Third Grade Quarter Three
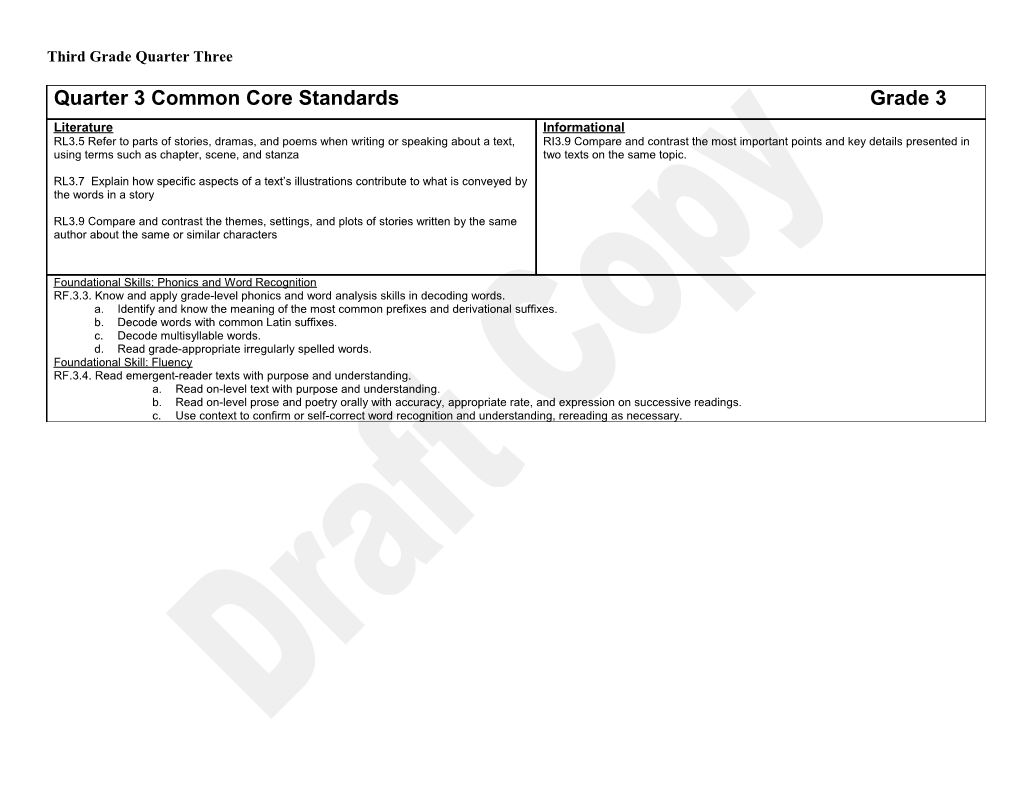
Quarter 3 Common Core Standards Grade 3 Literature Informational RL3.5 Refer to parts of stories, dramas, and poems when writing or speaking about a text, RI3.9 Compare and contrast the most important points and key details presented in using terms such as chapter, scene, and stanza two texts on the same topic.
RL3.7 Explain how specific aspects of a text’s illustrations contribute to what is conveyed by the words in a story
RL3.9 Compare and contrast the themes, settings, and plots of stories written by the same author about the same or similar characters
Foundational Skills: Phonics and Word Recognition RF.3.3. Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words. a. Identify and know the meaning of the most common prefixes and derivational suffixes. b. Decode words with common Latin suffixes. c. Decode multisyllable words. d. Read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words. Foundational Skill: Fluency RF.3.4. Read emergent-reader texts with purpose and understanding. a. Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b. Read on-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary. Third Grade Quarter Three
Speaking/Listening Standards Comprehension and Collaboration SL.3.1. Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 3 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. a. Come to discussions prepared, having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussions. 1 b. Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions (e.g., gaining the floor in respectful ways, listening to others with care, speaking one at a time about the topics and texts under discussion). c. Ask questions to check understanding on information presented, stay on topic, and link their comments to the remarks of others. d. Explain their own ideas and understanding in light of the discussion.
SL.3.2. Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud or information presented in idverse media and formats, including 2 visually, quantitatively, and orally. 3 SL.3.3. Ask and answer questions about information from a speaker, offering appropriate elaboration and detail. Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas SL.3.4 Report on a topic or text, tell a story, or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking clearly at 4 an understandable pace. SL.3.5. Create engaging audio recordings of stories or poems that demonstrate fluid reading at an understandable pace; add visual displays 5 when appropriate to emphasize or enhance certain facts or details. 6 SL.3.6. Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. Third Grade Quarter Three
Language Standards Conventions of Standard English L.3.1. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. a. Explain the function of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in general and their functions in particular sentences. b. Form and use regular and irregular plural nouns. c. Use abstract nouns (e.g., childhood) d. Form and use regular and irregular verbs. 1 e. Form and use the simple (e.g., /walked,/ walk; / will walk) verb tenses. f. Ensure subject-verb and pronoun-antecedent agreement.* g. Form and use comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs, and choose between them depending on what is to be modified. h. Use coordinating and subordinating conjunctions. i. Produce simple, compound, and complex sentences. L.3.2. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. a. Capitalize appropriate words in titles. b. Use commas in addresses. c. Use commas and quotation marks in dialogue. d. Form and use possessives. 2 e. Use conventional spelling for high-frequency and other studied words and for adding suffixes to base words (e.g., sitting, smiled, cries, happiness). f. Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. g. Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. Knowledge of Language L.3.3. Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening. 3 a. Choose words and phrases for effect. * b. Recognize and observe differences between the conventions of spoken and written standard English Vocabulary Acquisition and Use L.3.4. Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning word and phrases based on grade 3 reading and content, choosing flexibly from a range of strategies. a. Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. 4 b. Determine the meaning of the new word formed when a known affix is added to a known word (e.g., agreeable/disagreeable, comfortable/uncomfortable, care/careless/heat/preheat). c. Use a known root word as a clue to the meaning of an unknown word with the same root (e.g., company, companion). d. Use glossaries or beginning dictionaries, both print and digital, to determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases. L.3.5. Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships and nuances in word meanings. a. Distinguish the literal and nonliteral meanings of words and phrases in context (e.g., take steps). 5 b. Identify real-life connections between words and their use (e.g., describe people who are friendly or helpful). c. Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered). L.3.6. Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic, and domain-specific words and phrases, including those 6 that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner that night we went looking for them). Third Grade Quarter Three
3rd Grade English Language Arts and Technology Standards Reading: Literature Key Ideas and Details Technology Standards:
Craft and Structure
Integration of Knowledge and Ideas RL.3.7. Explain how specific aspects of a 3.CT.1.1 (Knowledge) Identify parts of an operating system. text’s illustrations contribute to what is conveyed by 3.CT.1.2 (Comprehension) Demonstrate use of home row keyboarding. the words in a story (e.g., create mood, emphasize aspects 3.CT.1.3 (Comprehension) Demonstrate proper care in the use of of a character or setting). hardware, software, peripherals, and storage media. 3.CT.1.4 (Application) Create, save, and retrieve folders. 3.CT.2.1 (Application) Use a word processor to develop a product. 3.CT.2.2 (Application) Develop documents in design applications 3.NC.4.1 (Application) Produce a variety of solutions to a defined problem
RL.3.9. Compare and contrast the themes, 3.CT.1.1 (Knowledge) Identify parts of an operating system. settings, and plots of stories written by the same 3.CT.1.2 (Comprehension) Demonstrate use of home row keyboarding. author about the same or similar characters (e.g., inbooks 3.CT.1.3 (Comprehension) Demonstrate proper care in the use of from a series). hardware, software, peripherals, and storage media. 3.CT.1.4 (Application) Create, save, and retrieve folders. 3.CT.2.1 (Application) Use a word processor to develop a product. 3.CT.2.2 (Application) Develop documents in design applications 3.NC.4.1 (Application) Produce a variety of solutions to a defined problem
Reading Information Text Technology Skills
Integration of Knowledge and Ideas RI.3.9. Compare and contrast the most 3.CT.1.1 (Knowledge) Identify parts of an operating system. important points and key details presented in two texts on the 3.CT.1.2 (Comprehension) Demonstrate use of home row keyboarding. same topic. 3.CT.1.3 (Comprehension) Demonstrate proper care in the use of hardware, software, peripherals, and storage media. 3.CT.1.4 (Application) Create, save, and retrieve folders. 3.CT.2.1 (Application) Use a word processor to develop a product. Third Grade Quarter Three 3.CT.2.2 (Application) Develop documents in design applications 3.NC.4.1 (Application) Produce a variety of solutions to a defined problem 3.SI.2.1 (Analysis) Recognize the advantages and disadvantages of technology on the individual. Reading: Foundational Skills
Fluency 3.CT.1.1 (Knowledge) Identify parts of an operating system. RF.1.4. Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support 3.CT.1.3 (Comprehension) Demonstrate proper care in the use of comprehension. hardware, software, peripherals, and storage media 3.CT.1.4 (Application) Create, save, and retrieve folders.
Standard: Reading Literature RL3.5 Refer to parts of stories, dramas, and poems when writing or speaking about a text, using terms such as chapter, scene, and stanza.
Foundational Skill: Fluency RF.3.4. Read emergent-reader texts with purpose and understanding. a. Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b. Read on-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.
Comprehension Strategy: Monitoring for Meaning; Schema; Inferring Content Objectives Guiding Questions Vocabulary Resources
I can use chapters to predict the events and What elements of plot (characters, setting, Chapters Picture Books: structure of a story. problem/solution, climax) would you expect Cause Fish by Gregory Mone to find in the first few chapters of this Effect The Mouse and the Motorcycle by Beverly Cleary (Chapter Book) book? Problem The Sixty-Eight Rooms by Marianne Malone (Chapter book) What elements of plot (characters, setting, Setting You Read to Me, I’ll Read to You by Mary Ann Hoberman (poetry) problem/solution, climax) would you expect Character Because of Winn Dixie by Kate DiCamillo to find in the final chapters of this book? Conflict The Miraculous Journey of Edward Tulane by Kate DiCamillo Where would you expect to find the Climax solution to the problem in this story? Solution Treasures Resources : How would chapter headings help you The Strongest One (Unit 2) determine the main idea for the chapter? Can you propose an alternative title for the Professional Resources: chapter? Mosaic of Thought by Keene & Zimmerman Guiding Readers and Writers: Grades 3-6 by Fountas & Pinnell Third Grade Quarter Three I can use scenes to predict the structure of a How are scenes used to organize a Scenes Strategies that Work by Harvey & Goudvis drama (play, reader’s theatre). drama? Stage directions Comprehension from the Ground Up by Sharon Taberski What are some reasons authors decide to Read! Perform! Learn! By Toni Buzzeo end/start a scene? Comprehension Connections by Tanny McGregor How do stage directions help readers comprehend a drama? Online Resources: How does drama compare to a story? www.eduplace.com/graphicorganizer What features are similar? What features www.mhln.com are different? www.busyteacherscafe.com www.apples4theteacher.com I can use stanzas to predict the structure of How is this poem organized? Stanza Three Way Graphic Organizer – Poem, Story, Drama a poem. How does a poem compare to a story or Rhythm drama? Rhyme Poetry What features are similar? What features Free verse www.underdown.org/poetry-formats.html are different? www.kidzone.ws/poetry/fiveline.html What is a stanza? Why do authors use http://www.mrsrenz.net/poetry.htm stanzas? http://www.mrsrenz.net/langarts.links.htm
Reader’s Theatre http://playbooks.com/free.shtml http://teacher.scholastic.com/products/instructor/readerstheater.html
Other Resources: Venn-Diagram of poems, stories, and dramas See The Comprehension Toolkit (See Instructional Coaches/ Library) Strategy Cluster 1 – Monitoring Comprehension Strategy Cluster 2 – Activate and Connect Strategy Cluster 4 – Inferring Assessment: Anecdotal Notes: How does the student respond to… How is a (poem, story, or drama) organized? How does a poem compare to a story or drama? How does the organization of a (poem, story or drama) help you better understand what you are reading? Graphic Organizer: Three- way Venn-Diagram of poems, stories and dramas. Writing: Given an example of a poem, story and drama, students describe what features are similar and what features are different. Students also describe how understanding the organization of a poem, story or drama helps them understand what they are reading better. Given a chapter heading, students write a prediction of coming events Use guiding questions and have students respond on an exit card or in reading response notebooks Highlight different stanzas within a poem and describe how stanzas help us understand a poem better Third Grade Quarter Three Standard: Reading Literature RL3.7 Explain how specific aspects of a text’s illustrations contribute to what is conveyed by the words in a story
Foundational Skill: Fluency RF.3.4. Read emergent-reader texts with purpose and understanding. a. Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b. Read on-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.
Comprehension Strategy: Monitoring for Meaning; Inferring; Visualizing
Content Objectives Guiding Questions Vocabulary Resources I can explain how illustrations How does ______help us better Illustrative Picture Books: help me understand the understand the text? Text The Three Little Fish and the Big Bad Shark by Ken Geist characters, setting and mood of How do illustrations give me clues about Speech The Gardener by Sarah Stewart a text. the purpose or meaning of a text? Bubble Twelve Terrible Things by Marty Kelley Tight Times by Barbara Shook Hazen The Sweetest Fig by Chris VanAllsburg Tuesday by David Wiesner July 4 by David Wiesner I can support my inferences by What in the illustration(s) supports your Inference Tough Boris by Mem Fox using aspects of the text’s inference about the character’s emotion, Emotion No David! By David Shannon illustrations. traits, etc.? Character Should I Share My Ice Cream by Mo Willems What in the illustration(s) supports your Traits Elephants Cannot Dance by Mo Willems inference about the setting of the text? Setting We are in a Book by Mo Willems What in the illustration(s) supports your Mood Today I Will Fly by Mo Willems inference about the mood of the text? Watch Me Throw the Ball by Mo Willems The Red Book by Barbara Lehman (wordless book) Museum Trip by Barbara Lehman (wordless book) The Secret Box by Barbara Lehman (wordless book) Goal by Mina Javaherbin
Treasures Resources: Seven Spools of Thread (Unit 4) Boom Town (Unit 5)
Professional Resources: Mosaic of Thought by Keene & Zimmerman Guiding Readers and Writers: Grades 3-6 by Fountas & Pinnell Strategies that Work by Harvey & Goudvis Comprehension from the Ground Up by Sharon Taberski Comprehension Connections by Tanny McGregor
Online Resources: http://www.readinglady.com/index.php? module=pagemaster&PAGE_user_op=view_page&PAGE_id=6 www.busyteacherscafe.com www.apples4theteacher.com Third Grade Quarter Three Graphic Organizers www.eduplace.com/graphicorganizer www.mhln.com Click on For Teachers - Content Key: NATRTE09 Other Resources: Non-fiction Articles See The Comprehension Toolkit (See Instructional Coaches/ Library) Graphic Organizers Strategy Cluster 1 – Monitoring Comprehension Strategy Cluster 4 – Infer Meaning
Assessment: Anecdotal Notes: How does the student respond to… How do illustrations give you clues about the purpose or meaning of a text? What in the illustration(s) supports your inference about the character’s emotion, traits, etc.? What in the illustration(s) supports your inference about the setting of the text? What in the illustration(s) supports your inference about the mood of the text? Graphic Organizer: Put an illustration on the SMARTBOARD and have students make an inference about the characters, setting or mood of a text. Fill in the graphic organizer - Sample excerpts could come from The Gardener by Sarah Stewart. Writing: Give students an illustration and have them write about what the author is trying to tell them through the illustration; What text might accompany this illustration? Respond to guiding questions on an exit card or in reading response notebook Third Grade Quarter Three Standard: Reading Informational Text RL3.9 Compare and contrast the themes, settings, and plots of stories written by the same author about the same or similar characters
Foundational Skill: Fluency RF.3.4. Read emergent-reader texts with purpose and understanding. a. Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b. Read on-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.
Comprehension Strategy: Monitoring for Meaning; Determining Importance and Synthesizing Content Objectives Guiding Questions Vocabulary Resources I can compare and contrast the theme of What is the theme of this story? Why do you think Theme Picture Books: stories. that? What in the text justifies the theme you Justify Patricia Polacco books selected? Compare Eve Bunting books How does the theme of this story Contrast Kevin Henkes books compare/contrast to the theme in ______? Anansi and the Moss Covered Rock by Eric Kimmel Anansi Goes Fishing by Eric Kimmel I can compare and contrast the setting Setting Anansi and the Talking Melon by Eric Kimmel of stories. What is the setting of this story? What in the text Anansi’s Party Time by Eric Kimmel justifies your setting is correct? Miss Nelson Books by James Marshall How does the setting of this story Jan Brett Books by Jan Brett compare/contrast to the setting in ______? Janell Cannon books I can compare and contrast the plots of Characters stories. What is plot? (characters, setting, Problem Treasures Resources: problem/solution/resolution, events) Solution Stone Soup (Unit 3) What are elements of plot found in this story? Resolution How does the plot of this story compare/contrast Plot Professional Resources to the plot of ______? Events Mosaic of Thought by Keene & Zimmerman Guiding Readers and Writers: Grades 3-6 by Fountas & Pinnell I can compare and contrast stories Strategies that Work by Harvey & Goudvis written by the same author about the How does this story compare/contrast to another Comprehension from the Ground Up by Sharon Taberski same or similar characters. story written by the same author? Comprehension Connections by Tanny McGregor How does this story compare/contrast to another story with similar characters? Online Resources: How are the characters similar or different? http://www.educationoasis.com/curriculum/GO/character_story. How are the themes similar or different? htm (Graphic organizers for character comparisons) How are the settings similar or different? How are the plots similar or different? Graphic Organizers www.eduplace.com/graphicorganizer www.mhln.com Click on For Teachers - Content Key: NATRTE09
Other Resources: Science and Social Studies Leveled Readers and Texts See The Comprehension Toolkit (See Instructional Coaches/ Library) Graphic Organizers Strategy Cluster 1 – Monitoring Comprehension Third Grade Quarter Three Strategy Cluster 5 – Determining Importance Strategy Cluster 6- Summarizing and Synthesizing Life Science (See Essentials Guide) Civics Unit (See Essentials Guide)
Assessment: Anecdotal Notes: How does the student respond to… How does this story compare/contrast to another story written by the same author? How does this story compare/contrast to another story with similar characters? How are the characters, setting, plot or theme similar/ different? Graphic Organizer: Use this comparison matrix to compare texts from the same author or texts with similar characters. Comparison Matrix Writing: After reading two stories by the same author or two stories with similar characters have the students respond in writing to the following questions. Thinking about the two stories we just read, describe how these stories were similar to each other and how they were different from each other. Be sure to discuss the main elements of literature like characters, setting, plot and theme. Venn diagrams comparing themes, settings, plots or characters of two texts Respond to guiding questions on an exit card or in reading response journals Fill out a plot map for a text(s); use plot maps to compare/contrast two texts Third Grade Quarter Three Standard: Reading Informational Text RI3.9 Compare and contrast the most important points and key details presented in two texts on the same topic.
Foundational Skill: Fluency RF.3.4. Read emergent-reader texts with purpose and understanding. d. Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. e. Read on-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. f. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.
Comprehension Strategy: Monitoring for Meaning; Determining Importance and Synthesizing Content Objectives Guiding Questions Vocabulary Resources I can identify the most important points in an What text features in informational text could you use to Informational Text Picture Books: informational text. help you determine the most important points? Non-Fiction Any informational text (Heading) Most Important Explain what you think a most important point was in Point this text? What from the text supports your answer? Key Details Treasures Resources: How do you know this is a most important point and not Penguin Chick (Unit 1) a detail? Animal Homes (Unit 5) Home-Grown Butterflies (Unit 6) I can identify key details that support the most What is the difference between a most important point important points in an informational text. and a key detail? Professional Resources What is a key detail that supports the most important Mosaic of Thought by Keene & Zimmerman point? Guiding Readers and Writers: Grades 3-6 by Fountas & Pinnell I can compare and contrast the most Looking at these two texts on ______, which most Strategies that Work by Harvey & Goudvis important points and key details presented in important points are the same? Which are different? Comprehension from the Ground Up by Sharon two texts on the same topic. What details are the same in both texts? What details Taberski are different in both texts? Comprehension Connections by Tanny McGregor
Online Resources: Nonfiction articles http://beyondpenguins.nsdl.org/ Good site for differentiated text http://www.sciencenewsforkids.org/ http://www.tweentribune.com/ http://www.dogonews.com/?page=2 http://www.timeforkids.com/TFK/ http://junior.scholastic.com/ Graphic Organizers www.eduplace.com/graphicorganizer www.mhln.com Click on For Teachers - Content Key: NATRTE09 Venn Diagram VIP and Key Details
Other Resources: Science and Social Studies Leveled Readers and Texts See The Comprehension Toolkit (See Instructional Third Grade Quarter Three Coaches/ Library) Graphic Organizers Strategy Cluster 1 – Monitoring Comprehension Strategy Cluster 5 – Determining Importance Strategy Cluster 6- Summarizing and Synthesizing Life Science (See Essentials Guide) Civics Unit (See Essentials Guide)
Assessment: Anecdotal Notes: How does the student respond to… Questions to ask when looking at a single text: Explain what you think a most important point was in this text? What from the text supports your answer? How do you know this is a most important point and not a detail? Questions to ask when comparing two informational texts on the same topic: Looking at these two texts on ______, which most important points are the same? Which are different? What details are the same in both texts? What details are different in both texts? Graphic Organizer: Option #1:Read an informational text and determine the most important points versus the key details in the text. Organize your thinking using the graphic organizer. Option #2: Read two informational texts on the same topic. Complete a Venn diagram comparing the most important points and key details of two texts on the same topic. Writing: Describe the difference between a most important point and a key detail. How can you tell the difference? When you are reading, how do key details help you determine a most important point? Respond to guiding questions on an exit card or in reading response journals Third Grade Quarter Three Standard: Foundational Skills: Phonics and Word Recognition RF.3.3. Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words. a. Identify and know the meaning of the most common prefixes and derivational suffixes. b. Decode words with common Latin suffixes. c. Decode multisyllable words. d. Read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words. Foundational Skill: Fluency RF.3.4. Read emergent-reader texts with purpose and understanding. a. Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b. Read on-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.
Comprehension Strategy: Monitor for Meaning Content Objectives Guiding Questions Vocabulary Resources I can use prefixes and suffixes to identify and What is a prefix? What is a suffix? Prefix Picture Books: know the meaning of words. What prefixes/suffixes do you recognize in this word? Suffix Any picture books How can this prefix/suffix help you understand the Context I can decode words with common Latin meaning of the word better? Multi-syllable Treasures Resources: suffixes. What are some examples of other words with the same Decode Any text in Treasures prefix/suffix? Chunk Professional Resources: Mosaic of Thought by Keene & Zimmerman I can “chunk” to decode multisyllable words. Are there any smaller parts in this word that you know? Guiding Readers and Writers: Grades 3-6 by Fountas & Pinnell I can read grade-appropriate irregularly Does it look right? Strategies that Work by Harvey & Goudvis spelled words. Does it sound right? Does it make sense? Online Resources: Non-fiction articles http://beyondpenguins.nsdl.org/ Good site for differentiated text http://www.sciencenewsforkids.org/ http://www.tweentribune.com/ http://www.dogonews.com/?page=2 http://www.timeforkids.com/TFK/ http://junior.scholastic.com/ http://www.nwf.org/kids http://howstuffworks.com Graphic Organizers www.eduplace.com/graphicorganizer www.mhln.com Click on For Teachers Content Key: NATRTE09
Other Resources: Science and Social Studies Leveled Readers and Texts See The Comprehension Toolkit (See Instructional Coaches/ Library) Life Science (See Essential Guide) Third Grade Quarter Three Civics Unit (See Essential Guide
Assessment: Anecdotal Notes: When showed a multi-syllable word, can the student: decode it? Identify a prefix, baseword, and/or suffix? Describe how the prefix/suffix of the word can help the reader understand the meaning of the word? Graphic Organizer: When given or reading a multi-syllable word, have students fill in the graphic organizer. The graphic organizer includes a column for: word, prefix, base word, suffix, what they think the meaning of the word is and how they determined the meaning. Writing: Write about a multi-syllable word you found while reading today. Describe how you chunked the word. Describe what prefixes or suffixes you recognized in that word and how they helped you determine the meaning of that word? Applies skills in writing DRA Third Grade Quarter Three Standard: RF.3.4. Read emergent-reader texts with purpose and understanding. a. Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b. Read on-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c.Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.
Comprehension Strategy: Monitor for Meaning Content Objectives Guiding Questions Vocabulary Resources I can monitor for meaning while reading text. Are there any smaller parts in this word that you know? Monitor Picture Books: Self-correct Any picture books Does it look right? Accuracy Does it sound right? Fluency Treasures Resources: Does it make sense? Expression Any text in Treasures Rate Reread Professional Resources: Mosaic of Thought by Keene & Zimmerman Guiding Readers and Writers: Grades 3-6 by Fountas & Pinnell Strategies that Work by Harvey & Goudvis
Online Resources: Non-fiction articles http://beyondpenguins.nsdl.org/ Good site for differentiated text http://www.sciencenewsforkids.org/ http://www.tweentribune.com/ http://www.dogonews.com/?page=2 http://www.timeforkids.com/TFK/ http://junior.scholastic.com/ http://www.nwf.org/kids http://howstuffworks.com Graphic Organizers www.eduplace.com/graphicorganizer www.mhln.com Click on For Teachers Content Key: NATRTE09
Other Resources: Science and Social Studies Leveled Readers and Texts See The Comprehension Toolkit (See Instructional Coaches/ Library) Life Science (See Essential Guide) Civics Unit (See Essential Guide) Assessment: Anecdotal Notes: Does the student read text with accuracy and appropriate fluency? (Use the district fluency rubric to assess fluency) Does the student self-correct mistakes while reading? What cueing system do they use? Visual (Does it look right?), meaning (Does it make sense?), structure (Does it sound right?) Third Grade Quarter Three Writing: This writing response does not directly assess the standard, but asks the student to reflect on reading processes. When you are reading orally, how is your accuracy? Rate? Expression? How do they affect your understanding of the story? Do you monitor for meaning while you read? If something doesn’t make sense, what do you do? Rereads for meaning/self corrects Comprehends text and can retell story