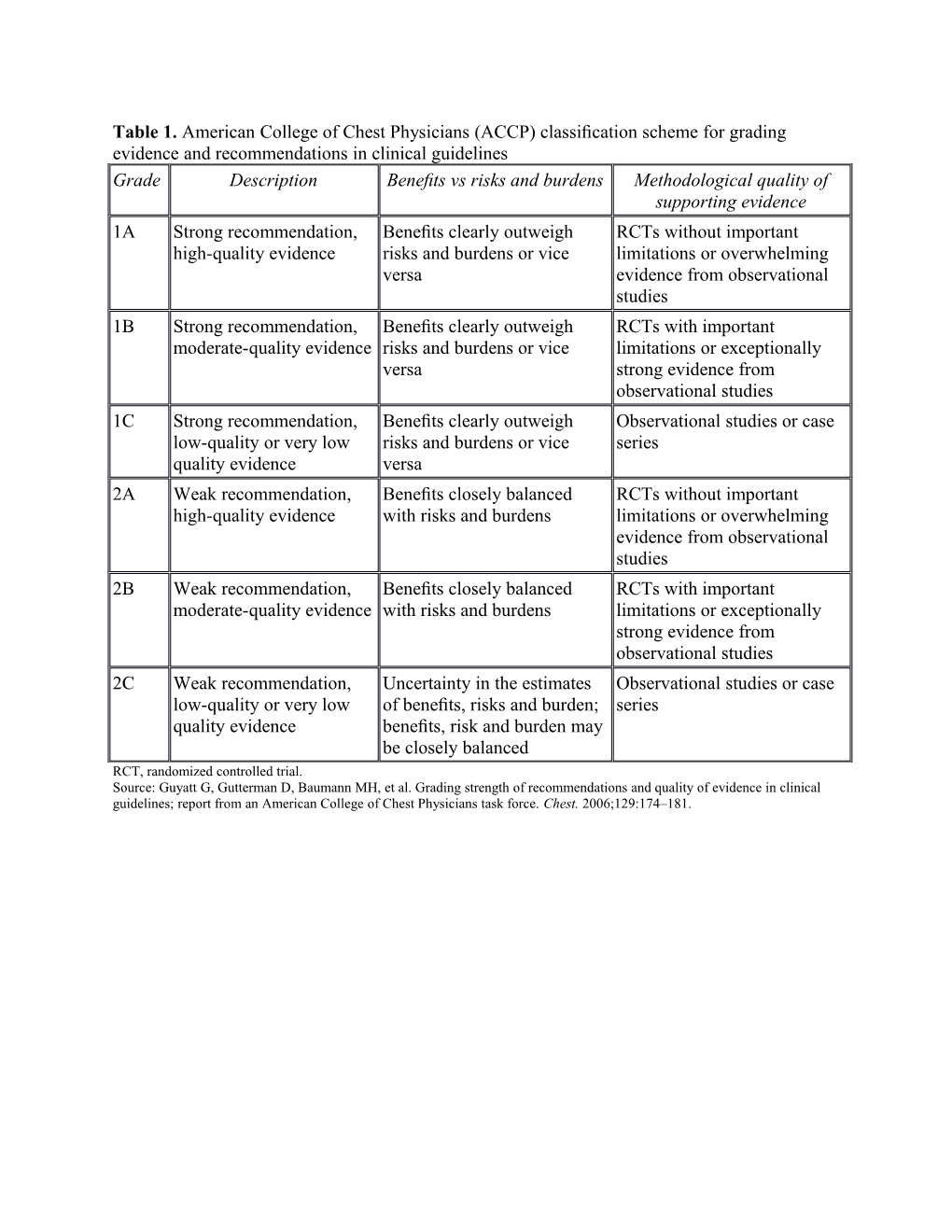
Table 1. American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) classification scheme for grading evidence and recommendations in clinical guidelines Grade Description Benefits vs risks and burdens Methodological quality of supporting evidence 1A Strong recommendation, Benefits clearly outweigh RCTs without important high-quality evidence risks and burdens or vice limitations or overwhelming versa evidence from observational studies 1B Strong recommendation, Benefits clearly outweigh RCTs with important moderate-quality evidence risks and burdens or vice limitations or exceptionally versa strong evidence from observational studies 1C Strong recommendation, Benefits clearly outweigh Observational studies or case low-quality or very low risks and burdens or vice series quality evidence versa 2A Weak recommendation, Benefits closely balanced RCTs without important high-quality evidence with risks and burdens limitations or overwhelming evidence from observational studies 2B Weak recommendation, Benefits closely balanced RCTs with important moderate-quality evidence with risks and burdens limitations or exceptionally strong evidence from observational studies 2C Weak recommendation, Uncertainty in the estimates Observational studies or case low-quality or very low of benefits, risks and burden; series quality evidence benefits, risk and burden may be closely balanced RCT, randomized controlled trial. Source: Guyatt G, Gutterman D, Baumann MH, et al. Grading strength of recommendations and quality of evidence in clinical guidelines; report from an American College of Chest Physicians task force. Chest. 2006;129:174–181. Supplementary Evidence Table 2. AMS/HACE Prevention Studies (listed in alphabetical order by first author)
Reference Setup Intervention Outcomes Overall assessmen t of quality Setting/ Eligibility Interventi Primary Sample Numbers Effect size Study criteria ons outcome size (primary design measure outcomes) Basnyat Prospecti Healthy Subjects Composit 222 Low dose: Composit A et al. ve non-Nepali randomiz e subjects 74 e randomize Aceta- double- subjects 18- ed to incidence enrolled; subjects; incidence d trial zolamide blind 65 years receive and 204 High dose: of AMS showing 125 mg randomiz old, with no acetazola severity subjects 82 24% in that low BD is not ed acute mide 125 of AMS (88%) subjects; low dose dose significan controlled infection, mg BID measured complete placebo: group vs. acetazola tly trial of history of (low by Lake d the 66 and 21% mide is as different trekkers cardiac, dose), Louise study subjects. in high effective from 375 ascending pulmonary acetazola Score protocol. dose as higher mg BD in between or other mide 375 (AMS group and doses with the 3440 m chronic mg BID defined 51% in fewer side preventio and 4928 diseases; (high as LLS≥3 placebo effects. n of acute m. and who dose) or including group. No Groups mountain (Khumbu had not placebo. headache significant are well sickness: Valley, slept above and at difference matched the Nepal) 2700 m or least one between and those prophylac taken other the low lost to tic acetazolami symptom and high follow-up acetazola de in ). dose had mide previous 2 Composit groups similar dosage weeks. e results regarding demograp comparis reflect AMS hics to on for patients scores but study efficacy reporting the high subjects. (PACE) AMS at dose The study trial. either the group had is limited High Alt midpoint more by Med Biol or parasthesi recruitme 2006. 1 endpoint as than the nt of assessme low-dose subjects at nts. group. 3440 m and loss of those who might develop AMS below that elevation. Beidlema Prospecti Healthy Over 30 AMS-C 11 11 Statisticall Rigorous n BA et ve, lowland days scores, subjects subjects y study with al. Effect unblinded residents following resting completed significant careful of six , non- without assessme end-tidal the study decrease control of days of randomiz exposure to nts in the CO2, protocol. in AMS experimen staging ed cross- >1500 m hypobaric arterial scores at tal on over for at least 2 chamber blood 4300 m conditions physiolog study months. (acute gases, following . Aided by ic examinin ascent), oxygen staged the fact adjustmen g subjects saturation ascent that ts and AMS-C spent 6 , heart compared subjects acute scores days at rate and to acute served as mountain and terrestrial mean ascent in a their own sickness physiolog 2200 m arterial hypobaric controls. during ic before pressure. chamber Questions ascent to parameter ascending (p<0.005). remain 4300 m. s to End-tidal about the High Alt following terrestrial and feasibility Med Biol acute 4300 m arterial of this 2 2009. exposure (staged CO2 were strategy to 4300 m ascent). lower and for AMS in a Two hour oxygen preventio hypobaric submaxi saturation n for chamber mal was many high and bicycle higher at altitude following ergometry 4300 m sojourners ascent to performe following . terrestrial d after staged 4300 m resting ascent after 6 assessme than with days of nts acute staging at complete ascent. 2200 m. d in the Resting (Pikes hypobaric heart rate Peak, chamber and mean Colorado) and at arterial terrestrial pressure high did not altitude. change in any of the test conditions . Bloch KE Prospecti Healthy Subjects AMS-C 34 Slow Higher This is the et al. ve, individuals randomiz scores climbers ascent: 16 AMS only Effect of randomiz with prior ed to assessed climbers; scores in randomize ascent ed mountaineer ascent at 5533 Fast “fast” d study protocol controlled ing exper- protocols m, 6265 ascent: 18 ascent examining on acute trial ience. calling m, 6865 climbers. group at the effect mountain examinin Excluded for m and each of ascent sickness g the individuals reaching 7546 m, evaluation rate on and effect of with cardiac the and point AMS success ascent or summit number (P<0.008) incidence. on rate on respiratory after 15 of . Climbers The Muztagh acute disease, (fast) or proceedin in the groups Ata, 7546 mountain regular use 19 (slow) g slow were well m. High sickness of any days of climbers. ascent matched, Alt Med score medications climbing. group but bad Biol during an or prior were able weather 2004. 3 expeditio history of to ascend interfered n to 7546 severe AMS according with pre- m . below 3500 to defined (Muztagh m, HAPE or protocol ascent Ata, HACE without protocols China) AMS for such that more days mean and were ascent more rates to successful the at summit reaching were the similar for highest the two camp at groups. 6865 m The without authors AMS than accounted climbers for the in the fast ascent ascent protocols group. in their analysis. Chow et Prospecti Unacclimati Subjects Lake 70 Ginkgo: Median Randomiz al. ve zed adult randomiz Louise subjects 17 LLS score ed Ginkgo double- volunteers ed to AMS 2 subjects; lower in controlled biloba blind (18-65 Ginkgo scores excluded Acetazola acetazola design. and randomiz years old) 120 mg and for mide: 20 mide The study acetazola ed whose po BID, incidence residence subjects; group was mide controlled primary acetazola of AMS above Placebo: than underpow prophylax trial residence mide 250 (diagnosi 1200 m; 20 placebo ered to is for comparin was ≤1200 mg po s 10 subjects. group but find 50% acute g Ginkgo m. BID or required withdrew not in relative mountain biloba Exclusions placebo headache before Ginkgo reduction sickness: and included BID plus at ascent; 1 group. in a acetazola travel to starting 5 least one withdrew AMS incidence randomiz mide in >2400 m days other after occurred of AMS, ed, the within 30 before symptom ascent. less but placebo- preventio days, ascent. and total frequently median controlled n of AMS contraindica The score in the AMS trial Arch with tions to high acetazola ≥3). acetazola scores Intern ascent altitude mide mide were Med from sea exposure, group group significant 2005. 4 level to pre-existing received (30%) ly 3800 m. use of placebo than in the different (White ginkgo for the 1st placebo between Mountain biloba or 4 days. group acetazola s, acetazola- (65%) mide and California mide. whereas placebo ) there was and no essentially difference the same between for Ginkgo Ginkgo group compared (60%) and to the placebo. placebo A useful group. strategy in this study in that Ginkgo used by subjects was obtained as most high altitude travelers would obtain it, by purchasin g from a chain suppleme nt store. Ellsworth Prospecti Healthy Subjects Combine 47 Acetazola At summit Small et al. A ve volunteer randomiz d climbers mide: 15 or high study with randomiz double- who resided ed to abbreviat subjects point well ed trial of blind at or near receive ed Dexameth achieved, matched dexameth randomiz sea level acetazola version a-sone: 17 dexameth groups. 9 asone and ed trial of and who mide 250 of ESQ subjects asone subjects, 6 acetazola acetazola lacked mg po, and a Placebo: group had of whom mide for mide and history of dexameth “General 15 less were acute dexameth peptic ulcer asone 4 High- subjects. headache taking mountain asone in … or mg po or Altitude and dexameth sickness the psychi-atric placebo Question several asone prophylax preventio disease. every 8 naire other spent an is Am J n of AMS hours modified symptoms extra day Med in beginning post-hoc than at 3000 m, 1987. 5 climbers 24 hours to placebo which ascending before exclude (p<0.05). may have to 4392 m ascent. confound Acetazola affected . (Mt. ing mide acclimatiz Rainier, symptom patients ation. Washingt s had AMS on) (primaril nausea measure y nausea and was caused fatigue at modified by lower post hoc. acetazola elevations Although mide (1300- the study prior to 1600 m) was ascent). that likely blinded obscured 57% of prophylact acetazola ic effects. mide With group, exclusion 24% of of dexameth subjects asone with group and acetazola 64% of mide side placebo effects at group low guessed elevations study drug , correctly. acetazola mide had similar magnitude benefit on symptoms as dexameth asone. Ellsworth Prospecti Climbers Subjects AMS-C 18 Acetazola AMS-C Small et al. ve making randomiz (cerebral) climbers mide: 8 and AMS- study but Aceta- randomiz separate ed to and subjects R scores subjects zolamide ed, ascents to receive AMS-R Dexameth and served as or double- 4392 m at acetazola (respirato asone: 10 incidence their own dexameth blind, least two mide 250 ry) scores subjects of AMS controls asone use placebo- weeks apart. mg po, from the Each while with the versus controlled Subjects dexameth Environ climber taking groups placebo crossover normally asone 4 mental received dexameth well to prevent trial resided at mg po or Symptom placebo on asone matched acute examinin sea level, placebo s their other were for age, mountain g role of had no every 8 Question climb. significant gender, sickness dexameth exposure to hours on naire. ly lower previous on Mount asone and high 2 separate than for ascents of Rainier acetazola altitude ascents of acetazola Mt. West J mide in within 3 Mt. mide Rainier Med preventio weeks of Rainier (p=0.025) and past 1991.6 n of AMS study, were starting and history of in free of 24 hours placebo AMS. climbers cardiorespir before (p=0.025). Unclear making atory ascent 8 of 10 why two disease, and subjects in acetazola ascents to diabetes, continuin dexameth mide 4392 m. sulfa g until asone lacked (Mt. allergy, descent. group benefit in Rainier, peptic ulcer Each preferred this study Washingt disease or climber the drug compared on) psych-iatric received climb to to earlier illness. placebo the study by on 1 placebo this group ascent climb on Mt. and one compared Rainier of the to only but may study three of reflect drugs on eight small the other subjects in sample ascent. the size, large Order of acetazola standard drug mide deviations versus group. of AMS placebo scores, was and the random. fact that acetazola mide side effects are similar to symptoms of AMS.
Forwand Prospecti Healthy Subjects Symptom 43 male Aceta- Headache One of the et al. ve male randomiz s as subjects zolamide: frequency earliest Effect of double- soldiers ed to assessed 21 and randomize acetazola blind without receive by 2 subjects; severity d trials on mide on randomiz recent acetazola questionn Placebo: were less this issue. acute ed disease or mide 250 aires and 22 in the Group mountain controlled history of mg po physician subjects. acetazola demograp sickness trial of serious pul- TID or s’ daily mide hics are N Engl J acetazola monary placebo histories; group on not Med mide in disease. for 32 arterial days 1-5 document 1968. 7 the hours blood at 3900 m. ed, but are preventio before gases. Upper- likely well n of AMS and 40 gastrointe matched in hours stinal tract in the two subjects after symptoms groups. transporte rapid and Study d rapidly transport insomnia populatio from sea to 3900 were less n is level to m. in the narrow 3900 m. acetazola and limits mide generaliza group on bility of days 1-3 the results and 2-3 but respective subsequen ly. t studies Acetazola in broader mide populatio treated ns have patients shown had similar greater benefit. increase in ventilation and alveolar oxygen tension and greater decrease in carbon dioxide and bicarbonat e than controls.
Gertsch et Prospecti Healthy Subjects Incidence 614 Ginkgo In Very large al. ve non-Nepali randomiz and trekkers biloba: intention trial but Randomis double- trekkers 18- ed to severity enrolled. 124 to treat 21% of ed, blind 65 yrs of receive of AMS 487 subjects; analysis, enrolled double randomiz age. Ginkgo (defined complete acet- incidence participan blind, ed, Excluded if biloba as Lake d the azolamide: of AMS ts broke placebo placebo they had 120 mg Louise study. 118 was 34% protocol controlled controlled known po, Score ≥3 subjects; in placebo or were comparis trial cardiac, acetazola with aceta- group, lost to on of examinin pulmonary mide 250 headache zolamide 12% in follow-up. ginkgo g use of or other mg po, and at + ginkgo acetazola Groups, biloba Ginkgo chronic ginkgo least 1 biloba: mide including and biloba disease, biloba other 126 group the group acetazola and AMS, 120 mg symptom subjects; (OR that did mide for acetazola significant po + ). placebo: compared not preventio mide for active acetazola 119 to placebo complete n of acute preventio infection or mide 250 subjects. 3.76), the study, mountain n of AMS had slept mg po or 35% in were sickness in above 4500 placebo Ginkgo similar in among trekkers m or used twice biloba age, sex Himalaya during Ginkgo daily. group and ascent n ascent biloba or (OR 0.95, profiles. trekkers: between acetazolami P=NS) Adequatel the 4280 or de in prior and 14% y powered preventio 4358 m two weeks. in to detect n of high and 4928 acetazola statisticall altitude m. mide + y illness (Khumbu Ginkgo significant trial Valley, biloba difference (PHAIT) Nepal) group between BMJ (OR groups at 2004. 8 3.04). expected Incidence incidence of severe of AMS. AMS The study (LLS ≥ 5) is limited significant by ly lower recruitme than nt of placebo in subjects at acetazola 4280 or mide and 4358 m acetazola and loss mide + of those Ginkgo who biloba might groups but develop not lower AMS than below placebo in those the ginkgo elevations biloba . group.
Gertsch et Prospecti Healthy Subjects Incidence 343 Intent to No Large trial al. ve, non-Nepali randomiz of subjects treat difference with Prospecti double- trekkers 18- ed to headache recruited; analysis: in groups ve, blind, 65 yrs of receive assessed 265 acetazola incidence well double- randomiz age. acetazola by Lake subjects mide: 97 of matched blind, ed Excluded if mide 85 Louise provided subjects; headache for age, randomiz placebo they had mg po, Question data at ibuprofen: between sex. Study ed, controlled any ibuprofen naire; endpoint 103 ibuprofen had a placebo- trial headache, 600 mg headache of study. subjects and large controlled comparin diagnosis of po or severity 48 Placebo: acetazola incidence comparis g use of AMS or placebo assessed participa 65 mide of on of ibuprofen significant three by visual nts subjects. (27.5 % protocol acetazola and acute times analog deviated vs. violations mide acetazola infection, daily. scale; from 27.1%); and versus mide for had slept > Subjects incidence study Headache authors ibuprofen preventio 4500 m or took three of AMS. protocol incidence had to for n of high taken doses at and were lower in rely on prophylax altitude NSAIDs or baseline excluded both intent to is against headache acetazolami before from groups treat high and AMS de in prior 3 resuming intent to than in analysis. altitude in days. trek. treat placebo; The study headache: trekkers analysis. Headache is limited the ascending severity by Headache between no recruitme Evaluatio 4280 or different nt of n at 4358 m between subjects at Altitude and 4928 ibuprofen, 4280 or Trial m. acetazola 4358 m (HEAT) (Khumbu mide and and loss Wilderne Valley, placebo of those ss Nepal) groups. who Environ No might Med difference develop 2010. 9 in AMS incidence below of AMS those between elevations ibuprofen or those and who acetazola might mide have used (13.7% ibuprofen vs. 18.8%, at lower p=NS). elevations .
Gertsch et Prospecti Healthy, Subjects Incidence 295 For intent In intent Large trial al. ve, non-Nepali randomiz and subjects to treat to treat with Altitude double- trekkers 18- ed to severity recruited; analysis: analysis; groups Sickness blind, 65 yrs of receive of AMS 183 Ibuprofen: incidence well in randomiz age. ibuprofen (defined complete 123 of AMS matched Climbers ed Excluded if 600 mg as Lake d the subjects less with for age, and placebo they had po TID or Louise study. 62 Placebo: ibuprofen sex and Efficacy controlled known placebo. Score ≥3 lost to 109 than with ascent of trial AMS, Subjects with follow- subjects. placebo profile. NSAIDs examinin significant took three headache up and (24% vs. The study Trial g use of active doses at and at 49 broke For 40% had a high (ASCEN ibuprofen infection or baseline least 1 trial analysis p=0.01). dropout T): for had slept before other protocol. excluding rate (21%) randomiz preventio above 4500 resuming symptom 232 those who In and ed, n of AMS m or used trek. ). participa broke analysis benefit controlled in ibuprofen or nts protocol: of only seen trial of trekkers acetazolami included Ibuprofen: participant in intent ibuprofen ascending de in prior 3 in intent 110 s who to treat versus between days. to treat subjects completed analysis. placebo 4280 or analysis. Placebo: the study, The study for 4358 m 73 incidence is limited preventio and 4928 subjects. of AMS by n of m. was not recruitme altitude (Khumbu significant nt of illness Valley, ly subjects at Wilderne Nepal) different 4280 or ss between 4358 m Environ ibuprofen and loss Med and of those 2012. 10 placebo who (17% vs. might 25% develop p=0.13) . AMS below Participan those ts who elevations broke or those protocol who had higher might incidence have used of AMS ibuprofen than fully at lower compliant elevations subjects. . No compariso n with acetazola mide.
Hackett Retrospec “Unacclima Trekkers AMS 330 Survey For Important PH et al. tive study tized – who symptom question data: 117 overall early The of hikers” had either score ≥2 naires trekkers study study on a incidence, trekkers going above trekked (study distribute walked population major importanc traveling Pheriche. from predates d. 278 from , trekking e, and through Kathman Lake complete Kathmand incidence circuit. prophylax 4243 m. du or first Louise d and u; 161 of AMS Although is of acute (Khumbu flew to Score). included trekkers was 42% limited by mountain Valley, Lukla in the flew to in those lack of sickness Nepal) (2800 m) analysis. 2800 m. who informatio Lancet -- were 52 of 330 trekked n 1976.11 administe (16%) Prevention from regarding red lost to trial: Kathmand how well questionn follow- Acetazola u versus matched aires in up. mide: 71 60% in the Pheriche. subjects; those who subjects Subjects Placebo: flew to were in were 49 Lukla each advised subjects; (p<0.001). group, the on how to Control: In control effect avoid 158 group (no sizes were AMS. subjects. medicatio large and Subsegme ns) 47% clearly nt of of establishe study trekkers d the populatio from benefit of n also Kathmand slow participat u ascent. ed in a developed Study prospecti AMS vs. results are ve 85% of affected randomiz those who by ed trial of flew to selection AMS Lukla bias as preventio (p<0.01). subjects n, Lowest who receiving incidence turned either of AMS back acetazola (14%) before mide (250 was in Pheriche mg po those who are not BID) or flew to included placebo. Lukla and in the Those took analysis. taking no acetazola tablets mide labeled as (p<0.01). controls.
Lipman et Prospecti Healthy 18- Subjects Incidence 89 Ibuprofen: Fewer Small al. ve 65 yr old randomiz and subjects 44 participant study with Ibuprofen double- volunteers ed to severity recruited. subjects: s in the groups prevents blind residing at receive of AMS All Placebo: ibuprofen well altitude randomiz <1240 m ibuprofen (defined complete 42 group matched illness: a ed without 600 mg as Lake d study subjects. developed for age randomiz placebo recent po or Louise but 3 AMS sex and ed controlled altitude placebo Score ≥3 excluded compared home controlled trial exposure. TID with post hoc with the altitude. trial for examinin Excluded if starting 6 headache by placebo Study preventio g use of they had hours and at predeter group (43 powered n of ibuprofen history of before least 1 mined vs. 69%; to detect altitude for HACE or ascent. other criteria. OR 0.3, reduction illness preventio HAPE, symptom number in AMS with n of AMS were ). needed to of 20%. nonsteroi individual pregnant, treat: 3.9). Ibuprofen dal anti- s had been > AMS did not inflammat ascending 1240 m in severity achieve ories Ann from past week was also the Emerg 1240 m to or had used higher in determine Med 3810 m. NSAIDs, the d 2012. 12 (White steroids or placebo clinically Mountain acetazolami group . significant s, de in week difference California prior to (> 2 ) study. points) in Lake Louise score relative to placebo. No compariso n with acetazola mide.
Moraga et Prospecti University Subjects Incidence 50 Acetazola Incidence Small al. ve students randomiz of AMS subjects mide: 12 of AMS study with Ginkgo double- residing at ed to (defined screened. subjects; lower groups biloba blind sea level. receive as Lake Thirteen Ginkgo with well decreases randomiz Exclusion EGb761 Louise excluded biloba: 12 Ginkgo matched acute ed, criteria: (Ginkgo Score > for prior subjects; biloba for age, mountain controlled previous biloba) 80 3) ; altitude Placebo: (0%) than weight, sickness trial experience mg po or oxygen exposure 12 acetazola height and in people comparin ≥1500 m, acetazola saturation and 2 subjects. mide BMI. ascending g Ginkgo history of mide 250 . excluded (36% Total LLS to high biloba seizure or mg po or for p<0.05) score and altitude at and recent pneu- placebo seizure and constituen Ollague acetazola monia. every 12 and placebo t scores (3696 m) mide for hours recent (56% by in preventio starting pneumon p<0.05). symptoms northern n of AMS 24 hours ia. 36 Incidence are Chile during before participa with reported Wilderne and after ascent nts (all acetazola as mean ± ss ascent to and male) mide SD rather Environ 3696 m continuin made the lower than than as Med (Ollagüe, g for 3 ascent. placebo total AMS 2007.13 northern days at (p<0.05); scores. Chile) 3696 m. Oxygen 0% saturation incidence with in Ginkgo ginkgo biloba biloba group similar to seems too that seen low to be with a true acetazola result, mide but particularl higher y in than compariso placebo. n to rates seen in other studies. Roncin et Prospecti Male Subjects AMS 44 Ginkgo Subjects Small al. EGb ve, expedition randomiz score by subjects biloba: 22 receiving study with 761 in randomiz members ed to ESQ subjects; Ginkgo well- control of ed double with history receive (AMS-C Placebo: biloba had matched acute blind, of AMS Ginkgo and 22 a lower groups. mountain placebo- during a biloba 80 AMS-R). subjects. incidence The sickness controlled previous mg po of altitude Ginkgo and trial expedition BID or illness group had vascular examinin (based on placebo. compared 2 current reactivity g role of AMS score to placebo and 3 ex- to cold EGb761 > 2). subjects smokers, exposure (Ginkgo when while the Aviat biloba) on assessed placebo Space preventio by AMS- group was Environ n of AMS C scores all non- Med 1996 in (0% smokers. .14 subjects versus ascending 41%, to 5400 m p=0.0014) .(Nepal) and AMS-R scores (14% vs. 82%, p<0.001). van Patot Prospecti Healthy Subjects Incidence 44 Acetazola Lower Although et al. ve subjects randomiz and subjects mide: 22 incidence a small Prophylac double- residing ed to severity subjects of AMS in study tic low- blind, between receive of AMS Placebo: the compared dose randomiz 1400 and acetazola based on 22 acetazola to trials in acetazola ed 1600 m. mide 125 AMS-C subjects mide Nepal, the mide controlled Exclusions mg PO score and group groups reduces trial of included BID or Lake (14% vs. were well the low-dose pregnancy, placebo, Louis 45%, matched incidence acetazola history of starting 3 Score. p=0.02). and the and mide in cardiac/pul days prior AMS AMS-C effect severity preventio monary to ascent, diagnosis and Lake sizes are of acute n of AMS disease and based on Louise large. All mountain with (except continuin AMS-C scores subjects sickness ascent asthma), g for 24 ≥ 0.7 and were were High Alt from alcohol hours at LLS ≥ 3 lower in residents Med Biol 1600 m to consumptio high plus acetazola of 2008.15 4300 m n <24 h altitude. presence mide moderate over 2 prior to of group. altitude, hours. ascent, headache which is a (Pikes current viral . difference Peak, illness or from other Colorado) travel above trials. 2000 m within past 2 weeks.
Abbreviations AMS Acute Mountain Sickness AMS-C cerebral AMS score AMS-R respiratory AMS score ESQ Environmental Symptom Questionnaire OR odds ratio 1. Basnyat B, Gertsch JH, Holck PS, et al. Acetazolamide 125 mg BD is not significantly different from 375 mg BD in the prevention of acute mountain sickness: the prophylactic acetazolamide dosage comparison for efficacy (PACE) trial. High Alt Med Biol. 2006;7(1):17-27. 2. Beidleman BA, Fulco CS, Muza SR, et al. Effect of six days of staging on physiologic adjustments and acute mountain sickness during ascent to 4300 meters. High Alt Med Biol. 2009;10(3):253-260. 3. Bloch KE, Turk AJ, Maggiorini M, et al. Effect of ascent protocol on acute mountain sickness and success at Muztagh Ata, 7546 m. High Alt Med Biol. 2009;10(1):25-32. 4. Chow T, Browne V, Heileson HL, Wallace D, Anholm J, Green SM. Ginkgo biloba and acetazolamide prophylaxis for acute mountain sickness: a randomized, placebo- controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(3):296-301. 5. Ellsworth AJ, Larson EB, Strickland D. A randomized trial of dexamethasone and acetazolamide for acute mountain sickness prophylaxis. Am J Med. 1987;83(6):1024- 1030. 6. Ellsworth AJ, Meyer EF, Larson EB. Acetazolamide or dexamethasone use versus placebo to prevent acute mountain sickness on Mount Rainier. West J Med. 1991;154(3):289-293. 7. Forwand SA, Landowne M, Follansbee JN, Hansen JE. Effect of acetazolamide on acute mountain sickness. N Engl J Med. 1968;279(16):839-845. 8. Gertsch JH, Basnyat B, Johnson EW, Onopa J, Holck PS. Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled comparison of ginkgo biloba and acetazolamide for prevention of acute mountain sickness among Himalayan trekkers: the prevention of high altitude illness trial (PHAIT). BMJ. 2004;328(7443):797. 9. Gertsch JH, Lipman GS, Holck PS, et al. Prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled comparison of acetazolamide versus ibuprofen for prophylaxis against high altitude headache: the Headache Evaluation at Altitude Trial (HEAT). Wilderness Environ Med. 2010;21(3):236-243. 10. Gertsch JH, Corbett B, Holck PS, et al. Altitude Sickness in Climbers and Efficacy of NSAIDs Trial (ASCENT): randomized, controlled trial of ibuprofen versus placebo for prevention of altitude illness. Wilderness Environ Med. 2012;23(4):307-315. 11. Hackett PH, Rennie D, Levine HD. The incidence, importance, and prophylaxis of acute mountain sickness. Lancet. 1976;2(7996):1149-1155. 12. Lipman GS, Kanaan NC, Holck PS, Constance BB, Gertsch JH. Ibuprofen prevents altitude illness: a randomized controlled trial for prevention of altitude illness with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. Ann Emerg Med. 2012;59(6):484-490. 13. Moraga FA, Flores A, Serra J, Esnaola C, Barriento C. Ginkgo biloba decreases acute mountain sickness in people ascending to high altitude at Ollague (3696 m) in northern Chile. Wilderness Environ Med. 2007;18(4):251-257. 14. Roncin JP, Schwartz F, D'Arbigny P. EGb 761 in control of acute mountain sickness and vascular reactivity to cold exposure. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1996;67(5):445-452. 15. van Patot MC, Leadbetter G, 3rd, Keyes LE, Maakestad KM, Olson S, Hackett PH. Prophylactic low-dose acetazolamide reduces the incidence and severity of acute mountain sickness. High Alt Med Biol. 2008;9(4):289-293.
Supplementary Table 3. AMS/HACE Treatment Studies (listed in alphabetical order by first author)
Reference Setup Intervention Outcomes Overall assessmen t of quality Setting/ Eligibility Interventi Primary Sample Numbers Effect Study criteria ons outcome size size design measure (primary outcomes) Bärtsch, Randomi Ascent by One hour AMS-C 71 High Oxygen High P., et al. zed foot to of score, mountain pressure: saturation quality Treatment control 4559 m, hyperbari clinical eers (35 31 rose to randomize of acute trial stayed at c score by in the first subjects; 90% d, mountain conducte altitude treatment interview season, 36 Low during controlled sickness d over for 12 hrs, at a and in the pressure: hyperbari study with by two and signs pressure physical second) 23 c relatively simulated seasons of AMS of 193 examinatio subjects treatment large descent: a assessing (defined mbar n and (23 mbar but sample randomise the as (equivale oxygen in first returned size d effectiven headache nt to saturation season, 16 to 72% demonstra controlled ess of and an descent of assessed mbar in after 12 ting trial BMJ hyperbari additional 2250 m) before, second hrs. No limited 1993. 1 c therapy symptom). or a immediate season); changes temporal at 4559 m Individual pressure ly after Bed rest: were seen benefit of (Capanna s with of 23 and 12 hrs 10 (Seven in oxygen hyperbari Margherit signs or mbar after patients saturation c a, Italy) symptoms (equivale treatment were in treatment. of HAPE nt to 300 excluded controls. The effect or who m) in the due to AMS-C of had taken first inadverten scores repeated aceta- season t treatment and treatments zolamide (16 mbar at the clinical was not or (equivale wrong scores assessed. nifedipine nt to a pressure) were The were descent of decreased control excluded. 200 m) or in the groups bed rest hyperbari were were used c therapy treated controls group differently in the relative to between second pre- the two season.) treatment seasons in levels which the immediat study was ely conducted following but the treatment small (p<0.005) difference but in returned administer to levels ed comparab pressures le to the is likely controls of little after 12 clinical hrs. significan ce.
Ferrazzini Randomi Climbers Dexameth AMS 35 Dexameth The AMS Randomiz , G. et al, zed, planning asone (8 symptom climbers asone: 17 symptom ed, Successfu double- to stay the mg po score, patients; score placebo- l blind, night at followed oxygen Placebo: improved controlled treatment placebo 4559 m by 4mg saturation, 18 by 4.1 data of acute controlle with AMS po at 6 forced patients. points in showing mountain d trial of (> 3 and 12 vital the improvem sickness dexameth points on hrs) or capacity, dexameth ents in with asone in a scale placebo. forced asone AMS dexameth the incorporat expiratory group vs. symptoms asone. treatment ing volume in 0.4 points and BMJ of AMS symptoms one in the oxygen 1987. 2 at 4559 m and second, placebo saturation (Capanna clinical minute group following Margherit examinati ventilation (p<0.001) treatment a, Italy) on); , retinal . with Subjects vessel Saturation dexameth with frank diameter. improved asone. HAPE or Assessmen in the The study HACE t before dexameth has a were and 12-16 asone larger excluded. hrs after group sample receiving from 75.5 size than treatment. to 82% the study while the by placebo Grissom went from et al. 76.2 to There is 77.8 % little (p<0.01). insight Forced into the vital effect on capacity symptoms and more than forced 12-16 expiratory hours volume in after one treatment. second showed modest improvem ents in the treatment group while no difference s were observed in minute ventilatio n or retinal diameter.
Grissom, Randomi Climbers Acetazola AMS 12 Aceta- After 24 Randomiz CK et al. zed with mide 250 symptom climbers zolamide: hours, 5 ed, Acetazola double- symptoms mg po or questionna 6 patients of 6 placebo mide in blind, of AMS placebo ire score, Placebo: 6 patients in controlled the placebo as defined every 8 oxygen patients the data treatment controlle by a score hours. saturation, acetazola showing of acute d study of >2 on One forced mide the mountain assessing the AMS subject vital group had efficacy sickness: the symptom with capacity, scores < 2 of clinical efficacy questionn history of peak on the acetazola efficacy of aceta- aire. sulfa- expiratory AMS mide in and effect zolamide Climbers allergy flow, end- symptom the on gas in the were was tidal questionn treatment exchange. treatment included assigned carbon aire, of AMS Ann of AMS within 24 non- dioxide while all both in Intern at 4200 hours of randomly (ET-CO2), of the terms of Med m. the onset to the arterial placebo improving 1992. 3 (Mt. of placebo blood gas. group still symptoms McKinle symptoms group. Alveolar- had and y, and were arterial scores > shortening
Alaska) excluded oxygen 2. the time if they had difference Individual course of signs or was metrics the symptoms measured indicated disease. of HAPE for 3 that the The study or HACE patients in acetazola is limited or had the mide by the used treatment group small acetazola group and experienc sample mide all patients ed fewer size and within the in the symptoms the lack of previous placebo (p=0.097) control week. group. , higher for how PaO2 long (p=0.045) individual , and s spent lower reaching alveolar 4200 m. arterial There was oxygen no difference informatio (p=0.024) n . No provided significan regarding t symptom difference developm s were ent upon noted in ascent to PaCO2 higher (p=0.12) . elevation.
Hackett, Observati Participan All Examinati 11 Symptom Treatment PH, et al. onal ts subjects on (body soldiers s efficacy Dexameth study included who weight, received improved data asone for assessing active developed minute treatment within limited by preventio efficacy duty AMS in ventilation for AMS two the small n and of soldiers the , forced with treatment number of treatment dexameth who preventio vital dexameth doses subjects, of acute asone for developed n study capacity, asone. with eight lack of a mountain treatment AMS were peak subjects placebo sickness of AMS following administe expiratory no longer arm and Aviat at 4400m rapid red flow, meeting the fact Space Conducte transport dexameth oxygen AMS that Environ d in (< 1hr) asone 4 saturation) criteria. treated Med. conjuncti from sea mg po or and Oxygen soldiers 1988. 4 on with a level to intramusc symptom saturation did not randomiz 4400 m. ular every scores increased receive ed, The 6 hours. (self- from similar placebo- subjects report 73.1% to therapy in controlle were questionna 81.4% the d study participant ire, after 36 preceding looking at s in a environme hrs preventio the role study of ntal (p<0.05). n study. of dexameth symptom Peak Observed dexameth asone for questionna expiratory improvem asone in AMS ire, AMS- flow ent on AMS prophylax C and increased dexameth preventio is as part AMS-R). from asone did n. of their Measurem 495.5 to not seem (Mt. ascent to ents were 560 l/min to be McKinle 4400 m taken 12 at 36 attributabl y, were, hours after hours e to the Alaska) otherwise arrival and (p<0.01). self- healthy, every 24 With limiting took no hrs for cessation nature of other three days of AMS medicatio during the treatment given that n, and had treatment after 5 6 of the no travel trial. doses, one 11 to altitude soldier experienc in had a ed preceding return of symptom 3 wks. AMS rebound after 12 after hrs and stopping four had the drug. AMS by the second day off treatment.
Keller, Randomi Individual One hour Lake 31 Hyperbari After 1 Well HR, et al. zed trial s who hyperbari Louise climbers c therapy: hour, conducted Simulated comparin ascended c score, 15; portable , descent v g to 4559 m, treatment clinical Dexameth hyperbari randomize dexameth dexameth planned to (of 193 score, asone: 16. c therapy d trial asone in asone and stay mbar, AMS-C was with clear treatment simulated overnight equivalent score, and superior outcomes of acute descent had to descent oxygen to indicating mountain via clinical of 2250 saturation dexameth that sickness: portable score > 3 m) or oral before, 1 asone hyperbari a hyperbari for AMS. dexameth hr scores by c randomise c Patients asone following 2.1 points treatment d trial. chamber. with frank (8mg po and 11 hrs for the provides BMJ In clinical followed after Lake more 1995. 5 individua signs of by 4mg treatment. Louise immediate ls with HAPE po every score, 2.5 relief of acute were 6 hours). points for symptoms mountain excluded. the , while sickness clinical dexameth at 4559 score, and asone m. 0.7 points yields (Capanna for the more Margherit AMS-C enduring a, Italy) score. benefits. After 11 The hours, the experimen dexameth tal design asone did not treatment include was groups superior receiving to neither or pressuriza both tion by interventi 5.4 points ons. for Lake While Louise, dexameth 3.1 points asone for provided clinical more exam, and benefit 11 1.3 points hours for AMS- following C treatment, (p<0.001) the study . Oxygen did not saturation provide was 2% insight higher into the one hour overall following duration hyperbari of effect. c therapy compared to dexameth asone treatment while 11 hours after treatment, oxygen saturation was higher in the dexameth asone treated group (p<0.01) Levine, Randomi No Subjects Environme 6 male 5 subjects Dexameth This study BD et al. zed, specific exposed ntal volunteers developed asone had a Dexameth double- eligibility to symptoms started the AMS in improved rigorous asone in blind, criteria: hypobaric questionna study; 5 both AMS-C experimen the placebo subjects hypoxia ire developed decompres componen tal design treatment controlle were equivalent administer AMS and sion t score by with of acute d, cross healthy to 3700 m ed at were periods 63% thoroughl mountain over adult for 48 baseline included and (p<0.05) y assessed sickness study of volunteers hours on (600m), in the received after 12 patients NEJM the effect . two hypoxic analysis. both hrs but is 1989. 6 of occasions baseline dexametha compared limited by dexameth separated (3700m), sone and with a the small asone on by 4 and 4 placebo. 23% sample subjects weeks. times daily One improvem size. with Those during subject did ent in the Dexameth AMS in a individual hypobaric not placebo asone (4 hypobaric s hypoxia. develop group that mg every chamber developin Physical symptoms. was not 6 hours at (equivale g AMS assessment statisticall the onset nt altitude received involving y of 3700 m). dexameth psychomet significan symptoms asone (4 ric testing, t. No ) mg every cardiopul significan effectivel 6 hours or monary t y relieved placebo. monitoring difference symptoms , chest in oxygen of AMS. radiograph saturation y, or pulse respiratory rate was sleep found patterns, between and blood dexameth panels. asone and placebo.
Taber, Observati Patients All Symptom 25 AMS: 10 Improvem While this RL. onal presenting patients assessment patients patients; ent in observatio Protocols study of to a clinic received at 10-15 HAPE 9 symptoms nal study for the the time at 4240 m oxygen min patients; noted in shows use of course of with (when intervals in HACE : 6 all groups that portable portable HAPE or available) the bag patients. of hyperbari hyperbari hyperbari HACE and and after patients c therapy c c who could dexameth leaving the with leads to chambers treatment not be asone (8 bag. AMS symptom for the of evacuated mg IV/po patients improvem treatment patients to lower then 4 mg requiring ent in of high with elevation every 6 on AMS, altitude AMS as well as hr) as average 2 HAPE disorders. HAPE or patients indicated hours for and J of HACE at with by symptom HACE, Wildernes 4240 m. AMS. individual improvem methodol s (Pheriche AMS symptoms ent, ogical Medicine , Nepal) defined as in HAPE issues 1990. 7 headache, addition patients limit the nausea/vo to requiring conclusio miting and medicatio 4 hours ns that loss of ns taken and can be appetite; before HACE drawn HAPE arrival at patients 6 from the defined as the clinic. hours. study. In dyspnea at All addition rest, patients to the tachypnea then small and rales; received sample HACE portable sizes in defined as hyperbari each loss of c therapy group, the fine motor (~ 550 authors coordinati Torr for did not on, slurred varying control speech, durations) for events disorienta- . leading up tion and to clinic ataxia. presentati on such as amount of descent prior to clinic arrival and use of adjunctive medicatio ns. Monitorin g time for possible rebound after treatment also varied from case to case while not all patients received suppleme ntal oxygen. 1. Bärtsch P, Merki B, Hofstetter D, Maggiorini M, Kayser B, Oelz O. Treatment of acute mountain sickness by simulated descent: a randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 1993; 306:1098 –1101. 2. Ferrazzini G, Maggiorini M, Kriemler S, Bartsch P, Oelz O. Successful treatment of acute mountain sickness with dexamethasone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1987;294: 1380– 1382. 3. Grissom CK, Roach RC, Sarnquist FH, Hackett PH. Acetazolamide in the treatment of acute mountain sickness: clinical efficacy and effect on gas exchange. Ann Intern Med. 1992;116:461– 465. 4. Hackett PH, Roach RC, Wood RA, et al. Dexamethasone for prevention and treatment of acute mountain sickness. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1988;59:950 – 954. 5. Keller HR, Maggiorini M, Bartsch P, Oelz O. Simulated descent v dexamethasone in treatment of acute mountain sickness: a randomised trial. BMJ. 1995;310: 1232–1235. 6. Levine BD, Yoshimura K, Kobayashi T, Fukushima M, Shibamoto T, Ueda G. Dexamethasone in the treatment of acute mountain sickness. N Engl J Med. 1989;321: 1707–1713. 7. Taber RL. Protocols for the use of portable hyperbaric chambers for the treatment of high altitude disorders. J Wild Med. 1990;1:181–192. Supplementary Evidence Table 4. HAPE Prevention or Treatment Studies (listed in alphabetical order by first author)
Referenc Setup Intervention Outcomes Overall e Setting/ Eligibility Interventio Primary Sample Numbers Effect size assessment Study criteria ns outcome size (primary of quality design measure outcomes) Baggish Prospecti Healthy, Over 7 Pulmonary 10 10 Mean While this et al. The ve, young weeks artery subjects pulmonary high- impact of unblinded active duty following pressure completed artery quality moderate , non- military assessme measured the entire pressure at study -altitude randomiz males, nts in the by study 4300 m demonstrat staging ed cross- resident at hypobaric echocardio protocol. was lower es that on over low chamber -graphy following staged pulmonar study altitude (direct following staged ascent y arterial examinin ascent), direct ascent to decreases hemodyn g subjects ascent to 4300 m pulmonary amics pulmonar spent 7 4300 m compared vascular after y artery days at and 90 to direct responses ascent to pressure terrestrial minutes ascent to to acute high responses 2200 m and 4 days the same hypoxia, altitude. following before following elevation the study High Alt acute ascending staged (25 + 4 does not Med Biol exposure to ascent to mm Hg vs. provide 2010.1 to 4300 terrestrial the same 37 + 8 mm evidence m in a 4300 m elevation Hg). regarding hypobaric (staged Estimated prevention chamber ascent) pulmonary of HAPE and artery in known following pressure susceptible ascent to remained individuals terrestrial unchanged . The 4300 m after 4 optimal after 7 days of regimen days of high for staged staging at altitude ascent is 2200 m. residence. not clear (Pikes based on Peak, this study. Colorado ) Bärtsch Prospecti History of Affected Diagnosis 21 Nifedipine Only 10% Important P, et al. ve, radiograph individua of HAPE subjects group: 10 of subjects early, high
Preventio randomiz ically ls by SpO2, subjects; receiving quality n of high ed, documente received clinical Placebo nifedipine study in altitude placebo d HAPE nifedipin examinatio group: 11 developed HAPE- pulmonar controlle and e 20 mg n, and subjects HAPE, susceptible y edema d, double continued slow chest while 64% patients by blind alpine release radiograph of subjects that nifedipin study climbing preparati y. receiving demonstrat e. N Engl examinin after a on po or placebo ed J Med g prior placebo developed effective 19912 nifedipin episode of every 8 HAPE. prevention e in HAPE. hours Those of HAPE treatment starting subjects with of HAPE. the day receiving nifedipine Subjects before nifedipine by ascended ascent had lower lowering in less and pulmonary pulmonary than 22 during artery artery hours ascent to systolic pressure. from 4559 m pressure by 1130 m and for echocardio to 4559 three graphy and m. days lower Ascent following alveolar- by cable arrival at arterial car to 4559 m oxygen 3200 m, difference. then climbing for 1.5 hrs to 3611 m for overnight stay, then climbing for 4 hrs to 4559 m (Capanna Margherit a, Italy) Deshwal Open Indian Affected Time to 110 All Those Adjunctive R, et al. label soldiers individua normalizati Indian patients patients treatment Nifedipin randomiz diagnosed ls on of soldiers were treated with e for the ed trial with received oxygen with treated with nifedipine treatment examinin HAPE nifedipin saturation, HAPE. with nifedipine adds no of high g efficacy based on e 30 mg resolution descent, in addition incrementa altitude of Lake sustained of oxygen, to oxygen l benefit to pulmonar nifedipin Louise release radiographi and bed and bedrest HAPE y edema. e in Criteria. BID or c infiltrates rest. did not patients Wilderne treatment placebo. and have already ss for Treatmen resolution improved treated Environ individua ts were of lung outcomes. with Med ls with administe crepitation, descent 2012.3 HAPE red in an and and evacuated alternatin duration of oxygen. from a g manner hospital The study mean in stay. does not altitude addition allow any of 3,581 to oxygen conclusion m to a and bed s about the hospital rest for role of at 1,370 all nifedipine m and patients. in the treated treatment with of patients oxygen at who are 4-6 l/min unable to and bed descend rest and/or (India). receive supplemen tal oxygen.
Hackett Case HAPE Affected Change HAPE Oxygen All agents This study, PH, et al. series of diagnosed individua from subjects was reduced which is The treatment according ls baseline in : 16; administer pulmonary limited by effect of of HAPE to clinical received pulmonary Controls ed to 10 artery the lack of vasodilat with findings suppleme artery : 10 HAPE pressure, randomiza ors on oxygen, and ntal pressure subjects with the tion and pulmonar pulmonar hypoxemia oxygen, measured and 6 greatest unequal y y as assessed nifedipin by control effect seen number of hemodyn vasodilat by pulse e (10 mg echocardio subjects. with subjects in amics in ors, or oximetry. sublingua -graphy. Nifedipine combined each high both l), given to administrat treatment altitude conducte hydralazi 10 HAPE ion of group, pulmonar d on ne (10-20 subjects oxygen and demonstrat y edema: patients mg IV), and 6 phentolami es that a with phentola controls. ne. several comparis HAPE on mine Hydralazi pulmonary on. Int J Mt. (1mg/min ne was vasodilator Sports McKinle for 10 given to 3 s are Med y (4300 minutes HAPE effective 1992.4 m) or at a then 0.5 subjects. in Colorado mg/min Phentolam reducing ski resort for 20 ine was pulmonary (2835 m). minutes given to 6 artery IV), or HAPE pressure in phentola subjects HAPE. mine plus and 5 These oxygen. controls. agents should be considered as potential adjunctive therapy to supplemen tal oxygen. Leshem Open Healthy Subjects Developme Betwee Acetazola Incidence Limitation E, et al. label trekkers assigned nt of n 2006 mide only: of HAPE s to this Tadalafil study of attempting to receive severe high and 27 was study and tadalafil a summit either altitude 2009, subjects; significantl include a acetazola and of Tadalafil illness 68 Tadalafil y lower in non- mide acetazola Kiliman- 20 mg po defined as climbers plus the blinded versus mide in jaro. QD and HAPE or deemed acetazola tadalafil and non- acetazola HAPE acetazola HACE eligible mide: 24 plus randomize mide for preventio mide 125 diagnosed for subjects. acetazolam d study the n in mg po using study. 70% or ide group design. It preventio healthy BID or established 55 met participant than in the does not n of trekkers acetazola criteria inclusio s were acetazolam support severe climbing mide 125 (HAPE n male. ide only the use of high to 5895 mg po defined by criteria group (4.2 acetazola altitude m using BID the 1991 and 51 vs. 22.2%; mide for illness. J an beginning Internation complet p=0.03). HAPE Travel identical on day 3 al Hypoxia ed the All cases prevention Med 6 day of the Symposiu study of HAPE and should 2012.5 ascent ascent. m Criteria) protocol diagnosed be profile. Participa . on summit considered (Mt. nts were day. only as a Kilimanja allocated hypothesis ro, to either generating Africa). group study according supporting to their the need preferenc for a study e. comparing acetazola mide and other pulmonary vasodilator s in HAPE prevention . Maggiori Prospecti Prior Subjects Developme Dexameth 78% High ni M, et ve, history of randomiz nt of asone: 10 incidence quality al. Both randomiz HAPE. ed to HAPE as subjects; of HAPE study in tadalafil ed, receive assessed by Tadalafil: with HAPE- and placebo tadalafil clinical 10 placebo susceptible dexameth controlle 10 mg po examinatio subjects; versus 12% individuals asone d, double BID or n and chest Placebo: 9 with demonstrat may blind dexameth radiograph subjects tadalafil ing benefit reduce study to asone 8 y after the (p<0.007) of the assess mg po first and 2 and 0% dexametha incidence efficacy BID, or second participant with sone and of high of placebo nights at s dexametha tadalafil in altitude tadalafil BID 4559 m or receiving sone HAPE pulmonar and starting when tadalafil (p<0.001). prevention y edema. dexameth the HAPE or developed When two although Ann asone in morning severe severe patients in outcome Intern preventio of the day AMS AMS on tadalafil in the Med n of before occurred. arrival to group who tadalafil 2006.6 HAPE. ascent to 4559 m withdrew group Subjects high and from the depends ascended altitude. withdrew study are on how the in less from the included in two than 24 study. analysis, subjects hrs from 30% would incapacitat 490 m to be deemed ed with 4559 m. as having AMS are Travel to incapacitati treated. 1130 m ng altitude With and then illness. tadalafil ascent by Both there is a cable tadalafil 10% care to an and incidence 3200 m, dexametha of HAPE climbing sone or a 30% for 1.5 resulted in incidence hrs to smaller of 3611 m increases incapacitat for an in ing overnight pulmonary altitude stay, then artery illness. a 4 hr systolic Benefit ascent to pressure with 4559 m compared dexametha for a two to placebo. sone was night stay an at that unexpecte elevation. d finding (Capanna for which Margherit the a, Italy) mechanis m remains unclear. Oelz O, Case HAPE Nifedipin In HAPE 6 male Pulmonary While the et al. control diagnosed e 10 mg subjects, subjects artery study Nifedipin study at by clinical sublingua PaO2 SpO2, with systolic suggests e for high 4559 m signs, l, alveolar- HAPE pressure nifedipine altitude comparin increased repeated arterial age 27 measured is an pulmonar g alveolar- x 1 if oxygen to 51. by effective y physiolog arterial SBP did difference, echocardio adjunctive oedema. ical oxygen not drop PaCO2 and graphy treatment Lancet parameter difference 10 mm radiographi significantl for HAPE 1989.7 s in and chest Hg or c score at 1 y because it HAPE radio- more hour, 14 to decreased lowers patients graphy. after 15 16 hours, with pulmonary treated minutes, and 34 to nifedipine artery with then 37 hours. therapy. In pressure, nifedipin nifedipin HAPE HAPE improves e with e 20 mg subjects' subjects, the subjects slow baseline PaO2 and alveolar who release parameters SpO2 did arterial remained po every were also not oxygen healthy at 6 hours. compared significantl difference, the same to healthy y increase and altitude subjects at with improves following the same nifedipine radiograph a similar altitude treatment, ic scores, ascent without but overall profile. HAPE. alveolar- study (Capanna arterial quality is Margherit oxygen limited, by a, Italy) difference the lack of and a radiographi randomize c score d were controlled significantl design y comparing decreased. use of
PaCO2 nifedipine significantl versus y increased placebo in in HAPE individuals subjects with treated HAPE. with nifedipine. HAPE subjects were more hypoxemic than controls at altitude without HAPE. Sartori C, Prospecti At least Subjects Diagnosis 37 Salmeterol HAPE High- et al. ve, one randomiz of HAPE subjects group = incidence quality Salmeter randomiz radiograph ed to by SpO2, 18; 74% with study ol for the ed, ically receive arterial Placebo placebo demonstrat preventio placebo documente inhalation blood gas, group = and 33% ing that n of high controlle d episode of 125 clinical 19 with inhaled altitude d, double of HAPE mcg of examinatio salmeterol salmeterol pulmonar blind within the salmetero n, and (P=0.02). is effective y edema. study prior four l or chest The HAPE in N Engl J examinin years. placebo radiograph patients preventing Med g use of every y. had higher HAPE in 2002.8 salmetero twelve radiographi HAPE- l for hours c scores, susceptible preventio starting were more individuals n of the hypoxemic . Two HAPE. morning , and had possible Subjects before higher mechanis ascended the day of mountain ms are in less ascent to sickness discussed, than 22 high scores. including, hours altitude. There was beta- from no adrenergic 1130 m difference enhancem to 4559 in ent of m. pulmonary alveolar Ascent artery fluid by cable pressure clearance care to determined by 3200 m, by stimulatio then echocardio n of climbing -graphy. transepithe for 1.5 lial hrs to sodium 3611 m transport for an and overnight possible stay, then beta- climbing adrenergic for 4.5 effect on hrs to hypoxic 4559 m. pulmonary (Capanna vasoconstr Margherit iction. a, Italy) Despite observed benefit, salmeterol still not used as monothera py for prevention . Scherrer Comparis HAPE- Administ Compariso 36 HAPE Nitric While U, et al. on of susceptible ration of n of pulse subjects prone oxide demonstrat Inhaled physiolog group: nitric oximetry, group: 18 decreased ing that nitric ic Radiograp oxide arterial subjects. pulmonary inhalation oxide for responses hically inhalation blood gas Control artery of nitric high to inhaled documente (40 ppm analysis group: 18 pressure oxide altitude nitric d HAPE with an and subjects more in improves pulmonar oxide in within the FIO2 of estimated HAPE- arterial y edema. individua prior 4 0.21) at pulmonary After 18 prone oxygenatio N Engl J ls with a years; 18 and 36 artery to 36 subjects n in Med history of Control hours systolic hours at than in HAPE, 1996.9 HAPE group: following pressure 4559 m, control this study and those alpine arrival at measured 56% of subjects. is more resistant mountaine 4559 m. by the Nitric useful in to the ers with echocardio HAPE- oxide providing disorder. repeated graphy prone improved insight All ascents while subjects oxygenatio into subjects over 4000 breathing developed n HAPE- disease traveled m and no ambient air HAPE prone pathophysi to 1130 history of and during while subjects ology m, HAPE. administrat none of who rather than ascended ion of the control developed treatment. by cable inhaled group HAPE and The care to nitric developed did not complexit 3200 m, oxide. HAPE. alter y of climbed oxygenatio administer for 1.5 n HAPE- ing nitric hrs to prone oxide 3611 m subjects precludes for an who common overnight remained use for stay, and healthy. treatment then Nitric of HAPE ascended oxide as over 4 hr worsened compared to 4559 oxygenatio to oxygen, m. n in which is (Capanna HAPE- more Margherit resistant readily a, Italy) subjects. available and much less expensive.
Schoene Case Clinical All SpO2, end 4 male EPAP Applicatio RB, et al. series of diagnosis subjects tidal subjects treatment n of EPAP High climbers of HAPE received carbon with led to improves altitude with with EPAP dioxide HAPE, significant clinical pulmonar HAPE at hypoxemia applied (ET-CO2) mean increases parameters y edema 4400 m by pulse with a mm Hg, age 33 in SpO2, in HAPE and treated oximetry, tight inspired ±10 (54% to patients, exercise with dyspnea, fitting minute years, 63%) but should at 4,400 expirator tachycardi face ventilation and decreased be meters on y positive a, and mask at 5 (Vi) mean RR (23 to considered Mount airway crackles and 10 respiratory SpO2, 54 13 bpm), an McKinle pressure on lung cm H2O. rate (RR), ±11 %. increased adjunctive y. Effect (EPAP) auscul- and heart ET-CO2. measure to of (Mt. tation rate (HR). No descent. expirator McKinle changes Although y positive y, observed in the airway Alaska) Vi and HR. improvem pressure. ent in Chest oxygenatio 1985.10 n is significant , the HAPE patients remained severely hypoxemic relative to the expected SpO2, at that elevation and would still require descent or supplemen tal oxygen. Study quality limited by the small numbers of subjects and lack of a control group.
Zafren K, Case Patients Selected Patients Of 58 Comparis On return While the et al. series aged 16 to HAPE were patients on of visit study Treatmen from two 69 years patients considered with baseline (usually demonstrat t of high primary diagnosed received improved confirm and one day es that altitude care with treatment on follow- ed follow-up later) some pulmonar centers HAPE. with bed up HAPE, parameter systolic patients y edema between rest and assessment 25 s was blood with by bed 2650 and suppleme if arterial (43%) performed pressure, HAPE can rest and 2950 m. ntal oxygen were in 25 heart rate, be safely suppleme (Colorad oxygen saturation treated HAPE respiratory treated ntal o) rather breathing by bed patients. rate, and with oxygen. than ambient air rest and temperatur supplemen Wilderne hospital increased supplem e all tal oxygen ss admissio by 10% or ental significantl as Environ n. symptoms oxygen y outpatients Med had and decreased. and 1996.11 improved were Oxygen remain at compared seen on saturation the same to initial return breathing elevation, evaluation. visits to ambient air the study the significantl suffers clinic. y from increased. selection bias in that those patients chosen for outpatient treatment were probably less sick then those admitted to the hospital.
1. Baggish AL, Fulco CS, Muza S, et al. The impact of moderate-altitude staging on pulmonary arterial hemodynamics after ascent to high altitude. High Alt Med Biol. 2010;11(2):139-145. 2. Bärtsch P, Maggiorini M, Ritter M, Noti C, Vock P, Oelz O. Prevention of high altitude pulmonary edema by nifedipine. The New England journal of medicine. 1991;325:1284- 1289. 3. Deshwal R, Iqbal M, Basnet S. Nifedipine for the treatment of high altitude pulmonary edema. Wilderness & environmental medicine. 2012;23(1):7-10. 4. Hackett PH, Roach RC, Hartig GS, Greene ER, BD. L. The effect of vasodilators on pulmonary hemodynamics in high altitude pulmonary edema, a comparison. Int J Sports med. 1992;13:S68-S71. 5. Leshem E, Caine Y, Rosenberg E, Maaravi Y, Hermesh H, Schwartz E. Tadalafil and acetazolamide versus acetazolamide for the prevention of severe high-altitude illness. Journal of travel medicine. 2012;19(5):308-310. 6. Maggiorini M, Brunner-La Rocca HP, Peth S, et al. Both tadalafil and dexamethasone may reduce the incidence of high-altitude pulmonary edema: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145(7):497-506. 7. Oelz O, Maggiorini M, Ritter M, Waber U, Jenni R. Nifedipine for high altitude pulmonary edema. Lancet. 1989;2:1241-1244. 8. Sartori C, Allemann Y, Duplain H, et al. Salmeterol for the prevention of high-altitude pulmonary edema. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(21):1631-1636. 9. Scherrer U., Vollenweider J., Delabays A., et al. Inhaled Nitric Oxide for High-altitude Pulmonary Edema. N Engl J. Med. 1996;334:624-629. 10. Schoene RB, Roach RC, Hackett PH, Harrison G, Mills WJ, Jr. High altitude pulmonary edema and exercise at 4,400 meters on Mount McKinley. Effect of expiratory positive airway pressure. Chest. 1985;87(3):330-333. 11. Zafren K, Reeves JT, Schoene R. Treatment of high-altitude pulmonary edema by bed rest and supplemental oxygen. Wilderness Environ Med. 1996;7(2):127-132.