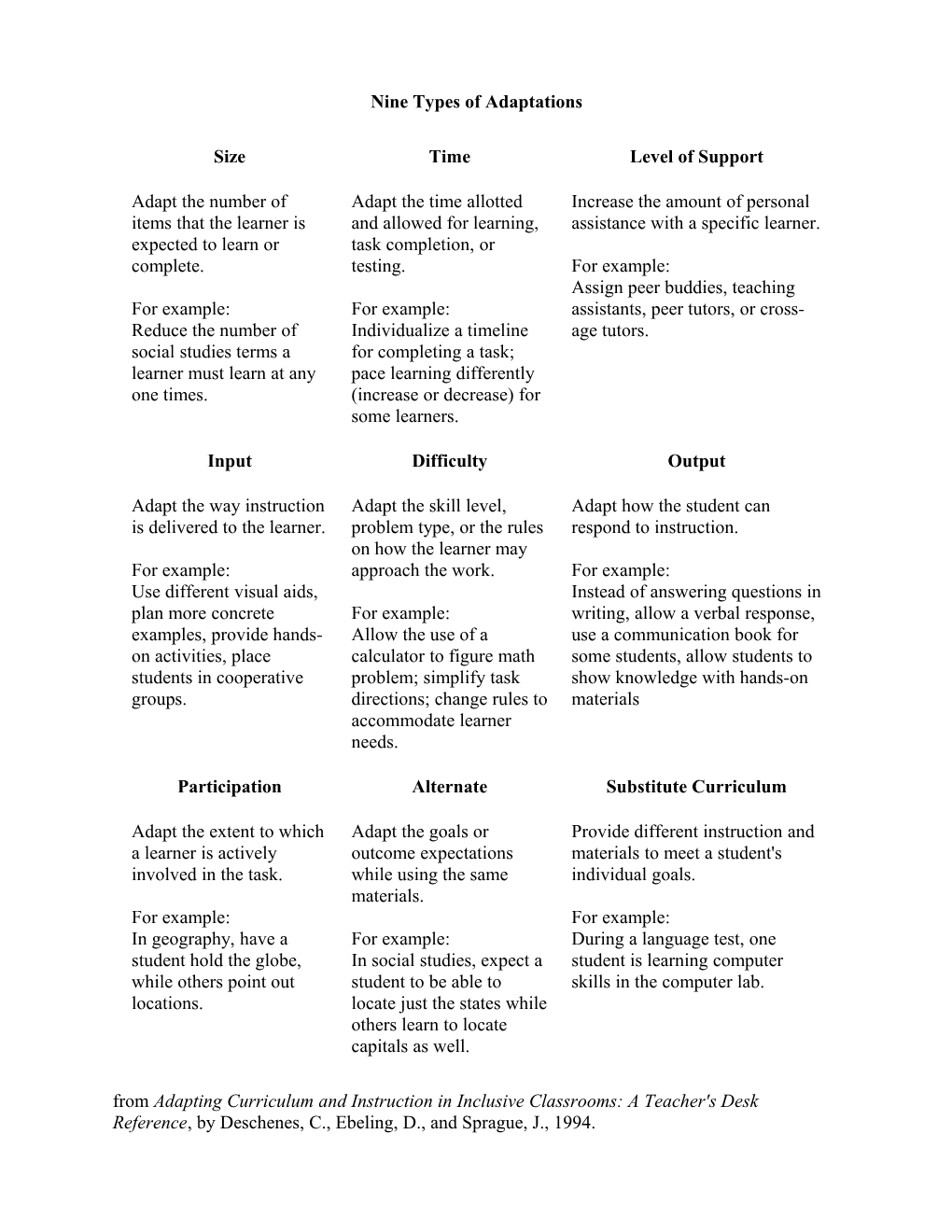
Nine Types of Adaptations
Size Time Level of Support
Adapt the number of Adapt the time allotted Increase the amount of personal items that the learner is and allowed for learning, assistance with a specific learner. expected to learn or task completion, or complete. testing. For example: Assign peer buddies, teaching For example: For example: assistants, peer tutors, or cross- Reduce the number of Individualize a timeline age tutors. social studies terms a for completing a task; learner must learn at any pace learning differently one times. (increase or decrease) for some learners.
Input Difficulty Output
Adapt the way instruction Adapt the skill level, Adapt how the student can is delivered to the learner. problem type, or the rules respond to instruction. on how the learner may For example: approach the work. For example: Use different visual aids, Instead of answering questions in plan more concrete For example: writing, allow a verbal response, examples, provide hands- Allow the use of a use a communication book for on activities, place calculator to figure math some students, allow students to students in cooperative problem; simplify task show knowledge with hands-on groups. directions; change rules to materials accommodate learner needs.
Participation Alternate Substitute Curriculum
Adapt the extent to which Adapt the goals or Provide different instruction and a learner is actively outcome expectations materials to meet a student's involved in the task. while using the same individual goals. materials. For example: For example: In geography, have a For example: During a language test, one student hold the globe, In social studies, expect a student is learning computer while others point out student to be able to skills in the computer lab. locations. locate just the states while others learn to locate capitals as well. from Adapting Curriculum and Instruction in Inclusive Classrooms: A Teacher's Desk Reference, by Deschenes, C., Ebeling, D., and Sprague, J., 1994.