Presentazione Standard Di Powerpoint
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Encyclop^Edia Biospeologica Indonesie
ENCYCLOP^EDIA BIOSPEOLOGICA INDONESIE par Philippe LECLERC*, Louis DEHARVENG**, Peter K. L. NG***, Christian JUBERTHIE**»* et Vasile DEÇU***** I - GENERALITES Le vaste archipel indonésien se compose de 13 000 îles, réparties sur 5 000 km d'est en ouest, et couvrant au total 1 900 000 km2. C'est encore en partie une terra incognito en biospéologie en raison de la dispersion de ces karsts et des difficultés d'accès à de nombreuses régions. II - HISTORIQUE Comme les autres peuples du sud-est asiatique, les Indonésiens pénètrent sous terre. On connaît, en effet, quelques grottes dont les entrées servent traditionnellement de sépulture. D'autres sont activement exploitées pour leur guano, leur phosphate, leurs nids d'hirondelles (Sumatra, Kalimantan), ou comme réserves d'eau (Gunung Sewu à Java, île de Muna à Sulawesi Selatan). Il existe également de nombreuses grottes ornées à Sulawesi (GLOVER, 1981) et à Kalimantan (CHAZINE, 1996 ; CHAZINE et FAGE, 1998). Dès le début du siècle, des naturalistes, la plupart Hollandais, ont exploré quelques cavités, surtout à Sumatra, Java et Sulawesi (ex-Célèbes), et y ont réalisé d'importantes récoltes et des observations. Ce sont principalement : JACOBSON (1912), DAMMERMAN (1932), LEEFMANS (1930, 1932) et van der MEER MOHR (1936). Les compilations publiées par STADLER (1927) puis WOLF (1935) fournissent quelques informations sommaires. Parallèlement, DANES (1910, 1915), ESCHER (1931), PANNEKOEK (1941), LEHMANN (1936, 1954), SUNARTADIRDJA et LEHMANN (1960), PFEIFFER (1970), BALAZS (1968, 1970, 1971), McDONALD (1976), et QUINIF et DUPUIS (1984), entre autres, ont étudié la géologie et l'hydrogéologie, principalement des karsts du Gunung Sewu à Java et de Maros à Sulawesi Selatan. -

President's Message
ISSN 2372-2517 (Online), ISSN 2372-2479 (Print) METALEPTEAMETALEPTEA THE NEWSLETTER OF THE ORTHOPTERISTS’ SOCIETY TABLE OF CONTENTS President’s Message (Clicking on an article’s title will take you By DAVID HUNTER to the desired page) President [email protected] [1] PRESIDENT’S MESSAGE [2] SOCIETY NEWS ear Society members, [2] OS Board Meeting Report at ICO2019 compiled by D. HUNTER After a very successful [5] Save the date: ECOCIII/DGfO ICO in Agadir, the plans 19-22 March 2020 by L. WILLEMSE [5] Announcing TETTIGONIIDAE are for the next Congress (Orthoptera) Species of Argentina and DD to be in Paris during Uruguay by H. BRAUN & G.E. ZUBARÁN 2022. I draw your attention to the re- [6] Polyneoptera Organized Meeting at 2019 ESA Meeting: “Small Orders, Big port of Board Meeting held in Agadir Ideas” by D.A. WOLLER ET AL. found later in this issue, which has de- [6] Reminder: Call for speakers for tails of initial plans for the Paris meet- ICE2020 by D.A. WOLLER ET AL. ing. The Board thanks the Officers of [7] New Book: A Guide to Crickets of Australia by D. RENTZ & Y. N. SU the Society and Regional Represen- [7] New Book: Grasshoppers & Crickets of tatives whose combined efforts are Italy by C. IORIO ET AL. taking our Society forward. The Trea- [8] IN MEMORIAM [8] Carlos S. Carbonell (December 22, surer’s Report shows that we are in a 1917 to August 15, 2019) by M.M. strong financial position because of CIGLIANO ET AL. the very generous donations by one of [10] REGIONAL REPORTS [10] Japan by H. -

NEW RECORDS of AEMODOGRYLLINAE (ORTHOPTERA: RHAPHIDOPHORIDAE) from CAVES of LAOS with DESCRIPTION of Eutachycines Cassani Chopard MALE
LEPCEY - The Journal of Tropical Asian Entomology 02 (1):37- 43 Published: 31 October 2013 ©HABITATS Conservation Initiative. ISSN 2012 - 8746 Short Communication NEW RECORDS OF AEMODOGRYLLINAE (ORTHOPTERA: RHAPHIDOPHORIDAE) FROM CAVES OF LAOS WITH DESCRIPTION OF Eutachycines cassani Chopard MALE Mauro Rampini1*, Claudio Di Russo1, Francesca Pavesi2 and Marina Cobolli1 1Dipartimento di Biologia e Biotecnologie “C. Darwin”, Università di Roma La Sapienza, Viale dell’Università 32 - 00185 Roma - Italy 2Associazione Culturale Onlus Oletepsiuchè, c/o Museo Civico di Zoologia, Via U. Aldrovandi, 18 – 00197 Roma - Italy Abstract New samples of Aemodogryllinae collected in cave habitats from Laos are reported with the description of the unknown male of Eutachycines cassani (Chopard, 1954).The distribution of Aemodogryllinae in Laos includes, at present, E. cassani in the Central Laos, two species of the genus Paradiestrammena, P. vitalisi (Chopard, 1919) in the Northern part of the country ; P. vernalis (Gorochov, 1998) in the Central Laos, and one representative of the genus Diestrammena (Brunner and Wattenwyl, 1888) from caves of Northern Laos close to the border with the Vietnam. Keywords: Eutachycines, Aemodogryllinae, Cave crickets, Laos, Rhaphidophoridae Geotags: Laos, [N17°37’449” – E 105°08’809” | N 17°26’670” – E 104°56’900” | N 20°42’032” – E 102°41’602”] vertices, the metatarsi and the genitalia INTRODUCTION (Storozhenko, 1990). Four of the seven living subfamilies of The subfamily Aemodogryllinae includes Rhaphidophoridae (Aemodogryllinae, at present 12 genera and about 165 species whose Rhaphidophorinae, Troglophilinae, and distribution goes from northern India (Assam) to Tropidischinae) are widespread in Asia (Di Russo Korea, Japan, and Siberia (Vladivostok) to the and Rampini, 2005; Eades et al., 2012). -
Soft Gel Viagra Tablets
Available online at http://scik.org Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci. 2020, 2020:59 https://doi.org/10.28919/cmbn/4830 ISSN: 2052-2541 CORRESPONDENCE BETWEEN BATS POPULATION AND TERRESTRIAL CAVE-DWELLING ARTHROPODS COMMUNITY IN TASIKMALAYA KARST AREA ISMA DWI KURNIAWAN1,*, CAHYO RAHMADI2, REZZY EKO CARAKA3,4,*, IMAN AULIA RAHMAN1, IDA KINASIH1, TONI TOHARUDIN5, RUNG CHING CHEN3, YOUNGJO LEE4 1Department of Biology, UIN Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung, Indonesia 2Museum Zoologicum Bogoriense, Indonesian Institute of Science (LIPI), Indonesia 3Department of Information Management, College of Informatics, Chaoyang University of Technology, Taiwan 4Department of Statistics, College of Natural Science, Seoul National University, South Korea 5Department of Statistics, Padjadjaran University, West Java, Indonesia Copyright © 2020 the author(s). This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract: Trogloxenes particularly bats play an important role in subterranean habitat. They provide organic material and induce cave microclimate that influence cave-dwelling biota, including arthropods. This study aimed to learn how bats population influences cave-dwelling arthropods community. Data collections were performed in three caves which had different bats species in Tasikmalaya karst area namely Liang Boeh, Liang Seungit and Sarongge. We recorded bats population, guano production, physicochemical condition of caves passage, and arthropods community in each cave. All samplings were only conducted in the specific sites of the dark zone where bat populations were aggregated. Data indicated that Liang Boeh was inhibited by Hipposideros sp (±472 individuals), *Corresponding authors E-mail addresses: [email protected] (I.D. -

Download (530KB)
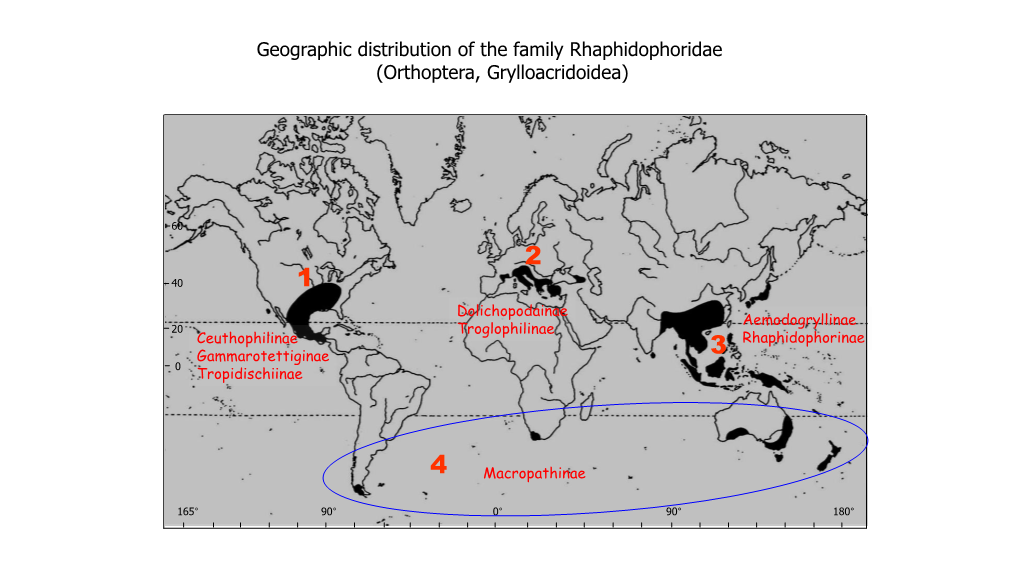
International Journal of Entomology Research International Journal of Entomology Research ISSN: 2455-4758; Impact Factor: RJIF 5.24 www.entomologyjournals.com Volume 2; Issue 2; March 2017; Page No. 55-58 A new species of the genus Rhaphidophora from Seram island (Moluccas, Indonesia) with notes on the geographic distribution of the subfamily Rhaphidophorinae (Orthoptera, Rhaphidphoridae) Claudio Di Russo, Mauro Rampini Laboratory of Biospeleology, Department of Biology and Biotecnology, Charles Darwin, University of Rome, La Sapienza. Viale dell, Università, Roma, Italy Abstract A new species of Rhaphidophora (R. barociniturricchiae n.sp.) is described from a cave of Seram Island (Moluccas, Indonesia). The new species shows affinities with R. wasile and R. amboinensis from Halmaera and Amboina Islands respectively. The geographic distribution of the genus Rhaphidophora and the close genus Stonycophora is discussed in relation to the Wallace and Liddeker lines. Keywords: Rhaphidophora, Stonycophora, Seram, Moluccas, Wallace line, Liddeker line 1. Introduction 1.1 Taxonomic background The subfamily Rhaphidophorinae togheter with the The generic classification of the Rhaphidophorinae is formal Aemodogryllinae are the more representative groups of the to some extent, since the morphology of the members of this Orthoptera Rhaphidophoridae living in the South East Asia and subfamily is rather uniform: the wings and sound organs are Oceania. In particular they encompass many regions of these undeveloped, and the genitalia are entirely membranous two continents including about 332 species widespread from without complex structures. Affinities in groups with such a the Himalaya to Japanese archipelagous [1]. Among the scanty set of characters can hardly be found based on numerous members of the Rhaphidophorinae, presently morphological examination. -
![Insects of Micronesia 5(4): 219–291]](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/4700/insects-of-micronesia-5-4-219-291-7314700.webp)
Insects of Micronesia 5(4): 219–291]
Micronesica 32(1):11–83. 1999 [Insects of Micronesia 5(4): 219–291] Insects of Micronesia Volume 5, no. 4 Gryllacridoidea, Rhaphidophorioidea and Tettigonioidea (Grylloptera) VERNON R. VICKERY1, D. KEITH MCE. KEVAN2, AND MARY-LYNN ENGLISH3 Lyman Entomological Museum and Department of Natural Resource Sciences, McGill University, Macdonald Campus, 21111 Lakeshore Road, Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue, QC, Canada, H9X 3V9. Abstract—Fifty-three species in six families occur in Micronesia. Kevan (1987) listed forty-three species, 20 of which were given as new but unde- scribed. Kevan (1990) listed eight species as introduced, seven of which were on his previous list, plus Mecopoda elongata (Linnaeus). Seven new species were described in the Conocephalidae, Phisidini, by Jin & Kevan (1992). Eighteen additional new species and a subspecies are described in this paper, seventeen by Vickery & Kevan and one by English & Kevan, nine in the Gryllacrididae: Niphetogryllacris marianae, N. tolensis, Anancistrogera palauensis, Neanias ogasawarensis, Prosopogryllacris palauensis, P. chuukensis, Melaneremus marianae marianae, M. m. rotaensis, M. saiensis, and M. kosraensis; two in the Rhaphidophoridae: Rhaphidophora ponapensis and Stonychophora palauensis; three in the Phaneropteridae: Casigneta palauensis, Isopsera yapanese and I. palauensis; one in the Mecopodidae: Ocica ponapensis English & Kevan; and three in the Conocephalidae: Spinisternum palauensis, Macroxiphus globiceratus and Salomona ponapensis. Nine species are added to the lists of Kevan (1987, 1990), including one described as new. Twenty-six species are known to be endemic in Micronesia. Introduction This paper completes the work on the Orthoptera (sens. str.) and Grylloptera [=Ensifera] of Micronesia, except for the crickets (Grylloidea). Previous papers include a preliminary list (Kevan 1987), the introduced species (Kevan 1990), 1Corresponding author. -

The Systematics and Biology of the Cave-Crickets of the North American Tribe Hadenoecini (Orthoptera Saltatoria: Ensifera: Rhaphidophoridae: Dolichopodinae)
MISCELLANEOUS PUBLICATIONS MUSEUM OF ZOOLOGY. UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN NO. 156 The Systematics and Biology of the Cave-Crickets of the North American Tribe Hadenoecini (Orthoptera Saltatoria: Ensifera: Rhaphidophoridae: Dolichopodinae) I> y Theodore H. Hubbell and Russell M. Norton Osborn Memorial Laboratories, Department of Biology, Yale University Ann Arbor MUSEUM OF ZOOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF MlCHIGAN August 1, 1978 MISCELLANEOUS PUBLICATIONS MUSEUM OF ZOOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN FRANCIS C. EVANS, EDITOR The publications of the Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan, consist of two series-the Occasional Papers and the Miscellaneous Publications. Both series were founded by Dr. Bryant Walker, Mr. Bradshaw H. Swales, and Dr. W. W. Newcomb. The Occasional Papers, publication of which was begun in 1913, serve as a medium for original studies bised principally upon the collections in the Museum. They are issued separately. When a sufficient number of pages has been printed to make a volume, a title page, table of contents, and an index are supplied to libraries and individuals on the mailing list for the series. The Miscellaneous Publications, which include papers on field and museum techniques, monographic studies, and other contribu1.ions not within the scope of the Occasional Papers, are published separately. It is not intended that they be grouped into volumes. Each number has a title page and, when necessary, a table of contents. A complete list of publications on Birds, Fishes, Insects, Mammals, Mollusks, and Reptiles and Amphibians is available. Address inquiries to the Director, Museum of Zoology, .4nn Arbor, Michigan 48109. MISCELLANEOUS PUBLICATIONS MUSEUM OF ZOOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN NO. -

The Difference on Arthropod Communities' Structure Within Show
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Binus University Repository Article-13 Eco. Env. & Cons. 24 (1) : 2018; pp. (81-90) Copyright@ EM International ISSN 0971–765X The difference on Arthropod communities’ structure within show caves and wild caves in Gunungsewu karst area, Indonesia Isma Dwi Kurniawan1, R.C. Hidayat Soesilohadi1, Cahyo Rahmadi2, Rezzy Eko Caraka3 and Bens Pardamean4 1Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada 2 Museum Zoologicum Bogoriense Indonesian Institute of Science (LIPI) 3School of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Science and Technology, The National University of Malaysia 4Computer Science Department, BINUS Graduate Program – Master of Computer Science, Bina Nusantara University (Recieved 15 August, 2017; accepted 28 September, 2017) ABSTRACT This study was conducted to determine the differences on Arthropod communities’ structure and climatic- edaphic factors within wild caves and show caves in Gunungsewu karst area, also analyze the climatic and edaphic components that give the strongest influence on Arthropods community. Arthropod Sampling was done by hand collecting, pitfall and bait traps, and Berlese extractor. The measured components of climatic factor comprise light intensity, air temperature, RH, and CO2 level, while the edaphic comprise soil temperature, SOC, N, P, soil moisture, and pH. Data wereanalyzedby richness, diversity, evenness, and dissimilarity indices measurement. We also conducted statistical analyze through Pearson correlation. All Arthropod samples were classified into six classes, 30 orders, and 209 morphospecies. The dark zones of wild caves with low human disturbance have lower richness, diversity, and evenness than the dark zones of show caves. Species richness of Arthropods in Show Caves is not always lower than wild caves, but the populations of common cavernicolous Arthropods (Rhaphidophora sp., Trachyjulus tjampeanus, Charon sp. -

Troisième Partie : Ectobiinae Et Theganopteryginae Blatellidae
Bull. Inst. r. Sci. nat. Belg. 47 38 Brux. 30.11.1971 Bull. K. Belg. Inst. Nat. Wet. CATALOGUE DES ORTHOPTEROIDES CONSERVES DANS LES COLLECTIONS ENTOMOLOGIQUES DE L'INSTITUT ROYAL DES SCIENCES NATURELLES DE BELGIQUE (1) BLATTARIAE : Troisième partie : Ectobiinae et Theganopteryginae Addendum : Blatellidae, Perisphaeridae et Pycnoscelidae SALTATOPTERA : Gryllacridae PAR P. Vanschuytbroeck (Bruxelles) Cette cinquième suite du catalogue des Orthoptéroïdes comprend la mise en ordre, la recherche et l'authentification des Saltatoptera Grylla¬ cridae, qui suit celle des Gryllidae. Cette très importante collection est basée sur divers apports de spé¬ cialistes et dons de récolteurs (Saussure, Brunner, Brisout, Bolivar, Fruhstorfer et Van Volxem). BLATTARIAE XX. — ECTOBIIDAE Jakobson & Bianki, 1902-05 Ectobiidae Jakobson & Bianki, 1902-06, Prjamkrylyja i loznosetcato- krylyja Ross, imp., pp. 116-124. (1) 1) Decmaptera in Bull. Inst. r. Sc. nat. Belg., 45.41.69. 2) Polyphagoidea et Blaberoidea in Bull. Inst., r. Sc. nat. Belg., 45, 14, 69. 3) Nyctiboridae, Epilampridae et Blattellidae in Bull. Inst. r. Sc. nat. Belg., 46, 20, 70. 4) Saltatoptera : Grillidae, Oecanthidae et Gryllotalpidae in Bull. Inst. r. Se. nat. Belg., 47, 15, 71. 2 P. VANSCHUYTBROECK 47, 38 ( = Ectobiidae Brunner; Ectobites Saussure; Ectobinae Kirby; Ectobinae Shelford; Pseudomopinae Bruijning). 1) Sous-famille des Ectobiinae Chopard, 1901 Ectobiinae Chopard, 1901, Faune de France 56, p. 13 124. — Ectobius Stephens, 1835, Illustr. brit. Ent. mandib. 6, London, p. 45. Type du genre: Blatta laportica Stephens. 276. — pallidus (Olivier), 1789, Encyclop. méthod. Hist. nat. 4, Paris, p. 319 (Blatta). (=lividus Fabric. : Blatta). 40 exemplaires : diverses localités (det. : Burr, Finot, Brunner). 277. — vittiventris Costa, 1847, Ann. -

Download Article (PDF)
XXVII ON SOME CA VERNICOLOUS DER-- MAPTERA AND ORTHOPTERA FROM ASSAM By L. CHOPARD, D.Sc. (Plates XXJ--XXIII.) In a previous papp.r (M em. A s. Soc. Beng. VI [r9IQ], pp .. 339-396) I described a Diestrammena from Cherr~punji which \vas the first cavernicolous Orthopteron collected in that region of India. Since then, Dr. N. Annandale has had the kindness to send me another collection of Orthoptera flom caves in Assam, contain ing the following species:- Forc'if;ula trisp~nosa; Dohr-n I Siju Cave. Chelisoches morio, F , Siju Cave. SPelaeoblatta (?) caeca, sp. nov., Rupmath Cave. Rhaphidophora ru!obrunnea, sp. nov., cave near Yawnghwe. Diestrammena brevi/rons, Chop., Rupmath Cave. Diestrammena indica, sp. nov., cave near Yawnghwe. Tachycines adelungi, sp. nov., Ngot bat Cave. Arachnomimus sp., Siju Cave. It may he seen from this short enumeration how little kno\lvn this cavernicolous fauna is. The Bla ttid hereafter descrihed is particularly of great interest, being completely hHnd and showing remarkable characters of adaptation to cavernicolous life. DERMAPTERA. The two species of Derma ptera here referred to, as well as the other few species of this group recorded fronl caves in various parts of the world, are common luci~olous species. They do not ~how any character of adaptation to cavernicolous life but seem nevertheless quite well accustomed to this special habitat. In fact both of them are represented by a certain number of indivi duals of both sexes and by immature stages which proves that they live completely and reproduce thenlselves inside the caves. Fam. FORFICTJLIDAE. -

III. the Orthoptera (Grasshoppers and Crickets)
United States Department of Invertebrates of the Agriculture Forest Service H.J. Andrews Experimental Forest, Pacific Northwest Research Station Western Cascades, Oregon: Research Note PNW-443 III. The Orthoptera (Grasshoppers May 1986 and Crickets) David C. Lightfoot F I L E C l } | Abstract An inventory of Orthoptera (grasshoppers and crickets) at the H.J. Andrews Experimen- tal Forest, near Blue River, Oregon, was conducted to determine the species present and ecological relationships. A key for identification and an annotated list are presented. From qualitative assessments of successional habitat relationships, generalized species associations of forest Orthoptera are proposed, and their responses to forest succession are predicted. Keywords: Invertebrata, keys (invertebrata), checklists (invertebrata), Oregon (H.J. Andrews Exp. For.). Introduction Orthoptera are important primary consumers in many terrestrial ecosystems (Odum and others 1962, Rodell 1977, Uvarov 1977). In temperate regions they are especially prevalent in grassland and scrub formations (Barnum 1964, Campbell and others 1974, Otte 1976). Relatively few Orthoptera occur in temperate forests of the Pacific Northwest and little is known about species composition or about orthopteran community patterns or processes. This study was conducted to inventory the Orthoptera of the H.J. Andrews Experimental Forest (HJA) (a long-term ecological research site of the National Science Foundation), Willamette National Forest, near Blue River, Oregon, and to provide information about and identify those species that occur there. Analysis of long-term ecological trends is of primary concern at the HJA. To determine how orthopteran communities change over time, patterns of habitat associations were qualitatively assessed for a series of sites at different stages of vegetational succession. -

The External Morphology and Phylogenetic Position of The
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Masters Theses 1911 - February 2014 1935 The external morphology and phylogenetic position of the woodland cave cricket (Ceuthophilus brevipes Scudder; Orthoptera; Tettigoniidae) Ashley Buell Gurney University of Massachusetts Amherst Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarworks.umass.edu/theses Gurney, Ashley Buell, "The external morphology and phylogenetic position of the woodland cave cricket (Ceuthophilus brevipes Scudder; Orthoptera; Tettigoniidae)" (1935). Masters Theses 1911 - February 2014. 1577. Retrieved from https://scholarworks.umass.edu/theses/1577 This thesis is brought to you for free and open access by ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst. It has been accepted for inclusion in Masters Theses 1911 - February 2014 by an authorized administrator of ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst. For more information, please contact [email protected]. 9B THE EXTERNAL MORPHOLOGY AND PHYLOGENETIC POSITION OF THE WOODLAND CAVE CRICKET ( Ceuthophilus brevipes Scudder ; Orthoptera ;Tettigoni idae) *3F Ashley Hue 11 Gurney Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Massachusetts State College Amherst, Massachusetts June, 1935 C ON T EH T 5 rage Acknowledgements 1 Introduction 2 External Morphology 4 Head 4 Thorax 11 Pro thorax 11 Me so thorax 16 Metathorax 19 Abdomen 21 Terminal structures of male 23 Terminal structures of female 28 Bibliography 31 Abbreviations 43 Explanation of plates « 46 Acknowledgements The preparation of this paper was undertaken at the suggestion of Dr. G. C Crampton and to him the author is deeply indebted for valuable advice during the morphological investigations and the writing of the manuscript. Dr. C- P. Alexander has shown a kind interest in the work throughout the study and to him the writer would express his appreciation for a critical reading of the manuscript.