Christopher Guardaro 3-21-11
AP Government & Politics Unit Four Review Ms. Ebner Period 5
The Budgetary Process:
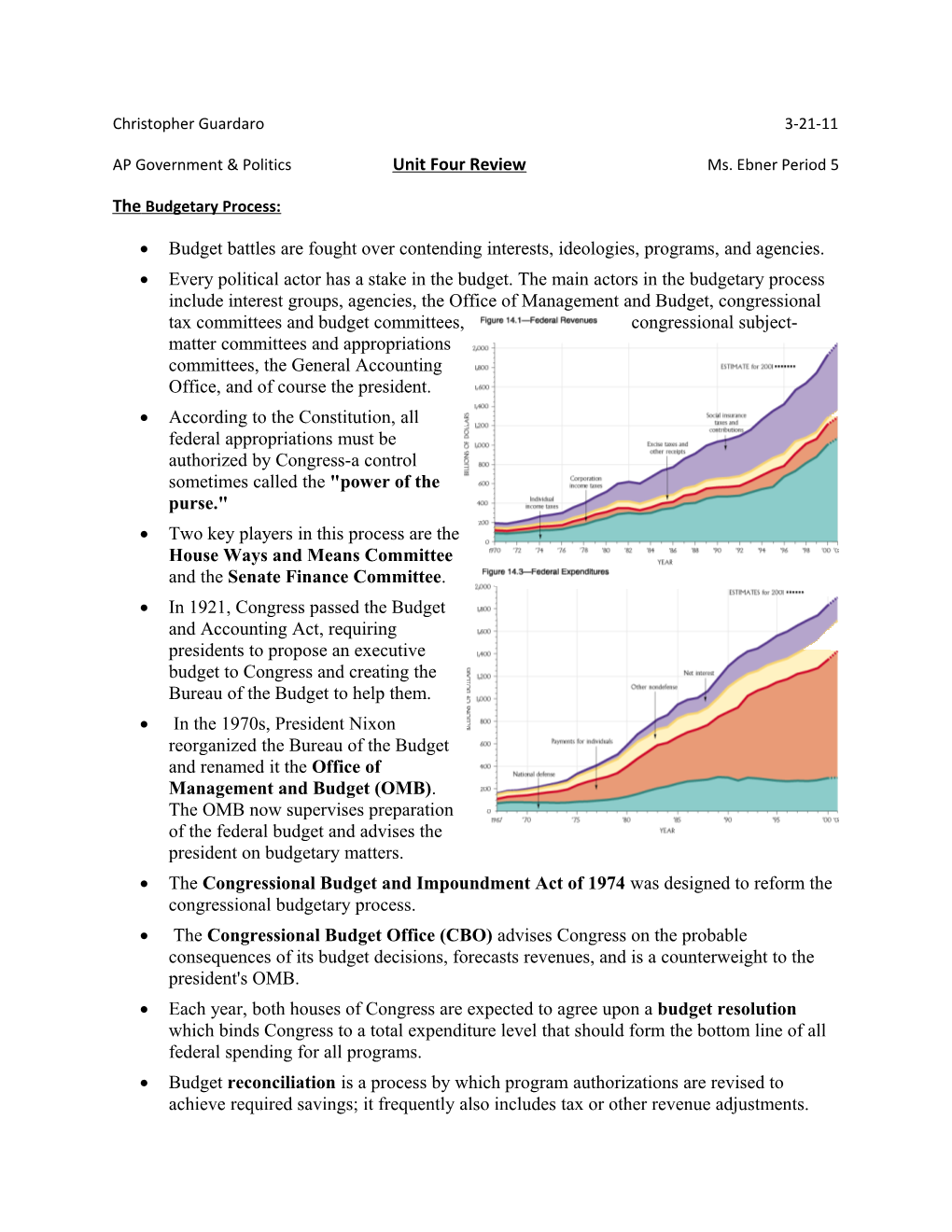
Budget battles are fought over contending interests, ideologies, programs, and agencies. Every political actor has a stake in the budget. The main actors in the budgetary process include interest groups, agencies, the Office of Management and Budget, congressional tax committees and budget committees, congressional subject- matter committees and appropriations committees, the General Accounting Office, and of course the president. According to the Constitution, all federal appropriations must be authorized by Congress-a control sometimes called the "power of the purse." Two key players in this process are the House Ways and Means Committee and the Senate Finance Committee. In 1921, Congress passed the Budget and Accounting Act, requiring presidents to propose an executive budget to Congress and creating the Bureau of the Budget to help them. In the 1970s, President Nixon reorganized the Bureau of the Budget and renamed it the Office of Management and Budget (OMB). The OMB now supervises preparation of the federal budget and advises the president on budgetary matters. The Congressional Budget and Impoundment Act of 1974 was designed to reform the congressional budgetary process. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) advises Congress on the probable consequences of its budget decisions, forecasts revenues, and is a counterweight to the president's OMB. Each year, both houses of Congress are expected to agree upon a budget resolution which binds Congress to a total expenditure level that should form the bottom line of all federal spending for all programs. Budget reconciliation is a process by which program authorizations are revised to achieve required savings; it frequently also includes tax or other revenue adjustments. An authorization bill is an act of Congress that establishes a discretionary government program or an entitlement, or that continues or changes such programs. An additional measure, called an appropriations bill, must be passed to fund programs established by authorization bills.
Understanding Budgeting: Almost all democracies have seen a substantial growth in government in the twentieth century. Economists argue that government grows in a democracy because of the equality of suffrage. Poorer voters will always use their votes to support public policies that redistribute benefits from the rich to the poor. The most rapidly growing expenditures are programs like Social Security, Medicaid, Medicare, and social welfare programs which benefit the poor more than the rich. Corporations support a big government that offers them contracts, subsidies, and other benefits. Poor and rich voters alike have voted for parties and politicians who promised them benefits. Government often grows by responding to groups and their demands. Conversely, some politicians compete for votes by promising not to spend money, in contrast with other nations, Americans have chosen to tax less and spend less on public services than almost all other democracies with developed economies. Politics and economics are powerful, intertwined forces shaping public policies and public lives. The United States is often described as operating under a capitalist economic system, it is more accurately described as a mixed economy, a system in which the government, while not commanding the economy, is still deeply involved in economic decisions. Government, Politics, and the Economy: Workers nearly everywhere are entitled to the minimum wage. Its workers also have a right to join a labor union, a worker's organization for bargaining with an employer. First guaranteed by law in 1935, labor unions engage in collective bargaining about wages and working conditions with their employers. The problem of unemployment is one component of policymakers' regular economic concern. Measuring how many workers are unemployed is one of the major jobs of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) in the Department of Labor. The unemployment rate would be higher if it included discouraged workers; people who have become so frustrated that they have stopped actively seeking employment. The problem of inflation is the other component of policymakers' regular economic concern. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is the key measure of inflation.
Policies for Controlling the Economy: The impact of government on the economic system is substantial, but it is also sharply limited by a basic commitment to a free enterprise system. Laissez-faire is the principle that government should not meddle with the economy Monetary policy involves the manipulation of the supply of money and credit in private hands. An economic theory called monetarism holds that the supply of money is key to the nation's economic health. The main agency for making monetary policy is the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System ("the Fed"). who set discount rates for the money that banks borrow from the Federal Reserve banks; set reserve requirements that determine the amount of money that banks must keep in reserve at all times; and exercising control over the money supply by buying and selling government securities in the market. Fiscal policy describes the impact of the federal budget-taxing, spending, and borrowing-on the economy. Fiscal policy is shaped mostly by the Congress and the president. Democrats favor Keynesian economic theory, a theory that the government must stimulate greater demand, when necessary, with bigger government (such as federal job programs).This theory emphasizes that government spending could help the economy weather its normal fluctuations, even if it means running in the red. Republicans advocate supply-side economics, which calls for smaller government to increase the incentive to produce more goods. Why it is Hard to Control the Economy: Some scholars argue that politicians manipulate the economy for short-run advantage to win elections; however, no one has shown that decisions to influence the economy at election time have been made on a regular basis. Government makes economic policy very slowly. Most policies must be decided upon a year or more before they will have their full impact on the economy. The budgetary process is dominated by uncontrollable expenditures. Given that the law already mandates so much spending; it is difficult to make substantial cuts. Arenas of Economic Policymaking: Liberals tend to favor active government involvement in the economy in order to smooth out the unavoidable inequality of a capitalist system. Conservatives maintain that the most productive economy is one in which the government exercises a hands-off policy of minimal regulation. Liberal or conservative, most interest groups seek benefits, protection from unemployment, or safeguards against harmful business practices. Understanding Economic Policymaking: As the voting power of the ordinary worker grew, so did the potential for government regulation of the worst aspects of the capitalist system. One of the consequences of democracy for economic policymaking is that groups that may be adversely affected by an economic policy have many avenues through which they can work to block it. The decentralized American political system often works against efficiency in government. Liberals focus on the imperfections of the market and what government can do about them while conservatives focus on the imperfections of government. Democrats try to curb unemployment more than Republicans, though they risk inflation in so doing, and Republicans are generally more concerned with controlling inflation. Multiple Choice Questions 1. The biggest slice of the budget pie belongs to
a. health expenditures. b. income security expenditures. c. Social Security payments. d. national defense. e. education aid. 2. The biggest uncontrollable expenditure in the federal budget is
a. The social security system b. Veterans aid c. Government retirement benefits d. Aid for natural disasters e. Interest on the national debt 3. The majority of government expenditures are determined by a. Agency requests b. The “allowance theory” c. How much Congress appropriates to an agency d. How many eligible beneficiaries there are for some particular program. e. Whether the president requests a budgetary increase for an agency 4. The purpose of budget reconciliation is to
a. Adjudicate disputes over the budget. b. Critique and analyze the president’s proposed budget. c. Revise program authorizations to achieve required savings. d. Decide punishments for programs that have exceeded their budget allotment. e. Establish a discretionary government program or entitlement 5. The official unemployment rate underestimates unemployment because it leaves out
a. Laid-off workers. b. Discouraged workers. c. People looking for jobs. d. People under the age of 18. e. Minorities. 6. Our key measure of inflation is called the
a. National Inflation Index b. Gross National Product c. Consumer Price Index d. Laffer Curve e. Consumer Inflation Index 7. The Republican Party is most likely to be concerned with
a. Expanding Governments Role. b. Corporate Corruption c. Unemployment. d. Inflation and Unemployment. e. Inflation 8. An example of a Keynesian economic policy is
a. Allowing the free market to determine economic health. b. Lowering tax rates. c. Creating government jobs to ease unemployment. d. Deregulating commerce and industry. e. Borrowing funds to cover the federal deficit. 9. Which of the following is a reason why it is hard to control the economy? a. The Government makes economic policy very slowly. b. The Government rarely makes economic policies. c. Republicans try to block government control of the economy. d. It is very difficult for the Government to implement economic policy. e. The president vetoes a large amount of proposed economic changes. 10. The agency that exercises control of the money supply by buying and selling government securities in the market is called the a. National Bank Association b. Federal trade commission c. Federal reserve system. d. National Currency agency e. Economic advisor committee. Free Response Question: What are the principle instruments available to policymakers for controlling the economy? Compare monetarism, Keynesian economic theory, and supply-side economics.
Answer Key: 1. B. The largest portion of the federal budget is income security expenditures. 2. A. The largest uncontrollable expenditure in the federal budget is the social security system. 3. D. The Government decides where expenditures should go based on how many eligible beneficiaries there are for the particular program. 4. C. For the most part when the Government decides to reconcile the budget they try to revise program authorizations to achieve the required savings necessary. 5. B. The unemployment rate leaves out discouraged workers, or unemployed people who no longer are looking for a job. 6. C. The key measure of inflation is called the Consumer Price Index. 7. A. The Republican party is a follower of Laissez faire economics or hands off in which the government has a very limited role. 8. C. The Keynesian economic policy is one that the government should be active in trying to benefit the economy. 9. A. It can take up to years for Economic policy to be passed and implemented so by the time it is implemented, it might not be needed anymore. 10. C. The Federal reserve system controls the money supply, and sets discount rates for the money that banks borrow FRQ: The Government uses Monetary Policy as the principle instrument for controlling the economy. Monetarism is an economic theory that the supply of money is key to the nation's economic health. The Keynesian economic theory is that the government should have an active role, and the government must stimulate greater demand when necessary. While supply-side economics calls for smaller government to increase the incentive to produce more goods.