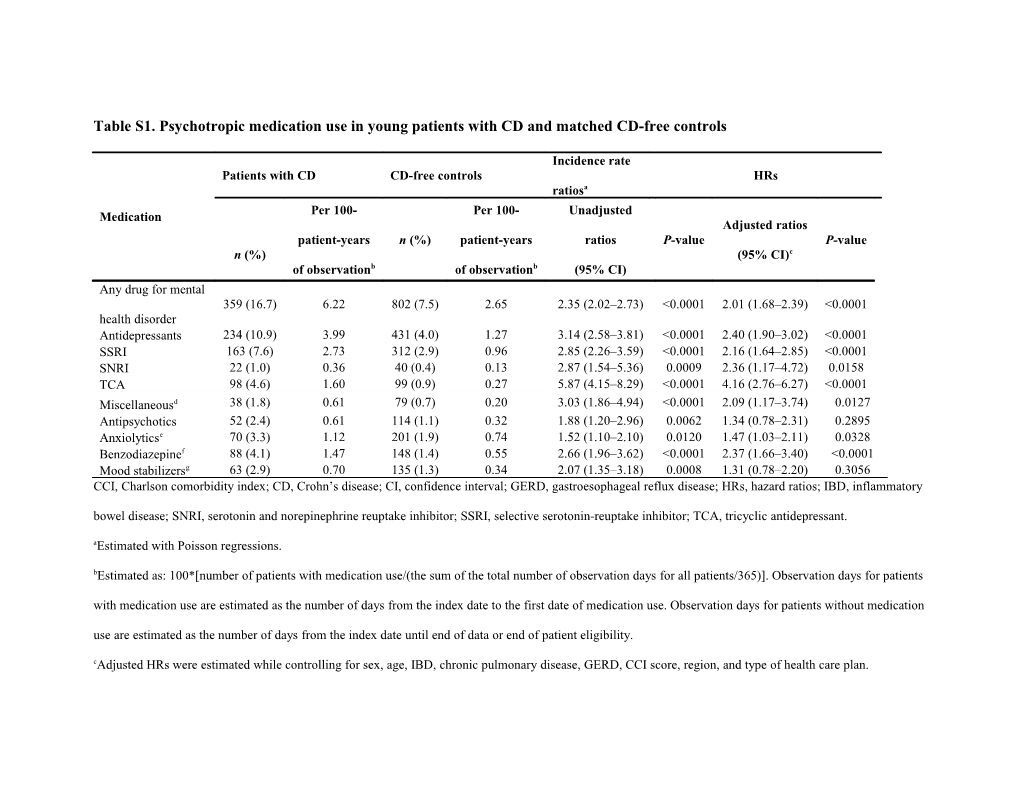
Table S1. Psychotropic medication use in young patients with CD and matched CD-free controls
Incidence rate Patients with CD CD-free controls HRs ratiosa Per 100- Per 100- Unadjusted Medication Adjusted ratios patient-years n (%) patient-years ratios P-value P-value n (%) (95% CI)c of observationb of observationb (95% CI) Any drug for mental 359 (16.7) 6.22 802 (7.5) 2.65 2.35 (2.02–2.73) <0.0001 2.01 (1.68–2.39) <0.0001 health disorder Antidepressants 234 (10.9) 3.99 431 (4.0) 1.27 3.14 (2.58–3.81) <0.0001 2.40 (1.90–3.02) <0.0001 SSRI 163 (7.6) 2.73 312 (2.9) 0.96 2.85 (2.26–3.59) <0.0001 2.16 (1.64–2.85) <0.0001 SNRI 22 (1.0) 0.36 40 (0.4) 0.13 2.87 (1.54–5.36) 0.0009 2.36 (1.17–4.72) 0.0158 TCA 98 (4.6) 1.60 99 (0.9) 0.27 5.87 (4.15–8.29) <0.0001 4.16 (2.76–6.27) <0.0001 Miscellaneousd 38 (1.8) 0.61 79 (0.7) 0.20 3.03 (1.86–4.94) <0.0001 2.09 (1.17–3.74) 0.0127 Antipsychotics 52 (2.4) 0.61 114 (1.1) 0.32 1.88 (1.20–2.96) 0.0062 1.34 (0.78–2.31) 0.2895 Anxiolyticse 70 (3.3) 1.12 201 (1.9) 0.74 1.52 (1.10–2.10) 0.0120 1.47 (1.03–2.11) 0.0328 Benzodiazepinef 88 (4.1) 1.47 148 (1.4) 0.55 2.66 (1.96–3.62) <0.0001 2.37 (1.66–3.40) <0.0001 Mood stabilizersg 63 (2.9) 0.70 135 (1.3) 0.34 2.07 (1.35–3.18) 0.0008 1.31 (0.78–2.20) 0.3056 CCI, Charlson comorbidity index; CD, Crohn’s disease; CI, confidence interval; GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disease; HRs, hazard ratios; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; SNRI, serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; SSRI, selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor; TCA, tricyclic antidepressant. aEstimated with Poisson regressions. bEstimated as: 100*[number of patients with medication use/(the sum of the total number of observation days for all patients/365)]. Observation days for patients with medication use are estimated as the number of days from the index date to the first date of medication use. Observation days for patients without medication use are estimated as the number of days from the index date until end of data or end of patient eligibility. cAdjusted HRs were estimated while controlling for sex, age, IBD, chronic pulmonary disease, GERD, CCI score, region, and type of health care plan. dMiscellaneous antidepressants include bupropion, maprotiline, and mirtazapine. eAnxiolytics included buspirone, chlormezanone, droperidol, hydroxyzine, and meprobamate. fBenzodiazepines included alprazolam, chlordiazepoxide, clonazepam, clorazepate dipotassium, diazepam, halazepam, lorazepam, oxazepam, and prazepam. gMood stabilizers included divalproex sodium, gabapentin, lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, valproate sodium, valproic acid, and verapamil. Table S2. Persistent depression and anxiety in young patients with CD and matched controls
Patients with CD CD-free controls Incidence rate ratiosb HRs
Persistent Per 100- Per 100- Unadjusted Adjusted mental health patient-years N (%) N (%) patient-years of ratios P-value ratios P-value a disorder of observationc (95% CI) (95% CI)d observationc 3.34 (2.24– 2.75 (1.73– 39 (1.8) 0.87 63 (0.6) 0.26 <0.0001 <0.0001 Depression 4.98) 4.38) 5.86 (3.28– 4.35 (2.22– 24 (1.1) 0.53 22 (0.2) 0.09 <0.0001 <0.0001 Anxiety 10.44) 8.50) CCI, Charlson comorbidity index; CD, Crohn’s disease; CI, confidence interval; GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disease; HRs, hazard ratios; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease. aPersistent disorder was defined as at least 1 year without more than 6 months between a diagnosis of anxiety/depression or any prescription filled for any of the following: antidepressants, anxiolytics, antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, and benzodiazepines. bEstimated using Poisson regressions. cEstimated as: 100*[number of patients with an event (persistent mental health disorder)/(the sum of the total number of observation days for all patients/365)].
Observation days for patients with an event are estimated as the number of days from the index date to the event date. Observation days for patients without an event are estimated as the number of days from the index date until end of data or end of patient eligibility. dAdjusted HRs were estimated while controlling for sex, age, IBD, chronic pulmonary disease, GERD, CCI, and type of health care plan.