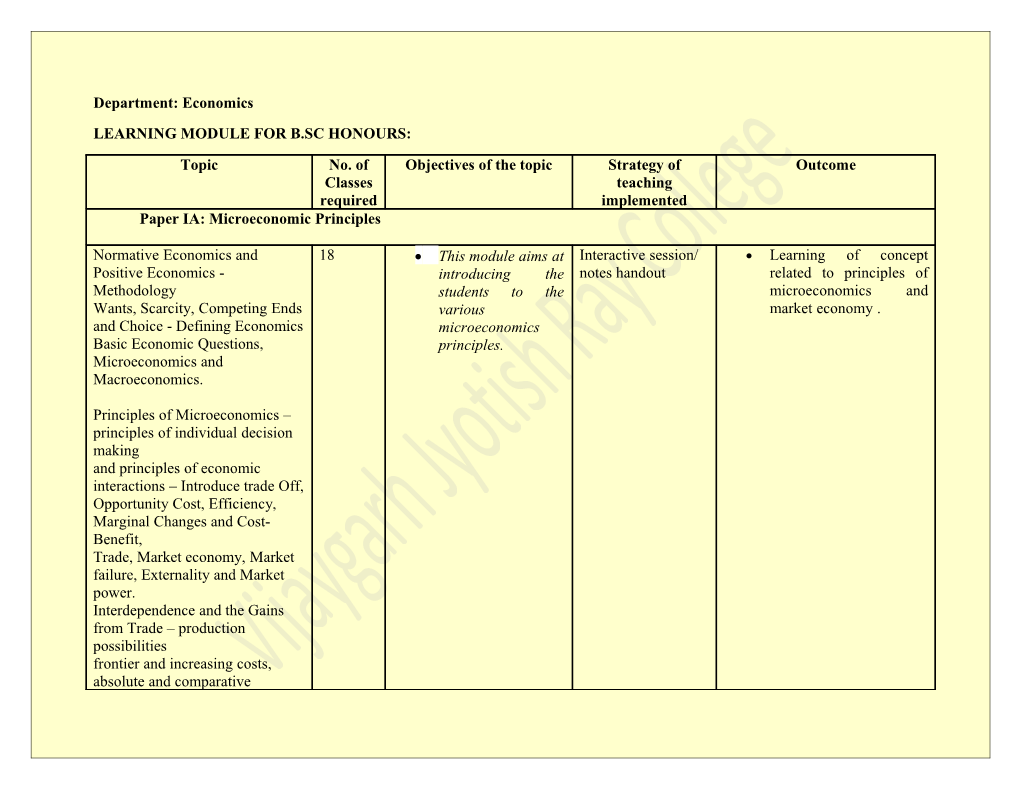
Department: Economics LEARNING MODULE FOR B.SC HONOURS:
Topic No. of Objectives of the topic Strategy of Outcome Classes teaching required implemented Paper IA: Microeconomic Principles
Normative Economics and 18 This module aims at Interactive session/ Learning of concept Positive Economics - introducing the notes handout related to principles of Methodology students to the microeconomics and Wants, Scarcity, Competing Ends various market economy . and Choice - Defining Economics microeconomics Basic Economic Questions, principles. Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
Principles of Microeconomics – principles of individual decision making and principles of economic interactions – Introduce trade Off, Opportunity Cost, Efficiency, Marginal Changes and Cost- Benefit, Trade, Market economy, Market failure, Externality and Market power. Interdependence and the Gains from Trade – production possibilities frontier and increasing costs, absolute and comparative advantage, comparative advantage and gains from trade. The Evolution of Market 25 This module aims at Interactive session/ Learning of market Economies. Price System and the introducing the notes structure, differentiate Invisible students to the the between public and Hand. concept of market private goods, common The Decision-takers – economy , public resources, how and what households, firms and central goods, private determines supply and authorities goods, various demand The Concepts of Markets – competitive market individual market, separation of structure. individual markets, interlinking of individual markets. Difference among markets – competitiveness, goods and factor markets, free and controlled markets. Market and non-market sectors, public and private sectors, economies – free market, command and mixed. Different Goods: Public goods, Private goods, Common resources and Natural Monopolies Market and competition; Demand and its determinants; Supply and its determinants; relation of Quantity Demand with Price (using arguments of income and substitution effects); relation of Quantity Supply with Price (using increasing costs argument); Laws of Demand and Supply; Demand and Supply as Planning Curves; movement along and shift of the curve; Demand, Supply and Other factors. Equilibrium and Disequilibrium Market Adjustment without Government (with illustrations) Importance of Elasticity in 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of choice Choice-Decisions introducing the notes decisions Method of Calculation – Arc students to demand Elasticity. Point Elasticity – and supply definition. elasticity. Demand and Supply Elasticities – types of elasticity and factors effecting elasticity. Demand Elasticity and Revenue Income and Cross Price elasticity Long run and Short Run elasticities of Demand and Supply Case Studies – OPEC and Oil Price, Illegal Drugs The Economic Role of 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of economic Government with respect to introducing the notes handout role of government Market:(i) Price students to role of Ceiling, Price Floor and Market government in Adjustment (with short case controlling market. studies of agricultural administered price, minimum wage and rent control); (ii) Black Market (iii) Tax and market adjustment; (iv) Elasticity and Tax incidence. The History of Utility Theory – 4 This module aims at Interactive session/ able to differentiate From Cardinal to Ordinal introducing the notes handout between cardinal and Approach. students to history ordinal approach Utility in Cardinal Approach – of Utility Theory Utility and choice, Total Utility ,Difference between and Ordinal and Marginal utility, Utility and Cardinal choice - maximization, marginal Approach.. utility theory of demand. Willingness to Pay and Consumer 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Able to differentiate Surplus introducing the notes handout between producer and Willingness to Sell and Producer students concepts of consumer surplus Surplus consumer surplus Market Efficiency and and producer . Deadweight Loss Deadweight Loss of Taxation. Market Failure (definition) and its 12 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knows how market fails, causes. introducing the notes handout solution to that problem Externalities and market students to the inefficiency: difference between various techniques social costs of market failure, and private costs, Positive and externalities. negative externalities, Private Solution to Externalities: Coase theorem, Public Policy towards Externalities: Regulation, Pigovion tax and subsidies, tradable permits. Public Goods and Common Resources: Pubic Good and the free rider problem. Common Resources and Tragedy of Commons. Examples of Public Goods and Common Resources. Conflicting and 1 Complementary Roles of Market and Government Paper IB: Macroeconomic Principles
Distinction between 12 This module aims at Interactive session/ A gross idea of what Macroeconomics and introducing the notes handout Macroeconomics is. Microeconomics – Goals and students to the Role of micro- Instruments of Macroeconomics, summary structure instruments in macro and Supply and Demand in of Macroeconomics their significance. Macroeconomics, Brief History and Gradual development of and Schools of Macroeconomics macroeconomic the present day – Keynesian, Classical, New thoughts over the Macroeconomics via Keynesian and New Classical Ages. various Macroeconomic schools of thoughts. The Circular Flow Explanation - 20 This module aims at Interactive session/ Economic Reasoning to Measuring Output – Gross introducing the notes handout individual & firm National Product - Nominal GNP, students to the behavior Real GNP and GNP Deflator. preliminaries of The Two Approaches to measure Macroeconomic Understand why GNP - The Final Goods variables and households, business, Approach and Income Approach. National Income government and global Intermediate goods and value (NI) Accounting. added approach Flow Statistics behavior determine the and Stock Statistics –Investment aggregate demand for – Consumption – Capital Stock. goods & services GNP, Gross Domestic product, Net National product, National Basic macro variables Income and Disposable Income, and the approaches to GNP and Economic Well Being. compute NI
Consumption and Savings – 14 This module aims at Interactive session/ The understanding of Consumption, Income and introducing the notes handout attributes related to Saving, students to the Income, Consumption, Consumption Function, Marginal preliminary Saving and Investment. Propensity to Consume, Marginal analytical skills Their interaction as well Propensity to Save. whose extended as implication in an Determinants of Consumption. significances could economy. Determinants of Investment. be revealed Knowledge to make Investment Demand Curve and overtime through distinction between the interest rate. the upcoming individual motive and the chapters of the business motives from an syllabus. economic stand-point. Preliminary concept of interest rate, a significant instrument of macroeconomics.
History of Economic Growth and 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ The four fundamental Why Growth Matters. introducing the notes handout determinants of growth Importance of productivity in students to the in real GDP growth. Determinants of understanding of productivity – growth, The main elements of physical capital, human capital, productivity and Neo-classical growth natural resources and public policies – theory. technological fiscal and knowledge. monetary. Understanding of productivity as a source Economic Growth and Public Policy – importance of saving and of economic growth. investment, diminishing returns Knowledge of using the and catch-up effect, foreign production function to investment, education, property rights and political stability, free determine how different trade,population control and variables affect output research and development (brief and productivity. illustration in the context of Indian economic reform)
Defining and Measuring the 12 This module aims at Interactive session/ Calculate the Unemployment Rate – Counting introducing the notes handout unemployment rate and of students to the the labor force Unemployed – Employed, different types and participation rate using Unemployed, Labour Force, measures of data on employment, job Discouraged unemployment. seeking behavior, and Workers. Okun’s Law. Economic population. Costs of High Unemployment. Explain the significance Types of Unemployment – of the unemployment Frictional Unemployment and Job rate and labor force Search, participation rate, and Structural Unemployment and their strengths and Cyclical Unemployment, weaknesses as measures Voluntary of current conditions in versus Involuntary the labor market and Unemployment. economic welfare. Sources of Inflexibility in wages Calculate the amount of – minimum wages, unions and unemployment caused by collective bargaining and the business cycle efficiency wages. (“Cyclical Unemployment”), and explain how it relates to the economy’s Natural Rate of Unemployment
The Classical and Modern View 12 This module aims at Interactive session/ Identify the key factors Definition and functions of equipping the notes handout that influence the Money. students with the quantity of money that Origins of Money including various concepts people desire to hold. Gresham’s Law. and workings of Understand the equation Money Creation, Models of money in of exchange and its Banking – ratios approach and circulation. importance in the crude competitive Introduction to the quantity theory of money banking system, money supply Banking system and and prices. and competitive banking. its behaviors. Understand monetarist, Money and Relative Values – supply-siders’, & New money as a veil, neutrality of Classical approaches to money, macroeconomic issues money illusion, real and monetary Describe how the effects and price level changes. CENTRAL BANK’S Reserve Bank of India, Targets Reserve’s tools of and instruments of monetary monetary policy affect policy. the level of real GDP and the price level. Explain why the CENTRAL BANK’S Reserve cannot stabilize both the money supply and the interest rate simultaneously.
Definition and measurement of 10 Introduction to the Define the Consumer Inflation rate – CPI and GNP Index number and Price Index (CPI), Deflator , Index-number problems its use in finding the explain how it is in measuring the cost of inflation. measured, and use it to livinTypes of Inflation – calculate the inflation Moderate inflation, Galloping rate. Inflation and Use the CPI and the hyperinflation. inflation rate to convert Impact of Inflation – nominal values redistribution of Income and (including nominal Wealth and distortions interest rates) to real on output and prices. Correcting values, and explain the economic variables from value and significance of inflationary effects. these conversions. Compare and contrast the methods and uses of various alternative measures of price levels, including the GDP Deflator and Core CPI.
PAPER: II A Data - Classification and 5 This module aims at Interactive session/ The knowledge of key presentation, Population and introducing notes handout terms in statistics. Sample, Collection of thestudents to the The knowledge of how Data - Variable and Attribute. basic concepts and to prepare a good Frequency distribution - terminologies questioner. Diagrammatic representation of which are required They know how to make frequency to be known for a survey. distribution. further Tabulation and understanding in presentation of data. statistics, data and Meaning and frequency. significance of the It also includes the various methods of data understanding of presentation. the various techniques through which data are collected, sorted, tabulated and presented.
Arithmetic Mean, Median and 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ The computational Mode (for both grouped and introducing the notes handout knowledge of mean, ungrouped students to the median and mode. data), Comparison of Mean, preliminary They know the Median and Mode, Geometric analytical skills manipulations required and whose extended for transformation of a Harmonic Mean, Composite significances could discrete class into a Mean. be revealed continuous class. Application: Index Numbers: overtime through They know the essence their concept as weighted the upcoming and implication of averages, chapters of the cumulative frequency. Problems in the Construction of syllabus. They are skilled in Index Numbers, Chain Index, handling classified data Cost of Living Index Number at the basic level. (different formulae) Wholesale The computational Price Index and Cost of Living knowledge of various Index in India, Uses of Index index numbers. Numbers. Application of statistics in economics. For the first time they have discovered the direct significance of statistics in economics, specifically macroeconomics (inflation). Above discovery intrigues them to explore statistics more.
Range, Mean Deviation Quartile 6 This module aims at Interactive session/ The significance and Deviation and Standard introducing the notes handout importance of variation Deviation, students to the in the practical field. Measures of Relative Dispersion, general behavior of Methods to find out the Curve of Concentration. the data i.e. their variations and deviations. Measurement of Economic variabilities and Understanding and Inequality: Gini Coefficient and methods to compute computation of Lorenz them. inequality. Curve. Another important Curve of Concentration aim is at developing and Gini coefficient is their skills in known to them. various methods to More equipped in data compute the analysis. inequality, a topic of much preference atleast in economics.
Central and non central moments, 3 This module aims at Interactive session/ Concepts mentioned in different measures of skewness equipping the notes handout the objectives and their and students with the various departures. kurtosis concepts of They are now well moment, symmetry equipped with all the and peakedness of concepts required to distribution. delve into the more important aspects – Probability, Sampling and Testing.
Elements of Probability Theory - 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Sample Space, Events Meaning introducing the notes handout of students to the Probability, Classical Definition concept of of Probability Probability theory The Addition Rule, The and related Multiplication Rule, Theorems of definitions. Total Probability, Conditional Probability and Statistical Independence Limitations of the Classical definition, Frequency definition, Axiomatic Approach, Bayes’ Rule Definition of random variable – 21 This module aims at Interactive session/ discrete and continuous random introducing the notes handout variable, probability mass students to the function and probability density various probability functions, distributions. Expectation and Variance of random variables 6.2 Univariate Probability Distributions: Binomial, Poisson, Hypergeometric, Normal and Standard Normal Distribution -Mean Variance, Skewness and Kurtosis. Moment Generating Functions, 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Limiting form of Binomial introducing the notes handout distribution students to concepts (with proof), Limiting form of related to Poisson distribution (no proof), probability. Importance of Normal Distribution in Statistics, Central Limit Theorem (statement only) 10 This is one of the Interactive session/ Techniques to explore Definition of bivariate data, most important notes handout the mutual scatter diagram, covariance - module which aims interdependence of the measure of at introducing bi- different variables. association - Coefficient of variate and multi- Significance of the Simple Correlation - Properties variate interdependence. and the understandings, From univariate cases method of calculation. their significance, they are academically as Concept of rank correlation behaviourism and well as skilfully evolved -Spearman's Rank Correlation methodologies to to the bi-variate cases Measure of influence - Simple compute the degree (multi variate being not a Linear Regression - Least Squares of influence among part of the syllabus). and the variables. Their problem solving Normal Equations and capacities and range of determination of regression problems have coefficient undergone extension and they can now handle more critical problems than before.
Measurements of mortality: 5 This is one of the most Interactive session/ Crude Death Rate, Specific death important module which notes handout Rate, aims at introducing Standardised death rate, Mortality measurements of birth rate, index, Infant mortality rate. death rate, fertility rate. Measurements of fertility: Crude birth rate, general fertility rate, agespecific fertility rate, total fertility rate, Gross Reproduction Rate, Net Reproduction Rate. Life Table: its uses. Paper IIB Mathematics for Economics
The concept of sets and their 12 This module aims at Interactive session/ The knowledge objective operations delivering the basic notes handout (maximisation of profit Cartesian product, vocabulary of skills for or minimisation of cost) functions, graphs, polynomials, optimisation optimisation. increasing and subjected to the Knowledge of how firms decreasing functions constraints that decide upon the Local, global maximum, linear plays a significant alternatives. and non-linear functions and their role in operation Skills to handle basic slopes researches and in resource allocation Differentiability and continuity of decision making of problems. a function the firms.
Use of first derivatives for 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of application of graphing, second derivatives and delivering the basic notes handout maxima and minima curvature skills to understand Maxima and minima (local and how individuals and global) firms select their Concepts of average and preferences with or marginal change, and elasticity without perfect knowledge at various levels of their interactions. It also explores how this selection is associated with their pay-offs Level curves 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of level curves Partial derivatives, second order delivering the notes handout monotonic transformation derivatives and use of chain rule, basicknowledge of convexity of derivatives level curves Monotonic transformation, 18homogeneous function, Euler’s theorem System of linear equations and its 18 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of linear equation solutions, Cramer’s rule introducing linear notes handout system in economics and how Comparative Static exercise, equations, input-output the problem of input-output is matrix operations of linear model. formed equation systems, system with multiple or no solutions Input-Output Matrices Formulation of a linear programming problem, concepts of feasible and basic feasible solution, duality Constrained and unconstrained 18 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of constrained and optimization with first-order and delivering the constrained notes handout unconstrained FOC and SOC second-order And unconstrained first Conditions and second order Homogeneous and homothetic conditions. functions, concave and quasi- concave functions and their programming Linear first-order difference 12 This module aims at doing Interactive session/ Knowledge of first difference equation and their solution sums on difference notes handout equation and second difference Linear second-order difference equations equation equation and their solution Linear first-order differential 15 This module aims at doing Knowledge of first order and equation sums on differential second order differential Linear second order differential equations equation equation with real equal and unequal roots and complex roots Concepts of Game, 15 This module aims at Knowledge of game theory, how representation, pure strategy and delivering the basic skills real life problems can be solved mixed strategy solutions to understand game theory by applying game theory Two person Zero sum game as a and related concepts linear programming problem, Constant & Nonconstant sum game Prisonner’s Dilemma, Dominance, Pure Stregy, Nash Equilibrium Paper IIIA Microeconomics Assumptions on preference 25 This module aims at Interactive session/ ordering, indifference curve, delivering the basic skills notes handout marginal rate of to understand demand substitution and convexity of IC, curve , indifference curve. budget constraint, consumers' equilibrium – interior and corner, Derivation of Demand Curves from ICs, composite good convention. Application: Cash subsidy versus subsidy in kind. 1.2 Income and price consumption curves Price effect - substitution effect (Hicks and Slutsky), inferior goods and Giffen goods, income effect, ordinary and compensated demand curves. Technology, Production 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of production and Functions and Isoquants, short delivering the basic skills notes handout concepts how production run and long run, to understandproduction functions are used production with one and two technology variable inputs, total average and marginal products, law of diminishing return, marginal rate of technical substitution, elasticity of substitution, economics of scale.
Types of production functions- Cobb-Douglas, fixed-coefficient and CES functions. Cost structure-implicit cost, explicit cost, accounting cost, sunk cost, economic cost, fixed cost, variable cost, total, average and marginal cost. Determinants of Short run cost, Cost Curves, cost minimization and expansion path, Short run versus long run cost curves, economies of scope Organization, Firms and Profit 30 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of marginal revenue Maximization. delivering the basic skills notes handout perfect competition in SR and 3.2 Marginal Revenue, Marginal to understand profit , LR, economic profit, other Cost and Profit Maximization. perfect competition, market structure like monopoly , 3.3 Perfect competition- short run economic rent monopoly monopolistic competition, competitive equilibrium of the market , monopolistic oligopoly. firm, short run market, oligopoly. supply curve of firm and industry, Output choice and competitive equilibrium in long run, Economic rent and profit, long- run industry supply – constant, increasing and decreasing cost.
Efficiency of competitive equilibrium, Government intervention and dead weight loss, Application – Minimum prices and price supports.
Monopoly and barriers to entry – output determination and price rule, measure and sources of monopoly power, social costs of monopoly power – deadweight loss. . Pricing with market power – first, second and third degree price discrimination.
Monopolistic competition – short run and long run equilibrium, excess capacity.
Oligopoly – Oligopoly equilibrium as Nash equilibrium, Cournot and Stackelberg Model, Competition versus collusion – the Prisoners’ Dilemma.
Basic concepts-derived demand, 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of marginal productivity of an input, marginal delivering the basic skills to notes handout productivity product understand marginal of an input, marginal revenue productivity, marginal product. profit,theory of distribution. Marginal productivity theory of distribution. Labor market-supply of labor, competitive labor markets, monopsony, collective bargaining. Land markets and rent. General Equilibrium and 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Learning of general equilibrium Economic Efficiency - Exchange, understanding general notes handout production and equilibrium welfare. Reasons for Market Failure
Markets with asymmetric information- adverse selection, moral hazards, agency problems (concepts only). Paper IIIB: Macroeconomics
The classical analysis of the real 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Know how classical sector-determination of introducing the notes handout school used to approach employment, income students to the macro foundations of an and interest rate classical economy. Know that price-output understandings of Job Loss, Job finding and Natural determination has Rate of Unemployment. macroeconomics extensions. and about Calculate the Money and Inflation - quantity unemployment. unemployment rate and theory of money, seigniorage and the labor force inflation tax, This module aims at participation rate using inflation and interest rates, introducing the data on employment, job nominal interest rate and demand students to the seeking behaviour, and for money. Quantity Theory of population. Money and its Understanding of Irving determinants. Fisher through Quantity Theory of Money
Knowledge of the various variables that are associated with money
Simple Keynesian analysis of 25 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of how aggregate demand without and introducing the notes handout economy functions in the with the students to the short run. government sector, multiplier. Simple Keynesian Simple Keynesian Model Model of income of income and output IS-LM, fiscal and monetary and output determination. policy. determination. Explanation of the This module aims at Keynesian view of short- integrating the run fluctuations in goods market and economic activity. the money market Knowledge to calculate for simultaneous the equilibrium level of determination of the output and the interest equilibrium interest rate in a closed economy rate with fixed wages and prices. Knowledge to evaluate how any change in the variables and the parameters of the IS–LM model alters the equilibrium levels of output and the interest rate. Understandings of how fiscal and monetary policies contribute to the determination of output and the interest rate in the short run, and their use as tools for macroeconomic stabilisation.
Economic Openness with an 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Meaning of Economic emphasis on Indian economy, equipping the notes handout Openness. balance of students with the BOP and its various payments, BOP and the Central corrective measures associated concepts. Bank, Financing Current Account of BOP deficits BOP corrective Deficit. under economic measures. Exchange Rate Concepts, openness. Knowledge of how Determination of Exchange Rate things are on-going – fixed and atleast with respect to the flexible, Importance of Foreign Indian economy. Currency Reserves with reference to India, Domestic Adjustment, BOP Crisis and Speculative Attack, Internal and External Balance under Fixed Rate, Advantages of Flexible exchange and Fixed Rates. Foreign exchange market reform in India, relation of Devaluation with purchasing power parity and inflation, purchasing power parity principle. IS-LM model without capital flows, Open economy with capital flows – the
Economic Openness with an 15 This is one of the Interactive session/ The conceptual emphasis on Indian economy, most important notes handout understanding of the balance of module which aims factors with respect payments, BOP and the Central both at the to exchange rate and Bank, Financing Current Account exchange rate BOP. Deficit. paradigm and the Exchange Rate Concepts, BOP issue. Determination of Exchange Rate – fixed and flexible, Importance of Foreign Currency Reserves with reference to India, Domestic Adjustment, BOP Crisis and Speculative Attack, Internal and External Balance under Fixed Rate, Advantages of Flexible exchange and Fixed Rates. Foreign exchange market reform in India, relation of Devaluation with purchasing power parity and inflation, purchasing power parity principle. IS-LM model without capital flows, Open economy with capital flows Consumption - Keynes and 15 The module Interactive session/ Various ideas of how one consumption function, inter- begins with notes handout plans his overtime temporal choice, life the consumption decision. cycle and permanent income Keynesian Various ideas of how one hypothesis. ideas of plans his overtime 4.2 Investment—business fixed consumption consumption decision. investment, neo-classical ; however, Knowledge of how risk approach, Tobin's q, basic governs investment Residential investment and objective is decisions, portfolio accelerator model of inventories. to make investment decisions acquaint Knowledge of how with the investment generates consumption income and output models. through accelerator model Understanding of the interaction between investment & inventories Understanding of the demand for money that is made for the purpose of investment Demand for money: Portfolio 5 Introduction to the Interactive session/ Understanding of the theory of money demand, different types of notes handout Baumol-Tobin analysis Baumol-Tobin investment models of cash management analysis of cash management. to express how decision for investment is made under different circumstances. Important is to note the importance of risk in governing it. At the same time this module posits on the demand for money for investment and techniques to manage the cash flows.
Solow model, Golden Rule of 10 Aims at explaining Interactive session/ Knowledge of the growth capital, impact of changes in the process of notes handout difference among the saving propensity, growth of any nations. population growth and nation and the Knowledge of the rule of technological progress. Growth essential factors for capital accumulation. accounting and Solow it. Knowledge of impact of residual. Also it relates to the growth of various causes of growth parameters on the overall Endogenous Growth Theory rate differences growth. (introduction). among nations. Knowledge of the role of technology in growth of a nation. Introduction to the preliminary ideas of endogenous growth theory Paper IVA: Development Theory
Nature, Questions and Values of 8 This module intends Interactive session/ The term ‘Growth’. Development, Meanings of to introduce the notes handout The term ‘Development’. development – students with the Their goals. economic growth, redistribution meanings and The The basic questions from growth and capabilities term ‘Growth’. which the theories approach to The term concerning growth and development, Objectives of ‘Development’. development seek to development. Their goals. answer. Measures of development – The basic questions Purchasing power parity and Per which the theories capita income as concerning growth an index of development, and development difference between growth and seek to answer. development, human development index. Definition of developing approaches to economy. development and Characteristics of a developing growth whose economy. extended significances would be revealed overtime through the upcoming chapters pertaining to this paper.
Concepts of Population: 4 This module aims at Interactive session/ The distinction between definitions of fertility, mortality, introducing the notes handout ‘Growth’ and birthrates, death students to the ‘Development’. rates, fertility rate, life various techniques They know the expectancy, infant mortality rate, to measure the level importance of the youth dependency of development and different indicators, both ratio growth of an economic and social. Theory of demographic transition economy. Besides, they know the limitations of the above measures and ‘what to use when’.
Complementarity and This module aims at Interactive session/ Learning of Poverty Trap of Coordination introducing the notes handout Nurkse and Big Push theory of models of growth. Rosenstein-Rodan, Gains from Poverty Trap of Nurkse and Big Trade Push theory of Rosenstein-Rodan Linkages – backward and forward; linkages, policy and big push.
Choice of technology and choice of scale (large vs small) and criteria for investment.
Gains from Trade – static, dynamic and vent for surplus, tariffs versus subsidies. Prebisch doctrine, Prebisch-Singer thesis and Terms of Trade. Development and Environmental This module aims at Interactive session/ Having known the – an overview. introducing the notes handout historical trajectory to Basic Issues of development and models of growth. growth, they now know environment - Sustainable the modern stages to development and growth. environment accounting, Laws that govern the population and resources, growth of an economy. poverty, rural Inter-linkage between development, urban development, market and growth, how global environment - rain forest one affects the other and destruction and greenhouse gases. in turn itself gets Policies for Environmental affected. Regulation. Paper IVB: Indian Economy Since Independence
Features of Indian Economy This module aims at Learning of Indian Economy around 1947-1950 and introducing the around 1947-1950 characteristics of economic students to know underdevelopment of India (with about Indian reference to colonial rule of Economy India) The background and Structure of 30 This module aims at Interactive session/ Learning of background and Indian Planning. introducing the notes handout Structure of Indian Planning. Uma Kapila, Chapters 1 and 2. students to Chakravarty, Chapter 1. background of Structural Constraints and India’s Indian Economy development strategy – Choice of industrialization strategies – public vs. private sector, capital goods versus consumer goods – Mahalanobis Plan Model (basic argument), import substitution vs. export promotion strategy. Uma Kapila, Chapter 3. Chakravarty Chapters 2 and 5 (page 69-75). Agriculture-industry relationship – demand side and supply side linkages– agriculture-industry terms of trade - food crisis of the 1960s and imperatives for agricultural growth, genesis of green revolution – fourth plan (basic argument).
Poverty Eradication, foreign aid and self-reliance – Fifth Five Year Plan Model (basic argument)
Regional inequality in India – causes; policies for balanced regional development.
Planning deficiencies and its abandonment– 7th five year plan and Indian economic crisis.
New Economic Policy – liberalisation, market and state (introduction) The background and Structure of This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of background and Indian Planning. introducing the notes handout Structure of Indian Planning. Uma Kapila, Chapters 1 and 2. students to the Agriculture-industry relationship Chakravarty, Chapter 1. various ways of Structural Constraints and India’s Indian Planning development strategy – Choice of system. industrialization strategies – public vs. private sector, capital goods versus consumer goods – Mahalanobis Plan Model (basic argument), import substitution vs. export promotion strategy. Uma Kapila, Chapter 3. Chakravarty Chapters 2 and 5 (page 69-75). Agriculture-industry relationship – demand side and supply side linkages– agriculture-industry terms of trade - food crisis of the 1960s and imperatives for agricultural growth, genesis of green revolution – fourth plan (basic argument). Chakravarty Chapter 3 and 5 (59- 64); Uma Kapila Chapter 11. 2.4 Poverty Eradication, foreign aid and self-reliance – Fifth Five Year Plan Model (basic argument) Chakravarty, Chapter 3. Wadhwa Chapters 5 and 7, Regional inequality in India – causes; policies for balanced regional development. Chakravarty Chapter 4 (45-52). Planning deficiencies and its abandonment– 7th five year plan and Indian economic crisis. Chakravarty Chapter 4 (39-44). Bardhan in Jalan (ed). New Economic Policy – liberalisation, market and state (introduction) Land and tenancy system- 20 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Land and tenancy sharecropping- Different introducing the notes handout system- sharecropping, Green dimensions of Land students to the the Revolution Reform – Productivity Debate – concept of land Marketable Surplus. reform and S.K. Ray in Uma Kapila, Chapter productivity debate, 12. Wadhwa Chapters 19, 20, green revolution 21, 22, 23 and 31. 2.2 Green Revolution – features of green revolution – positive and negative impacts of green revolution. Performance of Indian agriculture. Vaidyanathan. 1994. Chakravarty Chapter 3 (24-27). Wadhwa Chapters 29 and 30. 2.3 Agricultural Policies and Pricing – Agricultural Price commission – support price vs. procurement price – Public investment in agriculture - agricultural subsidies and tax. Hanumantha Rao in Jalan (ed). Uma Kapila Chapter 11. Wadhwa Chapters 24, 25, 26 and 27. Structure and composition of 18 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Structure and Industry – issues of introducing the notes handout composition of Industry, Foreign concentration, large vs students to the trade regime, protection and small industry – industrial industrial growth foreign competition, location. Small scale reservation patterns and policy. Trends foreign trade, and patterns of industrial growth. export , import. Uma Kapila, Chapter 18. Rakesh Mohan in Jalan (ed). 4.2 Foreign trade regime, protection and foreign competition, Productivity; import substitution versus export Competitiveness, effect on export competitiveness. Uma Kapila, Chapter 18. T.N. Srinivasan in Uma Kapila, Chapter 25. Rangarajan in Uma Kapila, Chapter 26. 4.3 Industrial Policies – Industrial licensing system. Uma Kapila, Chapter 18. Rakesh Mohan in Jalan (ed). The trends and pattern of 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ employment and wages in India – introducing the notes handout informalisation and tertiarisation students to the of employment - problems of various patterns of unemployment and under- employment. employment 5.2 Government policies on employment and wages and employment – employment guarantee scheme – minimum wage. Movement of prices in India – – trends and patterns – causes, consequences and policies adopted. Paper VA: International Economics
Ricardian Model: Comparative 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Ricardian Model: advantage. delivering the basic skills notes handout Comparative advantage. 1.2 One factor economy: to understand Ricardian production possibility frontier, model, international trade relative demand and relative supply and autarkic terms of trade. 1.2 Trade in Ricardian world: determination of international terms of trade, complete specialiszation, gains from trade Model of two factor economy: 18 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of two factor Assumptions, Factor prices and delivering the basic skills notes handout economy commodity to understand two factor prices (Stolper-Samuelson economy. effect)-correspondence, Resources & output, Rybzynski effect. 2.2 Effects of International Trade between two factor economies, Relative prices and and the pattern of Trade, Trade and distribution of Income, Factor Price Equalization. 2.3 Empirical studies - Leontief Paradox. Production Possibilities and 16 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Production relative supply, relative prices delivering the knowledge notes handout Possibilities, Economic growth and demand, from production welfare effects of changes in possibilities and economic terms of trade, determining growth. relative prices. 3.2 Economic growth: shift of RS curve, growth and production possibility frontier, RS and terms of trade, International effects of growth, International transfers of income: shifting RD curve, Transfer problem, effects of transfer on terms of trade, Tariffs and export subsidies. 2.3 Offer curves: Derivation, International Equilibrium Partial equilibrium analysis: 18 Interactive session/ Knowledge of Partial Tariff- cost and benefit, effective This module aims at notes handout equilibrium analysis, General rate of delivering the basic skills Equilibrium Analysis protection and intermediate to understand partial goods, quota, tariff- quota equilibrium analysis and equivalence and nonequivalence, general equilibrium export subsidy, voluntary export analysis. restraint. 4.2 General Equilibrium Analysis: Distinction between small and large open economy, welfare effects of tariff in a small country, optimum tariff for large open economy, Metzler's paradox. 4.3 Tariff & Import Quotas in presence of monopoly. Balance of payment accounts; 18 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Balance of national income accounting in an delivering the basic skills notes handout payment accounts , national open to understand balance of Income , Marshall-Lerner economy; monetary account; payments , fixed and condition 5.2 Determination of national flexible exchange rate , Income, multiplier analysis, the Marshall-Lerner condition. transfer problem, introduction of foreign country and repercussion effect. 5.3 Fixed and Flexible Exchange rates: Adjustments, Demand & Supply of foreign exchange, Effects of exchange rate changes on domestic prices and terms of trade, Marshall-Lerner condition, J-curve effect. Paper VB: Public Finance
The nature, scope and 2 This module aims at Interactive session/ significance of public economics delivering the basic skills notes handout Musgrave and Musgrave Page 3- to understand public 6. Bhatia Page 17-25. finance Different forms of government – 8 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Different forms unitary and federal. Tiers of delivering the basic skills notes handout of government – unitary and government in to understand functions of federal.( Central, State, Local ) the federal form- Central, State, government. Local (Introductory discussion with examples). 2.2 Functions of Government - Economic functions -allocation, distribution and stabilization. 2.3 Regulatory functions of the Government and its economic significance Federal Finance: Different layers 10 This module aims at of the government, Inter delivering the basic skills governmental to understand federal transfer—horizontal vs. vertical finance, grants equity. Musgrave and Musgrave Chapter 28, Page 457-461, Misra and Puri Chapter 53, page 694-698, 700-701. 3.2 Grants—merits and demerits of various types of grants— unconditional vs. conditional grants, tied grants, matching grants. Concept of public goods— 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Externality , characteristics of public goods, delivering the basic skills notes handout public goods. Market failure national vs. local to understand public public goods, determination of goods, externality provision of public good 4.2 Externality, concept of social versus private costs and benefits, merit goods, club goods. Musgrave and Musgrave, Chapter 4. McGuire in Bagchi (ed.) Chapter 5. 4.3 Provision versus production of public goods. Market failure and public provision. Pricing of public goods —vertical summation Government budget and its This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Government structure – Receipts and delivering the basic skills notes handout budget expenditure - concepts to understand government of current and capital account, budget ,and concepts balanced, surplus, and deficit related to budget. budgets, concept of budget deficit vs. fiscal deficit, functional classification of budget. Concept of Revenue Deficit. 5.2 Budget, government policy and its impact. Budget multipliers. Stiglitz, Blinder and Solow, Fisher and Easterly in Bagchi (ed), Chapters 9, 16, 17. Concept of tax, types of tax – 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of direct tax and direct tax and indirect tax, canons delivering the basic skills notes handout indirect tax of taxation, to understand taxation, subsidy, transfer policy. ability to pay approach . H.L.Bhatia Chapter 4 page 39-49, Chapter 20 page 467-470. 6.2 Principles of taxation -Ability to Pay principle (brief discussion), Benefit Approach (Actual Examples) Musgrave and Musgrave, Chapter 13, page 218-231 6.3 Tax Design - introduction – truth seeking mechanism. Effects of income tax on work 8 This module aims at Interactive session/ effort, saving and risk bearing delivering the basic skills notes handout (just brief to understand effect of tax. ideas). Musgrave and Musgrave Chapter 17, page 297-308, 311-312. 7.2 Excess burden of indirect taxes Musgrave and Musgrave Chapter 16, page 293-295. 7.3 VAT, Goods and Services Tax (pros and cons). Misra and Puri, 26th edition, page 662-663, Chelliah, Agarwal, Purohit and Rao in Bagchi (ed) Chapter 15. 7.4 Non-tax revenue resources- earnings from public undertakings, interest on loans. Instruments for stabilization 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Musgrave and Musgrave, Chapter delivering the basic skills notes handout 30 to understand public debt 8.2 Public Debt---internal and external. Musgrave and Musgrave Chapter 32, Misra and Puri, Chapter 51. 8.3 Public Finance and Public Choice: The Role of State Paper VIA: Comparative Development Experience
Differences in initial conditions 3 This module aims at Interactive session/ Learning of development of less of development of less developed delivering the basic skills notes handout developed countries countries and to understand difference present day developed countries. between developed and 1.2 Nature of development gap developing countries. prevailing at present between developed and less developed countries. Different types of social 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Learning of feudalism, organization, feudalism, delivering the basic skills notes handout precapitalist societies precapitalist societies other to understand industrial than feudalism, capitalism in the revolution. West, development of the Third World Ref: Bagchi, Ch 1 pp 1-18. 2.2 Industrial revolution in Great Britain - Causes – Why Great Britain became the pioneer? – Characteristics – Effects The Great Debate in Soviet Union 12 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of heavy industry on the assignment of priority on delivering the history of notes handout development Great debate on Soviet of heavy industry in the process Union of planned economic development. 3.2. The Great Depression of the 1930’s and recovery – Experiences of USA and Great Britain. Global Change, Welfare state and 20 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of International mixed economy. delivering the knowledge of notes handout Monetary Fund, World Bank, 4.2 Post War global institutions: understanding the post United Nations Conference on International Monetary Fund, World War effect on Trade and Development, Trade World Bank, United economy and Strategies of Development Nations Conference on Trade and Development. Ref: Todaro and Smith Chapter 14 (660-664). Thirlwall Chapter 15 (479-484), Chapter 16 (556). 4.3 Trade and Strategies of Development: Infant industry, Import substitution versus export promotion in less developed countries. Illustrations from South Asia, Latin America and East Asia. Ref: Meier and Rausch Chapter 3 (144-145), chapter 4(156-162). Todaro & Smith Ch 13 pp 589-601. Thirlwall Chapter 16. 4.4 Foreign Finance, Investment and Development: Private foreign direct investment and Multinational Corporations, private portfolio investment, development assistance debate. Dependency Approach. 5 5.2 Unequal exchange. Neo liberalism, Washington 24 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of General consensus, North-South Divide, delivering the basic skills notes handout Agreements on Tariff and Trade Recasting of IMF to understand (GATT)and World Trade and World Bank. neoliberalism, tariffs, Organization (WTO). Ref: Thirlwall Chapter 15 (479- quota, economic 484), Chapter 17 595-607). Sen integration Chapter 2. Stiglitz Chapters 1, 2 and 3. Stiglitz in Nayyar (ed). 6.2 General Agreements on Tariff and Trade (GATT) and the Dunkel Draft controversy-World Trade Organization (WTO). Ref: Sen Chapter 3. Sikdar Chapters 6 (123-131) and Chapter 7. Shukla in Nayyar (ed). 6.3 Economic Integration and Regional Trading Blocs. Ref: Todaro and Smith Chapter 13 (613-617). Sikdar 6 (146-148, 151-153). 6.4 Global Polarization. Nature of Development planning, 4 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Development Rationale for development delivering the basic skills notes handout planning, planning. to understand development Ref: Todaro and Smith: Ch 16 pp planning 714-718. 7.2 Washington Consensus, New Consensus and the State (i) China, (ii) Africa (iii) 6 Argentina. Paper VIB: Contemporary Economic Issues: India and West Bengal
Background of Indian Economic 20 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of New Economic Reforms – New Economic Policy. delivering the basic skills notes handout Policy Redefining India’s development to understand background strategy. Changing Role of State of Indian economic and reforms, industrial policy Market. Rangarajan in Uma Kapila, Chapter 5. Economic Survey 2009-10, Chapter 2 (21-24). Uma Kapila, Chapter 20. 1.2 Industrial Policy, Disinvestment policy and Privatization. Basu and Maertens (page 141- 146, 350-354, 366-371). Rangarajan in Uma Kapila, Chapter 21. Ahluwalia in Sachs, Varshney and Bajpai. 1.3 Financial sector reforms including banking reform. Monetary Policy of RBI. Basu and Maertens (246-251, 219-225, 255-261). Joshi and Little, Chapter 4. Ahluwalia in Sachs, Varshney and Bajpai. 1.4 Fiscal Policy Reform – tax reform, debt management, FRBM act and subsidies. Basu and Maertens (357-366, 141-146), Vijay Joshi in Ahluwalia and Little (ed). Ahluwalia in Sachs, Varshney and Bajpai. 1.5 External sector reforms: Foreign Exchange market, balance of payments, reform, convertibility, export-import policy, foreign direct investment. Post-reform Agricultural 13 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Post-reform Performance and its Crisis. delivering the basic skills notes handout Agricultural Performance and its Basu and Maertens (59-65, 83- to understand the post Crisis. 86). Mahendra Dev, Chapter 2. reform agriculture and Rao and poverty and government Jeromi in Uma Kapila, Chapter schemes 13. Vaidyanathan in Uma Kapila, Chapter 14. 2.2 Poverty and exclusion, NREGA, social security for unorganized workers and forest policy. Appraisal of Indian Economic 4 Reform. India’s Growth Experience. Inclusive development 18 This module aims at Interactive session/ Learning of Inclusive Mahendra Dev, Introduction. delivering the basic skills notes handout development Economic Survey 2009-10, to understand inclusive Chapter 2 (21-24). growth experience, food 4.2 Growth of the Service Sector. security Basu and Maertens (205-215). M Rakshit 2007. 4.3 Food security, Food Procurement and Public Distribution System. Basu and Maertens (484-489, 561-565). Mahendra Dev Chapter 3 (43-46, 62- 66), Chapter 5. Hanumantha Rao in Uma Kapila, Chapter15. Economic Survey 2009-10, Chapter 8 (198- 204) (or latest issues). 4.4 Migration and Urbanization. Basu and Maertens (443-447). Agarwal, Chapter 7 (86-101) 4.5 Land acquisition, SEZ and Industrialisation. Basu and Maertens (103-109, 164-68), Aradhana Agarwal 2006, Swapna Banerjee-Guha 2008. 4.6 Demographic dividend. Basu and Maertens (415-421). Chandrasekhar, Ghosh and Roy Choudhury Demographic dividend. Contemporary Economic Issues -West Bengal West Bengal Economy Structure 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ and Growth – based on state delivering the basic skills notes handout domestic to understand West Bengal product (SDP) data and economy structure. employment data from National Sample Survey and Census of India. 5.2 West Bengal Economy in relation to India and major states in recent decades: in terms of indicators on - per capita SDP, per capita consumption (rural and urban), income growth, human development Land Reforms, agricultural 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Land Reforms, growth and related current delivering the basic skills notes handout agricultural growth and related problems- growth of to understand land reforms current problems non-farm rural sector 6.2 Industrial development – problems and prospects; Tertiary sector growth – Informalisation in manufacturing and tertiary sectors. 6.3 Poverty alleviation, Employment generation, self- help-group and social security: Problems and policies Paper VIIA: Statistics & Basic Econometrics
Joint Probability Distribution – 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Joint Probability Idea of Independence, Marginal delivering the basic skills notes handout Distribution and Conditional to understand joint Distribution. Expectation of the probability distribution product of two variates. Population and Sample, 5 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of random sampling Parameter and Statistic, Random delivering the basic skills notes handout Sampling - to understand population Methods of Drawing Random and sample. samples –with replacement and without replacement, Random sampling Numbers. 2.2 Sampling Distribution,Standard Error. Sampling Distributions associated 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Sampling with Normal Population, delivering the basic skills notes handout Distributions Expectation and to understand sampling Standard Error of Sample Mean distribution for with replacement and without replacement random samples, 3.2 Chi-Square Distribution, Student t Distribution, F- Distribution (definition and important properties only- Idea of degrees of freedom. Estimators-Desirable properties 25 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of Desirable of estimators -Unbiasedness, delivering the basic skills notes handout properties of estimators Minimum to understand estimation Variance, Consistency and technique Sufficiency 4.2 Point Estimation - Maximum Likelihood Estimators and their properties – 4.3 Maximum Likelihood estimation of the parameters of Binomial, Poisson and Normal Distributions. Confidence Intervals -Testing of Hypothesis -p-Values -Type-I and Type -II Errors 4.5 Simple applications of tests for the Mean and Variance of a Univariate Normal Population. Classical Linear Regression 25 This module aims at Desirable properties of Classical Model (CLRM): Specification of delivering the basic skills Linear Regression Model the Model- to understand Classical (CLRM) Assumptions- Linearity in linear regression model variables and parameters, and related concepts Estimation of the Error Variance 5.2. Gauss Markov Theorem, Goodness of fit: R square – Coefficient of Determination 5.3 Inference in the Linear Regression Model- Confidence interval for the parameters and the Testing of Hypotheses -Prediction with the Simple Regression model. 5.4 Concepts of Heteroscadasticity and Autocorrelation problems. Time Series: Introduction, 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of time series Components, Measurements: delivering the basic skills notes handout Secular Trend (Free to understand time series hand curve fitting, Moving averages, fitting mathematical curves), Seasonal fluctuation (monthly averages, ratio to moving averages, ratio to trend) Paper VIIB: Applied Economics
Nature and Scope of Managerial 5 This module aims at Knowledge of managerial Economics; delivering the basic skills economics 1.2 Basic Economic Tools in to understand managerial Managerial Economics: economics Opportunity Cost Principle, Incremental Principle, Principle of Time Perspective, Discounting Principle and Equi-marginal Principle; Demand Analysis: Demand 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of demand analysis, Estimation for major consumer delivering the basic skills notes handout forecasting durables, nondurable to understand demand products; Demand forecasting analysis. techniques. Ref: Keat and Young Ch-5,6 (188-288) 2.2 Cost Estimation Ref: Keat and Young Ch-8 (355- 417) 2.3 Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis (Break-Even Analysis) : What is C-V-P Analysis? Objectives of C-V-P Analysis, Assumptions of C-V-P Analysis Determination of Break-even point, Profit-Volume Graph, Profit-Volume Ratio, Margin of Safety, Uses and Applications of Break-Even Analysis, Limitations of C-V-P Analysis. The Nature of the Firm, the 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of firm ownership Breadth of the Firm, Assigning delivering the basic skills notes handout and control Decision-Making to understand firm and Responsibilities, Monitoring & related decision making Rewarding performance, Separation of Ownership & Control in the Modern Corporation. Factors Governing Prices, 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of factors governing Objectives of Pricing Policy, delivering the basic skills notes handout prices Price Leadership, Full – to understand factors Cost Pricing, Mark-up Pricing, related to governing Limit Pricing, Marginal Cost policies. Pricing or Variable Cost Pricing, Rate of Return Pricing, Going-Rate Pricing, Peak- Load Pricing, Cyclical Pricing, Pricing over the life-cycle of a product (a) Skimming Price (b) Penetration Price (c) Pricing in Maturity; Product-line pricing, Price Discounts and Differentials, Price Forecasting. What is Capital Budgeting? Need 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of capital budgeting for Capital Budgeting; Different delivering the basic skills notes handout Steps in the to understand the concept Capital Budgeting Process; of capital budgeting Nature of Capital Budgeting Problem; Capital Budgeting Appraisal Methods (a) Payback Method (b) Accounting Rate of Return Method (c) Net Present Value Method (d) Internal Rate of Return Method (e) Benefit-Cost Ratio Method; Comparison between NPV and IRR Methods; Capital Rationing; Alternative Methods of Financing Investments. Cost of Debt Capital, Cost of 7 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of debt capital Preference Share Capital, Cost of delivering the basic skills notes handout Equity Capital, to understand debt Cost of Retained Earnings, capiytal, borrowing and Average Cost of Capital, The lending rate. Opportunity Cost Concept – Borrowing Rate vs. Lending Rate. Inventory Costs, Concept of 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of inventory Average Inventory; Various delivering the basic skills notes handout Inventory Models: (a) to understand inventory Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) costs. (b) Optimum number of Orders per year (c) Optimum no. of Days’ Supply per Order; Quantity Discounts – Cost Comparison Approach; EOQ Concept and Production Processes. Role of Institutional Investors, 8 This module aims at Knowledge of institutional Mechanisms and Controls – delivering the basic skills investors Internal and External to understand institutional Govt Controls, Problems of investors, corporate Corporate Governance, Role of governance. Accountant, Regulation – Rules & Principles, Enforcement, Action beyond obligation, Corporate Governance Models with emphasis on Anglo American Model, Impact of Corporate Governance on Firm Performance. aper VIIB: Applied Economics Group B: Mathematical Economics
Utility maximization, Lagrangian 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of of utility multiplier, Indirect Utility delivering the basic skills notes handout maximization and lagrangian function, Roy’s to understand Utility multiplier Identity, Derivation of Slutsky’s maximization function equation, Slutsky’s Equation in elasticity form, Compensated demand curve Different forms of Utility Function—Separable, quasi- linear, homogeneous and homothetic Labour-leisure choice Output maximization, Cost 15 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of output minimization, Homogeneous and delivering the basic skills notes handout maximization , CES production homothetic to understand the concept production functions, Elasticity of of output maximisation substitution, CES production function, Relationship between average cost and marginal cost 2.2 Factor demand curves, output elasticity, Analysis of firms in competitive equilibrium and monopoly, imposition of taxes 2.3 Analysis of factor demands in the long run 2.4 Fixed coefficient production functions, Leontief Input-Output system. Two person matrix games, 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of game strategies solving matrix games with mixed delivering the basic skills notes handout strategies to understand game theory Sequential Games and Decisions n-period utility maximization, 5 Time preference, Stocks and flows Uncertainty and Probability, State 5 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of probability and preference approach for delivering the basic skills notes handout uncertainty preferences to understand probability 5.2 Expected Utility Hypothesis, and uncertainty Risk aversion and its measures. Generalisation to n variables: 10 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of FOC and SOC First and Second order conditions delivering the basic skills notes handout 6.2 Profit maximisation: n factors to understand and Utility Maximisation macroeconomic model 6.3 National Income Model, IS- LM Model 6.2 Simple Trade Models Cobweb Model 20 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of cobweb model 7.2 Multiplier-Accelerator delivering the basic skills notes handout Interaction Model to understand Cobweb 7.3 Linear Systems via Eigen theorem values 7.4 Solution of linear systems by substitution 7.5 Phase diagrams of linear systems 7.6 Solow model Paper VIIIA: Indian Economic History
Economic condition in India on 3 the eve of British rule Land policy 25 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of land policy 2.2 Policy of Discriminating delivering the basic skills notes handout Protection to understand land policies 2.3 Early Industrial Development . and Managing Agency System 2.4 Currency and monetary policy 2.5 Infrastructure and Transport Deindustrialisation 25 This module aims at Interactive session/ Knowledge of 3.2 Commercialisation of delivering the basic skills notes handout deindustrialization agriculture to understand 3.4 Economic Drain deindustrialization. Early Economic planning 2 initiatives during British rule Paper VIIIB : Term Paper 15 Knowledge of Practical Application