Llllllllllllllillllllllllllllllllllllillllllllllllllllllllll
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Introduction to Virtualization
z Systems Introduction to Virtualization SHARE Orlando Linux and VM Program Romney White, IBM [email protected] z Systems Architecture and Technology © 2015 IBM Corporation Agenda ° Introduction to Virtualization – Concept – Server Virtualization Approaches – Hypervisor Implementation Methods – Why Virtualization Matters ° Virtualization on z Systems – Logical Partitions – Virtual Machines 2 z Systems Virtualization Technology © 2015 IBM Corporation Virtualization Concept Virtual Resources Proxies for real resources: same interfaces/functions, different attributes May be part of a physical resource or multiple physical resources Virtualization Creates virtual resources and "maps" them to real resources Primarily accomplished with software or firmware Resources Components with architecturally-defined interfaces/functions May be centralized or distributed - usually physical Examples: memory, disk drives, networks, servers Separates presentation of resources to users from actual resources Aggregates pools of resources for allocation to users as virtual resources 3 z Systems Virtualization Technology © 2015 IBM Corporation Server Virtualization Approaches Hardware Partitioning Bare-metal Hypervisor Hosted Hypervisor Apps ... Apps Apps ... Apps Apps ... Apps OS OS OS OS OS OS Adjustable partitions Hypervisor Hypervisor Partition Controller Host OS SMP Server SMP Server SMP Server Server is subdivided into fractions Hypervisor provides fine-grained Hypervisor uses OS services to each of which can run an OS timesharing of all resources -

Logical Partitioning
Power Systems Logical partitioning Power Systems Logical partitioning Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices” on page 233. This edition applies to IBM AIX Version 6.1, to IBM AIX 5L™ Version 5.3, to IBM i 6.1 (product number 5722-SS1) , to IBM Virtual I/O Server version 2.1.2.0, and to all subsequent releases and modifications until otherwise indicated in new editions. This version does not run on all reduced instruction set computer (RISC) models nor does it run on CISC models. © Copyright IBM Corporation 2007, 2009. US Government Users Restricted Rights – Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Contents Logical partitioning ...............................1 What's new in Logical partitioning ............................1 Logical partition overview ...............................2 Benefits of logical partitioning ............................2 Sharing resources between logical partitions ........................3 Managed systems.................................5 Manufacturing default configuration ..........................5 Logical partitioning tools ..............................6 Hardware Management Console ...........................6 Partition profile ...............................7 System profile ...............................11 Partitioning with the Integrated Virtualization Manager ..................11 Virtual Partition Manager.............................13 Physical and virtual hardware resources .........................14 -

IIP (System Z9 Integrated Information Processor) Computer CEC (Central Electronics Complex) Server
IBM System z z/VM Basics Arwed Tschoeke Systems Architect [email protected] © 2009 IBM Corporation © 2008 IBM Corporation Introduction We'll explain basic concepts of System z: – Terminology – Processors – Memory – I/O – Networking We'll see that z/VM virtualizes a System z machine: – Virtual processors – Virtual memory – … and so on Where appropriate, we'll compare or contrast: – PR/SM or LPAR – z/OS – Linux 2 z/VM: The Very Basics z/VM: The Very Basics 1 IBM System z © 2008 IBM Corporation System z Parts Nomenclature x86, UNIX, etc. System z Memory Storage (though we are moving toward "memory") Disk, Storage DASD – Direct Access Storage Device Processor Processor, Engine, PU (processing unit) IOP (I/O processor) CPU (central processing unit) CP (central processor) SAP (system assist processor) Specialty engines –IFL (Integrated Facility for Linux) –zAAP (System z Application Assist Processor) –zIIP (System z9 Integrated Information Processor) Computer CEC (central electronics complex) Server 3 z/VM: The Very Basics © 2008 IBM Corporation IBM System z Virtualization Genetics Over 40 years of continuous innovation in virtualization – Refined to support modern business requirements System z10 . – Exploit hardware technology for economical growth , .. ity System z9 z/VM V5 bil – LPAR, Integrated Facility for Linux, HiperSockets xi 64-Bit Fle – System z Application Assist Processors s, zSeries es VM/ESA Virtual Switch – System z Information Integration stn 9672 bu ESA Guest LANs Set Observer Ro Processors y, 9x21 ilit VM/XA Virtual Machine -

Let's Build a Z Environment
Let’s Build a z Environment - 101 z/OS Session 23330 Tuesday, August 14 at 10:00-11:00 AM STL CC, Room 242 Presented by Paul R. Robichaux NewEra Software, Inc. [email protected] 1 Abstract – Let’s Build a z Environment! The two presentations in this series focus on the building of a z Environment – Hardware, Software, Security – with the goal of establishing a ‘Trusted Computing Base’. A z/OS System that can provide the reliability needed to meet demanding service levels, integrity and security objectives. All are necessary to execute mission critical applications. This is Intended for those new to z Systems or just beginning their careers with organizations that capitalize on systems anchored to the power and reliability of the IBM Mainframe. In – 101 – the focus will be on the platform, in this case a z14, hardware divisions of the Central Processing Complex (CEC), its various channel pathways and related devices that define a UCW (Unit Control Work), the front half of the z System Device Chain. This segment continues with the definition of an associated Operating System configuration, its various I/O devices and related features that define a UCB (Unit Control Block), the back half of the z System Device. Detailing both the Power-On and IPL process will join UCWs and UCBs to form a fully addressable device across which data (encrypted or not) may flow to and from the CEC. In – 102 – the focus will shift to a discussion of Multiple Virtual Storage (MVS), what is z/OS, how to get it, install it, support it and upgrade/migrate from release to release. -

Systems Management Logical Partitions Version 6 Release 1
IBM System i Systems management Logical partitions Version 6 Release 1 IBM System i Systems management Logical partitions Version 6 Release 1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices,” on page 135. This edition applies to version 6, release 1, modification 0 of and IBM i5/OS (product number 5761–SS1) to all subsequent releases and modifications until otherwise indicated in new editions. This version does not run on all reduced instruction set computer (RISC) models nor does it run on CISC models. © Copyright IBM Corporation 1999, 2008. US Government Users Restricted Rights – Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Contents Logical partitions........... 1 Ordering a new server or upgrading an PDF file for Logical partitions ........ 1 existing server with logical partitions .... 45 Partitioning with a System i ......... 1 Providing hardware placement information Logical partition concepts ......... 1 to service providers......... 45 How logical partitioning works ...... 2 Designing your logical partitions ..... 46 How logical partitioning can work for you .. 3 Deciding what runs in the primary and Hardware for logical partitions ...... 4 secondary partition ......... 46 Bus .............. 5 Capacity planning for logical partitions .. 47 Bus-level and IOP-level I/O partitions ... 7 Using the System Planning Tool .... 47 Dynamically switching IOPs between Examples: Logical partitioning ...... 47 partitions ............ 7 Creating logical partitions ........ 48 IOP .............. 9 Managing logical partitions ........ 49 SPD and PCI ........... 11 Managing logical partitions by using System i Processor ............ 11 Navigator, DST, and SST ........ 50 Memory ............ 14 Starting System i Navigator ...... 53 Disk units ............ 15 Starting SST and DST for logical partitions 53 Removable media device and alternate Logical partition authority ..... -

Logical Partitioning Feature of CB Series Xeon Servers Suitable for Robust and Reliable Cloud
Hitachi Review Vol. 61 (2012), No. 2 65 Logical Partitioning Feature of CB Series Xeon Servers Suitable for Robust and Reliable Cloud Hitoshi Ueno, Ph. D., PE.jp OVERVIEW: LPAR is Hitachi’s own server virtualization feature for Shinichi Matsumura Hitachi Compute Blade servers. LPAR stands for logical partitioning used by mission-critical systems such as mainframes and offers excellent performance, including reliability, stability, and maintaining virtual server separation. The implementation of logical partitioning on Xeon*1 servers significantly expands the scope for applying virtualization in private clouds because it means that virtualization of mission-critical systems can be used even on Xeon servers. Hitachi is currently developing new solutions that improve ease-of-operation and simplify installation, and the number of sites using LPAR for cloud is increasing. LPAR is already a proven virtualization feature and Hitachi intends to continue with development to make further improvements in performance and reliability. INTRODUCTION is that, compared to the VM (virtual machine) method, HITACHI aims to create new value through its next it is easier to configure systems with higher reliability generation of IT (information technology) platforms and performance. However, very few virtualization and virtualization is a key technology for implementing products support the use of logical partitioning on the infrastructure clouds that will support this Xeon processors and other Xeon servers (see Table 1). endeavor. Within this, Hitachi Compute Blade (CB) Virtualization based on logical partitioning has logical partitioning feature (LPAR) provides a server been widely used for mission-critical applications virtualization feature critical to data processing. in the past and, unlike virtualization software from This article describes the characteristics of the other vendors, Hitachi’s LPAR feature also extends LPAR, a server virtualization feature that enhances this capability to Xeon servers. -

PR/SM Planning Guide Level 01A
zEnterprise System Processor Resource/Systems Manager Planning Guide SB10-7155-01 Level 01a zEnterprise System Processor Resource/Systems Manager Planning Guide SB10-7155-01 Level 01a Level 01a Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Safety” on page xi, Appendix D, “Notices,” on page 217, and IBM Systems Environmental Notices and User Guide, Z125-5823. This edition, SB10-7155-01, applies to the IBM zEnterprise 196 and zEnterprise 114 servers. This edition replaces SB10-7155-00. There might be a newer version of this document in a PDF file available on Resource Link.Goto http://www.ibm.com/servers/resourcelink and click Library on the navigation bar. A newer version is indicated by a lowercase, alphabetic letter following the form number suffix (for example: 00a, 00b, 01a, 01b). © Copyright IBM Corporation 2010, 2011. US Government Users Restricted Rights – Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Level 01a Contents Figures ..............vii Chapter 2. Planning considerations . 31 Overview ...............33 Tables ...............ix Planning the I/O configuration ........33 Planning considerations .........33 Safety ...............xi Maximum number of logical partitions ....35 Managing logical paths for ESCON and FICON Safety notices ..............xi channels ..............36 World trade safety information .......xi Managing the establishment of logical paths . 40 Laser safety information ..........xi Shared channel overview .........49 Laser compliance ...........xi Unshared ESCON or FICON channel recommendations ...........55 About this publication ........xiii Dynamically managed CHPIDs.......55 What is included in this publication ......xiv IOCP coding specifications ........56 Related publications ...........xv Coupling facility planning considerations ....66 z/Architecture ............xv Test or migration coupling configuration . -

Introduction to the System Z Hardware Management Console
Front cover Introduction to the System z Hardware Management Console Large scale hardware systems management concepts Design and implementation of a management controller Practical operational techniques and scenarios Merwyn Jones HMC & SE Development Team ibm.com/redbooks International Technical Support Organization Introduction to the System z Hardware Management Console February 2010 SG24-7748-00 Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices” on page xi. First Edition (February 2010) © Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2010. All rights reserved. Note to U.S. Government Users Restricted Rights -- Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Contents Notices . xi Trademarks . xii Preface . xiii The team who wrote this book . xiii Acknowledgements . xvi Become a published author . xvi Comments welcome. xvi Chapter 1. Introduction to System z Hardware. 1 1.1 General introduction: Mainframes in our midst . 2 1.2 System z hardware architecture . 3 1.2.1 Consolidation of mainframes . 3 1.2.2 An overview of the early architectures . 4 1.2.3 Early system design . 5 1.2.4 Current architecture . 7 1.3 The raised floor . 7 1.4 Hardware management console . 9 1.5 Frames and cages . 9 1.6 Processor units . 10 1.6.1 Multiprocessors. 10 1.6.2 Processor types . 11 1.7 Memory hierarchy . 13 1.8 Networking the mainframe . 14 1.9 Disk devices . 14 1.9.1 Types of DASD . 16 1.9.2 Basic shared DASD . 17 1.10 I/O connectivity (channels) . 18 1.10.1 Channel subsystem . -

IBM POWER Virtualization Best Practice Guide
IBM Power Systems Performance IBM POWER Virtualization Best Practices Guide Version 4.0 March 2020 Copyright © 2020 by International Business Machines Corporation. IBM Power Virtualization Best Practices Guide CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................................... 7 2 VIRTUAL PROCESSORS .......................................................................................................... 7 2.1 Sizing/configuring virtual processors ......................................................................................................... 9 2.2 Entitlement vs. Virtual processors ........................................................................................................... 10 2.3 Matching entitlement of an LPAR close to its average utilization for better performance ....................... 10 2.4 When to add additional virtual processors .............................................................................................. 11 2.5 How to estimate the number of virtual processors per uncapped shared LPAR ...................................... 11 3 AIX VIRTUAL PROCESSOR MANAGEMENT - PROCESSOR FOLDING ....................................... 11 3.1 VPM folding example .............................................................................................................................. 12 3.2 Tuning Virtual Processor Management Folding ....................................................................................... 13 3.3 -

PR/SM Planning Guide Operational Considerations
IBM IBM Z Processor Resource/Systems Manager Planning Guide SB10-7169-02 Level 02a IBM IBM Z Processor Resource/Systems Manager Planning Guide SB10-7169-02 Note: Before you use this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Safety” on page xi, Appendix C, “Notices,” on page 199, and IBM Systems Environmental Notices and User Guide, Z125-5823. This edition, SB10-7169-02, applies to the IBM Z and IBM LinuxONE servers. This edition replaces SB10-7169-01. There might be a newer version of this document in a PDF file available on Resource Link. Go to http://www.ibm.com/servers/resourcelink and click Library on the navigation bar. © Copyright IBM Corporation 2017, 2019. US Government Users Restricted Rights – Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Contents Figures .............. vii Extended TOD-clock facility ........ 26 Clock Comparator on Shared Processors.... 27 Tables ............... ix Chapter 2. Planning considerations .. 29 Safety ............... xi Planning the I/O configuration ........ 29 Maximum number of logical partitions .... 31 Safety notices .............. xi Managing logical paths for FICON channels .. 31 World trade safety information ....... xi Managing the establishment of logical paths .. 33 Laser safety information .......... xi Shared channel overview ......... 42 Laser compliance ............ xi Unshared ESCON or FICON channel recommendations ........... 48 About this publication ........ xiii Dynamically managed CHPIDs....... 48 What is included in this publication ...... xiii IOCP coding specifications ........ 49 Related publications ........... xiv 25GbE RoCE Express2 planning considerations .. 58 z/Architecture ............ xiv 10Gb RoCE planning considerations ...... 58 Enterprise Systems Architecture/390 (ESA/390) xiv Coupling facility planning considerations .... 59 Hardware............. -

LPAR Weight Concepts
Planning for any System z processor, especially image upgrades, consideration must be given to handling the impacts Determine Per CP Share - Vertical CP Management of PR/SM where the following factors should be considered: * Logical processors are classified as vertical high , medium or low - The number of partitions * PR/SM quasi-dedicates vertical high logicals to physical processors - The CP usage; either general purpose, traditional CPs or the use of IFL/ICF CPs and z/OS specialty processors. vertical medium - The remainder of the share is distributed to the LPAR A: 7.2 CPs – 6 VH,2 VM (60%), 1 VL - The partition mode, either dedicated or shared processors - The ratio of logical CPs to physical CPs defined * Vertical low processors are only given service when other partitions do - The number of logical CPs defined to the partitions not use their entire share and there is demand in the partition LPAR B: 1.8 CPs – 1 VH, 1 VM (80%), 7 VL - The type of system control program (z/OS, z/VM, Linux, etc.), and the workload characteristics in each partition. - The effect of the partitions shared weight and any impact of capping on the partition. * Vertical low processors are parked by z/OS when no extra service is available. Book 0 Important Concepts System z Partitioning Controls * LPAR weights become important only when the processor is extremely busy ( approaching 100%) or are capped * Example CEC 2827-704: Access to resources is relative to other partitions. * There are two dispatchers involved in making resource allocations: - PR/SM Every partition must have a relative weight, the relative weight is also known as the initial - Operating System processing weight (hard cap). -

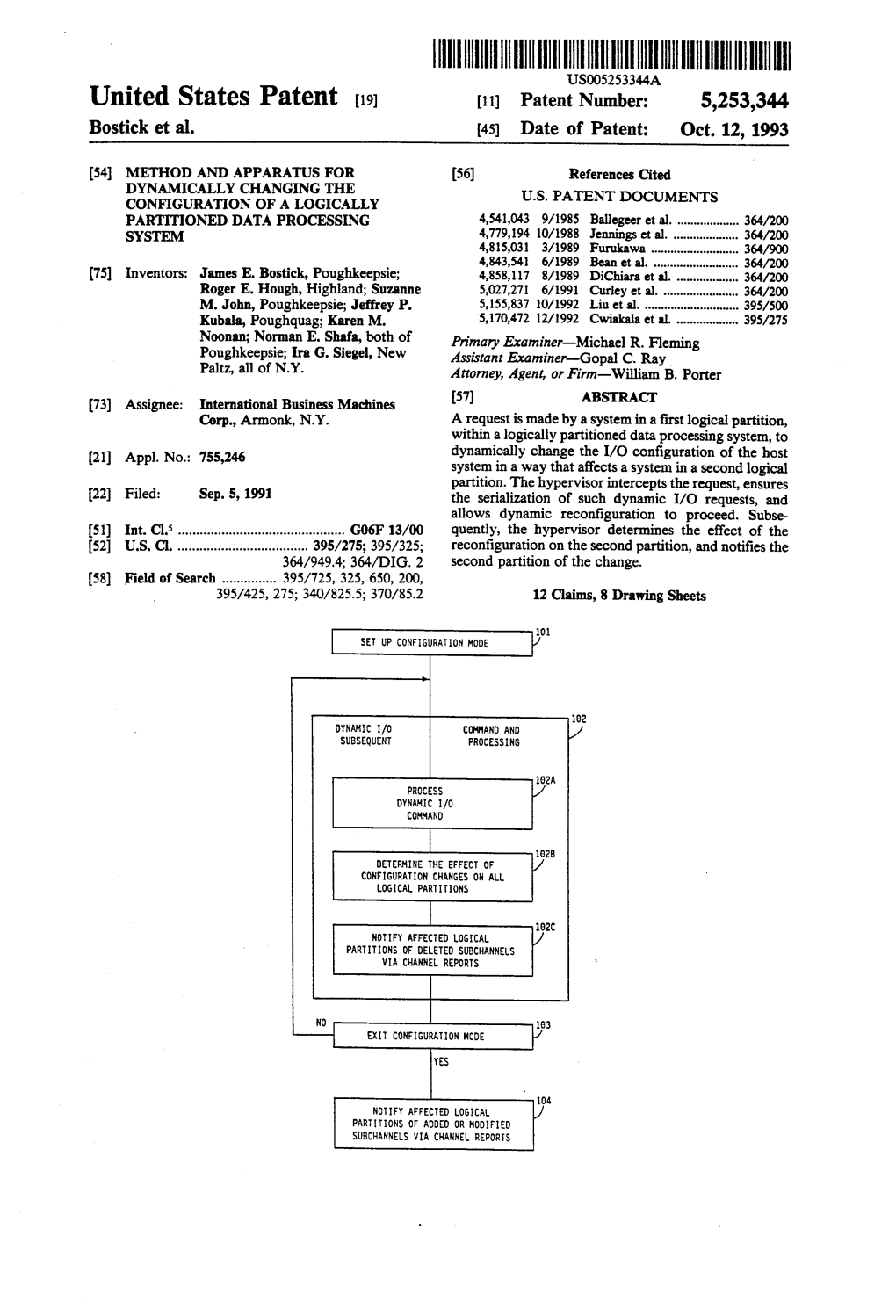
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,802,354 Kubala Et Al
IIIUSOO5802354A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,802,354 Kubala et al. 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 1, 1998 54 SESSESSEEogical :::::: y: a G. et al. ................... 395/551 PARTITIONS OF A PARTITIONED OTHER PUBLICATIONS NFORMATION HANDLING SYSTEM TO A TEST DATESOURCE "Enterprise Systems Architecture/390 Principles of Opera tion' IBM Publication, SA22-7201-02, Dec. 1994. (75) Inventors: JeffreyB. Mathias, P. Kubala, Vestal; Poughguag;Ira G. Siegel, Thomas New ocessor RResource/Systems C is S t sManager Planninging Uu1Guide” Paltz; David E. Whitney, IBM Publication, GA22-7236-01, Sep. 1996. Poughkeepsie, all of N.Y. Primary Examiner Thomas M. Heckler 73) Assignee: International Business Machines Attorney; Agent, or Firm-W. A. Kinnaman, Jr. Corporation. Armonk, N.Y. 57) ABSTRACT (21) Appl. No.: 871,429 A method and apparatus for synchronizing selected logical o partitions of a partitioned information handling system to a 22 Filed: Jun. 9, 1997 test datesource. A system operator is presented with a 6 display panel in which the operator may specify a set of test 2. 4 to spees ope-woo was seeds Pawa as aposuo Xu Pow Ge.K. partitions and a test clock value. Each partition designated as (58 Field of search an a wo be 44 440 x and see395551 555 a test partition is synchronized to the test clock value upon being newly activated, while production partitions are syn 395/200.78 chronized to a production clock value. The first test partition to be newly activated is synchronized to the test clock value 56) References Cited by calculating the difference between the test clock value U.S.