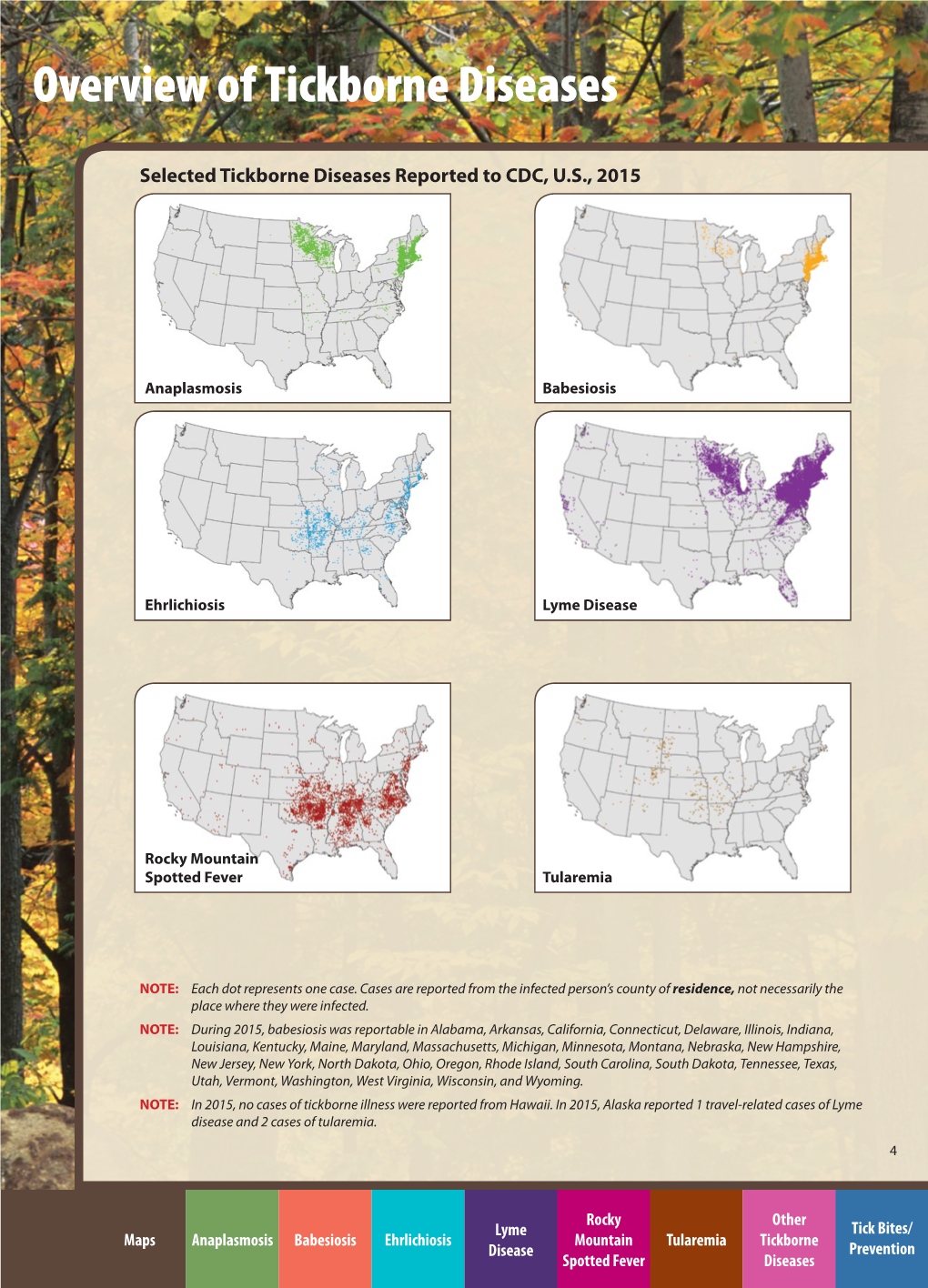
Overview of Tickborne Diseases
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Official Nh Dhhs Health Alert
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network [email protected] May 18, 2018, 1300 EDT (1:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20180518 Tickborne Diseases in New Hampshire Key Points and Recommendations: 1. Blacklegged ticks transmit at least five different infections in New Hampshire (NH): Lyme disease, Anaplasma, Babesia, Powassan virus, and Borrelia miyamotoi. 2. NH has one of the highest rates of Lyme disease in the nation, and 50-60% of blacklegged ticks sampled from across NH have been found to be infected with Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease. 3. NH has experienced a significant increase in human cases of anaplasmosis, with cases more than doubling from 2016 to 2017. The reason for the increase is unknown at this time. 4. The number of new cases of babesiosis also increased in 2017; because Babesia can be transmitted through blood transfusions in addition to tick bites, providers should ask patients with suspected babesiosis whether they have donated blood or received a blood transfusion. 5. Powassan is a newer tickborne disease which has been identified in three NH residents during past seasons in 2013, 2016 and 2017. While uncommon, Powassan can cause a debilitating neurological illness, so providers should maintain an index of suspicion for patients presenting with an unexplained meningoencephalitis. 6. Borrelia miyamotoi infection usually presents with a nonspecific febrile illness similar to other tickborne diseases like anaplasmosis, and has recently been identified in one NH resident. Tests for Lyme disease do not reliably detect Borrelia miyamotoi, so providers should consider specific testing for Borrelia miyamotoi (see Attachment 1) and other pathogens if testing for Lyme disease is negative but a tickborne disease is still suspected. -

2016 New Jersey Reportable Communicable Disease Report (January 3, 2016 to December 31, 2016) (Excl
10:34 Friday, June 30, 2017 1 2016 New Jersey Reportable Communicable Disease Report (January 3, 2016 to December 31, 2016) (excl. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, HIV/AIDS and Tuberculosis) (Refer to Technical Notes for Reporting Criteria) Case Jurisdiction Disease Counts STATE TOTAL AMOEBIASIS 98 STATE TOTAL ANTHRAX 0 STATE TOTAL ANTHRAX - CUTANEOUS 0 STATE TOTAL ANTHRAX - INHALATION 0 STATE TOTAL ANTHRAX - INTESTINAL 0 STATE TOTAL ANTHRAX - OROPHARYNGEAL 0 STATE TOTAL BABESIOSIS 174 STATE TOTAL BOTULISM - FOODBORNE 0 STATE TOTAL BOTULISM - INFANT 10 STATE TOTAL BOTULISM - OTHER, UNSPECIFIED 0 STATE TOTAL BOTULISM - WOUND 1 STATE TOTAL BRUCELLOSIS 1 STATE TOTAL CALIFORNIA ENCEPHALITIS(CE) 0 STATE TOTAL CAMPYLOBACTERIOSIS 1907 STATE TOTAL CHIKUNGUNYA 11 STATE TOTAL CHOLERA - O1 0 STATE TOTAL CHOLERA - O139 0 STATE TOTAL CREUTZFELDT-JAKOB DISEASE 4 STATE TOTAL CREUTZFELDT-JAKOB DISEASE - FAMILIAL 0 STATE TOTAL CREUTZFELDT-JAKOB DISEASE - IATROGENIC 0 STATE TOTAL CREUTZFELDT-JAKOB DISEASE - NEW VARIANT 0 STATE TOTAL CREUTZFELDT-JAKOB DISEASE - SPORADIC 2 STATE TOTAL CREUTZFELDT-JAKOB DISEASE - UNKNOWN 1 STATE TOTAL CRYPTOSPORIDIOSIS 198 STATE TOTAL CYCLOSPORIASIS 29 STATE TOTAL DENGUE FEVER - DENGUE 43 STATE TOTAL DENGUE FEVER - DENGUE-LIKE ILLNESS 3 STATE TOTAL DENGUE FEVER - SEVERE DENGUE 4 STATE TOTAL DIPHTHERIA 0 STATE TOTAL EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS(EEE) 1 STATE TOTAL EBOLA 0 STATE TOTAL EHRLICHIOSIS/ANAPLASMOSIS - ANAPLASMA PHAGOCYTOPHILUM (PREVIOUSLY HGE) 109 STATE TOTAL EHRLICHIOSIS/ANAPLASMOSIS - EHRLICHIA CHAFFEENSIS (PREVIOUSLY -

And Toxoplasmosis in Jackass Penguins in South Africa
IMMUNOLOGICAL SURVEY OF BABESIOSIS (BABESIA PEIRCEI) AND TOXOPLASMOSIS IN JACKASS PENGUINS IN SOUTH AFRICA GRACZYK T.K.', B1~OSSY J.].", SA DERS M.L. ', D UBEY J.P.···, PLOS A .. ••• & STOSKOPF M. K .. •••• Sununary : ReSlIlIle: E x-I1V\c n oN l~ lIrIUSATION D'Ar\'"TIGENE DE B ;IB£,'lA PH/Re El EN ELISA ET simoNi,cATIVlTli t'OUR 7 bxo l'l.ASMA GONIJfI DE SI'I-IENICUS was extracted from nucleated erythrocytes Babesia peircei of IJEMIiNSUS EN ArRIQUE D U SUD naturally infected Jackass penguin (Spheniscus demersus) from South Africo (SA). Babesia peircei glycoprotein·enriched fractions Babesia peircei a ele extra it d 'erythrocytes nue/fies p,ovenanl de Sphenicus demersus originoires d 'Afrique du Sud infectes were obto ined by conca navalin A-Sepharose affinity column natulellement. Des fractions de Babesia peircei enrichies en chromatogrophy and separated by sod ium dodecyl sulphate glycoproleines onl ele oblenues par chromatographie sur colonne polyacrylam ide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE ). At least d 'alfinite concona valine A-Sephorose et separees par 14 protein bonds (9, 11, 13, 20, 22, 23, 24, 43, 62, 90, electrophorese en gel de polyacrylamide-dodecylsuJfale de sodium 120, 204, and 205 kDa) were observed, with the major protein (SOS'PAGE) Q uotorze bandes proleiques au minimum ont ete at 25 kDa. Blood samples of 191 adult S. demersus were tes ted observees (9, 1 I, 13, 20, 22, 23, 24, 43, 62, 90, 120, 204, by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assoy (ELISA) utilizing B. peircei et 205 Wa), 10 proleine ma;eure elant de 25 Wo. -

Transmission and Evolution of Tick-Borne Viruses
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transmission and evolution of tick-borne viruses Doug E Brackney and Philip M Armstrong Ticks transmit a diverse array of viruses such as tick-borne Bourbon viruses in the U.S. [6,7]. These trends are driven encephalitis virus, Powassan virus, and Crimean-Congo by the proliferation of ticks in many regions of the world hemorrhagic fever virus that are reemerging in many parts of and by human encroachment into tick-infested habitats. the world. Most tick-borne viruses (TBVs) are RNA viruses that In addition, most TBVs are RNA viruses that mutate replicate using error-prone polymerases and produce faster than DNA-based organisms and replicate to high genetically diverse viral populations that facilitate their rapid population sizes within individual hosts to form a hetero- evolution and adaptation to novel environments. This article geneous population of closely related viral variants reviews the mechanisms of virus transmission by tick vectors, termed a mutant swarm or quasispecies [8]. This popula- the molecular evolution of TBVs circulating in nature, and the tion structure allows RNA viruses to rapidly evolve and processes shaping viral diversity within hosts to better adapt into new ecological niches, and to develop new understand how these viruses may become public health biological properties that can lead to changes in disease threats. In addition, remaining questions and future directions patterns and virulence [9]. The purpose of this paper is to for research are discussed. review the mechanisms of virus transmission among Address vector ticks and vertebrate hosts and to examine the Department of Environmental Sciences, Center for Vector Biology & diversity and molecular evolution of TBVs circulating Zoonotic Diseases, The Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station, in nature. -

Bitten Enhance.Pdf
bitten. Copyright © 2019 by Kris Newby. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. No part of this book may be used or reproduced in any manner whatsoever without written permission except in the case of brief quotations embodied in critical articles and reviews. For information, address HarperCollins Publishers, 195 Broadway, New York, NY 10007. HarperCollins books may be purchased for educational, business, or sales pro- motional use. For information, please email the Special Markets Department at [email protected]. first edition Frontispiece: Tick research at Rocky Mountain Laboratories, in Hamilton, Mon- tana (Courtesy of Gary Hettrick, Rocky Mountain Laboratories, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases [NIAID], National Institutes of Health [NIH]) Maps by Nick Springer, Springer Cartographics Designed by William Ruoto Library of Congress Cataloging- in- Publication Data Names: Newby, Kris, author. Title: Bitten: the secret history of lyme disease and biological weapons / Kris Newby. Description: New York, NY: Harper Wave, [2019] Identifiers: LCCN 2019006357 | ISBN 9780062896278 (hardback) Subjects: LCSH: Lyme disease— History. | Lyme disease— Diagnosis. | Lyme Disease— Treatment. | BISAC: HEALTH & FITNESS / Diseases / Nervous System (incl. Brain). | MEDICAL / Diseases. | MEDICAL / Infectious Diseases. Classification: LCC RC155.5.N49 2019 | DDC 616.9/246—dc23 LC record available at https://lccn.loc.gov/2019006357 19 20 21 22 23 lsc 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Appendix I: Ticks and Human Disease Agents -

Zoonotic Significance and Prophylactic Measure Against Babesiosis
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2015) 4(7): 938-953 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 7 (2015) pp. 938-953 http://www.ijcmas.com Review Article Zoonotic significance and Prophylactic Measure against babesiosis Faryal Saad, Kalimullah Khan, Shandana Ali and Noor ul Akbar* Department of Zoology, Kohat University of Science and Technology, Kohat, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan *Corresponding author ABSTRACT Babesiosis is a vector borne disease by the different species of genus Babesia, affecting a large no of mammals worldwide. Babesiosis has zoonotic significance all over the world, causing huge loss to livestock industry and health hazards in human population. The primary zoonotic vector of babesia is ixodes ticks. Keywo rd s Different species have different virulence, infectivity and pathogenicity. Literature was collected from the individual researchers published papers. Table was made in Babesiosis , the MS excel. The present study review for the current knowledge about the Prophylactic, babesia species ecology, host specificity, life cycle and pathogenesis with an Tick borne, emphasis on the zoonotic significance and prophylactic measures against Vector, Babesiosis. Prophylactic measure against Babesiosis in early times was hindered Zoonosis. but due to advancement in research, the anti babesial drugs and vaccines have been developed. This review emphasizes on the awareness of public sector, rural communities, owners of animal husbandry and health department about the risk of infection in KPK and control measure should be implemented. Vaccines of less price tag should be designed to prevent the infection of cattles and human population. Introduction Babesiosis is a tick transmitted disease, At specie level there is considerable infecting a wide variety of wild and confusion about the true number of zoonotic domestic animals, as well as humans. -

Anaplasmosis: an Emerging Tick-Borne Disease of Importance in Canada
IDCases 14 (2018) xxx–xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect IDCases journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/idcr Case report Anaplasmosis: An emerging tick-borne disease of importance in Canada a, b,c d,e e,f Kelsey Uminski *, Kamran Kadkhoda , Brett L. Houston , Alison Lopez , g,h i c c Lauren J. MacKenzie , Robbin Lindsay , Andrew Walkty , John Embil , d,e Ryan Zarychanski a Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada b Cadham Provincial Laboratory, Government of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada c Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada d Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Medical Oncology and Hematology, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada e CancerCare Manitoba, Department of Medical Oncology and Hematology, Winnipeg, MB, Canada f Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics and Child Health, Section of Infectious Diseases, Winnipeg, MB, Canada g Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada h Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Community Health Sciences, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada i Public Health Agency of Canada, National Microbiology Laboratory, Zoonotic Diseases and Special Pathogens, Winnipeg, MB, Canada A R T I C L E I N F O A B S T R A C T Article history: Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis (HGA) is an infection caused by the intracellular bacterium Received 11 September 2018 Anaplasma phagocytophilum. -

Joint Statement on Insect Repellents by EPA And
Joint Statement on Insect Repellents from the Environmental Protection Agency and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention July 17, 2014 The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are recommending that the public use insect repellents and take other precautions to avoid biting insects that carry serious diseases. The incidence of these diseases is on the rise. This joint statement discusses diseases that are transmitted by ticks and mosquitoes, the role of government in vector control and disease prevention, the history of repellents, how to use repellents as part of an integrated control program, and how to select and use a repellent. Introduction and Purpose CDC and EPA developed this joint statement to promote awareness of repellents and to highlight the effectiveness of repellents in preventing mosquito and tick bites. The agencies believe that promoting the use of repellents may reduce the impact of diseases and nuisance effects caused by these pests. Vector-borne diseases, such as those transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks, are among the world's leading causes of illness and death today. A wide variety of arthropods, including mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, black flies, sand flies, horse flies, stable flies, kissing bugs, lice and mites, feed on human blood. Among these, mosquitoes and ticks transmit some of the most serious vector- borne diseases both globally and within the United States. Diseases Transmitted by Mosquitoes and Ticks Mosquito-transmitted West Nile virus caused over 36,000 disease cases and 1,500 deaths in the United States between 1999 and 2012 (CDC, 2012). Mosquitoes also transmit other viruses that cause severe disease in the United States, including La Crosse encephalitis, eastern equine encephalitis and dengue. -

Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis Are Tick-Borne Diseases Caused by Obligate Anaplasmosis: Intracellular Bacteria in the Genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma
Ehrlichiosis and Importance Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are tick-borne diseases caused by obligate Anaplasmosis: intracellular bacteria in the genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma. These organisms are widespread in nature; the reservoir hosts include numerous wild animals, as well as Zoonotic Species some domesticated species. For many years, Ehrlichia and Anaplasma species have been known to cause illness in pets and livestock. The consequences of exposure vary Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis, from asymptomatic infections to severe, potentially fatal illness. Some organisms Canine Hemorrhagic Fever, have also been recognized as human pathogens since the 1980s and 1990s. Tropical Canine Pancytopenia, Etiology Tracker Dog Disease, Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are caused by members of the genera Ehrlichia Canine Tick Typhus, and Anaplasma, respectively. Both genera contain small, pleomorphic, Gram negative, Nairobi Bleeding Disorder, obligate intracellular organisms, and belong to the family Anaplasmataceae, order Canine Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, Rickettsiales. They are classified as α-proteobacteria. A number of Ehrlichia and Canine Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, Anaplasma species affect animals. A limited number of these organisms have also Equine Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, been identified in people. Equine Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, Recent changes in taxonomy can make the nomenclature of the Anaplasmataceae Tick-borne Fever, and their diseases somewhat confusing. At one time, ehrlichiosis was a group of Pasture Fever, diseases caused by organisms that mostly replicated in membrane-bound cytoplasmic Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis, vacuoles of leukocytes, and belonged to the genus Ehrlichia, tribe Ehrlichieae and Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, family Rickettsiaceae. The names of the diseases were often based on the host Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, species, together with type of leukocyte most often infected. -

Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis Definition: Anaplasmosis is an infection caused by the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilum. It is most commonly transmitted by the bite of an infected deer tick (Ixodes scapularis). Signs and symptoms: Symptoms of anaplasmosis can range from mild to very severe and may include: fever, headache, muscle pain, malaise, chills, nausea, abdominal pain, cough, and confusion. Severe symptoms may include: difficulty breathing, hemorrhage, renal failure, or neurological problems. It can be fatal if not treated correctly. People who are immunocompromised or elderly are at higher risk for severe disease. Transmission: Anaplasmosis is primarily transmitted to a person through the bite of an infected deer tick; this tick is endemic throughout Maine. Rarely, it can also be transmitted by receiving blood transfusions from an infected donor. Diagnosis: Anaplasmosis is diagnosed by clinical symptoms and laboratory tests. A blood test is necessary for confirmation. Co-infections with other tick-borne diseases may occur and should be considered. Role of the School Nurse: Prevention • Provide education on prevention efforts including: wearing protective clothing, using an EPA- approved repellent, using caution in tick infested areas, and performing daily tick checks. • Encourage the use of EPA approved repellents when outside (following local policy guidelines), and always performing a tick check when returning indoors. o School nurses can apply repellent with parental permission • If a tick is found, the school nurse should remove the tick using tweezers or a tick spoon. o Tick identification cards are available at: http://www.maine.gov/dhhs/mecdc/infectious- disease/epi/vector-borne/posters/index.shtml. o Testing of the tick is not recommended. -

Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis (HGA)
MASSACHUSETTS DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH FACT SHEET Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis (HGA) April 2014 | Page 1 of 3 What is human granulocytic anaplasmosis (HGA)? HGA is caused by bacteria (germs) that attack certain types of white blood cells called granulocytes. HGA is also known as human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. Where do cases of HGA occur? In the United States, HGA is most commonly found in the Northeast, mid-Atlantic and upper Midwest. In Massachusetts, the highest rates of disease occur on the islands of Nantucket and Martha’s Vineyard and in Barnstable and Berkshire counties, but it can occur anywhere in the state. How is HGA spread? HGA is one of the diseases that can be spread by the bite of an infected deer tick. The longer a tick remains attached and feeding, the higher the likelihood that it may spread the bacteria. Deer ticks in Massachusetts can also carry the germs that cause Lyme disease and babesiosis. Deer ticks are capable of spreading more than one type of germ in a single bite. When can I get HGA? HGA can occur during any time of year. The bacteria that cause HGA are spread by infected deer ticks. Young ticks (nymphs) are most active during the warm weather months between May and July. Adult ticks are most active during the fall and spring but will also be out searching for a host any time that winter temperatures are above freezing. How soon do symptoms of HGA appear after a tick bite? Symptoms of HGA usually begin to appear 7 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected tick. -

HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
TABLE OF CONTENTS AFRICAN TICK BITE FEVER .........................................................................................3 AMEBIASIS .....................................................................................................................4 ANTHRAX .......................................................................................................................5 ASEPTIC MENINGITIS ...................................................................................................6 BACTERIAL MENINGITIS, OTHER ................................................................................7 BOTULISM, FOODBORNE .............................................................................................8 BOTULISM, INFANT .......................................................................................................9 BOTULISM, WOUND .................................................................................................... 10 BOTULISM, OTHER ...................................................................................................... 11 BRUCELLOSIS ............................................................................................................. 12 CAMPYLOBACTERIOSIS ............................................................................................. 13 CHANCROID ................................................................................................................. 14 CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS INFECTION .................................................................