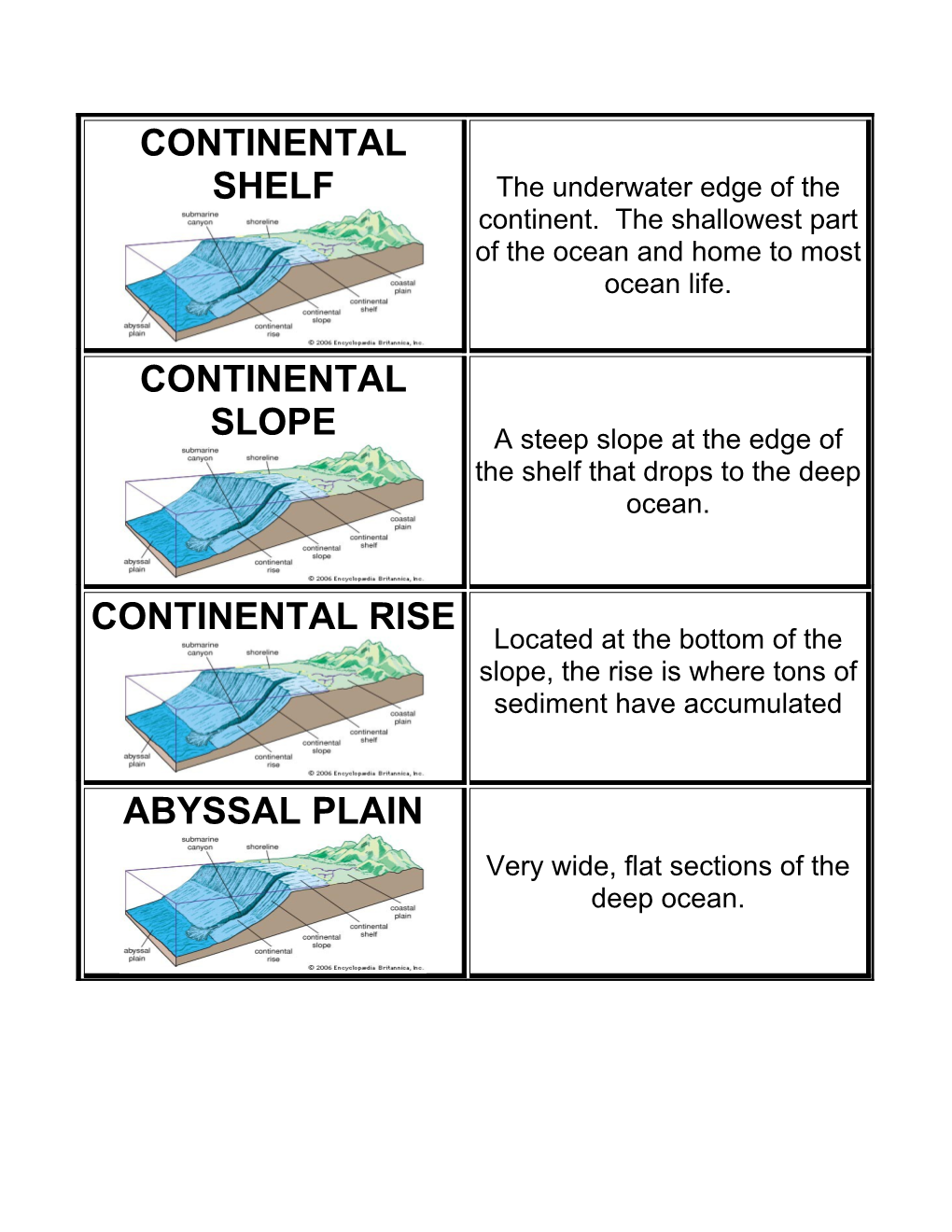
CONTINENTAL SHELF The underwater edge of the continent. The shallowest part of the ocean and home to most ocean life.
CONTINENTAL SLOPE A steep slope at the edge of the shelf that drops to the deep ocean.
CONTINENTAL RISE Located at the bottom of the slope, the rise is where tons of sediment have accumulated
ABYSSAL PLAIN Very wide, flat sections of the deep ocean. TRENCHES The deepest areas of the ocean. They are long canyon- like features that occur at subduction zones.
CURRENT
A body of water moving very quickly in a definite direction.
GULF STREAM One of the seven major global currents. It carries huge volumes of warm water north along the east coast of the United States. SALINITY The amount of salt in water. Salinity in water is a factor in creating some currents.
DENSITY The amount of mass packed into a space DEPTH A measure of how deep a body of water is.
WAVES Caused by the friction of wind blowing across the water’s surface.
TIDES Tides are the rise and fall of ocean of ocean water caused mainly by the Moon’s gravity.
SUNLIGHT ZONE Surface down to 200 meters. The sun’s rays and nutrients in the water make this the best zone for life.
TWILIGHT ZONE 200 meters to 1000 meters. The sun’s light grows faint. Many of the animals here swim up to the sunlight zone to eat after dark. MIDNIGHT ZONE 1000 meters to 4000 meters. No light and crushing pressure. Creatures here are adapted for this environment.
ABYSSAL ZONE 4000 meters to 6000 meters. It has crushing pressure and near freezing temperatures. Few creatures live here.
TRENCH WATER There is not much life here, but what is here is amazing. Here the food source is bacteria and chemicals.
PHYTOPLANKTON Is it a plant or an animal? Tiny plant-like organisms that form the base of the ocean food web and provide much of the Earth’s oxygen. ZOOPLANKTON Tiny animal-like organisms that also are an important part of the food web.