What Is Communication Signal and Technology:- Transmission Of
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Mapping Networks and Services Proc
Mapping Networks and Services Proc. INET ´93 J.S. Quarterman Mapping Networks and Services John S. Quarterman1 Smoot Carl-Mitchell2 Gretchen Phillips3 Abstract I . Introduction Four global networks carry most of the Computer networking is widespread, supported by international network traffic; FidoNet, UUCP, the global Matrix of interconnected computer BITNET, and the Internet. The first step in networks such as the Internet, BITNET, UUCP, looking at these networks involves collecting and FidoNet. Perhaps 20,000,000 people use this appropriate data for each and performing some global Matrix of computer networks, and several consistency checking. The data for these maps major global computer networks are growing was initially derived from their node lists exponentially, rapidly reaching new countries and (BITNET and FidoNet) or host lists (UUCP). The new classes of users. This growth prompts Internet data came from a domain walk by Mark network users and service providers to ask Lottor. questions like: The data available from the node lists, public d Where are these users? maps and the domain walk is not in a format that d What is the magnitude of the various network is readily usable for this type of mapping. Each communities? map or other source of network information tends d What are the available services? to include different details. We have correlated the d How are services distributed? data by using telephone country codes, area codes d And, finally, how can this data be represented and local exchanges for determining locations. A in a meaningful graphical way? more complete discussion of the methods is We have chosen Latin America and the Caribbean available in issues of Matrix News[5-7] (ALyC) as the geographic region for discussing these issues and demonstrating the mapping of II . -

How Special Librarians Really Use the Internet: Summary of Findings and Implications for the Library of the Future
DOCUILIff RESUME ED 345 751 IR 054 097 AUTHOR Ladner, Sharyn J.; Tillman, Hope N. TITLE How Special Librarians Really Use the Internet: Summary of Findings and Implications for the Library of the Future. PUB DATE 29 Nar 92 NOTE 12p.; "This report was posted on March 29, 1992, to nine computer conferences where call for participation announcements had been posted in the summer of 1991: BUSLIB-L, LIBREF-L, LIfflES, NEDLIB-L, PACS-L, LAW-LIB, LIBADMIN, MAPS-L, and PANnet." AVAILABLE FROM Internet, through anonymous file transfer protocol (ftp), using the following location (hydra.uwo.ca), directory (LibSoft), and filename (SPEC underscore Libs.txt). PUB TYPE Reports - Research/Technical (143) EDRS PRICE NF01/PC01 Plus Postage. DESCRIPTORS Access to Information; *Computer Networks; Databases; *Electronic Rail; Electronic Publishing; Information Networks; *Librarians; Library Surveys; Online Searching; Online Systems; *Special Libraries; Telecommunications; Teleconferencing; User Needs (Information); *Use Studies IDENTIFIERS BITNET; *INTERNET ABSTRACT A five-page electronic questionnaire was sent to 113 special librarians who responded to "Call for Participation" announcements posted on nine computer conferences in July 1991 and a similar announcement in the August 1991 issue of the monthly newsletter of the Special Libraries Association. Fifty-four librarians completed the questionnaire, which sought information on the computer conferences to which they subscribed; the length of time they had been using either BITNET or the Internet; and the type of training they had had in using either of the two networks. In addition, the respondents were asked to rank five functions or capabilities available on either BITNET or Internet--electronic mail and computer forums, remote database searching, file transiur and data exchange, research and publication on the Internet--by extent of use. -

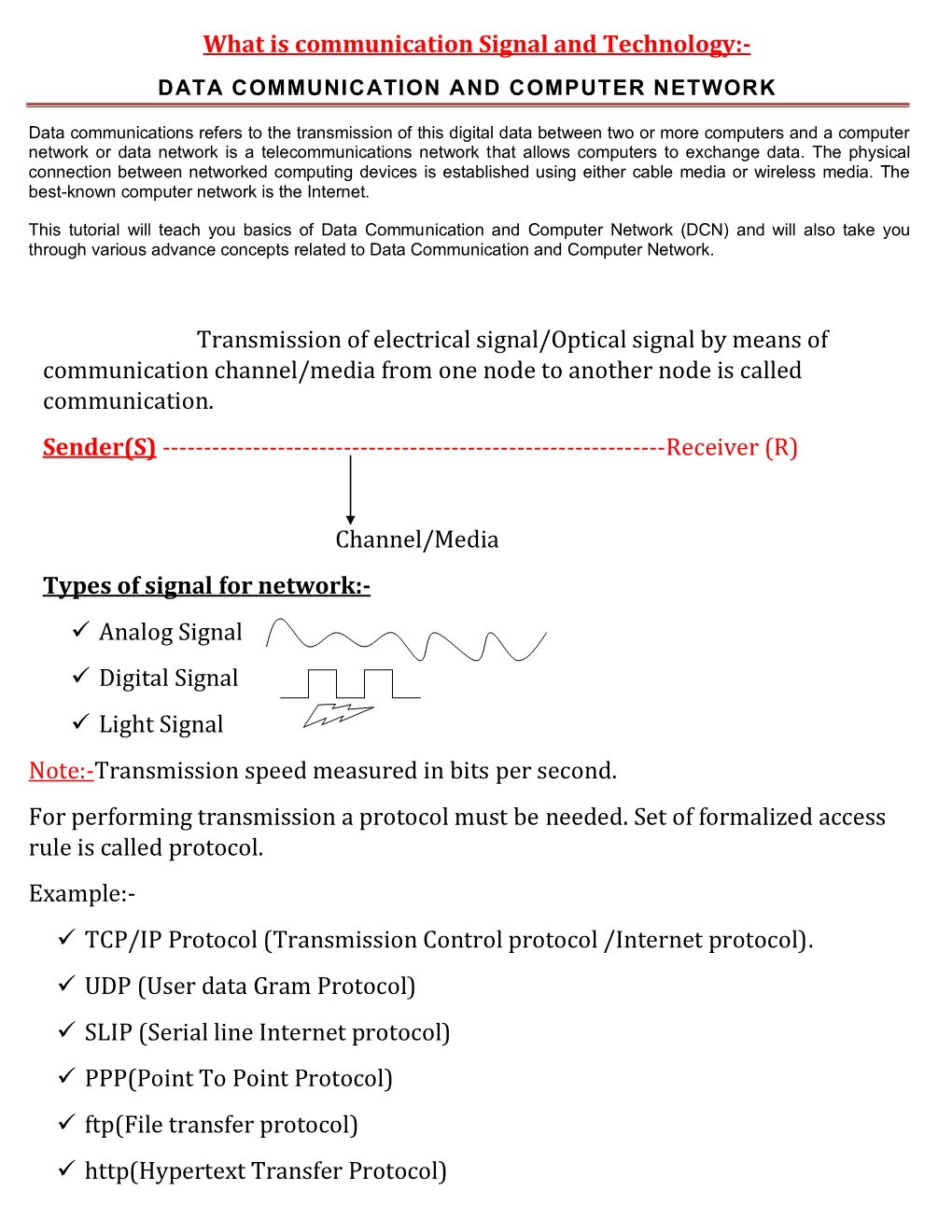
Network Infrastructure
Technology Then and Now at McGill Mforum – November 18, 2009 Gary Bernstein Director, NCS We’ve Come a Long Way, baby Moore’s Law • 1965: the number of components on a computer chip would double every year • Updated in 1975: the number of components would double every 2 years. Moore’s Law Microprocessor Year of Introduction # of Transistors 4004 1971 2,300 8080 1974 4,500 8086 1978 29,000 Intel 286 1982 134,000 Intel 386 1985 275,000 Intel 486 1989 1,200,000 Intel Pentium 1993 3,100,000 Intel Pentium II 1997 7,500,000 Intel Pentium III 1999 9,500,000 Intel Pentium 4 2000 42,000,000 Intel Itanium 2 2003 220,000,000 Intel Itanium 2 (9MB 2004 592,000,000 cache) Intel Core i7 2009 731,000,000 Networking Infrastructure 1989 2009 • 10 Mbps backbone • 2-10 Gbps backbone 2Mbps to desktop 1,000 Mbps to desktop • Finicky, temperamental, • Utility: Uptime essential downtime • ~30,000 connections • ~ 1,000 connections Regional Networks 1989 2009 • BITNET • RISQ • Emergence of RISQ – 100 Mps 1 Gbps – 56 Kbps within Montreal • Canarie (10 Gbps) – 19.2 Kbps across Quebec • McGill’s Link to Internet (1 Gbps) • McGill’s Link to RISQ (600 Mbps) Wireless 1989 2009 • Wireless coverage in classrooms, open spaces, library, research facilities... Remote Access 1989 2009 • Dial up • The Internet • Large physical modem pools • 10 Mbps • 1200 - 9600 bps Internet 1989 2009 • Text only E-mail, File Transfer • WWW • BITNET , Usenet • Browser-based world – point-to-point : e-mail May 2009: >109.5 million messages + files transmitted • from one server to the next websites -

Electronic Access to Research on Women: a Short Guide. INSTITUTION State Univ
DOCUMENT RESUME ED 358 823 IR 016 103 AUTHOR Hudson, Judith; Turck, Kathleen A. TITLE Electronic Access to Research on Women: A Short Guide. INSTITUTION State Univ. of New York, Albany. Inst. for Research on Women. PUB DATE 92 NOTE 12p. AVAILABLE FROM Institute for Research on Women, c/o Iris Berger, SS341, University at Albany, 1400 Washington Ave., Albany, NY 12222 ($2.50 shipping and handling). PUB TYPE Guides Non-Classroom Use (055) EDRS PRICE MFO1 /PCO1 Plus Postage. DESCRIPTORS *Access to Information; *Computer Networks; Databases; Data Collection; Electronic Mail; Feminism; Higher Education; Information Networks; Information Retrieval; Library Materials; Online Systems; Primary Sources; Reference Materials; Research Methodology; *Research Tools; Resource Materials; Womens Studies IDENTIFIERS BITNET; *Internet; *Listsery Discssion Groups ABSTRACT Electronic access to research on women is available in a variety of forms, from both primary and secondary sources. Both types of sources are growing dramatically in number and scope. This guide provides information on resources directly available to the researcher through electronic communications media. It includes enough technical information to get the user started. The use of ylectronic mail (e-mail) provides access to research and greatly :facilitates the research process. Two communications networks frequently used by academic institutions and researchers are BITNET and the Internet. Suggestions for using these and e-mail are given. A list is provided of computer discussion groups (facilitated by software known as Listserv) that may be of interest to researchers on women. Other tools that may be useful include news groups,different file distribution methods, Telnet, electronic conferencing, electronic journals, full-text databases, and numerical data sources. -

Two Electronic Serials on BITNET: the Public-Access Computer Systems Review and the Public-Access Computer Systems News
Two Electronic Serials on BITNET: The Public-Access Computer Systems Review and the Public-Access Computer Systems News By Charles W. Bailey, Jr. Preprint: 8/12/90. (Published as: Electronic (Online) Publishing in Action . The Public-Access Computer Systems Review and Other Electronic Serials) Introduction For many years, librarians have been reading about the potentials of electronic serials. An increasing number of full-text journals are available on database vendor systems, but these files are typically derived from print products. However, outside the commercial sector, a few pioneers on BITNET, an international computer network, have been quietly exploring publishing electronic digests, journals, magazines, and newsletters that have no print counterparts. These electronic serials are distributed to subscribers via e-mail messages or file transfers. This activity takes place in the larger context of electronic communication on BITNET. The major types of communication on BITNET are personal e-mail and computer conferences. There are thousands of computer conferences on BITNET, representing an increasing vital and important channel of scholarly communication. Given the diverse ways that communication is structured in these conferences, it is not always easy to tell where informal conference activity ends and formal electronic publication begins. This article focuses on electronic serials that bear some resemblance to their more traditional print counterparts; however, it should be emphasized that our conception of "serials" may need to be reconsidered in the network context. 1 The University of Houston Libraries has established a computer conference, an electronic journal, and an electronic newsletter on BITNET to examine issues related to public-access computer systems in libraries. -

Proceedings of the 15-17 October 1986 Joint Meeting of the Internet Engineering
Proceedings of the 15-17 October 1986 Joint Meeting of the Internet Engineering Internet Architecture Task Forces Prepared by: Phill|p Gross FOURTH IETF The MITRE Corporation 1820 Dolley Madison Boulevard McLean, Virginia 22102 Table of Contents - Meeting Notes for the Joint 15-17 October Meeting - Appendix A- Presentation Slides 1) Premises Technology Study, J. Herman (BBN) 2) Arpanet Congestion, M. Gardner (BBN) Workshop Reports - Routlng and EGP, M. St Johns (DDN) - DoD/ISO Interoperabillty, P. Gross (MITRE) - Name Domains for Milnet, M. Karels (UCB) 4) Cluster Mask RFCs, C-H. Rokltansk| (DFVLR) 5) NSFnet Status, H.W. Braun (VMich) and S. Brlm (Cornell) Multiple Satellite System Overview, D. Mills (UDel) - Appendix B - Additional Material Status of European Research Networks, provlded by H.W. Braun (UMich) Joint IETF and INARC 15-17 October 1986 Prepared by Phill Gross MITRE Corp. Jolnt IETF and INARC Table of Contents 1. Introduction................................................................................................... 1 2. Attendees....................................................................................................... 2 3. Agenda........................................................................................................... 3 4. MeetingNotes ............................................................................................... 4 4.1 October15, 1986.......................................................................................... 4 4.2 October16, 1986......................................................................................... -

DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS: a COMPARATIVE EVALUATION of the MIT and HARVARD ENVIRONMENTS by PHILLIP SEUNG-HO YOO
DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS: A COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF THE MIT AND HARVARD ENVIRONMENTS by PHILLIP SEUNG-HO YOO A.B., Engineering and Applied Science Harvard University (1983) Submitted to the Sloan School of Management in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements of the Degree of Master of Science in Management at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology May 1987 @ Phillip S. Yoo 1987 The author hereby grants to MIT permission to reproduce and to distribute copies of this thesis document in whole or in part. Signature of Author Sloan School of Management May 20, 1987 Certified by Stuart E. Madnick Associate Professor, Management Science Thesis Supervisor Accepted by Jeffrey A. Barks Associate Dean, Master's and Bachelor's Programs TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT ............................................................................... 3 BIOGRAPHICAL NOTE ................................................................ 4 1 Research Objective and Methodology.............................................5 1.1 The Use of Comparative Evaluation...................................... 7 1.2 Scope of the Evaluation .................................................. 7 2 Evaluation Methodology...............................................................9 2.1 User Community..........................................................9 2.2 Evaluation Criteria.......................................................9 3 Principal Protocols ................................................................. 15 3.1 TCP/IP.................................................................. -

Introduction Chapter 1: Roadmap
Chapter 1 Chapter 1: Introduction Introduction Our goal: Overview: v get “feel” and v what’s the Internet? terminology v what’s a protocol? v more depth, detail later in course v network edge; hosts, access net, physical media A note on the use of these ppt slides: v approach: We’re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). v network core: packet/circuit They’re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete slides § use Internet as (including this one) and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously Computer Networking: switching, Internet structure represent a lot of work on our part. In return for use, we only ask the A Top Down Approach , example following: th v v If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) in substantially unaltered form, that 5 edition. performance: loss, delay, you mention their source (after all, we’d like people to use our book!) Jim Kurose, Keith Ross v If you post any slides in substantially unaltered form on a www site, that throughput you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to) our slides, and Addison-Wesley, April note our copyright of this material. 2009. v security Thanks and enjoy! JFK/KWR v protocol layers, service models All material copyright 1996-2010 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved v history Introduction 1-1 Introduction 1-2 What’s the Internet: “nuts and bolts” Chapter 1: roadmap view PC v millions of connected Mobile network 1.1 What is the Internet? server computing devices: Global ISP 1.2 Network edge wireless hosts = -

Do Pre-Announcement Face-To-Face Interactions Increase the Returns to Acquisitions? Evidence from Smartphone Geolocational Data
Do Pre-Announcement Face-to-Face Interactions Increase the Returns to Acquisitions? Evidence from Smartphone Geolocational Data Marco Testoni,a Mariko Sakakibara,b Keith Chenc May 30, 2019 Information asymmetries make acquisitions risky, reducing firms’ ability to gain from these transactions. We test whether face-to-face interactions with the target’s employees before the acquisition provide informational advantages to the acquirer. For a sample of U.S. domestic acquisitions, we use smartphone geolocational data to measure the movement of people between merging companies’ headquarters in the months before the acquisition announcement and use the number of visits between the two companies as a proxy for face-to-face interactions. Using bad weather conditions in the two companies’ locations as a source of exogenous variation in intercompany mobility, we find evidence that more intense face-to-face interactions increase the abnormal returns on the acquirer’s stock at the acquisition announcement. Keywords: Mergers and acquisitions; abnormal returns; information asymmetry; monitoring; face-to-face interaction We would like to thank Marvin Lieberman, Natarajan Balasubramanian, Tony Bernardo, Chirantan Chatterjee, Mark Garmaise, seminar participants at UCLA, and annual meetings at the Academy of Management and Strategic Management Society for helpful comments. We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of UCLA Anderson School of Management and the Academic Senate of the University of California, Los Angeles. We are grateful to SafeGraph Inc. for providing us with the smartphone geolocational data used for this study. a,b,cUniversity of California, Los Angeles, Anderson School of Management e-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected] 1 1. -

Download This PDF File
African studies computer resources By Patricia S. Kuntz Internet/Bitnet Internet and beyond: African The most common network systems through linkages out the world are Internet and Bitnet. Internet is growing in popularity with the various com patible networks such as NetNorth (Canada), he “information highway” is very busy Janet (United Kingdom), and EARN (Europe). T among Africanists around the world. Schol Nearly all U.S. universities and most colleges ars based in Cameroon, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, purchase a connection to the Internet. This em Kenya, Mali, Senegal, South Africa, Tunisia, ployment benefit enables faculty, staff, and stu Zambia, and Zimbabwe with colleagues in the dents access to File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Americas, Europe, and Asia have coordinated Telnet, and UseNet. In contrast, Bitnet’s main conferences, written research papers, and feature is the automatic conversation lists called shared ideas on technology using one or more “Listserv.” One should not confuse the new of the four computer network services. software “Listserver” which is comparable for This essay focuses on African studies com the Internet. puter resources available in the U.S. with link ages to Africa. Four fundamental computer sys Electronic Mail tems exist: Intemet/Bitnet, Fidonet, UseNet, and Both Intemet/Bitnet networks provide electron BBS (dial-up bulletin board services). An up ic mail (e-mail) for sending public and private dated list of these network services is available messages. Messages from one network system from Arthur McGee.1 For a complete list of files, are tracked through gateways to other systems. contact: Internet-.<[email protected]> Consequently, readers having only an Internet <amcgee®eis.calstate.edu> BDPA BAC: [1-707- or Bitnet address can still send and receive 552-3314] to [Arthur McGee]; Data Bits Online: messages to the other network. -

Computer Networking: a Top Down Approach Seventh Edition
Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Seventh Edition Chapter 1 Introduction Slides in this presentation contain hyperlinks. JAWS users should be able to get a list of links by using INSERT+F7 Copyright © 2017, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Introduction (1 of 2) Our Goal: • get “feel” and terminology • more depth, detail later in course • approach: – use Internet as example Copyright © 2017, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Introduction (2 of 2) Overview: • What’s the Internet? • What’s a protocol? • network edge; hosts, access net, physical media • network core: packet/circuit switching, Internet structure • performance: loss, delay, throughput • security • protocol layers, service models • history Copyright © 2017, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Learning Objectives (1 of 7) 1.1 what is the Internet? 1.2 network edge – end systems, access networks, links 1.3 network core – packet switching, circuit switching, network structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in networks 1.5 protocol layers, service models 1.6 networks under attack: security 1.7 history Copyright © 2017, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved What’s the Internet: “Nuts and Bolts” View (1 of 2) • billions of connected computing devices: – hosts = end systems – running network apps • communication links – fiber, copper, radio, satellite – transmission rate: bandwidth • packet switches: forward packets (chunks of data) – routers and switches Copyright © 2017, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved What’s the Internet: “Nuts and Bolts” View (2 of 2) Copyright © 2017, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved “Fun” Internet-Connected Devices Web-enabled toaster + weather forecaster IP picture frame http://www.ceiva.com/ Tweet-a-watt: Slingbox: watch, monitor energy use control cable TV remotely sensorized, bed mattress Internet refrigerator Internet phones Copyright © 2017, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. -

Lesson 1 - Computer Networks and Internet - Overview
Computer Networking and Management Computer Networking and Management Lesson 1 - Computer Networks and Internet - Overview Introduction | What is the Internet? | What is a protocol? | The Network Edge | The Network Core | Access Networks | Physical Media | Delay and Loss in Packet-Switched Networks | Protocol Layers and Their Service Models | Internet History Lesson Outline Introduction Physical Media What Is the Internet:’ Nuts And Bolts View' Some Popular Physical Media What Is the Internet: A Service View Twisted Pair Copper Wire What Is A Protocol? Coaxial Cable A Human Analogy Broadband Coaxial Cable A Human Protocol and a Computer Network Fibre Optics Protocol Terrestrial and Satellite Radio Channels Network Protocols Delay and Loss in Packet-Switched Networks The Network Edge Types of Delay End Systems, Clients and Servers Comparing Transmission and Propagation Delay End-System Interaction Queuing Delay (Revisited) Connectionless and Connection -Oriented Services Real Internet Delays and Routes Connection-Oriented Service Protocol Layers and Their Service Models Connectionless Service Layer Functions The Network Core The Internet Protocol Stack, And Protocol Data Units Circuit Switching Application Layer Packet Switching Transport Layer Packet Switching Versus Circuit Switching Network Layer Routing Link Layer Virtual Circuit Networks Physical Layer Datagram Networks Internet History Access Networks Development and Demonstration of Early Packet Residential Access Networks Switching Principles: 1961-1972 A Hybrid Fire -Coax Access Network Internetworking and New Proprietary Networks: Company Access Networks 1972-1980 Mobile Access Networks Metcalfe’s Original Conception of the Ethernet Home Networks A Proliferation of Networks: 1980 -1990 Commercialization and the Web: The 1990s GOTO TOP Introduction Page 1 of 44 Computer Networking and Management This lesson provides a broad overview of the Computer Networking and the Internet.