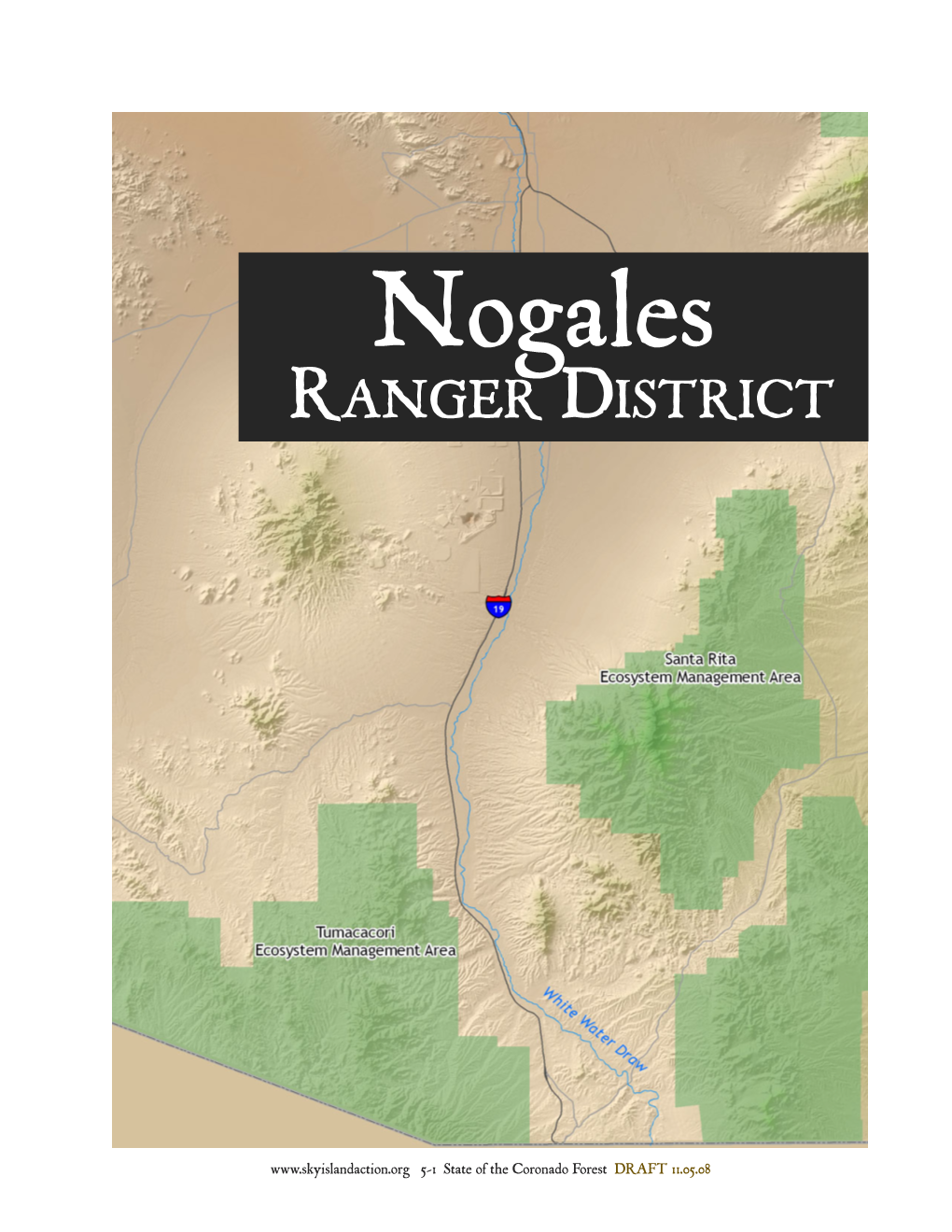
Chapter 5, Santa Rita Ecosystem Management Area
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Curriculum Vitae (Download PDF)
CATHY J. BUSBY- CV February, 2019 [email protected] Publications posted at: www.geol.ucsb.edu/faculty/busby PERSONAL Three daughters, born 1986 and 1989 PROFESSIONAL PREPARATION: University of California at Berkeley, Geological Sciences, B.S. 1977 Princeton University, Geological Sciences, Ph.D., 1983 APPOINTMENTS: Professor Emerita and Research Scientist, UC Davis, 2015-present Full Professor, UC Santa Barbara, 1993-2015 Jackson School of Geoscience, University of Texas at Austin, 2010-2011. U.S. Geological Survey, summer 1997, 1998. Associate Professor, UCSB, 1988-1993. Assistant Professor, UCSB, 1982-1988. Research Associate, Smithsonian Institution, 1980-1989. Research Assistant, Geochemistry, Caltech, 1981-1982. Research Assistant, Geology, Princeton University, 1978-1982. Lab Assistant, K-Ar Laboratory, UC Berkeley, 1976-1977. CURRENT PROFESSIONAL ACTIVITY: Convener, IODP Conference, Anatomy of a Long-Lived Oceanic Arc: Geology, Geophysics and Geochemistry of the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Arc System: with Harue Masuda, to be held in Japan in October 2019. International Ocean Discovery Program Distinguished Lecturer, 2016-2017. Editorial Board, International Geology Review, July 1, 2013-2018. Editorial Board, Geosphere, 2017-2020. Advisory board member, California Geological Survey, 2003-present. GSA Student Grants Review Panel, 2017-2021. Fellow of the Geological Society of America, 1990-present. INVITED TALKS AT UNIVERSITIES (past 8 years): Texas Bureau of Economic Geology, University of Texas Institute of Geophysics, Jackson School -

Draft Coronado Revised Plan
Coronado National United States Forest Department of Agriculture Forest Draft Land and Service Resource Management August 2011 Plan The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, and where applicable, sex, marital status, familial status, parental status, religion, sexual orientation, genetic information, political beliefs, reprisal, or because all or part of an individual’s income is derived from any public assistance program. (Not all prohibited bases apply to all programs.) Persons with disabilities who require alternative means of communication of program information (Braille, large print, audiotape, etc.) should contact USDA’s TARGET Center at (202) 720-2600 (voice and TTY). To file a complaint of discrimination, write to USDA, Director, Office of Civil Rights, 1400 Independence Avenue, SW, Washington, DC 20250-9410, or call (800) 795-3272 (voice) or (202) 720-6382 (TTY). USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. Printed on recycled paper – Month and Year Draft Land and Resource Management Plan Coronado National Forest Cochise, Graham, Pima, Pinal, and Santa Cruz Counties, Arizona Hidalgo County, New Mexico Responsible Official: Regional Forester Southwestern Region 333 Broadway Boulevard SE Albuquerque, NM 87102 (505) 842-3292 For more information contact: Forest Planner Coronado National Forest 300 West Congress, FB 42 Tucson, AZ 85701 (520) 388-8300 TTY 711 [email protected] ii Draft Land and Management Resource Plan Coronado National Forest Table of Contents Chapter 1: Introduction ...................................................................................... 1 Purpose of Land and Resource Management Plan ......................................... 1 Overview of the Coronado National Forest ..................................................... -

Coronado National Forest Draft Land and Resource Management Plan I Contents
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Coronado National Forest Southwestern Region Draft Land and Resource MB-R3-05-7 October 2013 Management Plan Cochise, Graham, Pima, Pinal, and Santa Cruz Counties, Arizona, and Hidalgo County, New Mexico The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, and where applicable, sex, marital status, familial status, parental status, religion, sexual orientation, genetic information, political beliefs, reprisal, or because all or part of an individual’s income is derived from any public assistance program. (Not all prohibited bases apply to all programs.) Persons with disabilities who require alternative means for communication of program information (Braille, large print, audiotape, etc.) should contact USDA’s TARGET Center at (202) 720-2600 (voice and TTY). To file a complaint of discrimination, write to USDA, Director, Office of Civil Rights, 1400 Independence Avenue SW, Washington, DC 20250-9410, or call (800) 795-3272 (voice) or (202) 720-6382 (TTY). USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. Front cover photos (clockwise from upper left): Meadow Valley in the Huachuca Ecosystem Management Area; saguaros in the Galiuro Mountains; deer herd; aspen on Mt. Lemmon; Riggs Lake; Dragoon Mountains; Santa Rita Mountains “sky island”; San Rafael grasslands; historic building in Cave Creek Canyon; golden columbine flowers; and camping at Rose Canyon Campground. Printed on recycled paper • October 2013 Draft Land and Resource Management Plan Coronado National Forest Cochise, Graham, Pima, Pinal, and Santa Cruz Counties, Arizona Hidalgo County, New Mexico Responsible Official: Regional Forester Southwestern Region 333 Broadway Boulevard, SE Albuquerque, NM 87102 (505) 842-3292 For Information Contact: Forest Planner Coronado National Forest 300 West Congress, FB 42 Tucson, AZ 85701 (520) 388-8300 TTY 711 [email protected] Contents Chapter 1. -

WHETSTONE MOUNTAINS ECOSYSTEM MANAGEMENT AREA Transportation Analysis Plan
CORONADO NATIONAL FOREST WHETSTONE MOUNTAINS ECOSYSTEM MANAGEMENT AREA Transportation Analysis Plan March 2011 Edited By ELI CURIEL JR. ID Core Team Leader Approved By /C/ Annette H. Chavez March 4, 2011 Annette H. Chavez, Sierra Vista District Ranger Date Table of Contents INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................................ 1 STEP 1 – SETTING UP THE ANALYSIS ......................................................................................................... 3 STEP 2- DESCRIBING THE SITUATION ....................................................................................................... 5 TABLE 2.1 – EXISTING TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM ......................................................................................... 7 TABLE 2.2 - EXISTING ROAD CLASSIFICATIONS ............................................................................................ 13 STEP 3- IDENTIFYING ISSUES ..................................................................................................................... 13 STEP 4- ASSESSING BENEFITS, PROBLEMS AND RISKS OF THE EXISTING ROAD SYSTEM ... 21 LANDS .............................................................................................................................................................. 22 SOIL, WATER, AIR, AND FORESTRY ............................................................................................................... 31 Figure 4.1 Whetstone Watershed -

Summits on the Air – ARM for the USA (W7A
Summits on the Air – ARM for the U.S.A (W7A - Arizona) Summits on the Air U.S.A. (W7A - Arizona) Association Reference Manual Document Reference S53.1 Issue number 5.0 Date of issue 31-October 2020 Participation start date 01-Aug 2010 Authorized Date: 31-October 2020 Association Manager Pete Scola, WA7JTM Summits-on-the-Air an original concept by G3WGV and developed with G3CWI Notice “Summits on the Air” SOTA and the SOTA logo are trademarks of the Programme. This document is copyright of the Programme. All other trademarks and copyrights referenced herein are acknowledged. Document S53.1 Page 1 of 15 Summits on the Air – ARM for the U.S.A (W7A - Arizona) TABLE OF CONTENTS CHANGE CONTROL....................................................................................................................................... 3 DISCLAIMER................................................................................................................................................. 4 1 ASSOCIATION REFERENCE DATA ........................................................................................................... 5 1.1 Program Derivation ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 6 1.2 General Information ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 6 1.3 Final Ascent -

Major Geologic Structures Between Lordsburg, New Mexico, and Tucson, Arizona Harald D
New Mexico Geological Society Downloaded from: http://nmgs.nmt.edu/publications/guidebooks/29 Major geologic structures between Lordsburg, New Mexico, and Tucson, Arizona Harald D. Drewes and C. H. Thorman, 1978, pp. 291-295 in: Land of Cochise (Southeastern Arizona), Callender, J. F.; Wilt, J.; Clemons, R. E.; James, H. L.; [eds.], New Mexico Geological Society 29th Annual Fall Field Conference Guidebook, 348 p. This is one of many related papers that were included in the 1978 NMGS Fall Field Conference Guidebook. Annual NMGS Fall Field Conference Guidebooks Every fall since 1950, the New Mexico Geological Society (NMGS) has held an annual Fall Field Conference that explores some region of New Mexico (or surrounding states). Always well attended, these conferences provide a guidebook to participants. Besides detailed road logs, the guidebooks contain many well written, edited, and peer-reviewed geoscience papers. These books have set the national standard for geologic guidebooks and are an essential geologic reference for anyone working in or around New Mexico. Free Downloads NMGS has decided to make peer-reviewed papers from our Fall Field Conference guidebooks available for free download. Non-members will have access to guidebook papers two years after publication. Members have access to all papers. This is in keeping with our mission of promoting interest, research, and cooperation regarding geology in New Mexico. However, guidebook sales represent a significant proportion of our operating budget. Therefore, only research papers are available for download. Road logs, mini-papers, maps, stratigraphic charts, and other selected content are available only in the printed guidebooks. Copyright Information Publications of the New Mexico Geological Society, printed and electronic, are protected by the copyright laws of the United States. -

Stories of the Sky Islands: Exhibit Development Resource Guide for Biology and Geology at Chiricahua National Monument and Coronado National Memorial
Stories of the Sky Islands: Exhibit Development Resource Guide for Biology and Geology at Chiricahua National Monument and Coronado National Memorial Prepared for the National Park Service under terms of Cooperative Ecosystems Studies Unit Agreement H1200-05-0003 Task Agreement J8680090020 Prepared by Adam M. Hudson,1 J. Jesse Minor,2,3 Erin E. Posthumus4 In cooperation with the Arizona State Museum The University of Arizona Tucson, AZ Beth Grindell, Principal Investigator May 17, 2013 1: Department of Geosciences, University of Arizona ([email protected]) 2: School of Geography and Development, University of Arizona ([email protected]) 3: Laboratory of Tree-Ring Research, University of Arizona 4: School of Natural Resources and the Environment, University of Arizona ([email protected]) Table of Contents Introduction ........................................................................................................................3 Beth Grindell, Ph.D. Ch. 1: Current research and information for exhibit development on the geology of Chiricahua National Monument and Coronado National Memorial, Southeast Arizona, USA..................................................................................................................................... 5 Adam M. Hudson, M.S. Section 1: Geologic Time and the Geologic Time Scale ..................................................5 Section 2: Plate Tectonic Evolution and Geologic History of Southeast Arizona .........11 Section 3: Park-specific Geologic History – Chiricahua -

Environmental Change at Kartchner Caverns: Trying to Separate Natural and Anthropogenic Changes
Environmental Change at Kartchner Caverns: Trying to Separate Natural and Anthropogenic Changes Rickard S. Toomey, III, and Ginger Nolan Kartchner Caverns State Park, Arizona State Parks, Benson, AZ Abstract—Cave temperature and moisture levels are important factors in the environmental health of Kartchner Caverns. Monitoring indicates the cave has warmed and moisture levels have fallen over the past 14 years. Timing and patterns of change within the cave suggest that changes are due to development as a show cave. However, changes in other caves, surface temperature and precipitation, and in shallow local aquifers suggest that cave changes relate to regional patterns. Changes at Kartchner Caverns represent a combination of anthropogenic and regional natural causes. Separating these different factors is an important on-going goal in protecting the cave. Kartchner Caverns State Park (KCSP) is a show cave in The primary long-term temperature and humidity data southeastern Arizona. The cave was discovered in 1974 and from the cave come from Environmental Monitoring Stations became a State Park in 1988 (Tufts and Tenen 1999). After (EMS) within the cave (figure 1). These are locations at pre-development studies to assess the condition of the cave, which air, water, and soil temperature, relative humidity, to establish baseline data, and to determine how best to de- and pan evaporation are measured manually on a periodic velop the cave, Arizona State Parks began development of basis, usually weekly or monthly. Temperatures are measured the cave for ecological education and tourism. The develop- with small, digital probe thermometers; relative humidity is ment included creating tunnel entrances to the cave, building measured using a digital probe thermometer equipped as a trails for tours, and installing a lighting system. -

Environmental Assessment
DRAFT ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT RE-ESTABLISHMENT OF THE TARAHUMARA FROG, SYCAMORE AND BIG CASA BLANCA CANYONS, SANTA CRUZ COUNTY, ARIZONA Prepared By: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service 2321 West Royal Palm Road, Suite 103 Phoenix, Arizona 85021 Date Prepared: September 1, 2003 Section I: PURPOSE AND NEED FOR ACTION A. Purpose of the Proposed Action: The purpose of the proposed action is to conserve the Tarahumara frog (Rana tarahumarae). Conservation would reduce threats to the species and minimize the likelihood that it would need protection under the Endangered Species Act of 1973 (16 U.S.C. 1531-1544), as amended (ESA). Our ability to effectively conserve and manage this species is limited because it has been extirpated from Arizona and the United States since 1983. This action would be undertaken cooperatively by the Arizona Ecological Services Office of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (AESO) and the Arizona Game and Fish Department (AGFD), in coordination with the Tarahumara Frog Conservation Team (TFCT). The TFCT, which was first convened in 1991, consists of representatives from AGFD, AESO, Coronado National Forest, Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum, U.S. Geological Survey - Biological Resources Division, Instituto del Medio Ambiente y el Desarrollo Sustentable del Estado de Sonora (IMADES), University of Arizona, and other interested parties. Both the AGFD and AESO have an interest in re-establishing species extirpated from Arizona. B. Need for Taking the Proposed Action: Conservation through re-establishment of the Tarahumara frog in Arizona is consistent with the Arizona Game and Fish Department’s Wildlife 2006 Nongame and Endangered Wildlife subprogram narrative, a goal of which is restoration of native biological diversity and recovery of imperiled species. -

Coronado National Forest
CORONADO NATIONAL FOREST FIRE MANAGEMENT PLAN Reviewed and Updated by _/s/ Chris Stetson ___________ Date __5/18/10 __________ Coronado Fire Management Plan Interagency Federal fire policy requires that every area with burnable vegetation must have a Fire Management Plan (FMP). This FMP provides information concerning the fire process for the Coronado National Forest and compiles guidance from existing sources such as but not limited to, the Coronado National Forest Land and Resource Management Plan (LRMP), national policy, and national and regional directives. The potential consequences to firefighter and public safety and welfare, natural and cultural resources, and values to be protected help determine the management response to wildfire. Firefighter and public safety are the first consideration and are always the priority during every response to wildfire. The following chapters discuss broad forest and specific Fire Management Unit (FMU) characteristics and guidance. Chapter 1 introduces the area covered by the FMP, includes a map of the Coronado National Forest, addresses the agencies involved, and states why the forest is developing the FMP. Chapter 2 establishes the link between higher-level planning documents, legislation, and policies and the actions described in FMP. Chapter 3 articulates specific goals, objectives, standards, guidelines, and/or desired future condition(s), as established in the forest’s LRMP, which apply to all the forest’s FMUs and those that are unique to the forest’s individual FMUs. Page 1 of 30 Coronado Fire Management Plan Chapter 1. INTRODUCTION The Coronado National Forest developed this FMP as a decision support tool to help fire personnel and decision makers determine the response to an unplanned ignition. -

THE ARCHAIC OCCUPATION of the ROSEMONT AREA, NORTHERN SANTA RITA MOUNTAINS, SOUTHEASTERN ARIZONA by Bruce B. Huckell K with Cont
THE ARCHAIC OCCUPATION OF THE ROSEMONT AREA, NORTHERN SANTA RITA MOUNTAINS, SOUTHEASTERN ARIZONA by Bruce B. Huckell K with contributions by Lisa W. Huckell Robert S. Thompson Cultural Resource Management Division Arizona State Museum University of Arizona Archaeological Series No. 147, Vol. I THE ARCHAIC OCCUPATION OF THE ROSEMONT AREA, NORTHERN SANTA RITA MOUNTAINS, SOUTHEASTERN ARIZONA by Bruce B. Huckell Contributions by Lisa W. Huckell Robert S. Thompson Submitted by Cultural Resource Management Division Arizona State Museum University of Arizona Prepared for ANAMAX Mining Company 1984 Archaeological Series No. 147, Vol. I CONTENTS FIGURES vii TABLES PREFACE xiii ACKNOWLEDGMENTS xvi ABSTRACT xviii Chapter 1. INTRODUCTION 1 The Archaic Period 2 Previous Research 5 2. THE ENVIRONMENT OF THE ROSEMONT AREA AND SURROUNDING REGIONS 11 General Geography 11 Geology 13 Climate 17 Vegetation 19 Fauna 28 The Paleoenvironment 29 Recent Changes in the Local Biotic Communities 30 Long-Term Changes in the Environment 32 3. A FRAMEWORK FOR RESEARCH AT THE ROSEMONT ARCHAIC SITES 35 Hunter-Gatherer Organization 35 Research Domains 38 Problem Domain I: Subsistence-Settlement Systems 38 Problem Domain II: Cultural and Temporal Affinities 40 Site Selection 41 4. INVESTIGATIONS AT AND DESCRIPTIONS OF THE SITES 43 Field Methods 43 Results of Excavations: Site Descriptions 46 AZ EE:2:62--The Wasp Canyon Site 48 Investigation 50 Features 52 Structures 52 Rock Clusters 56 Artifacts 58 iii iv Contents AZ EE:2:65 59 Investigation 59 -

You Can Learn More About the Chiricahuas
Douglas RANGER DISTRICT www.skyislandaction.org 2-1 State of the Coronado Forest DRAFT 11.05.08 DRAFT 11.05.08 State of the Coronado Forest 2-2 www.skyislandaction.org CHAPTER 2 Chiricahua Ecosystem Management Area The Chiricahua Mountain Range, located in the Natural History southeastern corner of the Coronado National Forest, The Chiricahua Mountains are known for their is one of the largest Sky Islands in the U.S. portion of amazing variety of terrestrial plants, animals, and the Sky Island region. The range is approximately 40 invertebrates. They contain exceptional examples of miles long by 20 miles wide with elevations ranging ecosystems that are rare in southern Arizona. While from 4,400 to 9,759 feet at the summit of Chiricahua the range covers only 0.5% of the total land area in Peak. The Chiricahua Ecosystem Management Area Arizona, it contains 30% of plant species found in (EMA) is the largest Management Area on the Forest Arizona, and almost 50% of all bird species that encompassing 291,492 acres of the Chiricahua and regularly occur in the United States.1 The Chiricahuas Pedragosa Mountains. form part of a chain of mountains spanning from Protected by remoteness, the Chiricahuas remain central Mexico into southern Arizona. Because of one of the less visited ranges on the Coronado their proximity to the Sierra Madre, they support a National Forest. Formerly surrounded only by great diversity of wildlife found nowhere else in the ranches, the effects of Arizona’s explosive 21st century United States such as the Mexican Chickadee, whose population growth are beginning to reach the flanks only known breeding locations in the country are in of the Chiricahuas.