The Electronic Structure of the Atoms of Five Elements Are Shown in the Figure Below. the Letters Are Not the Symbols of The
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Tables of Parameters Tables of Parameters for Extended Hückel Calculations Calculations
TABLES OF PARAMETERS FOR EXTENDED HÜCKEL CALCULATIONS Santiago Alvarez Universitat de Barcelona 1999 - 1 - PART 1. STANDARD Hii's and SLATER EXPONENTS AND COEFFICIENTS. H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe Cs Ba Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Fr Ra Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Ac Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr Parameters for all elements except the shaded ones are included in these Tables. - 2 - General Observations References are to the original paper which first reported EH calculations with the given Hii for a related set of molecules or solids. For some elements, when no EH calculations have been reported, the experimental ionization potentials are given and the references correspond to those experimental values. Although these tables are intended to be of some use in locating atomic parameters, reference to the original work is encouraged. Ionization potentials ( Hii) a) All energies are in eV. Hii's for most transition metals are charge-iterated for model compounds like metal carbonyls or typical organometallic molecules with Cp, CH3, CO, etc. Exceptions, including bulk metals are conveniently indicated. For cases in which charge-iterated Hii's are not available, the standard sources are the Hinze and Jaffé's tables of ionization potentials.1 b) When alternative sets of Hii's were available for the same element, the one which fits better with the trend along a group or a period of the periodic table has been chosen. -

Chapter 1. Periodic Properties and Variation of Properties
Chapter 1. Periodic Properties and Variation of Properties PAGE NO : 16 Solution 1: Modern periodic law states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers i.e., if the elements are arranged in the order of their atomic numbers, the elements with similar properties are repeated after definite regular intervals. Concept Insight: The elements are characterized by their atomic number as well as atomic weight. Modern periodic law uses atomic number which is number of protons or number of electrons present in an atom of an element. Solution 2: Modern periodic table consists of eighteen groups and seven periods. Concept Insight: Classification of elements on the basis of increasing atomic number is known as Modern Periodic Table. The vertical columns are called groups and the horizontal rows are called periods. Solution 3: The recurrence of similar properties of elements after certain regular intervals when they are arranged in the order of increasing atomic numbers is called periodicity. Concept Insight: Periodicity in properties is due to the repetition of similar outer electronic configuration of elements at certain regular intervals. Solution 4: In general, the elements belonging to a group have the same number of valence electrons .For example, all the group 1 elements have valency one since they have only one electron in their outermost shell. In general, the elements belonging to a period do not have same valency but their valence shell remains the same. For example, second period has 8 elements with atomic number 3 to 10 but in all of them the valence electrons are present in shell number two. -

Combined Science Chemistry Booklet
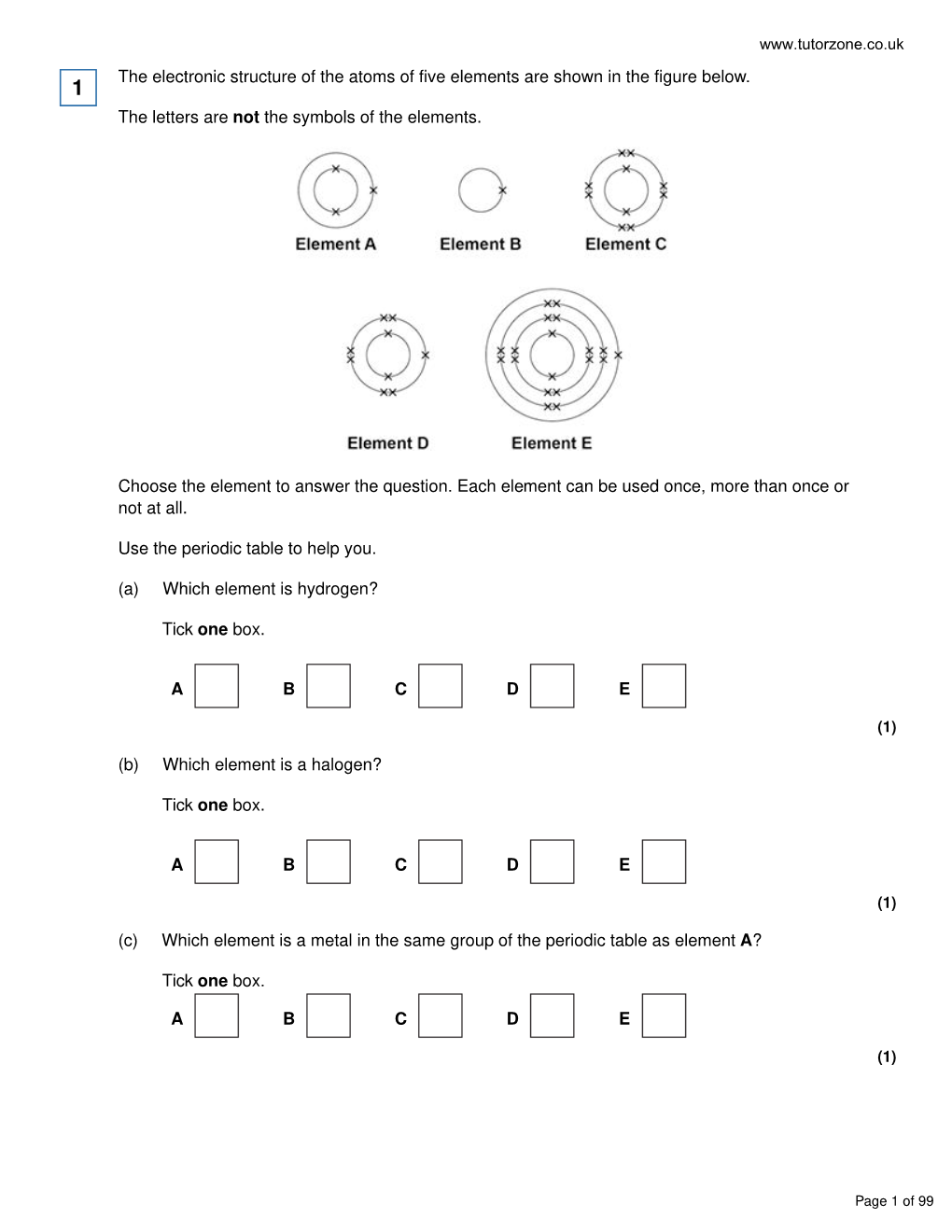
COMBINED SCIENCE CHEMISTRY BOOKLET TASK: Complete the questions that your teacher sets on Show My Homework and use the mark scheme at the end of the document to check your responses. Topic 1 – Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Q1. The periodic table on the Data Sheet may help you to answer these questions. (a) Part of the periodic table is shown below. The letters are not the symbols of the elements. Choose your answers only from the letters shown in the periodic table above. Which letter, A, B, C, D, E or F, represents (i) aluminium (1) Page 1 of 66 (ii) a Group 5 element (1) (iii) an alkali metal (1) (iv) the element with atomic (proton) number of 47 (1) (v) an element with seven electrons in its outer shell? (1) (b) The table shows the boiling points of the Group 7 elements. The elements are arranged in alphabetical order. Group 7 element Name Symbol Boiling point in °C Astatine At 337 Bromine 58 Chlorine Cl -34 Fluorine F -188 Iodine I 184 (i) The symbol for bromine is missing from the table. What is the symbol for bromine? Symbol = _______________ (1) (ii) Arrange these elements in order of decreasing boiling point. The first one and the last one have been done for you. At ______ ______ ______ F Highest boiling Lowest boiling point point Page 2 of 66 (1) (c) The table shows some statements about Group 7 elements. Tick ( ) the two correct statements. Tick ( ) They are halogens. They are metals. They become less reactive down Group 7. -

The Periodic Table: a Very Short Introduction VERY SHORT INTRODUCTIONS Are for Anyone Wanting a Stimulating and Accessible Way Into a New Subject
The Periodic Table: A Very Short Introduction VERY SHORT INTRODUCTIONS are for anyone wanting a stimulating and accessible way into a new subject. They are written by experts, and have been translated into more than 45 different languages. The series began in 1995, and now covers a wide variety of topics in every discipline. The VSI library currently contains over 600 volumes—a Very Short Introduction to everything from Psychology and Philosophy of Science to American History and Relativity—and continues to grow in every subject area. Very Short Introductions available now: ABOLITIONISM Richard S. Newman ACCOUNTING Christopher Nobes ADAM SMITH Christopher J. Berry ADOLESCENCE Peter K. Smith ADVERTISING Winston Fletcher AFRICAN AMERICAN RELIGION Eddie S. Glaude Jr AFRICAN HISTORY John Parker and Richard Rathbone AFRICAN POLITIC Ian Taylor AFRICAN RELIGIONS Jacob K. Olupona AGEING Nancy A. Pachana AGNOSTICISM Robin Le Poidevin AGRICULTURE Paul Brassley and Richard Soffe ALEXANDER THE GREAT Hugh Bowden ALGEBRA Peter M. Higgins AMERICAN CULTURAL HISTORY Eric Avila AMERICAN FOREIGN RELATIONS Andrew Preston AMERICAN HISTORY Paul S. Boyer AMERICAN IMMIGRATION David A. Gerber AMERICAN LEGAL HISTORY G. Edward White AMERICAN NAVAL HISTORY Craig L. Symonds AMERICAN POLITICAL HISTORY Donald Critchlow AMERICAN POLITICAL PARTIES AND ELECTIONS L. Sandy Maisel AMERICAN POLITICS Richard M. Valelly THE AMERICAN PRESIDENCY Charles O. Jones THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION Robert J. Allison AMERICAN SLAVERY Heather Andrea Williams THE AMERICAN WEST Stephen Aron AMERICAN WOMEN’S HISTORY Susan Ware ANAESTHESIA Aidan O’Donnell ANALYTIC PHILOSOPHY Michael Beaney ANARCHISM Colin Ward ANCIENT ASSYRIA Karen Radner ANCIENT EGYPT Ian Shaw ANCIENT EGYPTIAN ART AND ARCHITECTURE Christina Riggs ANCIENT GREECE Paul Cartledge THE ANCIENT NEAR EAST Amanda H. -

LN–2 IDLE MIND SOLUTIONS 1. We Recognize That, According To
LN–2 LN–2 IDLE MIND SOLUTIONS 1. We recognize that, according to Pauling’s electronegativity scale, compounds with Δx > 1.7 are strongly ionic and exhibit properties which reflect the electrostatic interactions under conditions of energy minimization: (1) Non–directionality of the electrostatic forces will thus lead to an ordered solid (crystalline). (2) Octet stabilization makes the solid non–conducting (electrical insulator). (3) Stability will also most likely make the material transparent in the visible. (4) The magnitude of the attractive forces may make the solid melt at elevated temperature only. (5) Etc. 2. (a) C2Cl3H in Lewis notation: Cl H C = C Cl Cl Note that the H may be located on any one of the 4 (sp2) hybrid orbitals without changing the properties of the compound. (b) On each carbon there are: three equivalent sp2 bonding orbitals in sp2 a plane and one p orbital normal to the sp2 sp2 plane. sp2 p On each chlorine there is: one singly occupied p orbital. Cl p On the hydrogen we have: one singly occupied 1s orbital. H LN–2 σ 2. (c) 2 sp2–sp2 orbitals → 1σ C–C π 2 p–p orbitals → 1π C–C 6 bonds 3 sp2–p orbitals → 3σ C–Cl 1 sp2–s orbital → 1σ C–H 3. Silicon (Si) is a group 4 element like C (carbon) and wil also exhibit sp3 hybridization: 4 sp3 orbitals at B.A. = 109o. Unlike carbon, silicon cannot form double or triple bonds (by lateral p orbital overlap) because the atom is too large to permit lateral overlap! (a) Si + 2Cl2 → SiCl4 Si is in the center of a tetrahedron with the chlorine atoms as the four corners. -

Week 1 Slides
Adventures in Chemistry Instructor: Abi Oyeyemi Week 1 States of matter Boiling point, Melting point Atoms Types of Chemistry Hazards PPE Atoms consist of: Neutrons Protons Electrons 0 + - In In shells of atoms Nucleus States of Matter Solid, liquid, gas Week 2 Flame tests Orbitals Periodic table Octet Groups and Periods Experiment: Making a non-Newtonian Fluid Periodic Table Groups Each group tells how many electrons are in the outer shell. In chemistry, a group (also known as a family) is a column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements. The elements in each group have the same number of electrons in the outer orbital. Those outer electrons are also called valence electrons Periodic table 118 elements total 8 groups Group 1- Alkali metals Group 2- Alkali earth metals Group 7 –Halogens Group 8-Noble gases Elements structure Includes abbreviated name of element Atomic number-number of protons Always same number of protons and neutrons Mass number- average no. of neutrons and protons Amu: atomic mass units Isotopes Periodic table: Periods A period in the periodic table is a row of chemical elements. All elements in a row have the same number of electron shells/orbitals Week 3 More on the periodic table Electronic configuration Isotopes Chemical vs Physical changes Compounds vs Mixtures Ionic and Covalent bonds Demonstration Lava Lamp Activity: Making models Why do elements react? Octet, want a full outer shell How? By taking or giving electrons (ionic bonding) Or by sharing electrons (covalent bonding) Compounds- A compound is a substance formed when two or more chemical elements are chemically bonded together. -

Chemistry of Superheavy Elements Matthias Schädel*
Reviews M. Schädel DOI: 10.1002/anie.200461072 Superheavy Elements Chemistry of Superheavy Elements Matthias Schädel* Keywords: Dedicated to Professor Günter Herrmann atom-at-a-time chemistry · periodic on the occasion of his 80th birthday table · relativistic effects · superheavy elements · transactinides Angewandte Chemie 368 www.angewandte.org 2006 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 368 – 401 Angewandte Superheavy Elements Chemie The number of chemical elements has increased considerably in the From the Contents last few decades.Most excitingly, these heaviest, man-made elements at the far-end of the Periodic Table are located in the area of the long- 1. Introduction and Historical Remarks 369 awaited superheavy elements.While physical techniques currently play a leading role in these discoveries, the chemistry of superheavy 2. Nuclear Aspects 372 elements is now beginning to be developed.Advanced and very sensitive techniques allow the chemical properties of these elusive 3. Atom-at-a-Time Chemistry 374 elements to be probed.Often, less than ten short-lived atoms, chemi- 4. Objectives for Superheavy cally separated one-atom-at-a-time, provide crucial information on Element Chemistry 375 basic chemical properties.These results place the architecture of the far-end of the Periodic Table on the test bench and probe the 5. Experimental Techniques 376 increasingly strong relativistic effects that influence the chemical 6. Chemical Properties 380 properties there.This review is focused mainly on the experimental work on superheavy element chemistry.It contains a short contribu- 7. Summary and Perspectives 394 tion on relativistic theory, and some important historical and nuclear aspects. -

WO 2017/161171 A2 21 September 2017 (21.09.2017) P O P C T
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (10) International Publication Number (43) International Publication Date WO 2017/161171 A2 21 September 2017 (21.09.2017) P O P C T (51) International Patent Classification: (81) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every B01J 23/10 (2006.01) B82Y 30/00 (201 1.01) kind of national protection available): AE, AG, AL, AM, B01J 35/02 (2006.01) C07C 2/84 (2006.01) AO, AT, AU, AZ, BA, BB, BG, BH, BN, BR, BW, BY, BZ, CA, CH, CL, CN, CO, CR, CU, CZ, DE, DJ, DK, DM, (21) Number: International Application DO, DZ, EC, EE, EG, ES, FI, GB, GD, GE, GH, GM, GT, PCT/US20 17/022787 HN, HR, HU, ID, IL, IN, IR, IS, JP, KE, KG, KH, KN, (22) International Filing Date: KP, KR, KW, KZ, LA, LC, LK, LR, LS, LU, LY, MA, 16 March 2017 (16.03.2017) MD, ME, MG, MK, MN, MW, MX, MY, MZ, NA, NG, NI, NO, NZ, OM, PA, PE, PG, PH, PL, PT, QA, RO, RS, (25) Filing Language: English RU, RW, SA, SC, SD, SE, SG, SK, SL, SM, ST, SV, SY, (26) Publication Language: English TH, TJ, TM, TN, TR, TT, TZ, UA, UG, US, UZ, VC, VN, ZA, ZM, ZW. (30) Priority Data: 62/309,284 16 March 2016 (16.03.2016) US (84) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every kind of regional protection available): ARIPO (BW, GH, (71) Applicant: SILURIA TECHNOLOGIES, INC. GM, KE, LR, LS, MW, MZ, NA, RW, SD, SL, ST, SZ, [US/US]; 409 Illinois Street, Suite 5032, San Francisco, TZ, UG, ZM, ZW), Eurasian (AM, AZ, BY, KG, KZ, RU, California 94158 (US). -

Syntheses, Structures, Optical Properties, and Theoretical Calculations of Cs2bi2zns5,Cs2bi2cds5, and Cs2bi2mns5 Fu Qiang Huang, Rebecca C
ARTICLE IN PRESS Journal of Solid State Chemistry 174 (2003) 334–341 Syntheses, structures, optical properties, and theoretical calculations of Cs2Bi2ZnS5,Cs2Bi2CdS5, and Cs2Bi2MnS5 Fu Qiang Huang, Rebecca C. Somers, Adam D. McFarland, Richard P. Van Duyne, and James A Ibersà Department of Chemistry, Northwestern University, 2145 Sheridan Road, Evanston, IL 60208-3113, USA Received 24 December 2002; received in revised form 14 April 2003; accepted 25 April 2003 Abstract Three new compounds, Cs2Bi2ZnS5,Cs2Bi2CdS5, and Cs2Bi2MnS5, have been synthesized from the respective elements and a reactive flux Cs2S3 at 973 K. The compounds are isostructural and crystallize in a new structure type in space group Pnma of the orthorhombic system with four formula units in cells of dimensions at 153 K of a=15.763(3), b=4.0965(9), c=18.197(4) A˚ , ˚ 3 ˚ ˚ 3 V=1175.0(4) A for Cs2Bi2ZnS5; a=15.817(2), b=4.1782(6), c=18.473(3) A, V=1220.8(3) A for Cs2Bi2CdS5; and a=15.830(2), ˚ ˚ 3 2 2À b=4.1515(5), c=18.372(2) A, V=1207.4(2) A for Cs2Bi2MnS5. The structure is composed of two-dimensional N[Bi2MS5 ] (M=Zn, Cd, Mn) layers that stack perpendicular to the [100] axis and are separated by Cs+ cations. The layers consist of edge- 1 6À 1 4À sharing N[Bi2S6 ] and N[MS3 ] chains built from BiS6 octahedral and MS4 tetrahedral units. Two crystallographically unique Cs atoms are coordinated to S atoms in octahedral and monocapped trigonal prismatic environments. The structure of Cs2Bi2MS5,is 0 0 related to that of Na2ZrCu2S4 and those of the AMM Q3 materials (A=alkali metal, M=rare-earth or Group 4 element, M = Group 11 or 12 element, Q=chalcogen). -

Syllabus Outline
Syllabus Syllabus outline Syllabus component Recommended teaching hours SL HL Core 95 1. Stoichiometric relationships 13.5 2. Atomic structure 6 3. Periodicity 6 4. Chemical bonding and structure 13.5 5. Energetics/thermochemistry 9 6. Chemical kinetics 7 7. Equilibrium 4.5 8. Acids and bases 6.5 9. Redox processes 8 10. Organic chemistry 11 11. Measurement and data processing 10 Additional higher level (AHL) 60 12. Atomic structure 2 13. The periodic table—the transition metals 4 14. Chemical bonding and structure 7 15. Energetics/thermochemistry 7 16. Chemical kinetics 6 17. Equilibrium 4 18. Acids and bases 10 19. Redox processes 6 20. Organic chemistry 12 21. Measurement and analysis 2 Option 15 25 A. Materials 15 25 B. Biochemistry 15 25 C. Energy 15 25 D. Medicinal chemistry 15 25 20 Chemistry guide Syllabus outline Syllabus component Recommended teaching hours SL HL Practical scheme of work 40 60 Practical activities 20 40 Individual investigation (internal assessment—IA) 10 10 Group 4 project 10 10 Total teaching hours 150 240 The recommended teaching time is 240 hours to complete HL courses and 150 hours to complete SL courses as stated in the document General regulations: Diploma Programme (2011) (page 4, Article 8.2). Chemistry guide 21 Syllabus Approaches to the teaching of chemistry Format of the syllabus The format of the syllabus section of the group 4 guides is the same for each subject physics, chemistry and biology. This new structure gives prominence and focus to the teaching and learning aspects. Topics or options Topics are numbered and options are indicated by a letter. -

Macrocycles Containing 1, 1'-Ferrocenyldiselenolato Ligands On
Dalton Transactions View Article Online PAPER View Journal | View Issue Macrocycles containing 1,1’-ferrocenyldiselenolato ligands Cite this: Dalton Trans., 2018, 47, 5415 on group 4 metallocenes† Clara Sanchez-Perez,a,b Caroline E. Knapp, b Minna M. Karjalainen,a Raija Oilunkaniemi,a Claire J. Carmalt *b and Risto S. Laitinen *a 5 5 t Macrocyclic [Fe(η -C5H4Se)2M(η -C5H4R)2]2 [M = Ti (1), Zr (2), Hf (3), R = H; and M = Zr (4), Hf (5), R = Bu] were prepared and characterized by 77Se NMR spectroscopy and the crystal structures of 1–3 and 5 were determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The crystal structure of 4 is known and the complex is iso- morphous with 5. 1–5 form mutually similar macrocyclic tetranuclear complexes in which the alternating Received 23rd January 2018, Fe(C5H4Se)2 and M(C5H4R)2 centers are linked by selenium bridges. The thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) Accepted 9th March 2018 of 1–3 under a helium atmosphere indicated that the complexes undergo a two-step decomposition DOI: 10.1039/c8dt00300a upon heating. The final products were identified using powder X-ray diffraction as FexMSe2, indicating Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence. rsc.li/dalton their potential as single-source precursors for functional materials. Introduction been widely developed after the discovery that these materials may be used as precursors for semiconducting binary metal Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) have been widely chalcogenides.13 Extension of this area to include various studied over the years due to their ability to intercalate species metallocene dichalcogenides has been possible because of the with apparent implications in catalytic and biological development of equipment for air-sensitive synthesis. -

1St Halfchemnotes
Science 10 Chemistry Notes Matter and Classification Purpose of classification: to gain a better understanding and appreciate similarities or differences Matter: Has mass and occupies space. We can divide matter into two categories as follows: Matte Pure Mixtur Heterogeneo Homogeneo Elemen Alloy Solutio Metal Nonmeta Compou Ioni Molecul PURE SUBSTANCES Substances that are the same or consistent throughout. Can be a single element or a combination of elements. Elements: Substance composed of only one kind of atom. 109 on the periodic table. Each has a unique international symbol. Can be combined to make other pure substances. Compound: Combination of two or more elements in specific proportions. Once combined the compound acts as one, with consistent chemical and physical properties. Chemical vs. Physical Properties Chemical - describes the reactivity of a substance. Physical -no new substance formed. Has similar properties in each form. Usually a change in phase. ie. Liquid, solid or gas. Chemical Reactions The process that occurus whena subtance or substances reacts to creat a different substance. - involve the production of new substances - involve the flow of energy (exothermic and endothermic) - involves formation of a gas - involves the formation of a solid in a liquid Periodic Table Elements on the periodic table are classified and arranged according to four basic patterns: 1. Atomic number: the number of protons (positively charged particle) in the nucleus of an element. The number of electrons in an atom 2. Metals vs. non-metals: separated by the staircase line. 3. Groups (or families): vertical columns that have similar properties. 4. Periods: horizontal rows which indicate the number of electron shells an atom has.