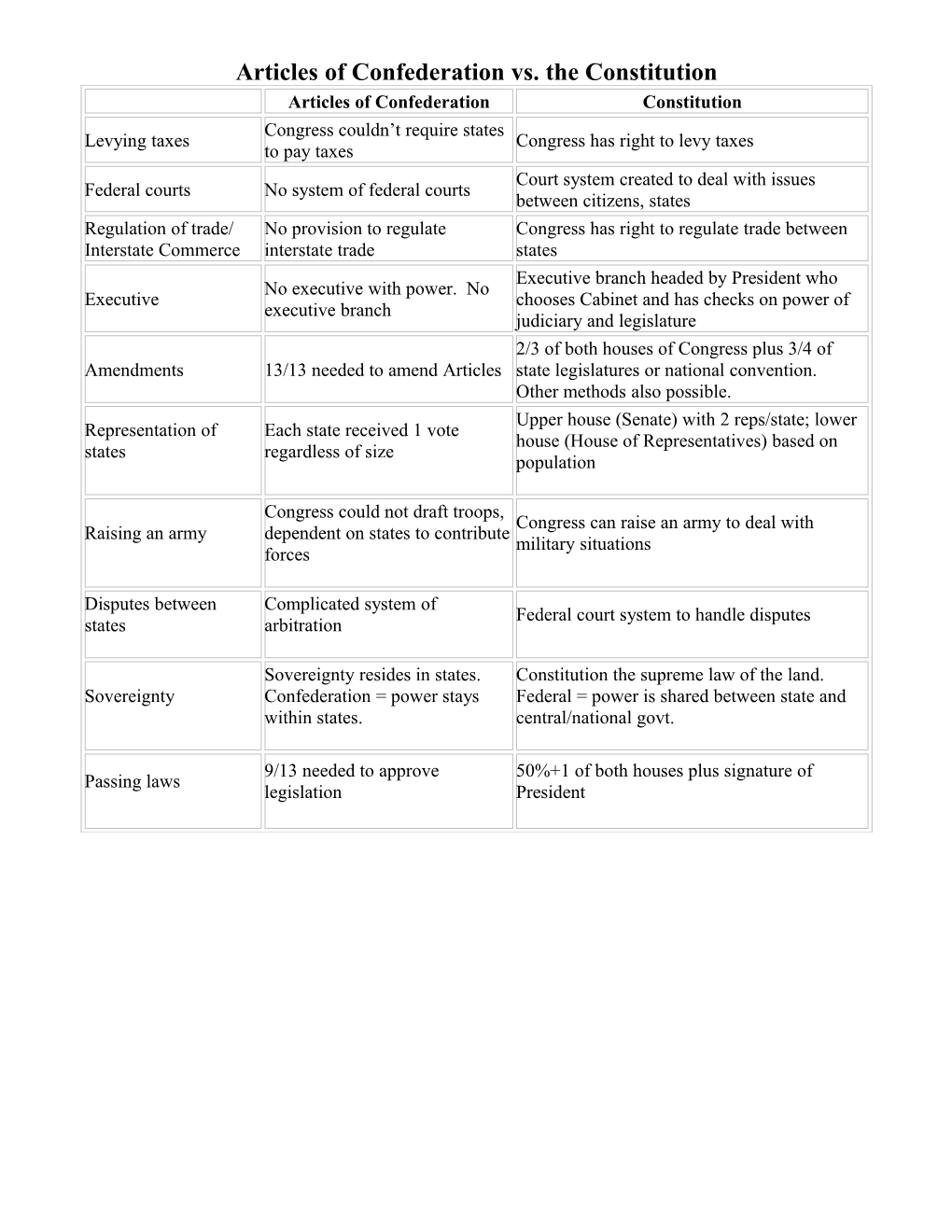
Articles of Confederation vs. the Constitution Articles of Confederation Constitution Congress couldn’t require states Levying taxes Congress has right to levy taxes to pay taxes Court system created to deal with issues Federal courts No system of federal courts between citizens, states Regulation of trade/ No provision to regulate Congress has right to regulate trade between Interstate Commerce interstate trade states Executive branch headed by President who No executive with power. No Executive chooses Cabinet and has checks on power of executive branch judiciary and legislature 2/3 of both houses of Congress plus 3/4 of Amendments 13/13 needed to amend Articles state legislatures or national convention. Other methods also possible. Upper house (Senate) with 2 reps/state; lower Representation of Each state received 1 vote house (House of Representatives) based on states regardless of size population
Congress could not draft troops, Congress can raise an army to deal with Raising an army dependent on states to contribute military situations forces
Disputes between Complicated system of Federal court system to handle disputes states arbitration
Sovereignty resides in states. Constitution the supreme law of the land. Sovereignty Confederation = power stays Federal = power is shared between state and within states. central/national govt.
9/13 needed to approve 50%+1 of both houses plus signature of Passing laws legislation President
Consider the following:
- The United States and individual states owed money to individual foreigners and foreign nations = war debts. Without the power to tax, there was little way to pay back these debts = bad international reputation.
- The Treaty of Paris required that Loyalist property, much of which had been confiscated during the war, be returned to its owners. The national/central government under the Articles of Confederation did not have the power to enforce this.
- 14 forms of currency = all basically worthless paper (not backed by gold/silver = hard money). - Tariffs existed for each individual state – and often against products being “imported” from other states!
- Boundary disputes – especially in Northwest Territory.
- B/c of weaknesses and lack of respect, foreign nations tried to take advantage of U.S. o The British did not leave forts on the western frontier for many years, b/c the U.S. had little means to force them out. o The Spanish were also trying to take advantage of the U.S. by expanding their influence in the territory beyond the Mississippi River. . This territory HAD been owned by the French, but was sold to the Spanish in 1762. The territory was then sold back to the French in 1800 (Napoleon), and finally sold to the United States in the Louisiana Purchase in 1803.