BANKIER PRIMARY SCHOOL LEARNING SKILLS PROGRESSION THEME: GLOBAL GOAL 12 - RESPONSIBLE CONSUMPTION AND PRODUCTION
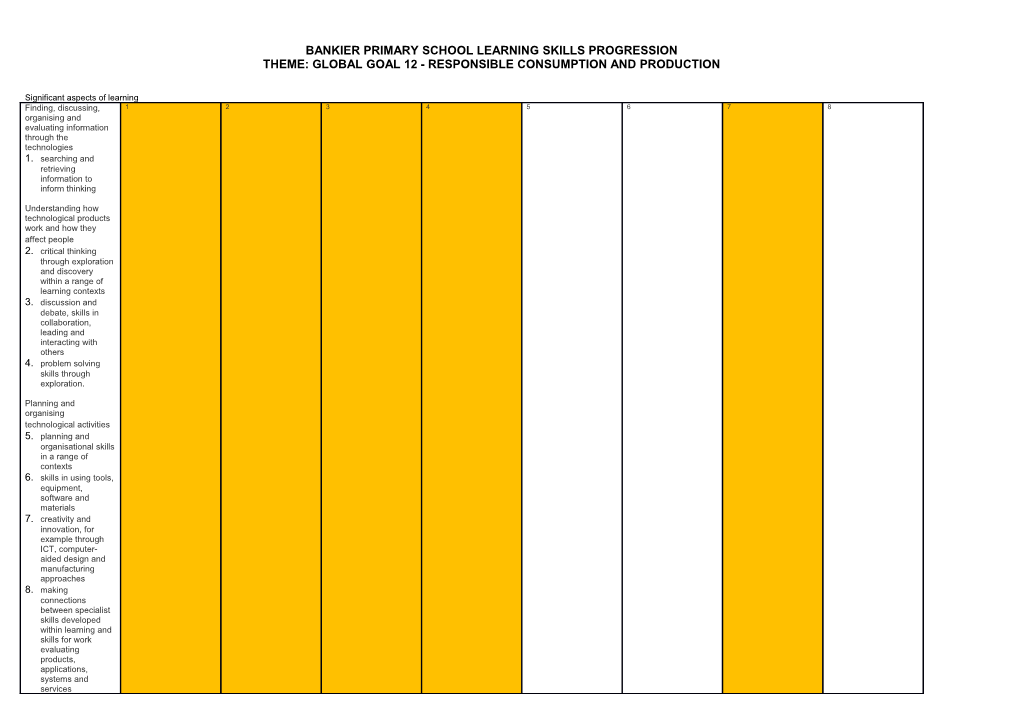
Significant aspects of learning Finding, discussing, 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 organising and evaluating information through the technologies 1. searching and retrieving information to inform thinking
Understanding how technological products work and how they affect people 2. critical thinking through exploration and discovery within a range of learning contexts 3. discussion and debate, skills in collaboration, leading and interacting with others 4. problem solving skills through exploration.
Planning and organising technological activities 5. planning and organisational skills in a range of contexts 6. skills in using tools, equipment, software and materials 7. creativity and innovation, for example through ICT, computer- aided design and manufacturing approaches 8. making connections between specialist skills developed within learning and skills for work evaluating products, applications, systems and services presentation skills.
Experiences and Outcomes Bundle 6a: Within and beyond my place of learning, I Throughout all my learning, I take Having analysed how lifestyle can impact on From my studies of sustainable can reduce, re-use and recycle resources I appropriate action to ensure conservation of the environment and Earth’s resources, I can development, I can reflect on the implications use, to help care for the environment. materials and resources, considering the make suggestions about how to live in a and ethical issues arising from technological TCH 0-02a impact of my actions on the environment. more sustainable way. developments for individuals and societies. TCH 1-02a TCH 2-02a TCH 3-02a Learning Intentions - We are learning to: To reduce, re-use and recycle resources. To conserve materials and resources to To plan for sustainable living by examining To consider implications and ethical issues reduce the impact on the environment. the impact lifestyle has on the earth’s arising from technological developments in resources. society. Progression Framework: Demonstrate an understanding of the importance Apply knowledge of environmental issues by taking Analyse and evaluate how lifestyle can impact on Reflect on the implications and ethical issues of reducing, reusing and recycling products. appropriate action to ensure conservation of the environment and earth’s resources and make arising from technological developments for materials and resources. suggestions about how to live in a more individuals and societies. sustainable way. Bloom’s Success Criteria / Skills - I can…: 0.1 0.2 0.3 1.1 1.2 1.3 2.1 2.2 2.3 3.1 3.2 3.3 Creating Use waste Re-use materials Make recycling Design school Compile lists of Make up an Invent a Compose a Write a news Create a Produce a Construct a flow materials to to make things, posters. recycling mascot. items that can acrostic poem. recycling board waste report on impact multimedia report documentary chart to illustrate make play e.g. toilet roll and cannot be game. minimisation of waste on the showing ethical regarding ethical sustainable objects, e.g. tubes for recycled. song or rap. environment. issues related to issues of waste development. tyres, plastic binoculars. waste minimisation. bags to make minimisation. kites, add objects to play with sand and water. Evaluating Choose waste Decide how to Consider how Say how I know Interpret labelling Convince others Explain what Consider the Appraise how Assess the Justify why Persuade materials to re- re-use materials re-using and which things can to ascertain that careful use of happens to impact of non- lifestyle impacts impact of individuals and individuals to live use in for play. recycling helps be recycled by which packaging resources can waste that is not recycled waste on the sustainable societies need to a more imaginative play. care for the finding the can be recycled. reduce waste. re-used or on the environment and development on develop more sustainable environment. symbol on the recycled. environment. earth’s individuals and sustainable lifestyle through package. resources. societies. lifestyles. a campaign. Analysing Discover ways to Select waste Sort out which Classify Investigate which Survey amounts Compare waste Research Examine the Research Compare waste Investigate the re-use waste materials to re- materials can packaging waste types of of recycling production in the Scottish and differences technological management in reasons why materials in play. use in play. be re-used and generated in packaging can packaging, food home and international between Scottish developments to the western world some societies recycled. school. be recycled and and liquid waste school. waste systems to minimise waste. to waste recycle and re- how. in the dinner hall. management manage waste management in use materials statistics. with one other the third world. more than developed others. country. Applying Experiment with Make use of a Demonstrate Calculate the Connect how Say what Administer a Make Interview Falkirk Associate Interpret how and Develop a waste waste materials variety of waste the ability to number of much is recycled happens to our questionnaire to suggestions on Council Waste technological why waste is management that can be re- materials in recycle packages that in the school to waste: recycling, parents on how to live in a management developments managed strategy for a used in imaginative play. containers and have been how much is re-using and recycling at more sustainable officers on the with differently in developing imaginative play. food waste in recycled in recycled in a landfill and how home. way. council’s waste improvements in different strategy. the dinner hall. school within a plant, e.g this affects the management waste societies. week. clothing bank environment. policies. management. Understanding Talk about what Say how I have Explain why I Give examples of Discuss ways to Report on how Estimate how Know how Cite ways that Explain how Give examples of Discuss ethical waste materials used waste should re-use how resources reduce waste in much packaging, much the school materials are re- less developed developments in how waste is issues related to can be changed materials in and recycle. can be wasted in the environment. food and liquid recycles in a used and countries can technology managed in waste into for play, e.g. imaginative play. the classroom. waste is recycled year. recycled in learn from more improve waste different minimisation. box – car, bag – in the dinner hall. industry, e.g. developed management. societies. kite. clothing bank, countries to glass recycling. reduce waste. Remembering Find waste Know which bin Identify various List items that Memorise waste Recall which Recognise how Record List countries in Recognise the Trace the journey Write to key materials that is for recycling. recycling bins. can be recycled, minimisation materials can and much we information from order of availability of of waste through people, e.g can be re-used e.g. packaging, slogans. cannot be recycle at home research. performance in technology the systems in politicians, to to make food waste. recycled. and school. waste impacts on different support our something for minimisation. societies’ ability societies. campaign. imaginative play. to minimise waste. CONTEXT FOR LEARNING: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle 4 ASPECTS OF LEARNING EXPERIENCES Curriculum areas and Interdisciplinary Ethos and life of the Opportunities for subjects Single area = learning school personal achievement discrete learning = Multiple areas (School as a (wider achievement for community / Multistage) all) State how: State how: Literacy / English Technologies Contributing to eco school award Numeracy / Social Studies Mathematics Expressive Art Health & Wellbeing Religious and Moral Sciences Education Partnership working Parental involvement State who and how: State how: 7 PRINCIPLES: Breadth Progression Depth Personalisati Coherence Challenge Relevance on and and choice enjoyment 4 CAPACITIES: SUCCESSFUL LEARNERS CONFIDENT INDIVIDUALS with with enthusiasm and motivation for learning self-respect determination to reach high standards of achievement a sense of physical, mental and emotional wellbeing openness to new thinking and ideas secure values and belief and able to ambition use literacy, communication and numeracy skills and able to use technology for learning relate to others and manage themselves think creatively and independently pursue a healthy and active lifestyle learn independently and as part of a group be self-aware make reasoned evaluations develop and communicate their own beliefs and view of the world link and apply different kinds of learning in new situations live as independently as they can assess risk and take informed decisions achieve success in different areas of activity RESPONSIBLE CITIZENS EFFECTIVE CONTRIBUTORS with with respect for others an enterprising attitude commitment to participate responsibly in political, resilience economic, social and cultural life self-reliance and able to and able to develop knowledge and understanding of the world and communicate in different ways and in different settings Scotland’s place in it understand different beliefs and cultures work in partnership and in teams make informed choices and decisions take the initiative and lead evaluate environmental, scientific and technological issues apply critical thinking in new contexts develop informed, ethical views of complex issues create and develop solve problems ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE (making learning visible) (make, do, say or write) Teacher’s/ key worker’s notes Photographs Transcripts Audio recordings Written work Art / display work Graphs / diagrams Models/ objects Information charts Technological media Video clips Parental feedback Other (specify): LEARNING COMPLETED PROGRESS (tick) ION ACTIVITIES Differentiate according to where children are on skills pathway.
Targets:
End viole nce in the worl d and deat hs relat ed to it.
End the abus e, expl oitati on, traffi ckin g, and all form s of viole nce and tortu re agai nst child ren. Ensu re that ever yone has equa l acce ss to justic e in their coun try or inter natio nally .
Com bat crim e and corru ption in any form.
Ensu re citize ns are cons ulted and their gove rnme nts mak e deci sion s with the inter est of child ren and adult s in mind . For exa mple , child ren and youn g peop le must be cons ulted befor e a legal law that affec ts their lives is sign ed.
Ensu re all child ren are give n an ident ity inclu ding birth regis tratio n.
Ensu re all peop le have free acce ss to infor mati on.
Stre ngth en instit ution s to prev ent viole nce, terro rism and crim e. Plan with pupils Discuss how we can reduce waste. Count pieces of paper in recycling bag. Watch http://www.s ciencekids.c o.nz/videos/n ature/energy savingtips.ht ml Walk around the school and look at where energy is wasted. Make recycling signs and posters for the classroom reminding people to reduce waste eg turn off light, turn off tap, use both sides of a piece of paper don’t add too much to your plate. https://www. youtube.com /watch? v=TjnNOCbu oCA Discuss what children know about reusing items and how we reuse items at school. Use materials to create new products eg Plastic bottles into bird feeders http://www.s ciencekids.c o.nz/videos/n ature/plastic bottlerecyclin g.html Watch film showing how water can be reused https://www. youtube.com /watch? v=ZS_wGKY F8AU Plan ways to reuse water at school. Look at different recycling bins in the school and at home. Visit the bins in the school including food waste bins. Ask children to explain why we should reduce, reuse and recycle. Sort items to show which bin they would go in to and why. Online recycling game: http://www.b bc.co.uk/sch ools/barnaby bear/games/r ecycle.shtml http://www.n gkids.co.uk/e ntertainment/ recycling- festival- museum-of- london- docklands http://www.b bc.co.uk/edu cation/clips/z j2qxnb http://www.s ciencekids.c o.nz/gamesa ctivities/recy cling.html Look at different symbols that tell us to recycle. Draw a picture of the symbol. Play recognition game. http://www.re cyclenow.co m/recycle/pa ckaging- symbols- explained Watch film showing how waste is recycled. https://www. youtube.com /watch? v=j5Z- 91ZCNEw Cut and stick sequences steps in the recycling process. Recycle scrap paper to make new paper. http://www.k enburn.co.uk /recycling- for-kids/ Discuss why we reduce, reuse and recycle. Watch film on global warming http://www.s ciencekids.c o.nz/videos/e arth/globalw arming.html Design a poster to encourage others to reduce, reuse and recycle. http://www.re cycleforscotl and.com/re- use/passing- it
Additional activities arising from pupils’ plan not already covered above.
BANKIER PRIMARY CURRICULUM PUPILS’ PLANNER
Teacher: Class: Session: Term: Our Launch What we know already? What would I like to learn? (What?) Our BIG Questions
Our Learning experiences/Core Activities (How) I CAN...... (Why? - E & O bundles – delete as necessary) What would I like to learn? How would I like to learn? Our Little Questions
Within and beyond my place of learning, I can reduce, re-use and recycle resources I use, to help care for the environment. TCH 0-02a
Activities/Workshops for our Audience Who? Where? When? How will I share my learning? Our Sources