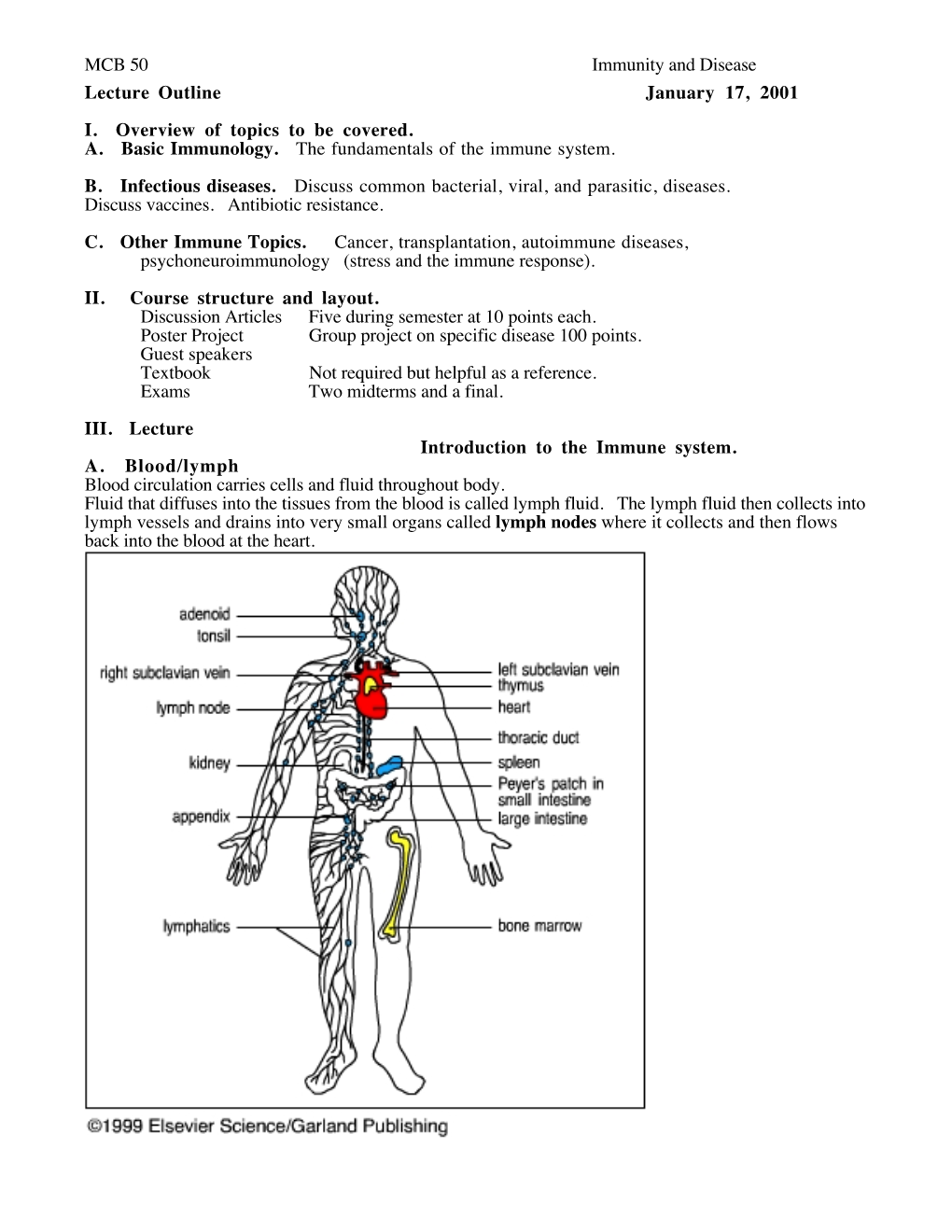
MCB 50 Immunity and Disease Lecture Outline January 17, 2001 I
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Thalassemia and the Spleen
Thalassemia and the Spleen 4 Living with Thalassemia are developing an infection (fever, chills, sore throats, unexplained coughs, listlessness, muscle pain, etc.) and Issues in Thalassemia report them to your doctor right away. Thalassemia Care • Sometimes a splenectomy can lead to an exceptionally and the Spleen high platelet count, which can in turn lead to blood clotting. by Marie B. Martin, RN, and Craig Butler Your doctor should monitor your platelet count on a regular basis and may ask you to take baby aspirin daily. This sounds kind of frightening. Is a splenectomy really a What is the spleen? wise choice? The spleen is a small organ (normally That’s a decision that must be made in each individual case. about the size of a fist) that lies in the A doctor with significant experience with thalassemia is upper left part of the abdomen, near going to be in the best position to offer advice about this; the stomach and below the ribcage. however, most people who are splenectomized are able to What does it do? manage the challenges it presents with relatively little The spleen has a number of functions, the most important of difficulty. which are filtering blood and creating lymphocytes. It also acts as a “reservoir” of blood, keeping a certain amount on Of course, it’s best to avoid any circumstances that can lead hand for use in emergencies. to the need for a splenectomy in the first place. For a person with thalassemia, this means following a transfusion In its filtering capacity, the spleen is able to remove large regimen that keeps hemoglobin levels above 9 or 10gm/dL. -

Osteopathic Approach to the Spleen
Osteopathic approach to the spleen Luc Peeters and Grégoire Lason 1. Introduction the first 3 years to 4 - 6 times the birth size. The position therefore progressively becomes more lateral in place of The spleen is an organ that is all too often neglected in the original epigastric position. The spleen is found pos- the clinic, most likely because conditions of the spleen do tero-latero-superior from the stomach, its arterial supply is not tend to present a defined clinical picture. Furthermore, via the splenic artery and the left gastroepiploic artery it has long been thought that the spleen, like the tonsils, is (Figure 2). The venous drainage is via the splenic vein an organ that is superfluous in the adult. into the portal vein (Figure 2). The spleen is actually the largest lymphoid organ in the body and is implicated within the blood circulation. In the foetus it is an organ involved in haematogenesis while in the adult it produces lymphocytes. The spleen is for the blood what the lymph nodes are for the lymphatic system. The spleen also purifies and filters the blood by removing dead cells and foreign materials out of the circulation The function of red blood cell reserve is also essential for the maintenance of human activity. Osteopaths often identify splenic congestion under the influence of poor diaphragm function. Some of the symptoms that can be associated with dysfunction of the spleen are: Figure 2 – Position and vascularisation of the spleen Anaemia in children Disorders of blood development Gingivitis, painful and bleeding gums Swollen, painful tongue, dysphagia and glossitis Fatigue, hyperirritability and restlessness due to the anaemia Vertigo and tinnitus Frequent colds and infections due to decreased resis- tance Thrombocytosis Tension headaches The spleen is also considered an important organ by the osteopath as it plays a role in the immunity, the reaction of the circulation and oxygen transport during effort as well as in regulation of the blood pressure. -

Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant for Sickle Cell Disease Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant
Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant for Sickle Cell Disease Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant for Sickle Cell Disease 1 Produced by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital Departments of Hematology, Patient Education, and Biomedical Communications. Funds were provided by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, ALSAC, and a grant from the Plough Foundation. This document is not intended to take the place of the care and attention of your personal physician. Our goal is to promote active participation in your care and treatment by providing information and education. Questions about individual health concerns or specifi c treatment options should be discussed with your physician. For more general information on sickle cell disease, please visit our Web site at www.stjude.org/sicklecell. Copyright © 2009 St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital How did bone marrow (stem cell) transplants begin for children with sickle cell disease? Bone marrow (stem cell) transplants have been used for the treatment and cure of a variety of cancers, immune system diseases, and blood diseases for many years. Doctors in the United States and other countries have developed studies to treat children who have severe sickle cell disease with bone marrow (stem cell) transplants. How does a bone marrow (stem cell) transplant work? 2 In a person with sickle cell disease, the bone marrow produces red blood cells that contain hemoglobin S. This leads to the complications of sickle cell disease. • To prepare for a bone marrow (stem cell) transplant, strong medicines, called chemotherapy, are used to weaken or destroy the patient’s own bone marrow, stem cells, and infection fi ghting system. -

Adaptive Immune Systems
Immunology 101 (for the Non-Immunologist) Abhinav Deol, MD Assistant Professor of Oncology Wayne State University/ Karmanos Cancer Institute, Detroit MI Presentation originally prepared and presented by Stephen Shiao MD, PhD Department of Radiation Oncology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Disclosures Bristol-Myers Squibb – Contracted Research What is the immune system? A network of proteins, cells, tissues and organs all coordinated for one purpose: to defend one organism from another It is an infinitely adaptable system to combat the complex and endless variety of pathogens it must address Outline Structure of the immune system Anatomy of an immune response Role of the immune system in disease: infection, cancer and autoimmunity Organs of the Immune System Major organs of the immune system 1. Bone marrow – production of immune cells 2. Thymus – education of immune cells 3. Lymph Nodes – where an immune response is produced 4. Spleen – dual role for immune responses (especially antibody production) and cell recycling Origins of the Immune System B-Cell B-Cell Self-Renewing Common Progenitor Natural Killer Lymphoid Cell Progenitor Thymic T-Cell Selection Hematopoetic T-Cell Stem Cell Progenitor Dendritic Cell Myeloid Progenitor Granulocyte/M Macrophage onocyte Progenitor The Immune Response: The Art of War “Know your enemy and know yourself and you can fight a hundred battles without disaster.” -Sun Tzu, The Art of War Immunity: Two Systems and Their Key Players Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity Dendritic cells (DC) B cells Phagocytes (Macrophages, Neutrophils) Natural Killer (NK) Cells T cells Dendritic Cells: “Commanders-in-Chief” • Function: Serve as the gateway between the innate and adaptive immune systems. -

Study Guide Medical Terminology by Thea Liza Batan About the Author
Study Guide Medical Terminology By Thea Liza Batan About the Author Thea Liza Batan earned a Master of Science in Nursing Administration in 2007 from Xavier University in Cincinnati, Ohio. She has worked as a staff nurse, nurse instructor, and level department head. She currently works as a simulation coordinator and a free- lance writer specializing in nursing and healthcare. All terms mentioned in this text that are known to be trademarks or service marks have been appropriately capitalized. Use of a term in this text shouldn’t be regarded as affecting the validity of any trademark or service mark. Copyright © 2017 by Penn Foster, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of the material protected by this copyright may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the copyright owner. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to Copyright Permissions, Penn Foster, 925 Oak Street, Scranton, Pennsylvania 18515. Printed in the United States of America CONTENTS INSTRUCTIONS 1 READING ASSIGNMENTS 3 LESSON 1: THE FUNDAMENTALS OF MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY 5 LESSON 2: DIAGNOSIS, INTERVENTION, AND HUMAN BODY TERMS 28 LESSON 3: MUSCULOSKELETAL, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM TERMS 44 LESSON 4: DIGESTIVE, URINARY, AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM TERMS 69 LESSON 5: INTEGUMENTARY, NERVOUS, AND ENDOCRINE S YSTEM TERMS 96 SELF-CHECK ANSWERS 134 © PENN FOSTER, INC. 2017 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY PAGE III Contents INSTRUCTIONS INTRODUCTION Welcome to your course on medical terminology. You’re taking this course because you’re most likely interested in pursuing a health and science career, which entails proficiencyincommunicatingwithhealthcareprofessionalssuchasphysicians,nurses, or dentists. -

Bone Marrow Biopsy
Helpline (freephone) 0808 808 5555 [email protected] www.lymphoma-action.org.uk Bone marrow biopsy This information is about a test called a bone marrow biopsy. You might have one to check if you have lymphoma in your bone marrow. On this page What is bone marrow? What is a bone marrow biopsy? Who might need one? Having a bone marrow biopsy Is a bone marrow biopsy safe? Getting the results We have separate information about the topics in bold font. Please get in touch if you’d like to request copies or if you would like further information about any aspect of lymphoma. Phone 0808 808 5555 or email [email protected]. What is bone marrow? Bone marrow is the spongy tissue in the middle of some of the bigger bones in your body, such as your thigh bone (femur), breastbone (sternum), hip bone (pelvis) and back bones (vertebrae). Your bone marrow is where blood cells are made. It contains cells called blood (‘haemopoietic’) stem cells. Stem cells are undeveloped cells that can divide and grow into all the blood cells you need. This includes red blood cells, platelets and all the different types of white blood cells. Page 1 of 8 © Lymphoma Action Figure: The different blood cells that develop in the bone marrow What is a bone marrow biopsy? A bone marrow biopsy is a test that involves taking a sample of bone marrow to be examined under a microscope. The samples are sent to a lab where an expert examines them. -

Cells, Tissues and Organs of the Immune System
Immune Cells and Organs Bonnie Hylander, Ph.D. Aug 29, 2014 Dept of Immunology [email protected] Immune system Purpose/function? • First line of defense= epithelial integrity= skin, mucosal surfaces • Defense against pathogens – Inside cells= kill the infected cell (Viruses) – Systemic= kill- Bacteria, Fungi, Parasites • Two phases of response – Handle the acute infection, keep it from spreading – Prevent future infections We didn’t know…. • What triggers innate immunity- • What mediates communication between innate and adaptive immunity- Bruce A. Beutler Jules A. Hoffmann Ralph M. Steinman Jules A. Hoffmann Bruce A. Beutler Ralph M. Steinman 1996 (fruit flies) 1998 (mice) 1973 Discovered receptor proteins that can Discovered dendritic recognize bacteria and other microorganisms cells “the conductors of as they enter the body, and activate the first the immune system”. line of defense in the immune system, known DC’s activate T-cells as innate immunity. The Immune System “Although the lymphoid system consists of various separate tissues and organs, it functions as a single entity. This is mainly because its principal cellular constituents, lymphocytes, are intrinsically mobile and continuously recirculate in large number between the blood and the lymph by way of the secondary lymphoid tissues… where antigens and antigen-presenting cells are selectively localized.” -Masayuki, Nat Rev Immuno. May 2004 Not all who wander are lost….. Tolkien Lord of the Rings …..some are searching Overview of the Immune System Immune System • Cells – Innate response- several cell types – Adaptive (specific) response- lymphocytes • Organs – Primary where lymphocytes develop/mature – Secondary where mature lymphocytes and antigen presenting cells interact to initiate a specific immune response • Circulatory system- blood • Lymphatic system- lymph Cells= Leukocytes= white blood cells Plasma- with anticoagulant Granulocytes Serum- after coagulation 1. -

Terminology Resource File
Terminology Resource File Version 2 July 2012 1 Terminology Resource File This resource file has been compiled and designed by the Northern Assistant Transfusion Practitioner group which was formed in 2008 and who later identified the need for such a file. This resource file is aimed at Assistant Transfusion Practitioners to help them understand the medical terminology and its relevance which they may encounter in the patient’s medical and nursing notes. The resource file will not include all medical complaints or illnesses but will incorporate those which will need to be considered and appreciated if a blood component was to be administered. The authors have taken great care to ensure that the information contained in this document is accurate and up to date. Authors: Jackie Cawthray Carron Fogg Julia Llewellyn Gillian McAnaney Lorna Panter Marsha Whittam Edited by: Denise Watson Document administrator: Janice Robertson ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We would like to acknowledge the following people for providing their valuable feedback on this first edition: Tony Davies Transfusion Liaison Practitioner Rose Gill Transfusion Practitioner Marie Green Transfusion Practitioner Tina Ivel Transfusion Practitioner Terry Perry Transfusion Specialist Janet Ryan Transfusion Practitioner Dr. Hazel Tinegate Consultant Haematologist Reviewed July 2012 Next review due July 2013 Version 2 July 2012 2 Contents Page no. Abbreviation list 6 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) 7 Acidosis 7 Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT) 7 Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome -

The Bridge Between Bone Marrow Adipocytes and Hematopoietic Cells Ziru Li and Ormond A
EDITORIALS Stem cell factor: the bridge between bone marrow adipocytes and hematopoietic cells Ziru Li and Ormond A. MacDougald Department of Molecular & Integrative Physiology, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, MI, USA. E-mail: ZIRU LI - [email protected] doi:10.3324/haematol.2019.224188 hite adipocytes serve as an energy reservoir to in the bone marrow supernatant, which indicates that store excessive calories in the form of lipid BMAT is a primary source of SCF in bone marrow.5 Wdroplets and protect other tissues or organs from Deficiency of SCF in BMAT reduces the bone marrow cellu- ectopic lipid accumulation. Brown adipocytes express larity, hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC), com- uncoupling protein 1 and are integral to adaptive thermoge- mon myeloid progenitors (CMP), megakaryocyte-erythro- nesis. Whereas the functions of adipocytes in either white or cyte progenitor (MEP) and granulocyte-monocyte progeni- brown adipose tissues are well documented, our knowledge tors (GMP) under steady-state condition. Consistent with of bone marrow adipocytes (BMA) remains in its infancy. these changes in the progenitor cells of bone marrow, mice Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT) occupies approximate- deficient for adipocyte SCF develop macrocytic anemia and ly 50-70% of the bone marrow volume in human adults.1 It reduction of neutrophils, monocytes and lymphocytes in cir- is a dynamic tissue and responds to multiple metabolic con- culation. In contrast to results in this study, Zhou et al. ditions. For example, BMAT -

Isolation of Cells from Spleen, Thymus, and Lymph Nodes 1 Purpose
ISOLATION OF CELLS FROM SPLEEN, THYMUS, AND LYMPH NODES 1 PURPOSE The purpose of this Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is to outline procedures for isolating and cryopreserving cells from spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes. 2 SCOPE This SOP will be applied to fresh tissue processed for cell isolation. 3 RESPONSIBILITIES 3.1 Managers and supervisors are responsible for making sure that technicians are properly trained and equipment and facility are maintained in good working order. 3.2 Laboratory personnel are responsible for reading and understanding this SOP and related documents and to perform these tasks in accordance with the SOPs. They are responsible for following clinical laboratory and tissue banking best practices. 4 EQUIPMENT and MATERIALS The materials, equipment and forms listed in the following list are recommendations only and alternative products as suitable may be substituted for the site specific task or procedure. 70% Ethanol (EtOH) 100x Antibiotic/Antimycotic solution (Sigma, Cat. No. A9909), aliquot 10 ml and store at -20°C Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline (D-PBS), Mg2+ Ca2+ free (Invitrogen, Cat. No. 10010-023), store refrigerated Collagenase type II (Invitrogen, Cat. No. 17101015) Dissecting instruments (scissors, forceps, scalpels, #10 or 11 blades) Cell culture dish (100 mm) Cell strainer, 100 um (BD, Cat. No. 352360) Syringes (3 or 5 ml), centrifuge tubes (15 or 50 ml conical), graduated pipettes (i.e., 2, 5, 10, 25, 50 ml), transfer pipettes Centrifuge (swinging bucket rotor), capable of maintaining 18-26°C, 250-800 g-force spins with brake (on/off) 0.17M Ammonium chloride solution (Stemcell, Cat. No. -

Nomina Histologica Veterinaria, First Edition
NOMINA HISTOLOGICA VETERINARIA Submitted by the International Committee on Veterinary Histological Nomenclature (ICVHN) to the World Association of Veterinary Anatomists Published on the website of the World Association of Veterinary Anatomists www.wava-amav.org 2017 CONTENTS Introduction i Principles of term construction in N.H.V. iii Cytologia – Cytology 1 Textus epithelialis – Epithelial tissue 10 Textus connectivus – Connective tissue 13 Sanguis et Lympha – Blood and Lymph 17 Textus muscularis – Muscle tissue 19 Textus nervosus – Nerve tissue 20 Splanchnologia – Viscera 23 Systema digestorium – Digestive system 24 Systema respiratorium – Respiratory system 32 Systema urinarium – Urinary system 35 Organa genitalia masculina – Male genital system 38 Organa genitalia feminina – Female genital system 42 Systema endocrinum – Endocrine system 45 Systema cardiovasculare et lymphaticum [Angiologia] – Cardiovascular and lymphatic system 47 Systema nervosum – Nervous system 52 Receptores sensorii et Organa sensuum – Sensory receptors and Sense organs 58 Integumentum – Integument 64 INTRODUCTION The preparations leading to the publication of the present first edition of the Nomina Histologica Veterinaria has a long history spanning more than 50 years. Under the auspices of the World Association of Veterinary Anatomists (W.A.V.A.), the International Committee on Veterinary Anatomical Nomenclature (I.C.V.A.N.) appointed in Giessen, 1965, a Subcommittee on Histology and Embryology which started a working relation with the Subcommittee on Histology of the former International Anatomical Nomenclature Committee. In Mexico City, 1971, this Subcommittee presented a document entitled Nomina Histologica Veterinaria: A Working Draft as a basis for the continued work of the newly-appointed Subcommittee on Histological Nomenclature. This resulted in the editing of the Nomina Histologica Veterinaria: A Working Draft II (Toulouse, 1974), followed by preparations for publication of a Nomina Histologica Veterinaria. -

B-Cell Development, Activation, and Differentiation
B-Cell Development, Activation, and Differentiation Sarah Holstein, MD, PhD Nov 13, 2014 Lymphoid tissues • Primary – Bone marrow – Thymus • Secondary – Lymph nodes – Spleen – Tonsils – Lymphoid tissue within GI and respiratory tracts Overview of B cell development • B cells are generated in the bone marrow • Takes 1-2 weeks to develop from hematopoietic stem cells to mature B cells • Sequence of expression of cell surface receptor and adhesion molecules which allows for differentiation of B cells, proliferation at various stages, and movement within the bone marrow microenvironment • Immature B cell leaves the bone marrow and undergoes further differentiation • Immune system must create a repertoire of receptors capable of recognizing a large array of antigens while at the same time eliminating self-reactive B cells Overview of B cell development • Early B cell development constitutes the steps that lead to B cell commitment and expression of surface immunoglobulin, production of mature B cells • Mature B cells leave the bone marrow and migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues • B cells then interact with exogenous antigen and/or T helper cells = antigen- dependent phase Overview of B cells Hematopoiesis • Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) source of all blood cells • Blood-forming cells first found in the yolk sac (primarily primitive rbc production) • HSCs arise in distal aorta ~3-4 weeks • HSCs migrate to the liver (primary site of hematopoiesis after 6 wks gestation) • Bone marrow hematopoiesis starts ~5 months of gestation Role of bone