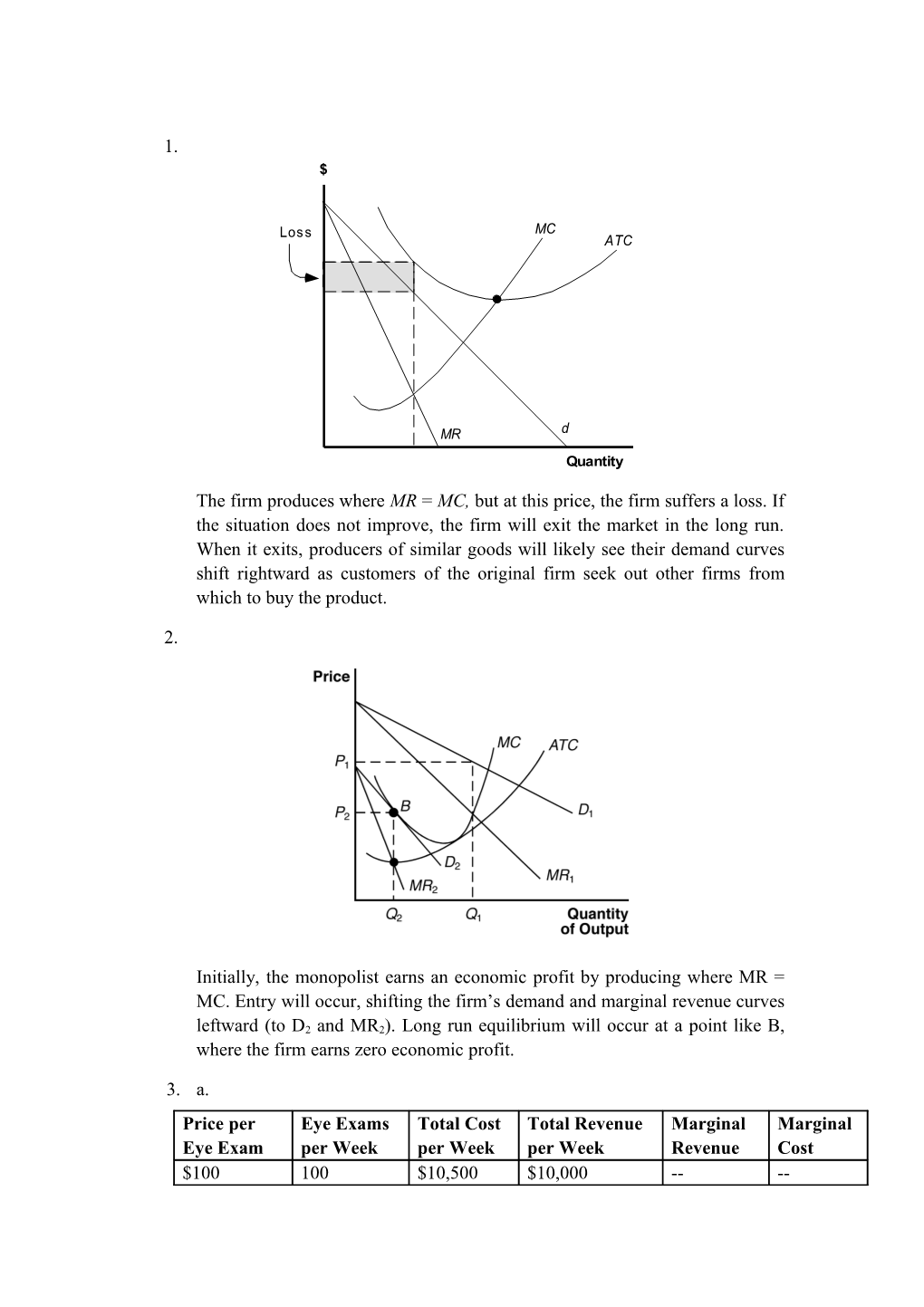
1. $
Loss MC ATC
MR d Quantity
The firm produces where MR = MC, but at this price, the firm suffers a loss. If the situation does not improve, the firm will exit the market in the long run. When it exits, producers of similar goods will likely see their demand curves shift rightward as customers of the original firm seek out other firms from which to buy the product.
2.
Initially, the monopolist earns an economic profit by producing where MR = MC. Entry will occur, shifting the firm’s demand and marginal revenue curves
leftward (to D2 and MR2). Long run equilibrium will occur at a point like B, where the firm earns zero economic profit.
3. a. Price per Eye Exams Total Cost Total Revenue Marginal Marginal Eye Exam per Week per Week per Week Revenue Cost $100 100 $10,500 $10,000 -- -- $30 $7.50 $80 140 $10,800 $11,200 $13.33 $8.33 $60 200 $11,300 $12,000 $3.64 $9.00 $40 310 $12,290 $12,400 -$5.83 $10.29 $20 550 $14,760 $11,000
b. An optometry practice might face a downward sloping demand curve if it could differentiate its product through location, hours of operation, ambiance, quality of service, or frame selection. c. The profit-maximizing price is $60 and the profit-maximizing number of eye exams per week is 200.
4. a. Price per Taco plates Total Cost Total Marginal Marginal Taco Plate per Week per Week Revenue per Revenue Cost Week $5 50 $30 $250 $2.33 $0.67 4 80 $50 $320 $1.86 $1.80 3 150 $176 $450 $1.77 $2.00 2 800 $1476 $1600 -$1.67 $2.20 1 1100 $2136 $1100
Tino should expand his output as long as MR exceeds MC. His profit- maximizing price is $3 and his profit-maximizing number of taco plates is 150.
b. Tino’s customers will substitute away from Tino’s tacos towards food from his competitor. Demand for Tino’s tacos will fall, and Tino’s profits will fall. c. Price per Taco plates Total Cost Total Marginal Marginal Taco Plate per Week per Week Revenue per Revenue Cost Week $5 60 $130 $300 $2.33 $0.55 4 96 $150 $384 $1.86 $1.50 3 180 $276 $540 $1.76 $1.66 2 960 $1576 $1920 -$1.67 $1.83 1 1320 $2236 $1320
Tino’s profit-maximizing price is $2, and his profit-maximizing number of taco plates is 960. Since Tino earns an economic profit of $344 with this combination, entry will occur until Tino’s economic profit falls to $0.
5. [Note: The question actually refers to Problem #3, not Problem #2.] He should not shut down in the short run, because he is covering his average variable costs (P = $60, AVC = $56.50).
6. a. $
MC ATC
MR d
Quantity
The typical plastics firm produces the output level where MC = MR, charges the corresponding price given by the demand curve, and earns zero economic profit. b.
Oil is a variable input, so when oil prices increase, the ATC curve and the MC curve at all firms shift upward. In the short run, the typical plastics firm suffers economic losses. c. If prices remained high, and profits remained negative, some firms would exit. Other firms would experience a rightward shift of their demand curves, and in long-run equilibrium, the remaining firms would earn zero economic profit. 7. a.
b.