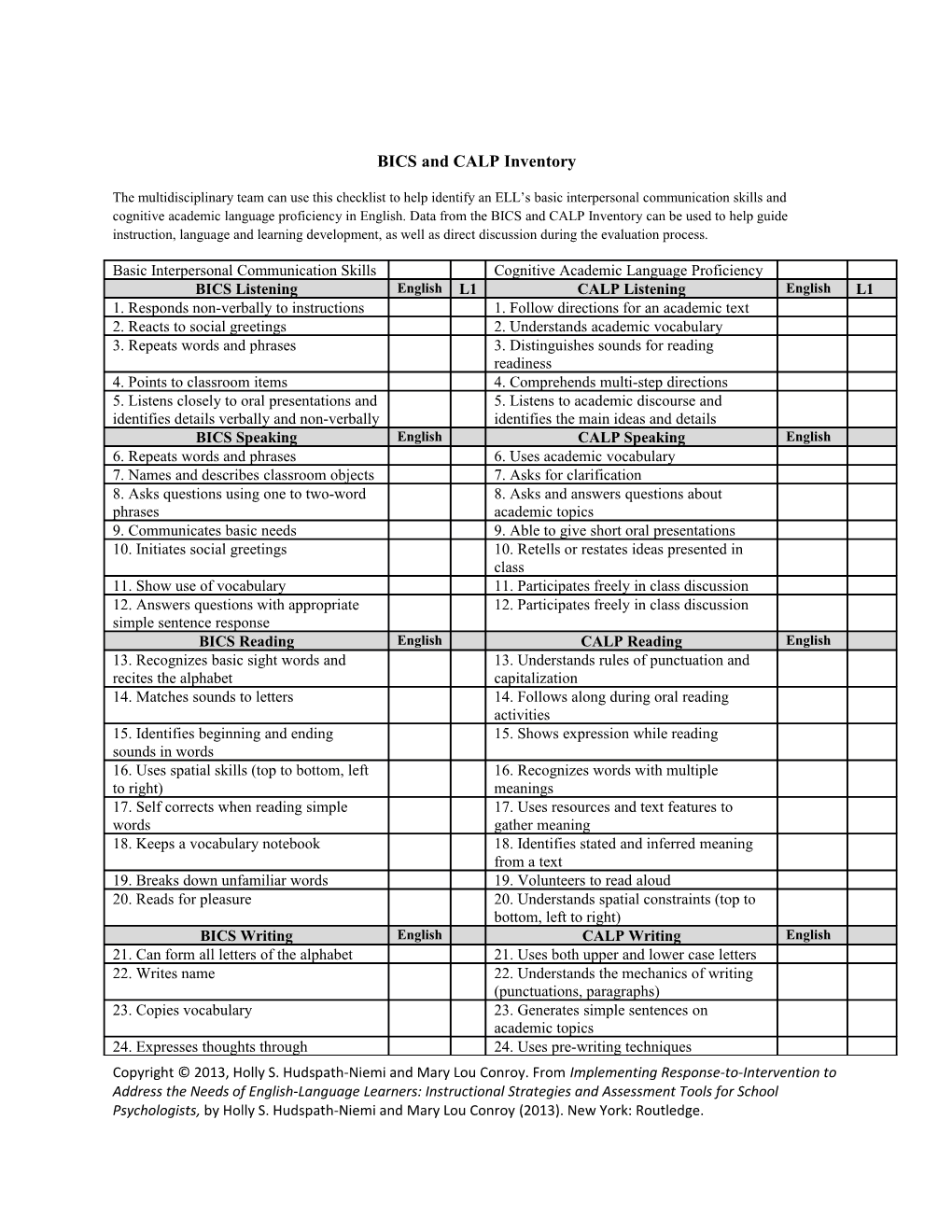
BICS and CALP Inventory
The multidisciplinary team can use this checklist to help identify an ELL’s basic interpersonal communication skills and cognitive academic language proficiency in English. Data from the BICS and CALP Inventory can be used to help guide instruction, language and learning development, as well as direct discussion during the evaluation process.
Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency BICS Listening English L1 CALP Listening English L1 1. Responds non-verbally to instructions 1. Follow directions for an academic text 2. Reacts to social greetings 2. Understands academic vocabulary 3. Repeats words and phrases 3. Distinguishes sounds for reading readiness 4. Points to classroom items 4. Comprehends multi-step directions 5. Listens closely to oral presentations and 5. Listens to academic discourse and identifies details verbally and non-verbally identifies the main ideas and details BICS Speaking English CALP Speaking English 6. Repeats words and phrases 6. Uses academic vocabulary 7. Names and describes classroom objects 7. Asks for clarification 8. Asks questions using one to two-word 8. Asks and answers questions about phrases academic topics 9. Communicates basic needs 9. Able to give short oral presentations 10. Initiates social greetings 10. Retells or restates ideas presented in class 11. Show use of vocabulary 11. Participates freely in class discussion 12. Answers questions with appropriate 12. Participates freely in class discussion simple sentence response BICS Reading English CALP Reading English 13. Recognizes basic sight words and 13. Understands rules of punctuation and recites the alphabet capitalization 14. Matches sounds to letters 14. Follows along during oral reading activities 15. Identifies beginning and ending 15. Shows expression while reading sounds in words 16. Uses spatial skills (top to bottom, left 16. Recognizes words with multiple to right) meanings 17. Self corrects when reading simple 17. Uses resources and text features to words gather meaning 18. Keeps a vocabulary notebook 18. Identifies stated and inferred meaning from a text 19. Breaks down unfamiliar words 19. Volunteers to read aloud 20. Reads for pleasure 20. Understands spatial constraints (top to bottom, left to right) BICS Writing English CALP Writing English 21. Can form all letters of the alphabet 21. Uses both upper and lower case letters 22. Writes name 22. Understands the mechanics of writing (punctuations, paragraphs) 23. Copies vocabulary 23. Generates simple sentences on academic topics 24. Expresses thoughts through 24. Uses pre-writing techniques Copyright © 2013, Holly S. Hudspath-Niemi and Mary Lou Conroy. From Implementing Response-to-Intervention to Address the Needs of English-Language Learners: Instructional Strategies and Assessment Tools for School Psychologists, by Holly S. Hudspath-Niemi and Mary Lou Conroy (2013). New York: Routledge. illustrations 25. Write one to two word response 25. Writes short paragraphs 26. Uses models to write sentences 26. Performs editing tasks 27. Writes familiar words and sentences 27. Revises feedback without prompting
Developed from: Berhard and Loera, (1992); California Department of Education, (1981); Erickson and Omark, (1981); Krashen and Terrel, (1983)