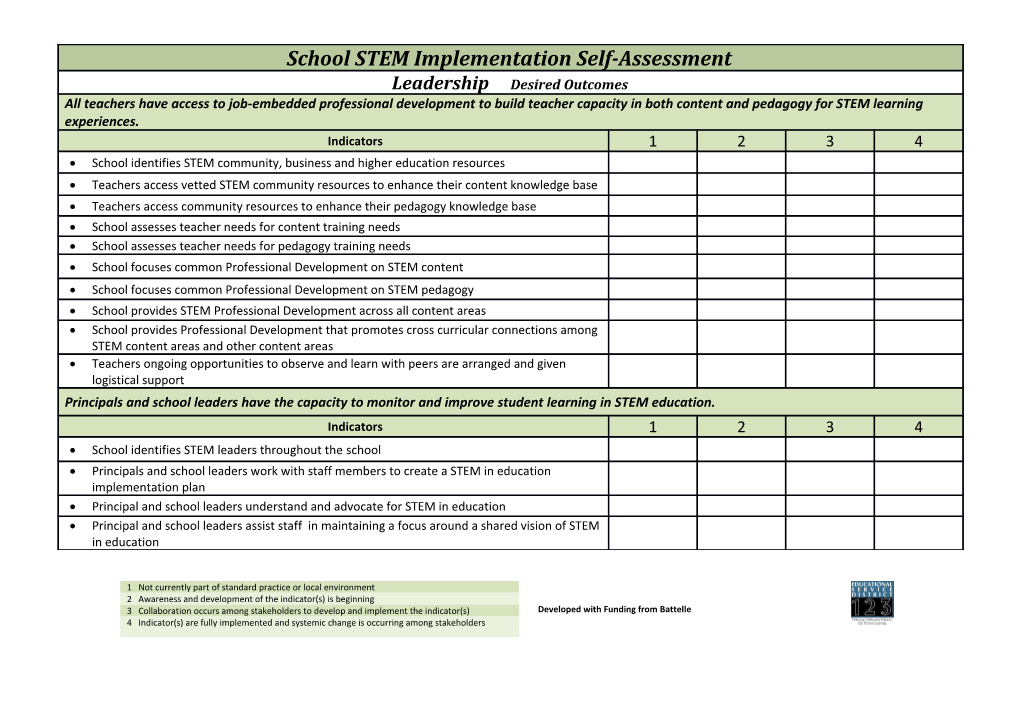
School STEM Implementation Self-Assessment Leadership Desired Outcomes All teachers have access to job-embedded professional development to build teacher capacity in both content and pedagogy for STEM learning experiences. Indicators 1 2 3 4 School identifies STEM community, business and higher education resources Teachers access vetted STEM community resources to enhance their content knowledge base Teachers access community resources to enhance their pedagogy knowledge base School assesses teacher needs for content training needs School assesses teacher needs for pedagogy training needs School focuses common Professional Development on STEM content School focuses common Professional Development on STEM pedagogy School provides STEM Professional Development across all content areas School provides Professional Development that promotes cross curricular connections among STEM content areas and other content areas Teachers ongoing opportunities to observe and learn with peers are arranged and given logistical support Principals and school leaders have the capacity to monitor and improve student learning in STEM education. Indicators 1 2 3 4 School identifies STEM leaders throughout the school Principals and school leaders work with staff members to create a STEM in education implementation plan Principal and school leaders understand and advocate for STEM in education Principal and school leaders assist staff in maintaining a focus around a shared vision of STEM in education
1 Not currently part of standard practice or local environment 2 Awareness and development of the indicator(s) is beginning 3 Collaboration occurs among stakeholders to develop and implement the indicator(s) Developed with Funding from Battelle 4 Indicator(s) are fully implemented and systemic change is occurring among stakeholders The school supports the expansion of innovative K-12 schools and/or K-12 program models based on STEM themes. Indicators 1 2 3 4 School identifies innovative program models in schools School leaders and school board members actively work to develop promote, support, evaluate, and recognize STEM in education School leadership routinely communicates to the community about STEM in education School supports structures that promotes authentic STEM learning STEM opportunities and experiences are provided with a focus on minority, high-poverty, and underserved communities. Indicators 1 2 3 4 School partners with community resources and afterschool programs to engage underrepresented populations in STEM experiences. School leverages higher education resources that provide services to underserved communities. School uses community role models and mentors to engage underrepresented populations in STEM in education.
1 Not currently part of standard practice or local environment 2 Awareness and development of the indicator(s) is beginning 3 Collaboration occurs among stakeholders to develop and implement the indicator(s) Developed with Funding from Battelle 4 Indicator(s) are fully implemented and systemic change is occurring among stakeholders Teaching and Learning Desired Outcomes Schools provide engaging, advanced STEM related academic and Career & Technical Education programs of study. Indicators 1 2 3 4 Students and teachers interact through hands-on learning in cross curricular projects Teachers have access to high quality, research based instructional strategies and materials Teachers use high quality research based instructional strategies and materials Programs of study are connected to regional STEM partners and offer real life applications and relevance Accelerated, rigorous and relevant courses are available to every student (e.g. Advanced Placement, International Baccalaureate) Career certification programs that lead to dual credits in high school and college are available to every student Schools provide adequate instruction time in mathematics and science content areas. Indicators 1 2 3 4 Schools facilitate teacher interactions to foster cross-curricular lesson development (e.g. teaching teams, planning meetings, etc.) Schools leverage time by emphasizing the integration of content areas Mathematics, Science, and Career & Technical Education courses of study and materials are rigorous and research and standards-based. Indicators 1 2 3 4 Instruction is problem and inquiry based that asks students to apply their learning Instructional materials and practices are aligned to the most current standards available Enrichment and intervention support is embedded into the course of study Course work offers opportunities to exceed the standards
1 Not currently part of standard practice or local environment 2 Awareness and development of the indicator(s) is beginning 3 Collaboration occurs among stakeholders to develop and implement the indicator(s) Developed with Funding from Battelle 4 Indicator(s) are fully implemented and systemic change is occurring among stakeholders Mathematics, science, and CTE content are delivered through engaging, high-quality, authentic instruction. Indicators 1 2 3 4 Delivered instruction is aligned with intended curriculum Inquiry and questioning are embedded in instructional strategies Formative assessment process is an integral part of STEM instruction Clear and explicit integration occurs among all content areas in a structure that makes sense within the context of learning
Standards-based assessments and grading are incorporated into the instructional framework for the school. Indicators 1 2 3 4 Classroom assessments are aligned to the standards, the instructional curriculum and the classroom instruction School has adopted and implemented a standards-based grading policy Culturally relevant activities and strategies for English Language Learners (ELL) are integrated into the mathematics and science classroom. Indicators 1 2 3 4 Students of all demographics have equal access to content and materials in the classroom Teachers use a variety of strategies for grouping and organizing students to accommodate learning styles Teachers connect to student’s background and life experiences
Teachers emphasize vocabulary acquisition and retention in all STEM courses
1 Not currently part of standard practice or local environment 2 Awareness and development of the indicator(s) is beginning 3 Collaboration occurs among stakeholders to develop and implement the indicator(s) Developed with Funding from Battelle 4 Indicator(s) are fully implemented and systemic change is occurring among stakeholders Community Awareness and Partnerships Desired Outcomes Community members are able to identify attributes and outcomes of STEM education. Indicators 1 2 4 Community members can identify STEM occupations, activities, professionals and opportunities within their community Community members recognize the value of STEM education beyond a particular career path Every parent and student understands that STEM in education is essential regardless of their student’s career choices. Indicators 1 2 4 All students and parents have the opportunity to engage in discussions about STEM- related academic opportunities and STEM literacy within the P-16 education system Every student has adequate academic and career guidance Curriculum and support engages all students and their families Every student has the opportunity to take the appropriate middle and high school courses to prepare him/her for successful participation in STEM-related pathways The school has partnerships with businesses, community organizations and higher education. Indicators 1 2 4 School identifies and communicates areas in which community and professional STEM support is needed or could be complementary to classroom objectives Stakeholders are providing and/or supporting P-12 STEM activities Local businesses and community partners engage in advisory committees, especially in underrepresent ed populations Businesses, community partners and higher education partner provide: * Extended day programs * STEM contests * Internships * Summer programs Businesses and community partners provide professional development and opportunities for teachers to return to industry to enhance their skills Businesses, community partners and higher education support and provide authentic, project-based learning opportunities for all students and teachers Businesses, community partners and higher education support innovative partnerships with private industries and apprenticeship programs 1 Not currently part of Developed with Funding standard practice or local from Battelle environment 2 Awareness and development of the indicator(s) is beginning 3 Collaboration occurs among stakeholders to develop and implement the indicator(s) 4 Indicator(s) are fully implemented and systemic change is occurring among stakeholders