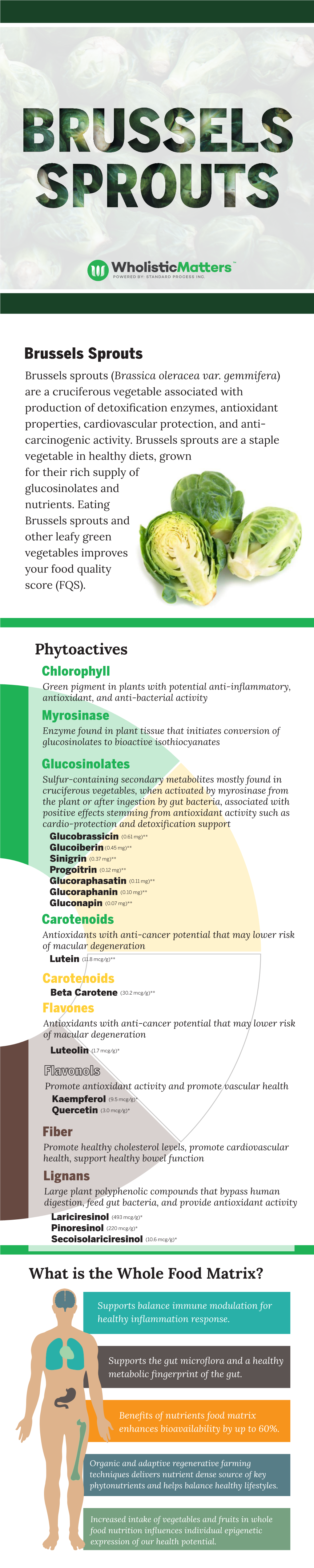
Brussels Sprouts Phytoactives What Is the Whole Food Matrix?
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Environmental and Genetic Variation in Essential Mineral Nutrients and Nutritional Value Among Brassica Vegetables
Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 10, No. 7; 2018 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Environmental and Genetic Variation in Essential Mineral Nutrients and Nutritional Value Among Brassica Vegetables Moo Jung Kim1, Tyler J. Simpson1, Yu-Chun Chiu1, Talon M. Becker2, John A. Juvik3 & Kang-Mo Ku1 1 Division of Plant and Soil Sciences, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV, USA 2 Extension-Commercial Agriculture, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Benton, IL, USA 3 Department of Crop Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, USA Correspondence: Kang-Mo Ku, Division of Plant and Soil Sciences, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV 26505, USA. Tel: 1-304-293-2549. E-mail: [email protected] Received: March 20, 2018 Accepted: April 28, 2018 Online Published: June 15, 2018 doi:10.5539/jas.v10n7p1 URL: https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v10n7p1 Abstract Dietary minerals play an important role in human nutrition and proper metabolism. We grew various Brassica crops under field conditions in 2012 and 2013 and analyzed 8 essential minerals from edible tissues of those crops. Among the investigated crops, pak choi (Brassica rapa), mustard greens (B. juncea; B. nigra), and komatsuna (B. rapa) were generally high in most minerals, according to dry weight-based concentrations. The percentage recommended daily intake (RDA) or adequate intake (AI) values, calculated using fresh weight-based concentrations, suggest that Brassica vegetables are a good source of iron, calcium, and manganese, providing > 20% of %RDA/AI depending on crop. Kale (B. oleracea; B. napus) was generally higher in %RDA/AI, in particular for calcium (Ca), phosphorous (P), magnesium (Mg), and manganese (Mn). -

Crispy Brussels Sprout & Saffron Risotto
Crispy Brussels Sprout & Saffron blueapron.com Risotto with Parmesan Cheese 2 SERVINGS | 25–35 MINS R IS P Ingredients C & Serve with Blue Apron M wine that has this symbol Y I N L L blueapron.com/wine 1/2 lb Brussels E R A 1 cup Carnaroli Rice 2 cloves Garlic Sprouts 1 Lemon 1 Shallot 2 Tbsps Butter 2 Tbsps Mascarpone 1/4 cup Grated 1 pinch Saffron Cheese Parmesan Cheese 1/4 tsp Crushed Red Pepper Flakes 1 Prepare the ingredients 3 Make the risotto • Place an oven rack in the center • To the pot of cooked shallot, of the oven; preheat to 450°F. add the rice, saffron, and 3 cups • Wash dry the fresh produce. of water (carefully, as the liquid may splatter); season with salt • Peel and finely chop the shallot. and pepper. Heat to boiling • Peel and roughly chop 2 cloves on high. of garlic. • Once boiling, reduce the heat • Combine the chopped shallot to medium-high. Cook, stirring and chopped garlic in a bowl. occasionally, 15 to 17 minutes, or • Quarter and deseed the lemon. until most of the liquid has been absorbed and the rice is al dente (still slightly firm to the bite). • Cut off and discard the stem ends of the brussels sprouts; quarter lengthwise. • Turn off the heat. Add the butter, mascarpone, and the juice of 2 lemon wedges; stir until thoroughly combined and the butter 2 Cook the shallot is melted. • In a medium pot, heat • Taste, then season with salt and pepper if desired. 2 teaspoons of olive oil on medium-high until hot. -

Brussels Sprout
Brussels Sprout Introduction: At this club in October 2011 Dick Turvey told us that he believed that growing Brussels Sprouts was an easier way for two people to eat cabbage greens than growing cabbages. He planted seedlings in the first week of October, November and December for succession and claimed “Maxim” was the best variety. My own experience has been that they are at least as easy to grow as cabbages and provide a more continuous yield. We can pick what we need for a meal rather than picking a whole cabbage and a brussels sprout crops over a longer period than a cabbage. Growing: You can have Brussels Sprouts virtually all year round in Dunedin (apart for the hungry gap between October and December). Plant seedlings as soon as growth starts in the spring (September-October) for the summer and autumn and again in January for winter and early spring. They should be 30cm apart in rows that are 60 cm apart. We grow six plants in Spring and six in January. Like all the cabbage family they grow fastest if you have lots of nitrogen in the soil. They grow in temperatures of 7 – 24 ⁰ C with highest yields at 15 – 18 ⁰ C and home gardeners have an advantage over commercial growers in that you can harvest them over many weeks and they are not affected by freezing temperatures – some say it even enhances the flavour. They are part of the cabbage family and so put them in the same plot as Broccoli, cabbage & Chinese cabbage, cauliflower, radish, swede, kale, kohlrabi, mustard, radish and rocket. -

Red Brussels Sprout Greens Brussels Sprout Stalk
Full Harvest Farm, LLC size boxes they go with, and label the containers as 7112 County Road S well. Take one stalk. Hartford, WI 53027 Brussels sprout greens are the leaves from the Brussels 262 673-6760 sprout plant. The leaves are thick and green with a [email protected] Box #19 waxy feel, a bit like collards. We’ve found them to be Odd Week delicious, especially after the plants have gone thru 28 October 2015 several frosts. To use them, strip off the stems, wash the leaves and cut them into bite-sized pieces. Cook up some bacon, add some onion and garlic, and cook Contents until the onion is transparent. Add a cup of stock or Beets: Red water, the Brussels sprout greens, cover and simmer Brussels Sprout Greens slowly for 15-20 minutes, or until the leaves are tender Brussels Sprout Stalk -- WILL BE DELIVERED and a lighter green. Brussels sprout greens should be a IN SEPARATE CONTAINERS part of our fall diet. They’re sweeter than collards and Celeriac kale, and quite nutritious. Garlic The cabbage worms like Brussels sprout greens too, so Leeks some of your leaves will have holes in them. That Onions doesn’t affect their flavor. Wash them well as a bit of Potatoes: Red dirt may have splashed up on some leaves. Winter Squash: Butternut Store the greens in a plastic bag in the vegetable drawer. Their thicker leaf holds more water, so they New Stuff: Brussels sprouts, Brussels sprout greens, should keep for a week or 2. They’ll taste better if you celeriac, leeks cook them soon. -

Communityharvest Local Producer Features + Produce Highlights + Recipes + Healthy Tips
COMMUNITYHARVEST LOCAL PRODUCER FEATURES + PRODUCE HIGHLIGHTS + RECIPES + HEALTHY TIPS WHAT’S IN THE CSA THIS WEEK? • Broccoli - Grandview Farms • Brussels Sprouts - Wolff Farms • Radishes - One Farm • Kale - Wolff Farms • Potatoes - Bridgewater • Carrots - Pekareks HEALTHY TIP BENEFITS OF BRUSSELS SPROUTS These cruciferous veggies are packed with antioxidants, fiber, vitamin C, and more. Brussels sprouts (yes with an s, like the city) are named after the veggie’s history of cultivation in Belgium. Part of the cruciferous vegetable family, the sprouts’ cousins include cauliflower, kale, broccoli, cabbage, collard greens, and bok choy. • Low in calories. At less than 40 per cup, Brussels sprouts are also low-carb, packing just 8 grams per cup raw, including 3 grams as fiber. • Brussels sprouts are antioxidant powerhouses. • High in fiber. The fiber in Brussels sprouts (about 4 grams per cooked cup) helps regulate blood sugar levels, supports digestive health, and helps feed the beneficial gut bacteria tied to positive mood, immunity, and anti-inflammation. • Pack a vitamin C punch. One cup of cooked Brussels sprouts packs over 150% of the minimum daily vitamin C target. This important nutrient acts as an antioxidant, supports immunity, vision, and iron absorption, and is needed for collagen production. • Loaded with vitamin K. Per cup, cooked Brussels sprouts pack over 250% of the recommended daily target for vitamin K. In addition to helping to clot blood, this nutrient plays a role in bone health and may help protect against bone loss. Adapted from: https://www.health.com/nutrition/benefits-brussels-sprouts RECIPE: BRUSSELS SPROUTS YOUR KIDS WILL LOVE A MESSAGE FROM REAL MOM NUTRITION Full disclosure: I never ate a Brussels sprout until I was in my 30s. -

Facts About Antioxidants1 Kaitlin G
FSHN14-02 Facts about Antioxidants1 Kaitlin G. Clark and Wendy J. Dahl2 Our bodies are made up of cells. Chemical reactions, Antioxidant Activity known collectively as metabolism, are constantly occurring The amount of antioxidants in a food can be determined inside our cells. These reactions are necessary for life, as “antioxidant activity,” which is a measure of how well but sometimes they create free radicals. Free radicals are they inhibit free radicals. The fruits highest in antioxidant highly reactive molecules that can initiate damaging chain activity are blueberries, pomegranates, blackberries, reactions in our cells (Jenkins and Honig 1996). This is strawberries, and raspberries (Wolfe et al. 2008). The known as oxidative stress. Research has linked oxidative vegetables highest in antioxidant activity are beets, red stress to many diseases: arthritis, lung diseases (such as peppers, eggplant, Brussels sprout, and broccoli (Song et al. emphysema), heart disease, stroke, ulcers, hypertension, 2010). Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases, muscular dystrophy, and others. Oxidative stress also contributes to the normal aging process (Lobo et al. 2010). Recommended Intake The Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) for antioxi- Antioxidants can inactivate free radicals and protect our dant vitamins are given in Table 2. Because smokers have cells from oxidative stress and the damage it causes. Anti- higher levels of oxidative stress, an additional 35 mg per oxidants also can help our immune system defend against day of vitamin C is recommended (IOM 2001). bacteria, fungi, viruses, and some cancers (Mandelker 2008). The body produces some of its own antioxidants, but Other antioxidants are not vitamins and do not have eating a plant-based diet increases the level of antioxidants recommended intakes. -

Cabbage History Cabbage Began As a Wild Plant in Europe and the Mediterranean Along Bodies of Water
Cabbage History Cabbage began as a wild plant in Europe and the Mediterranean along bodies of water. Ancient Egyptians and Greeks had great respect for cabbage, as they thought it had medicinal qualities. The Greeks began cultivating cabbage as early as 600 B.C., and the Romans began growing it too. Later, it was introduced to the British Isles. Because cabbage is fairly easy to grow and can adapt to various conditions, it is grown around the world today. China is the leading producer and consumer of cabbage. Cabbage prefers a cool, mild temperature. Too much exposure to cold or hot temperatures will cause the seeds to grow into flowers instead of leafy heads. The head is ready for harvest when it is firm, typically after 2-3 months. Pick it by hand and store in the refrigerator for up to one week. Cabbage is a low-calorie food with an excellent amount of vitamin K, which helps regulate blood and its flow. Varieties Cannonball cabbage is called a “mammoth Brussels sprout” because they only grow to be one foot wide. The leaves are dense and used for shredding into sauerkraut or coleslaw. January King cabbage has curly blue-green leaves with splashes of purple. It can be planted in the fall and harvested into the winter. It only grows to be one pound per head. Napa cabbage is oblong with frilled yellow-green leaves. It is softer and sweeter than most cabbage. Red Drumhead cabbage is a tough, red cabbage that is usually shredded for salads. Savoy cabbage has yellow to green leaves and a mildly earthy taste. -

RENEW FOOD PLAN Weekly Planner and Recipes
RENEW FOOD PLAN Weekly Planner and Recipes Version 2 RENEW FOOD PLAN – A WEEK OF MEALS & SNACKS DAY 1 DAY 2 DAY 3 DAY 4 DAY 5 DAY 6 DAY 7 Breakfast n CranBlueberry n Southwestern n Nut Porridge* n Poached n Raspberry n Mediterranean n Almond Kale Egg Muffins* n Blueberries Organic Eggs Chia Seed Egg & Cacao Smoothie* Pudding* Vegetable Smoothie* n Green Tea n Green Tea n Sautéed n Green Tea Spinach, n Green Tea Scramble* n Peppermint LO Broccoli, n Berries Green Tea Garlic and n Green Tea Onion Snack n Hard Boiled n Unsweetened n Pumpkin n Sunflower n Hard Boiled n LO Raspberry n Pumpkin and Egg Coconut Seeds Seeds Egg Chia Seed Sunflower n Kiwi Yogurt n Balsamic n Strawberries* n Pomegranate Pudding* Seed Mixture n Carrots n Cherries Roasted n Green Tea Seeds n Raspberries n Chia Seeds Beets* n Coconut flakes Lunch n Zucchini n Curried n LO Ginger n LO Halibut* n Caesar n Vegetable n Green Noodles with Broccoli Basil over Salad* with Shirataki Chicken and Pesto and Soup* Vegetable n Lemon LO Coconut Noodle Stir-Fry* Vegetable Organic n LO Herbed Stir-Fry with Avocado Lime Roasted Soup* Tempeh* Turkey Burger* Mung Bean Salad* Chicken* n Crispy Brussels & Edamame Sprout Chips* Pasta* Snack n Roasted n Avocado n Celery, n Cinnamon n Jicama, n Chewy n Sliced Rosemary (sliced/ Jicama, and Coconut Celery and Crunchy Road Zucchini Almonds* chopped) Carrot Sticks Yogurt Cucumbers Mix* n Nut Cheese* n Blackberries with Cumin, n Guacamole* n Blueberries n Beet Salt, Pepper, n Walnuts Edamame and Lemon Hummus* Juice Dinner n Herbed n Ginger Basil -

Supplementary Information Table S1 Cultivars Grown in Experiments
Supplementary information Table S1 Cultivars grown in Experiments 3 and 4 Cultivar Morphotype number Bor 1 Borecole Bor 2 Borecole Bor 3 Borecole Bor 5 Borecole Bor 6 Borecole Bor 4$ Borecole Bro 7 Broccoli Bro 8 Broccoli Bro 9 Broccoli Bro 10 Broccoli Bro 11 Broccoli Bro 12 Broccoli Bro 13 Broccoli Bro 14 Broccoli Bro 15 Broccoli Bro 16 Broccoli BrSp 17 Brussels sprout BrSp 18 Brussels sprout BrSp 19 Brussels sprout BrSp 20 Brussels sprout BrSp 21 Brussels sprout BrSp 22 Brussels sprout BrSp 23 Brussels sprout Cab 24 Cabbage Cab 25 Cabbage Cab 26 Cabbage Cab 27 Cabbage Cab 28 Cabbage Cab 29 Cabbage Cab 30 Cabbage Cab 31 Cabbage Cab 32 Cabbage Cab 33 Cabbage Cab 34 Cabbage Cab 35 Cabbage Cab 36 Cabbage Cab 37 Cabbage Cab 75# Cabbage Cau 38 Cauliflower Cau 39 Cauliflower Cau 41 Cauliflower Cau 42 Cauliflower Cau 43 Cauliflower Cau 44 Cauliflower Cau 46 Cauliflower Cau 47 Cauliflower Cau 48 Cauliflower Cau 49 Cauliflower Cau 40# Cauliflower ChKa 50 Chinese kale Ka 51 Kale Ka 52 Kale Ka 53 Kale Ka 54 Kale Ka 55 Kale Ka 56 Kale Ko 59 Kohlrabi Ko 60 Kohlrabi Ko 61 Kohlrabi Ko 64 Kohlrabi Ko 65 Kohlrabi Ko 57$% Kohlrabi Ko 58$% Kohlrabi Ko 62$% Kohlrabi Ko 63# Kohlrabi SaCa 66 Savoy cabbage SaCa 67 Savoy cabbage SaCa 68 Savoy cabbage SaCa 69 Savoy cabbage SaCa 70 Savoy cabbage SaCa 71 Savoy cabbage SaCa 72 Savoy cabbage SaCa 73 Savoy cabbage SaCa 74 Savoy cabbage SaCa 76# Savoy cabbage $ Denotes cultivars grown only in Experiment 3 # Denotes cultivars grown only in Experiment4 %Denotes genebank accessions. -
Big Nutrition in a Small Package
Big Nutrition in a Small Package Funded by The Beef Checkoff Frequently Asked Questions about Beef We all know beef tastes great – but did you know that beef can be good for you, too? Here are some answers to your most pressing questions when it comes to beef and your health. Q: Can I enjoy beef regularly as part of a healthy, balanced diet? A: Absolutely! A 3-ounce serving of beef—about the size of an iPhone or deck of cards—provides more than 10 essential nutrients and about half of your Daily Value for protein in around 170 calories, on average (and just 150 calories for a serving of lean beef). Four-Seasons Beef and Brussels Sprout Chopped Salad Q: How much beef should I eat at a meal to meet my daily protein TOTAL RECIPE TIME: 15 MINUTES | MAKES 4 SERVINGS requirements? A: The Dietary Guidelines recommends adults eat 5.5 ounces 12 ounces cooked (leftover) beef Steak or Roast, thinly sliced of protein foods per day. Currently—and contrary to popular 4 cups thinly sliced Brussels sprouts (about 10 ounces) belief—Americans consume 1.7 ounces of beef daily, on average. 1 medium tart red or green apple or pear, thinly sliced The fact is, beef is a natural source of essential nutrients, which 1 cup thinly sliced celery makes it a great protein option that you can enjoy any day. ½ cup dried sweetened cranberries ½ cup reduced-fat champagne vinaigrette or honey mustard dressing Q: What nutritional benefits does beef offer me that other proteins ¼ cup crumbled Gorgonzola, goat or feta cheese don’t? ¼ cup toasted chopped walnuts or pecans (optional) A: Beef is a nutrition powerhouse in many ways. -

EVENT MENU OPTIONS Winter 2016/2017
EVENT MENU OPTIONS Winter 2016/2017 COCKTAIL HOUR Seasonal Soup Cortado Chickpea Fritters - sriracha mayo (v) Green Hummus Bocas - small pita pockets, chickpeas, toasted garlic tahini, everything green (v, vg) Steamed Mussels - charred lemon broth, baguette Grilled Oysters - maple bourbon butter Seared Scallop - brussels sprout apple slaw, smoked tamarind Griddled Flatbread - goat cheese, mushrooms, balsamic, whole grain farro (v) Grilled Cheese Finger Strips - Shelburne Farm aged cheddar, Reid’s Farm apple (v) Three-Cheese Hot Dip - asiago, aged cheddar, goat cheese; spinach, kale, arugula Meatballs - roasted almond red pepper romesco, cranberry habanero bbq, mushroom duxelle Beef Burger Sliders - caramelized onion, Shelburne Farm aged cheddar, Roseda Farm aged beef Fried Chicken Squares - red cabbage sriracha slaw Chicken or Steak Skewers - salsa verde CHEESE COURSE Two/Three/Five Served with Crackers & House-Made Tomato Jam Mt. Alice, Pasteurized Cow's Milk (Von Trapp Farmstead, VT) Grayson, Raw Cow’s Milk (Meadow Creek Dairy, VA) Harbison, Pasteurized Cow’s Milk (Jasper Hill Farm, VT) Gisele, Pasteurized Goat-Cow Milks (Boston Post Dairy, VT) Mad River Blue, Organic Pasteurized Cow’s Milk (Von Trapp Farmstead, VT) Bayley Hazen Blue, Raw Cow’s Milk (Jasper Hill Farm, VT) APPETIZER COURSE Cauliflower Piccata - lemon, butter, herb mayo (v) Rainbow Beet Salad - garden herbs, citrus dressing, goat cheese crumble (v) Roasted Brussels Sprouts - pickled red cabbage (v) Skillet Roasted Vegetables - winter root -

Ockendon, 1974
Heredity (1977), 39(1),149-152 RARESELF-INCOMPATIBILITY ALLELES IN A PURPLE CULTIVAR OF BRUSSELS SPROUTS D. J. OCKENDON National Vegetable Research Station, Wellesbourne, Warwick, England Received1O.i.77 SUMMARY Two samples of a purple Brussels sprout, cv. Rubine, were tested for their self-incompatibility alleles. One sample had only four S-alleles, of which three (S12, 18 and 28) have not previously been reported from Brussels sprouts, while the fourth (S35) is very rare. The other sample had the same four S-alleles plus Sl4 at a low frequency. It is suggested that S12, 18, 28 and possibly S35 were transferred from red cabbage to Brussels sprouts and that S 14 was a contaminant. This transfer can be accounted for by tight linkage between the S locus and the anthocyanin pigment gene. Dominance relation- ships were determined, and in the stigma S28 was found to be recessive to $18 and 35 but not to $12. S28 had a much higher frequency than any of the other S-alleles found, supporting the general conclusion that recessive S-alleles are commoner than dominant ones. A further example of the probable intro- duction of new S-alleles into Brussels sprouts is given and the role of this process in the evolution of Brussels sprouts is considered. 1. INTRODUCTION IN a survey of 16 cultivars of Brussels sprouts (Brassica oleracea var. gemmfera) Ockendon (1974) found 19 different S-alleles. Some occurred in a high proportion of the cultivars tested and were found at high frequencies, whereas others occurred at low frequencies and were detected in only a few cultivars.