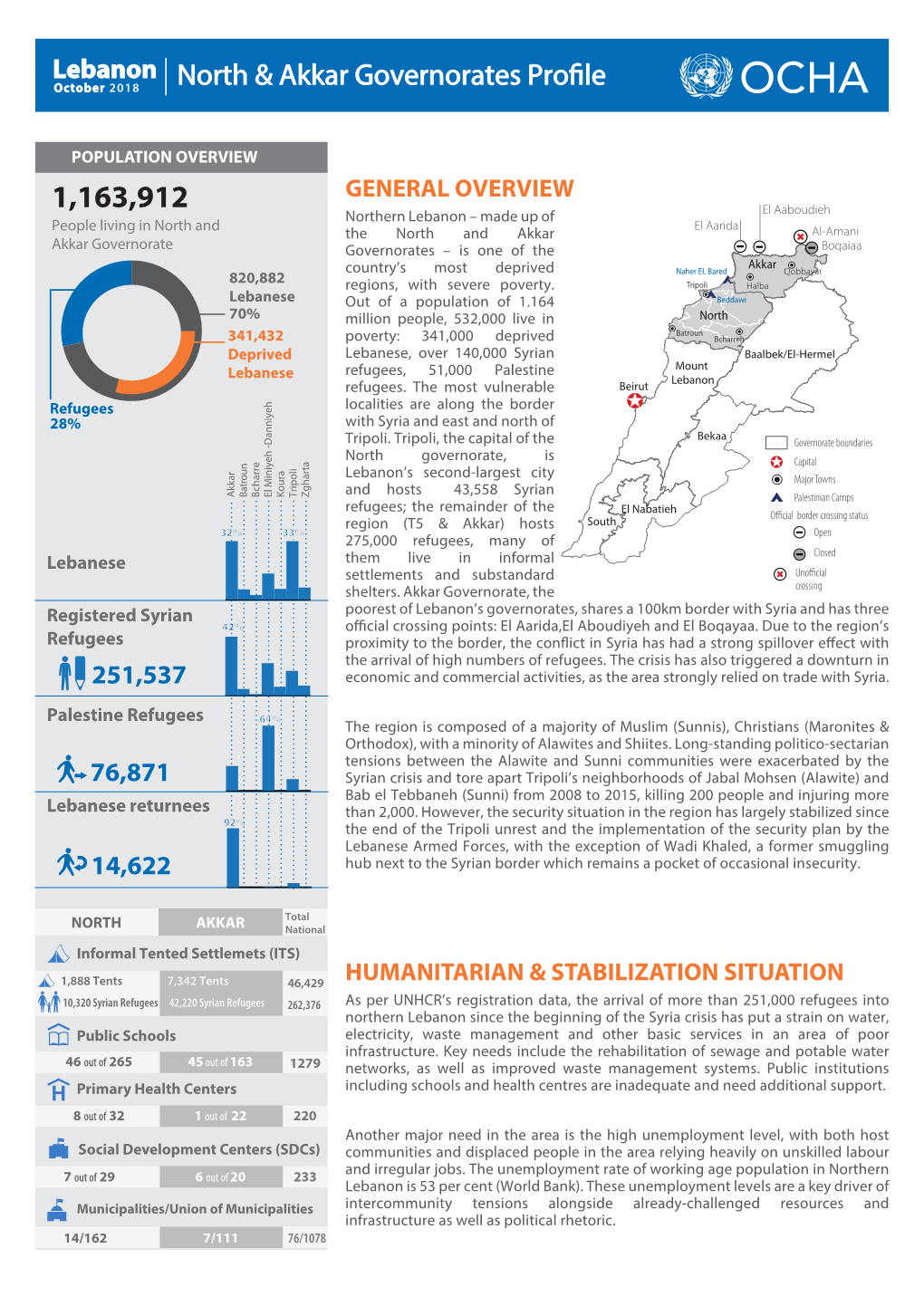
Lebanon Akkar Governorate Profile (June 2015) GENERAL OVERVIEW North Lebanon, which previously constituted one governorate with seven districts, was split into two governorates in 2014: Tripoli and five surrounding districts (T5) maintained the denomination of North Governorate, while the district of Akkar became a governorate in its own right. Akkar Governorate, which covers 788 km2, is one of the most deprived rural regions in Lebanon and shares a 100km border with Syria. Akkar is divided into three main areas; Al-Sahel, Middle and Higher Dreib. There are 27 villages along the border with Syria, with two official crossing points: El Aarida and El Aaboud- ieh. Akkar is predominantly Sunni with Christian, Alawite and Shiite communities. The average altitude is at 700m above sea level while the peak of the Governorate is situated at 1,900m. Inter-agency coordination and sector coordination meetings for Akkar take place in Qobbayat. Location Map Al-Amani POPULATION OVERVIEW El Aaboudieh Boqaiaa Akkar El Aarida Qobbayat People are living in Akkar Governorate Halba 389,899 North 64.8% 252,623 Lebanese Baalbek/El-Hermel Mount Beirut Lebanon 3.6% (0 – 5 Years) 3.9% (0 – 5 Years) Open official 11.1% (6 – 17 Years) 12.5% (6 – 17 Years) border crossing Closed official 29.5% (18 – 59 Years) 28.2% (18 – 59 Years) Bekaa border crossing 5.4% (60+ Years) 5.8% (60+ Years) Unofficial crossing El Nabatieh Governorate 38% 147,532 Deprived Lebanese South boundaries Capital 2.8% 10,937 Lebanese returnees SOCIO ECONOMIC OVERVIEW 106,935 registered Syrian refugees 27.4% DEC 2014 39.8% of Syrian refugees living in substandard JUN 2014 JUN 2015 108,910 shelter 107,017 106,935 398 Informal Settlements, hosting 26,721 registered Syrian refugees 16,700 Palestine refugees in Lebanon 4.3% 3.4% refugees living in collective shelters 171 public schools. -

Stakeholder Engagement Plan
Sustainable Akkar Project Stakeholder Engagement Plan TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Objectives 1.2 Methodology 1.3 Project Description 1.3.1 Project Location 1.3.2 Project Components 2 POLICY, LEGAL AND INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK 2.1 National Framework and Requirements 2.1.1 Existing Legislation 2.1.2 National Requirements for Stakeholder Engagement and Public Participation 2.2 International Conventions, Treaties and Protocols 2.3 International Guidelines 2.3.1 IFC Performance Standards 2.3.2 IFC EHS Guidelines 2.3.3 EIB Environmental and Social Standards 2.3.4 IFC and EIB Standards for Stakeholder Engagement and Public Participation 2.4 Sustainable Akkar (SA) Project Policies 3 STAKEHOLDER IDENTIFICATION AND ANALYSIS 3.1 Affected Communities 3.1.1 Direct Area of Influence (DAOI) 3.1.2 Indirect Area of Influence (IAOI) 4 INITIAL STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT PLAN 4.1 Summary of Previous Stakeholder Engagement Activities 4.1.1 2011 Activities 4.1.2 2013 Activities 4.1.3 2017 Activities 4.1.4 2018 Activities 4.1.5 2019 Activities 4.1.6 Public Participation Outcomes Sustainable Akkar Project Stakeholder Engagement Plan 5 CONTINUATION OF THE STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT PLAN 5.1 SA Project Communication Plan 5.2 Involvement of the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) 6 TIMETABLE 6.1 Preliminary Timetable of Future Stakeholder Engagement Activities 7 RESOURCES AND RESPONSIBILITIES 7.1 Community Relations Department organizational structure 7.2 Stakeholder Engagement Budget 8 EXTERNAL COMMUNICATIONS AND COMMUNITY GRIEVANCE MECHANISM 8.1 External Communications -

15+ Perfect Hiking Spots in Lebanon for When You Need to Get Away Maria Zakhour· Guides
15+ Perfect Hiking Spots In Lebanon For When You Need To Get Away Maria Zakhour· Guides Carlos Bou Nafeh With everything that is going on in Lebanon as well as around the world, people feel the need to hide from reality; and what better place is there to hide than in the heart of nature? We’ve brought you 18 perfect hiking spots in Lebanon, so you can embrace nature and appreciate the good it has to offer: #1 Al-Shouf Cedar Reserve Open Souq This is the largest nature reserve in Lebanon. It stretches from Dahr El- Baidar in the north to Niha Mountain in the South and has an area of 550 km2, which is nearly 5.3% of the Lebanese territory. The reserve’s most famous attractions are the cedar forests of Maasser El-Shouf, Barouk, and Ain Zhalta – Bmohary. Claude Abou Chacra In this reserve in the Chouf district, you will find not only 2,000-year-old trees but if you’re lucky enough you’ll get to see some of its 32 species of wild mammals, its 200 species of birds, and its 500 species of plants. People come to Al-Shouf Cedar Nature Reserve to hike, mountain bike, or snowshoe, but also to get a glimpse at its rich habitat. #2 Balou’ Bala’a This Big Wild World Balou Balaa, or the Baatara Gorge Waterfall, is near Balaa in Tannourine, Lebanon. This waterfall drops 255 meters into the Balaa pothole. The cave, known as The Cave Of The Three Bridges is of Jurassic limestone. -

Usaid/Lebanon Citizen Perception Survey (Cps) – Wave 2 May 2021
BERUIT, LEBANON. WIKIMEDIA COMMONS USAID/LEBANON CITIZEN PERCEPTION SURVEY (CPS) – WAVE 2 MAY 2021 This publication was produced at the request of the United States Agency for International Development. It was prepared independently by Social Impact’s Lebanon PMSPL II project. Findings in this report do not necessarily represent the views of USAID. USAID/LEBANON CITZEN PERCEPTION SURVEY (CPS) – WAVE 2 MAY 2021 Contracted under AID-268-C-15-0001 Performance Management and Support Program for Lebanon (PMSPL II) for USAID/Lebanon Social Impact, Inc., Corporate Office 2300 Clarendon Boulevard Suite 1000 Arlington, VA 22201 Tel: (703) 465 – 1884 [email protected] Social Impact, Inc., Lebanon Office Arz Street Librex Bldg. Bloc B – 3rd Floor Zalka, Ment, Lebanon Tel: +961-1-879260 i | LEBANON CITIZEN PERCEPTION SURVEY (CPS) 2021, WAVE 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents .................................................................................................................. ii Table of Tables and Figures ................................................................................................ iv Acronyms ............................................................................................................................. vii 1 Introduction and Purpose ............................................................................................... 1 2 Methodology .................................................................................................................... 2 2.1 Sampling ................................................................................................................................................. -

! ! Syrian Arab Republic
LEBANON - Akkar Governorate For Humanitarian Use Only Activity Info - Education Sector Mapping for Akkar Operational Area - September 2014 Production date : 10 November 2014 Syrian Dayret Nahr El-Kabir Arab Republic Aabboudiye Sammaqiye AAridet Cheikh Zennad Hokr Ed-Dahri Khalsa Janine Kfar Kharnoubet Noun Aaouaainat Qarha Dibbabiye Chir Hmairine Aakkar Tall Bire Noura Et-Tahta Aakkar Tall Aakkar Qachlaq Machta Kneisset Hmayra Hammoud Aakkar Srar Fraydes Aakkar Rmah Cheikhlar Cheikh Massaaoudiye Hnaider Zennad Mighraq Mounjez Aamayer Aamaret Darine Ouadi El-Baykat Kouachra El-Haour Haytla Baghdadi Aamriyet Aakkar Tall Meaayan Saadine Mazraat En-Nahriye Kneisset Tall Kiri Barde Hnaider Tall Aabbas Ech-Charqi Ghazayle Tleil Aain Khirbet Qleiaat Aakkar Haouchab Biret Aakkar Saidnaya Ez-Zeit Daoud Hayssa Aakkar Aandqet Aain Tinta Tall Aabbas El-Gharbi Charbila Rihaniyet Aakkar Douair Khirbet Bsatine Aadouiye Char Aakkar Rmoul Berbara Sindianet Sammouniye Aakkar Zeidane Hokr Majdel Qaabrine Etti Kfar Deir Jannine Akkar Khreibet Harra Qbaiyat Ej-Jindi Knisse Hedd Mazareaa Kfar Aakkar Jabal Melki Akroum Aakkar Souaisset Balde Mqaiteaa Tall Aakkar WaMazraatBalde Kroum Sebaal El-Aarab Halba Hayzouq Beino Nfisse Semmaqli Machha Daouret Qoubbet Chamra Marlaya Aakkar Aarqa Melhem Dahr Laissine Jdidet Ej-Joumeh Beit Aaiyat Mellat Qboula Aamaret Cheikh Taba Idbil Aayoun Minyara Chaqdouf Aakkar Deir Aakkar Dalloum Hakour Zouq El Karm Jebrayel Aakkar Hosniye Aasfour Qantarat Aakkar El-Aatiqa Mhammaret -

Syria Refugee Response
SYRIA REFUGEE RESPONSE Distribution of MoPH network and UNHCR Health Brochure Selected PHC as of 6 October, 2016 Akkar Governorate, Akkar District - Number of syrian refugees : 99,048 Legend !( Moph Network Moph Network !< and UNHCR Dayret Nahr Health El-Kabir 1,439 Brochure ") UNHCR Health Brochure Machta Hammoud Non under 2,246 MoPH network 30221 ! or under 30123 35516_31_001 35249_31_001 IMC No partner Wadi Khaled health center UNHCR Health Al Aaboudiyeh Governmental center !< AAridet Sammaqiye !( 713 Aaouaainat Khalsa Brochure Cheikh Hokr Hokr Dibbabiye Aakkar 1 30216 Zennad Jouret Janine Ed-Dahri 67 Kfar 6 35512_31_001 6 Srar 13 !( Aamayer Kharnoubet Noun No partner 13,361 Barcha Khirbet Er Aakkar 8 Alaaransa charity center Most Vulnerable Massaaoudiye 7 Aarme Mounjez Remmane 386 Noura ! 29 25 13 Qachlaq Et-Tahta 35512-40-01 Localities Tall Chir 28 17 Hmayra No partner Cheikh Kneisset Hmairine Aamaret Fraydes ! 105 1,317 Srar Aakkar Cheikhlar Wadi Khaled SDC Qarha Zennad Aakkar Tall El-Baykat 108 7 Rmah 62 Aandqet !< Aakkar 257 Mighraq 33 Bire 462 Most Mzeihme Ouadi 49 401 17 44 Aakkar 11 El-Haour Kouachra 168 Baghdadi Vulnerable Haytla 636 1,780 Qsair Hnaider 30226 !( Darine 10 Aamriyet Aakkar 1,002 35229_31_001 124 Aakkar 35 Mazraat 2nd Most No partner Tall Aabbas Saadine Alkaram charity center - Massoudieh Ech-Charqi 566 En-Nahriye Kneisset Tleil Barde 958 878 Hnaider Vulnerable !< 798 35416-40-01 4 Ghazayle 1,502 30122 38 No partner ! 35231_31_001 Bire Qleiaat Aain Ez-Zeit Kafr Khirbet ")!( IMC Aain 3rd Most Aakkar Hayssa Saidnaya -

Lebanon – Future Movement – Political Violence – Hezbollah – Akkar – State Protection
Refugee Review Tribunal AUSTRALIA RRT RESEARCH RESPONSE Research Response Number: LBN33661 Country: Lebanon Date: 9 September 2008 Keywords: Lebanon – Future Movement – Political violence – Hezbollah – Akkar – State protection This response was prepared by the Research & Information Services Section of the Refugee Review Tribunal (RRT) after researching publicly accessible information currently available to the RRT within time constraints. This response is not, and does not purport to be, conclusive as to the merit of any particular claim to refugee status or asylum. This research response may not, under any circumstance, be cited in a decision or any other document. Anyone wishing to use this information may only cite the primary source material contained herein. Questions 1. Are Future Party members currently at risk of harm by Hezbollah? If so, to what extent? 2. Is Danbo an area of particular safety/risk for such people? 3. Might active Future Party members be refused protection by the authorities from harm because of their political allegiances? RESPONSE Executive Summary Reports of clashes between supporters of Hezbollah (party of God; also Hizbollah, Hizbullah, etc) and supporters of the Future Party (Tayyar Al Mustaqbal; generally referred to as the Future Movement and also as the Future Current) have appeared regularly during 2008 with major outbreaks of violence reportedly occurring in January 2008 and May 2008 in Beirut. The recent May 2008 clashes in Beirut ended as a victory for Hezbollah and its pro Syrian opposition allies Amal (a sometime rival Shiite party) and the Syrian Socialist National Party (SSNP). Hezbollah and its allies reportedly occupied Future Movement strongholds in west- Beirut and destroyed certain Future Movement offices before withdrawing (though it should be noted that, according to the International Crisis Group, “there were differences between the more provocative Amal militants and more disciplined Hizbollah fighters who, in some cases, went so far as to protect Sunni religious sites”). -

Syria Refugee Response; Lebanon
SYRIA REFUGEE RESPONSE LEBANON North Governorate, Tripoli, Batroun, Bcharreh, El Koura, El Minieh-Dennieh, Zgharta Districts (T+5) Distribution of the Registered Syrian Refugees at the Cadastral Level As of 30 April 2014 N " 0 ' 0 3 ° 4 3 Zouq Bhannine Rihaniyet-Miniye 2,979 Tripoli + 5 Districts 17 Trablous El Hadid Minie 41,399 Trablous Ez-Zahrieh Total No. of Household Registered 506 17,334 2,737 Trablous Es-Souayqa Raouda-Aadoua Total No. of Individuals Registered Trablous Er-Remmaneh 94 159 165,453 Trablous et Tabbaneh Trablous En-Nouri Merkebta 6,533 Mina N 3 60 220 2,585 Nabi Youcheaa Deir Aammar 216 3,527 Borj El-YahoudHiyreaiqis Mina N 1 Beddaoui 17 5 15,920 Mina N 2 Terbol-Miniye Mzraat Kefraya Mina Jardin 37 9 5,042 Boussit Qarhaiya Trablous Et-Tell Trablous El-Qobbe Aasaymout 4,009 9,772 Aazqai Trablous jardins Hailan 150 Harf Es-Sayad Debaael 2,603 Mejdlaiya Zgharta 202 43 1 Qarne Aalma Kfar Chellane Btermaz Beit Haouik 3,129 Trablous El Mhatra 654 373 111 21 33 Miriata Harf Es-Sayad Haouaret-Miniye Trablous El-Haddadine, El-Hadid, El-Mharta Tripoli Arde Aachach Mrah Es-Srayj 1,661 2,132 21 136 43 24 Trablous Ez-Zeitoun 567 Bakhaaoun 18,587 Kfar Habou 2,185 Aardat 582 tarane Qemmamine 4 Rachaaine 145 Sfire 368 Jayroun Ras Masqa 468 Beit Zoud Kharroub-Miniye Kfar Bibnine Tallet Zgharta Zgharta 11 3,862 4 2 Haql el Aazime Mrah Es-Sfire Aain Et-Tine-Miniyé 24 3,078 Kfardlaqous Danha 48 3 Qraine 69 93 2 Qattine-Miniyé Mazraat Ajbeaa 43 Hazmiyet-Miniye Beit El-Faqs Aassoun 161 Qarsaita Qalamoun Barsa Asnoun Hariq Zgharta Bkeftine