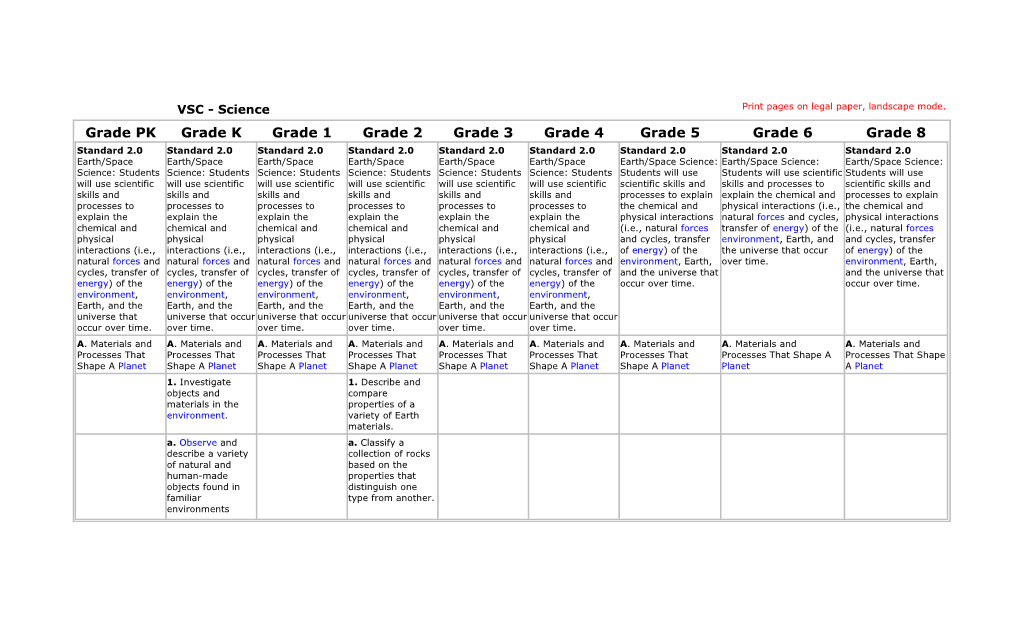
VSC - Science Print pages on legal paper, landscape mode. Grade PK Grade K Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 8 Standard 2.0 Standard 2.0 Standard 2.0 Standard 2.0 Standard 2.0 Standard 2.0 Standard 2.0 Standard 2.0 Standard 2.0 Earth/Space Earth/Space Earth/Space Earth/Space Earth/Space Earth/Space Earth/Space Science: Earth/Space Science: Earth/Space Science: Science: Students Science: Students Science: Students Science: Students Science: Students Science: Students Students will use Students will use scientific Students will use will use scientific will use scientific will use scientific will use scientific will use scientific will use scientific scientific skills and skills and processes to scientific skills and skills and skills and skills and skills and skills and skills and processes to explain explain the chemical and processes to explain processes to processes to processes to processes to processes to processes to the chemical and physical interactions (i.e., the chemical and explain the explain the explain the explain the explain the explain the physical interactions natural forces and cycles, physical interactions chemical and chemical and chemical and chemical and chemical and chemical and (i.e., natural forces transfer of energy) of the (i.e., natural forces physical physical physical physical physical physical and cycles, transfer environment, Earth, and and cycles, transfer interactions (i.e., interactions (i.e., interactions (i.e., interactions (i.e., interactions (i.e., interactions (i.e., of energy) of the the universe that occur of energy) of the natural forces and natural forces and natural forces and natural forces and natural forces and natural forces and environment, Earth, over time. environment, Earth, cycles, transfer of cycles, transfer of cycles, transfer of cycles, transfer of cycles, transfer of cycles, transfer of and the universe that and the universe that energy) of the energy) of the energy) of the energy) of the energy) of the energy) of the occur over time. occur over time. environment, environment, environment, environment, environment, environment, Earth, and the Earth, and the Earth, and the Earth, and the Earth, and the Earth, and the universe that universe that occur universe that occur universe that occur universe that occur universe that occur occur over time. over time. over time. over time. over time. over time. A. Materials and A. Materials and A. Materials and A. Materials and A. Materials and A. Materials and A. Materials and A. Materials and A. Materials and Processes That Processes That Processes That Processes That Processes That Processes That Processes That Processes That Shape A Processes That Shape Shape A Planet Shape A Planet Shape A Planet Shape A Planet Shape A Planet Shape A Planet Shape A Planet Planet A Planet 1. Investigate 1. Describe and objects and compare materials in the properties of a environment. variety of Earth materials. a. Observe and a. Classify a describe a variety collection of rocks of natural and based on the human-made properties that objects found in distinguish one familiar type from another. environments (school, neighborhood, etc.). b. Examine and b. Collect soil from describe Earth different locations materials. and compare the properties of the samples. rocks soil Color Texture water Reaction to water
Remains of living things c. Using examples, c. Use examples of describe that observations from objects and places around the materials, such as school and trees, rocks, and neighborhood to hills on Earth's describe ways surface can Earth materials change. can change.
Changes caused by humans and other animals
Changes caused by water, wind, etc. 2. Recognize and 2. Cite and describe 2. Cite evidence to explain how the processes that demonstrate and explain physical cause rapid or slow that physical weathering weathering and changes in Earth's and chemical weathering erosion cause surface. cause changes to Earth changes to the materials. earth's surface. a. Investigate and a. Identify and a. Identify examples of describe how describe events such physical weathering, such weathering wears as tornadoes, as the effect of wind, ice, down Earth's hurricanes, volcanic etc. and describe the surface. eruptions, changes caused in each. earthquakes, and Water flooding which change surface Ice features rapidly.
Wind b. Cite evidence to b. Recognize that the b. Describe the changes show that erosion natural force of in materials caused by shapes and gravity causes each of the chemical reshapes the changes in the weathering processes earth's surface as Earth's surface listed: it moves from one features as it pulls location to things towards Earth, Rusting/tarnishing another. as in mud and rock slides, avalanches, Dissolving by acid Water etc. rain Ice
Wind c. Cite examples that c. Compare physical and demonstrate how the chemical weathering and natural agents of provide examples if wind, water, and ice changes caused in Earth produce snow materials or features by changes on the each of these processes. Earth's surface such as carving out deep canyons and building up sand dunes.
3. Explain how rock is formed from combinations of different minerals and that smaller rocks come from the breakage and weathering of bedrock (solid rock underlying soil components) and larger rocks; soil is made partly from weathered rock, partly from plant remains-and also contains many living organisms. a. Observe and classify a collection of minerals based on their physical properties.
Color Luster Hardness
Streak b. Identify components of a variety of rocks and compare the physical properties of rocks with those of minerals to note major differences. c. Describe ways that the following processes contribute to changes always occurring to the Earth's surface.
Erosion Transport
Deposit 4. Differentiate among sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks based upon the processes by which they are formed. a. Identify and describe the processes that form sedimentary rock.
Deposition Compaction
Cementation b. Identify and describe the processes that form igneous rocks.
Volcanic eruptions
Igneous intrusions c. Identify and describe the processes that form metamorphic rocks.
High Temperature
Pressure d. Cite features that can be used as evidence to distinguish among the three types of rocks and relate these features to the processes that form each rock type.
e. Describe the processes that change one form of rock into another (rock cycle).
B. Earth History B. Earth History B. Earth History B. Earth History B. Earth History B. Earth History B. Earth History B. Earth History B. Earth History 1. Explain how sedimentary rock is formed periodically, embedding plant and animal remains and leaving a record of the sequence in which the plants and animals appeared and disappeared. a. Explain how sedimentary rock buried deep enough may be reformed by pressure and heat and these reformed rock layers may be forced up again to become land surface and even mountains. b. Cite evidence to confirm that thousands of layers of sedimentary rock reveal the long history of the changing surface of the Earth. c. Explain why some fossils found in the top layers of sedimentary rock are older then those found beneath in lower layers.
Folding Breaking Uplift Faulting
Tilting 2. Recognize and 2. Recognize and explain that fossils explain that fossils provide evidence found in layers of about the plants sedimentary rock and animals that provide evidence of lived long ago and changing life forms. about the nature of the environment at that time. a. Recognize and a. Recognize how explain that the different types of remains or fossils are formed, imprints of plants such as petrified or animals can remains, imprints, become fossils. molds and casts. b. Describe the b. Recognize and physical structures explain that the fossil of an animal or record of plants and plant based on its animals describes fossil remains. changes in life forms over time. c. Identify what an animal or plant fossil is able to tell about the environment in which it lived. Water
Land C. Plate Tectonics C. Plate Tectonics C. Plate Tectonics C. Plate Tectonics C. Plate Tectonics C. Plate Tectonics C. Plate Tectonics C. Plate Tectonics C. Plate Tectonics 1. Gather 1. Recognize and describe information and the internal and external provide evidence structure of the Earth. about the physical environment, becoming familiar with the details of geological features, observing and mapping locations of hills, valleys, rivers, and canyons. a. Identify and a. Recognize and describe describe some that the Earth's mantle natural features of continents. Lies between the core and the crust Mountains Is very hot Valleys Rivers Has properties of both solids and Canyons liquid b. Describe the b. Recognize and describe natural features in that the Earth's core their immediate outdoor Is at the center of environment, and the Earth compare the features with those of another region Is very hot in Maryland. Is dense and metallic c. Identify and c. Identify and describe describe some the Earth's crust. features of the ocean floor. The solid crust consists of Mountains separate plates Valleys The plates constantly move Canyons at a slow pace in different directions
The plates interact with one another as a result of plate motion. d. Recognize and explain that an ocean floor is land covered by water.
2. Recognize and explain how major geologic events are a result of the movement of Earth's crustal plates. a. Recognize and describe the evidence for plate movement.
Shape of continents Continuity of geologic features and fossils on the continents Ocean rifts, seafloor spreading
Global patterns of earthquakes and volcanoes b. Recognize and explain that major geologic events (earthquakes, volcanic activity, sea floor spreading) occur along crustal plate boundaries.
D. Astronomy D. Astronomy D. Astronomy D. Astronomy D. Astronomy D. Astronomy D. Astronomy D. Astronomy D. Astronomy 1. Observe 1. Observe and 1. Identify and 1. Identify and 1. Recognize that objects 1. Identify and celestial objects describe changes describe the compare properties, of our solar system are describe the that are visible in over time in the variety of objects location, and interrelated. components of the the day and night properties, in the universe movement of universe. sky. location, and through first-hand celestial objects in motion of celestial observations using our solar system. objects. the unaided eye, binoculars or telescopes or videos and/or pictures from reliable sources. a. Identify and a. Identify and a. Observe and a. Recognize that like a. Recognize that Earth a. Recognize that a describe the sun, record observable describe the stars all planets and stars, and its closest star, the galaxy contains moon and stars. properties of the and the planets as the Earth is spherical sun, are part of a disk- billions of stars that sun, moon, and seen through a in shape. shape galaxy of stars and cannot be stars. telescope, that our galaxy is one of distinguished by the graphically in billions of galaxies. unaided eye because pictures or in video of their great clips from reliable distance from Earth, sources. and that there are billions of galaxies. b. Describe ways b. Identify and b. Identify the sun b. Identify the b. Construct models with b. Identify that our in which the record the as the Earth's properties of the accurate scale that solar system is a daytime and apparent visible closest star. planet Earth that represent the position of component of the nighttime skies are changes in the make it possible for the Earth relative to the Milky Way Galaxy. different. shape of the moon the survival of life as sun and to other planets. over two months we know it. of observations. Temperature Location Presence of an atmosphere
Presence of water (solid, liquid, and gas) c. Observe and c. Recognize that c. Compare the c. Identify and describe c. Identify and record changes in stars are like the properties of at least the general pattern of describe the various the location of the sun, some are one other planet in movement of all objects in types of galaxies sun and moon in smaller and some our solar system to our solar system. the sky over time. larger. those of Earth to determine if it could support life, as we know it.
d. Describe and d. Recognize and d. Identify and d. Recognize that the pull d. Identify and compare the describe that the describe physical of gravity causes the describe the type, patterns of change stars are not all properties of comets, pattern of motion of size, and scale, of the that occur in the the same in asteroids, and celestial objects. Milky Way Galaxy. sun and the moon. apparent meteors. brightness.
e. Recognize that e. Provide evidence the pattern of stars that supports the in the sky stays idea that our solar the same although system is sun- their locations in centered. the sky appear to change with the seasons.
2. Recognize that 2. Recognize and 2. Identify and there is a describe the causes explain celestial relationship of the repeating phenomena using the between the sun patterns of celestial regular and and the earth. events. predictable motion of objects in the solar system. a. Identify ways a. Describe the a. Identify and that the sun rotation of the planet describe the affects the earth Earth on its axis. relationships among including that the the period of sun warms the revolution of a planet, earth and provides the length of its solar light. year, and its distance from the sun.
b. Recognize and b. Identify and describe that the explain the rotation of planet relationship between Earth produces the rotation of a observable effects planet or moon on its axis and the length of The day and the solar day for that celestial object. night cycle.
The apparent movement of the sun, moon, planets, and stars c. Describe the c. Identify and revolution of the explain the cause of planet Earth around the phases of the the sun. moon. d. Recognize and d. Describe how lunar describe that the and solar eclipses revolution of the occur. planet Earth produces effects.
The observable patterns of stars in the sky stay the same although different stars can be seen in different seasons.
Length of year e. Verify with models e. Identify and and cite evidence describe how the that the moon's shape and location of apparent shape and the orbits of asteroids position change. and comets affect their periods of revolution.
3. Recognize and explain the effects of the tilt of Earth's axis. a. Recognize and describe that Earth's axis is tilted about 23¼° from vertical with respect to the plane of its orbit and points in the same direction during the year.
b. Recognize and describe that the tilt of Earth's axis causes
Changes in the angle of the sun in the sky during the year
Seasonal differences in the northern and southern latitudes c. Recognize and describe how the tilt of Earth's axis affects the climate in Maryland.
4. Recognize and explain how the force of gravity causes the tides. a. Identify and describe the cause of high and low tides.
E. Interactions of E. Interactions of E. Interactions of E. Interactions of E. Interactions of E. Interactions of E. Interactions of E. Interactions of E. Interactions of Hydrosphere and Hydrosphere and Hydrosphere and Hydrosphere and Hydrosphere and Hydrosphere and Hydrosphere and Hydrosphere and Hydrosphere and Atmosphere Atmosphere Atmosphere Atmosphere Atmosphere Atmosphere Atmosphere Atmosphere Atmosphere 1. Describe 1. Recognize and 1. Recognize and 1. Recognize and 1. Cite evidence to observable describe that the describe that water describe that the explain the changes in water surface of Earth is can be found as a amount of water on relationship between on the surface of more than half liquid or a solid on Earth continues to the hydrosphere and the Earth. covered with the Earth's surface stay the same even atmosphere. water. and as a gas in the though it may Earth's change from one atmosphere. form to another. a. Cite examples of a. Identify the a. Describe that air a. Describe how a. Describe the the sun's effect on many locations is a substance that water on Earth composition of the what happens to where water is surrounds us and changes. atmosphere and water on the found. contains such hydrosphere. Earth's surface. things as oxygen, Condensation water vapor (gas), Precipitation pollen, dust, etc. Water Evaporation disappears from 44. Water puddles, wet surfaces Wonders, Part A after rain, any open 44. Water container, Wonders, etc. Enrichment
Water can be a liquid or a solid and go back and forth from one form to another b. Describe the b. Observe and b. Explain that the b. Recognize and changes that occur explain what sun is the main describe the water to water found happens when source of energy that cycle as the anywhere. liquid water causes the changes distribution and disappears. in the water on circulation of Earth's Earth. water through the Turns into glaciers, surface water water, groundwater, oceans, and vapor 44. Water atmosphere. (gas) in Wonders, Part A the air Can 44. Water reappear Wonders, 44. Water as a liquid Enrichment Wonders, Part A or solid when 44. Water cooled, Wonders, such as Enrichment clouds, fog, rain, snow, etc. 44. Water Wonders, Part A
44. Water Wonders, Enrichment
c. Describe the c. Identify and relationship between describe how the the amount of energy temperature and from the sun and the precipitation in a quantity of water geographic area are that is changed. affected by surface features and changes in atmospheric and ocean content.
Relative location of mountains Volcanic eruptions Proximity to large bodies of water Heat energy of ocean currents
29. Rain Reasons,, Part C d. Describe the processes that maintain a continuous water cycle.
44. Water Wonders, Part A 2. Describe the 2. Investigate and 2. Describe that 2. Recognize and 2. Recognize and weather using gather information some events in describe that each describe the various observations. about changes in nature have season has factors that affect weather. repeating patterns. different weather climate. conditions a. Observe and a. Observe and a. Observe and a. Describe a. Identify and describe the describe different compare day-to- different seasonal describe how the weather using weather conditions day weather weather conditions temperature and senses. using senses. changes. using data precipitation of an collected from area are affected by weather surface and ocean instruments, features. models or drawings. Relative location of mountains Proximity to large bodies of water Warm and cold ocean currents
29. Rain Reasons, Part C b. Describe b. Record b. Observe, b. Compare b. Recognize and qualititative observations using record, and average daily describe the global changes in pictures, compare weather temperatures effects of volcanic weather, such as pictographs, or changes from during different eruptions, temperatures, written/oral month to month. seasons. greenhouse gases, precipitation, language. and El Nino. wind, etc.
c. Describe c. Compare c. Compare qualitative changes temperatures and average daily wind in weather, such type and amount speed and as temperatures, of precipitation direction during precipitation, wind, across the months. different seasons. etc
d. Identify the d. Compare impact of weather average daily changes on daily precipitation activities. during different seasons.
Amount
Type e. Identify and describe patterns of weather conditions based on data collected.
3. Identify and describe the atmospheric and hydrospheric conditions related to weather systems. a. Identify and describe weather patterns associated with high and low pressure systems and frontal systems.
b. Identify and describe the atmospheric and hydrospheric conditions associated with the formation and development of hurricanes, tornadoes, and thunderstorms.
c. Identify and describe how various tools are used to collect weather data and forecast weather conditions.
Barometer Thermometer Anemometer
Psychrometer Note: Highlighting identifies proposed assessment limits. All highlighted Indicators will be tested on the Grades 5 and 8 MSA. The highlighted Objectives under each highlighted Indicator identify the limit to which MSA items can be written. Although all content standards are tested on MSA, not all Indicators and Objectives are tested. Objectives that are not highlighted will not be tested on MSA, however are an integral part of Instruction. Date: 12/30/2005