Supplementary Table 1: Neuropsychological tests, test domains and description of measure
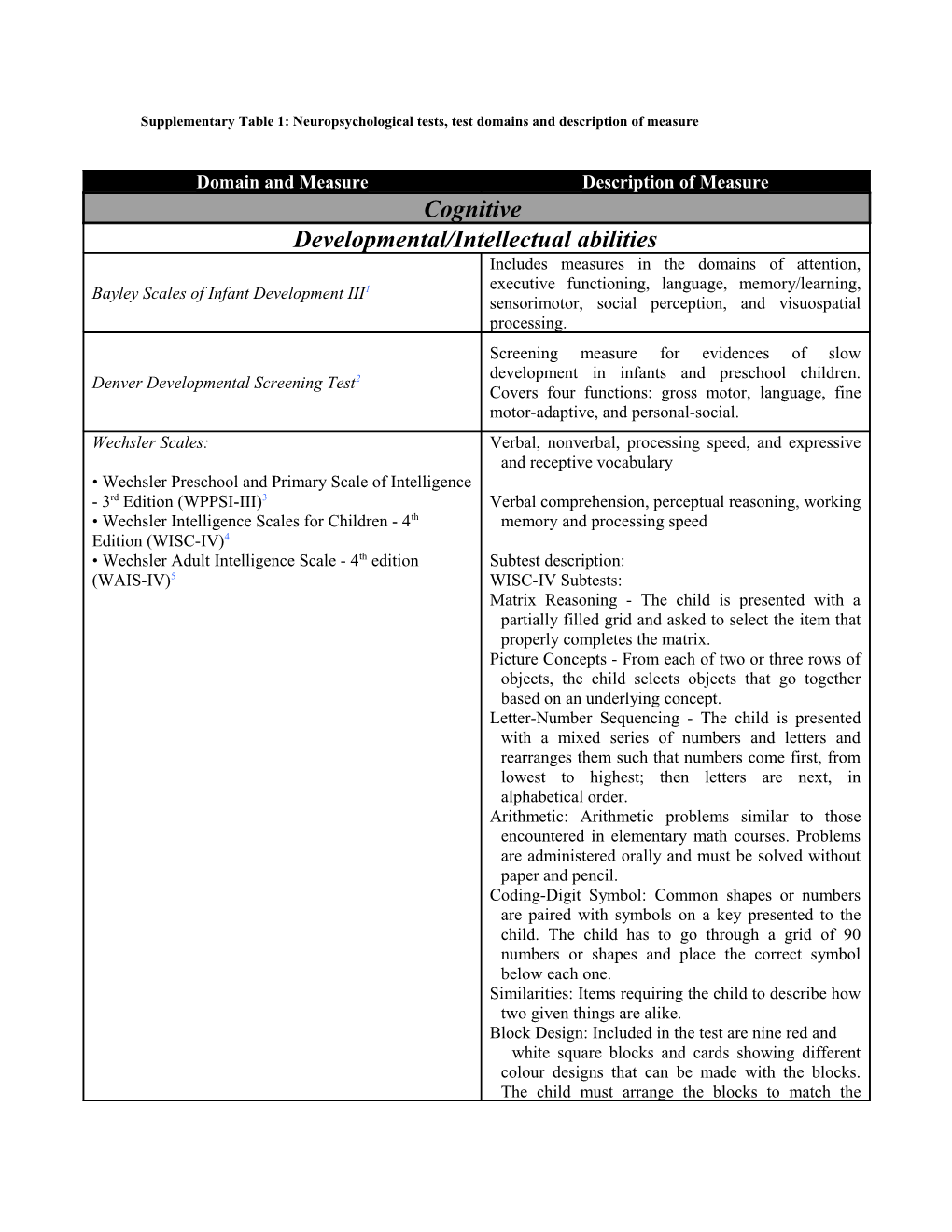
Domain and Measure Description of Measure Cognitive Developmental/Intellectual abilities Includes measures in the domains of attention, executive functioning, language, memory/learning, Bayley Scales of Infant Development III1 sensorimotor, social perception, and visuospatial processing. Screening measure for evidences of slow development in infants and preschool children. Denver Developmental Screening Test2 Covers four functions: gross motor, language, fine motor-adaptive, and personal-social. Wechsler Scales: Verbal, nonverbal, processing speed, and expressive and receptive vocabulary • Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence - 3rd Edition (WPPSI-III)3 Verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working • Wechsler Intelligence Scales for Children - 4th memory and processing speed Edition (WISC-IV)4 • Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale - 4th edition Subtest description: (WAIS-IV)5 WISC-IV Subtests: Matrix Reasoning - The child is presented with a partially filled grid and asked to select the item that properly completes the matrix. Picture Concepts - From each of two or three rows of objects, the child selects objects that go together based on an underlying concept. Letter-Number Sequencing - The child is presented with a mixed series of numbers and letters and rearranges them such that numbers come first, from lowest to highest; then letters are next, in alphabetical order. Arithmetic: Arithmetic problems similar to those encountered in elementary math courses. Problems are administered orally and must be solved without paper and pencil. Coding-Digit Symbol: Common shapes or numbers are paired with symbols on a key presented to the child. The child has to go through a grid of 90 numbers or shapes and place the correct symbol below each one. Similarities: Items requiring the child to describe how two given things are alike. Block Design: Included in the test are nine red and white square blocks and cards showing different colour designs that can be made with the blocks. The child must arrange the blocks to match the design. Information: Items on a variety of information. No specialized or academic information included. Comprehension: Items that require the child to explain what should be done in certain circumstances, the meaning of proverbs and other similar items. Similarities: Items requiring the child to describe how two given things are alike. Digit Span: Digits forward and digits backwards have to be repeated by the child (auditory and verbally). Picture Completion: Several pictures, each having a part missing. The child must identify the missing part. Symbol Search: The child is presented with several rows of items/symbols. The child must determine the correct symbols amongst a variety of different ones. K-ABC measures intelligence (ability, problem- solving) and achievement (knowledge of facts) separately. Test was designed so that language plays a minimal role in the measurement of intelligence. Problem-solving subtests: Hand Movements, Number Recall, and Word Order, analogic spatial Kaufman-Assessment Battery for Children (K-ABC and organizational tasks (i.e. Matrix Analogies, III)6 Spatial Memory). Achievement subtests contain measures of what have traditionally been identified as verbal intelligence (verbal concept formation, vocabulary), general information and acquired school skills (arithmetic, letter and word reading, and word and sentence comprehension).
M-ABC is a widely used, standardized assessment of Movement-Assessment Battery for Children (M-ABC)7 motor performance in children used to identify children who are either definitely impaired or at risk for motor impairment CPM measures intelligence in persons with severe Coloured Progressive Matrices (CPM)8 motor impairment and speech limitations. Obtains measures in linguistic, visuoperceptual, and memory domains. CFT-20 is a culture-fair test of intelligence. Aims to separate environmental (cultural) and genetic factors. Suggests that general intelligence consists of fluid intelligence and crystallized intelligence. Crystallized Cattell Culture Fair Intelligence Test (CFT-20)9 intelligence refers to that aspect of cognition in which initial intelligent judgments have become crystallized as habits. Fluid intelligence, the factor assessed by the CFT-20, is more fundamental, impacts responses to entirely new situations. Attention/Alertness Sustained Attention: • Test of Attentional Performance for Children Computerized task requiring monitoring of visual (KiTAP)10 targets • Test of Attentional Performance (TAP)11 Visual Search: Time-limited test requiring coding of symbols and • Symbol Search, Symbol Coding (WISC-IV/WAIS- visual detection of targets from an array of symbols IV)4,5 Attention Span: Repetition of auditory sequences of digits (or digits • Verbal span tasks (WPPSI-III, WISC-IV, WAIS)3-5 and letters) of increasing length; manually pointing • Word order subtest (K-ABC)6 out a sequence of pictures presented orally in • Letter-Number Sequencing (WISC-IV/WAIS-IV)4,5 increasing length Alertness Computerized task assessing response time (RT) for • Test of Attentional Performance for Children tonic (intrinsic) alertness in response to a visual (KiTAP)10 target, and phasic alertnes in response to a visual • Test of Attentional Performance (TAP)11 target preceded by a warning tone cue Divided Attention • Test of Attentional Performance for Children Computerized task requiring monitoring two stimuli (KiTAP)10 (auditory and visual) simultaneously • Test of Attentional Performance (TAP)11 Executive Functioning
Working Memory: • Digit Span (Backward, Sequencing), Arithmetic, Measures require the child to hold information in Letter-Number Sequencing (WISC-IV/WAIS-IV)4,5 mind and mentally manipulate it • Working memory scale (K-ABC)6
Cognitive Flexibility (Shift of Set): Switching Tests: • Letter-Number Sequencing (WISC-IV, WAIS-IV)4,5 • Shift from Digit Span Forward to Digit Span Measures require the child to alternate between two Backward (WISC-IV, WAIS-IV)4,5 response sets or stimuli, cognitive flexibility • Word Order Subtest (K-ABC)6
Visual Search: • Symbol Search and Symbol Coding (WISC- Cognitive flexibility, visual and sequential processing IV/WAIS-IV)4,5 Computerized tasks that provide reaction times Processing speed: reported from the alertness and divided attention • Test of Attentional Performance for Children subtests through a composite speed score (KiTAP)10 • Test of Attentional Performance (TAP)11 Symbol search: Measure of speed and accuracy with • Symbol Search and Symbol Coding (WISC- which the child processes nonverbal information IV/WAIS-IV)4,5 Symbol coding indirectly also measure the child's skills in learning the coding process as well as fine motor and visual motor Inhibition: Measures inhibitory processes that require inhibition Go/NoGo Test: to an automatic or prepotent response through a • Test of Attentional Performance for Children computerized task presenting visual stimuli: ”x”- (KiTAP)10 marks (Go-Stimulus) or “+”-marks (No-Go • Test of Attentional Performance (TAP)11 Stimulus). Planning and Organization: Measures that assess ability to analyze and synthesize • Block Design Subtest (WPPSI-III, WISC-IV)3,5 abstract visual stimuli and nonverbal concept formation (Block Design) • Symbol Search and Symbol Coding (WISC- IV/WAIS-IV)4,5 Measures that allow the examiner to assess how the child goes about organizing or planning a task Memory Visual Memory: Measures that assess encoding, storage and retrieval • Block design subtest (WPPSI-III)3 of visual information (e.g., designs, pictures, hand • Hand Movements subtest (M-ABC)6 positions) by including measures of immediate and delayed recall and recognition. Verbal Memory: • Digit Span (Backward, Sequencing), Arithmetic, Letter-Number Sequencing (WPPSI-III, WISC-IV, Measures that assess encoding, storage and retrieval WAIS-IV)3-5 of verbal information by including measures of • Word order, Number recall (K-ABC-III (K-ABC)6 immediate recall
Language Receptive Language: • Comprehension subtest (WPPSI-III, WISC-IV, Assessment of comprehension of language at lexical, WAIS-IV)3-5 morphological and sentence levels, verbal reasoning • Information subtest (K-ABC)6 • Similarities subtest (WISC-IV, WAIS-IV)4,5 Expressive Language: Assessment of language expression at lexical, • Vocabulary subtest (WPPSI-III, WISC-IV, WAIS- morphological and sentence levels, verbal concept IV)3-5 formation Visual Motor / Visual Spatial Visual Construction/Organization: • Block Design Subtest (WPPSI-III, WISC-IV, WAIS- IV)3-5 Visual perception, visual discrimination,visual-motor • Cattell Culture Fair Intelligence Test (CFT-20)9 coordination, visuospatial organization
Visual-Perceptual: (WPPSI-III, WISC-IV, WAIS- IV)3-5 •Symbol Search/Coding Subtests Visual perception, visual-motor, and eye-hand •Block Design Subtest coordination, spatial relations, visual discrimination, • Picture Concept/Matrix Reasoning closure • Test of Attentional Performance for Children (KiTAP)10 • Test of Attentional Performance (TAP)11 Visual-Spatial Imagination: (WPPSI-III, WISC-IV, Requires visual-spatial imagination/manipulation WAIS-IV)3-5 •Letter-Number Sequencing Subtest skills •Block Design Subtest
Abstract Reasoning
Visual/Verbal abstract Reasoning (Fluid Visual classifications, analogical reasoning, and serial Intelligence): (WPPSI-III, WISC-IV, WAIS-IV)3-5 reasoning. • Matrix Reasoning Subtest Picture Concept: fluid intelligence, whole to part/part • Picture Concept Subtest to whole organization, abstract categorical reasoning. • Comprehension Comprehension: Verbal reasoning. • Arithmetic Subtest Arithmetic: Numerical reasoning ability, sequencing, • Similarities Subtest fluid reasoning, and logical reasoning. Similarities: Measures concrete, functional, and abstract concept formation.
Assesses the child's ability to acquire, retain, and Visual/Verbal abstract Reasoning (Crystalline retrieve general factual knowledge, commonly Intelligence): referred to as general fund of knowledge. Involves crystallized intelligence, long-term memory, • Information and Comprehension Subtest (WPPSI-III, ability to retain and retrieve knowledge from school WISC-IV, WAIS-IV, K-ABC-III)3-6 and environment. Also involves auditory perception and comprehension and verbal expressive ability. Sensorimotor
Assesses gross and fine motor ataxia, oculomotor Brief Ataxia Rating Scale (BARS)12 ataxia and dysarthria.
Behavior / Emotional Regulation The BDI-II is a self-report questionnaire for measuring the severity of affective and somatic Depression Inventory: symptoms of depression in adolescents and • German Depression Inventory for Children (DIKJ)13 • Beck Depression Inventory II (BDI-II)14 adults. The DIKJ is a 26-item, symptom-oriented questionnaire for children.
Symptom oriented interview questionnaire designed Self and Parent Interview of Behavior and and used at the test center. Emotional Problems Screens for DSM-IV emotional and behavioral Disorders.
References to the instruction manuals have been added in lieu of uploading all the examinations for neuropsychological testing.
REFERENCES 1. Reuner G, Rosenkranz J, Pietz J, Horn R. Bayley-II. [German Version]. Frankfurt
am Main: Pearson Assessment & Information; 2006.
2. Frankenburg, William K. Developmental surveillance and screening of infants
and young children. Pediatrics 2002; 109(1): 144–145.
3. Petermann F, Petermann U (eds.). Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of
Intelligence – III - German Version. Frankfurt am Main: Pearson Assessment;
2009.
4. Petermann F, Petermann U (eds.). Hamburg-Wechsler-Intelligencetest for
Children-IV, 3rd edition. Bern: Huber; 2007.
5. Aster von M, Neubauer A, Horn R (eds.). Wechsler Intelligencetest for Adults.
[German-language edition and adaptation of the WAIS-III by David Wechsler],
2nd corr. edition. Frankfurt am Main: Pearson Assessment; 2006.
6. Kaufman AS, Kaufman NL. Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children, 6th
edition, [German Edition of P. Melchers and U. Preuß]; 2006. 7. Petermann F (ed.). Movement Assessment Battery for Children, 2nd edition,
(Movement - ABC-2). [German Version by Henderson SE, Sudgen DA, Barnett
LA]. Frankfurt am Main: Pearson Assessment; 2001.
8. Raven J, Raven JC, Court JH. Manual for Raven's Progressive Matrices and
Vocabulary Scales. San Antonio: Harcourt Assessment; 2004.
9. Weiß RH. Grundintelligenztest Skala 2 – Revision [German Version, Culture Fair
Intelligence Test, CFT 20-R]. Goettingen: Hogrefe; 2006.
10. Zimmermann P, Godnan M, Fimm B. Test of attentional performance in children
[German Version (KiTAP)]. Herzogenrath: Psytest; 2002.
11. Zimmermann P, Fimm B. Test of attentional performance [German Version 2.2
(TAP)]. Herzogenrath: Psytest; 2009.
12. Schmahmann JD, Gardner R, MacMore J, Vangel MG. Development of a brief
ataxia rating scale (BARS) based on a modified form of the ICARS. Mov Disord.
2009; 24(12): 1820–1828.
13. Stiensmeier-Pelster J, Schuermann M, Duda K. Depression Inventory for Children
and Adolescents (DIKJ), 2nd edition. [German Version]. Goettingen: Hogrefe;
2000. 14. Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK. Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II), 2nd edition.
[German Version], Frankfurt am Main: Harcourt Test Services; 2006.