Curriculum Map for HDFS435
Course Understandings Course Essential Questions Course Knowledge Course Skills Unit I: Foundations, Disability, and Individual Learning Differences
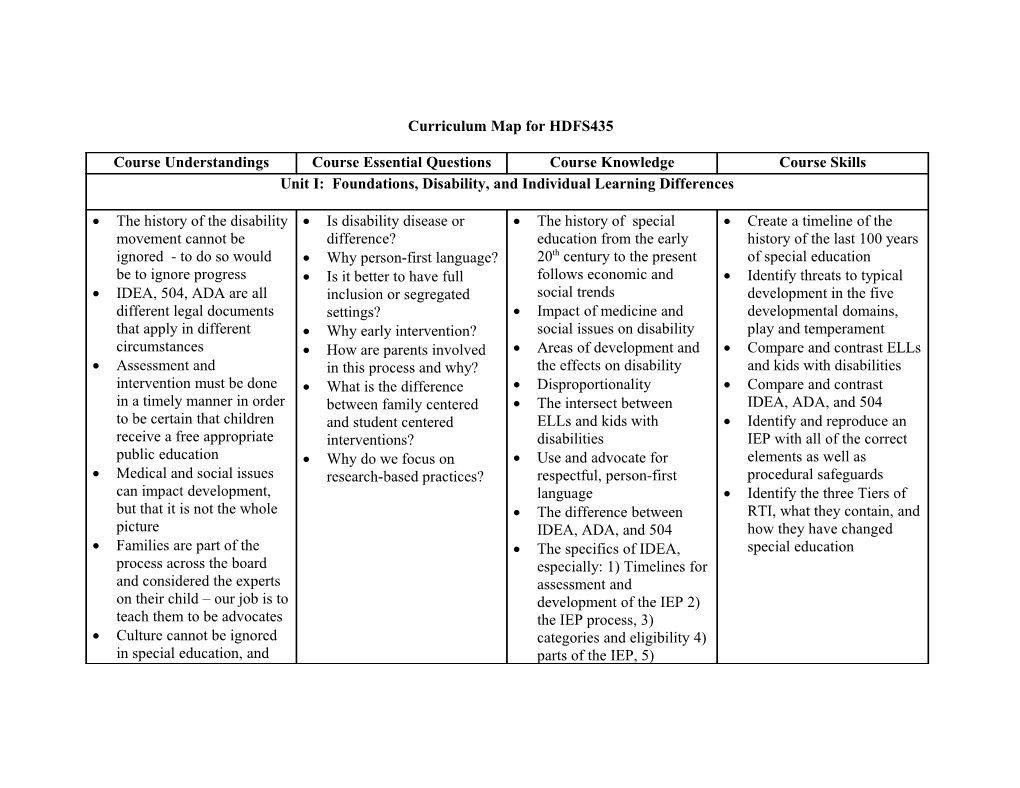
The history of the disability Is disability disease or The history of special Create a timeline of the movement cannot be difference? education from the early history of the last 100 years ignored - to do so would Why person-first language? 20th century to the present of special education be to ignore progress Is it better to have full follows economic and Identify threats to typical IDEA, 504, ADA are all inclusion or segregated social trends development in the five different legal documents settings? Impact of medicine and developmental domains, that apply in different Why early intervention? social issues on disability play and temperament circumstances How are parents involved Areas of development and Compare and contrast ELLs Assessment and in this process and why? the effects on disability and kids with disabilities intervention must be done What is the difference Disproportionality Compare and contrast in a timely manner in order between family centered The intersect between IDEA, ADA, and 504 to be certain that children and student centered ELLs and kids with Identify and reproduce an receive a free appropriate interventions? disabilities IEP with all of the correct public education Why do we focus on Use and advocate for elements as well as Medical and social issues research-based practices? respectful, person-first procedural safeguards can impact development, language Identify the three Tiers of but that it is not the whole The difference between RTI, what they contain, and picture IDEA, ADA, and 504 how they have changed Families are part of the The specifics of IDEA, special education process across the board especially: 1) Timelines for and considered the experts assessment and on their child – our job is to development of the IEP 2) teach them to be advocates the IEP process, 3) Culture cannot be ignored categories and eligibility 4) in special education, and parts of the IEP, 5) race and ethnicity have procedural rights and historically been ways of safeguards, 6) exclusion or seclusion from interdisciplinary high-quality education assessment and RTI is a method for intervention increasing access to high quality instruction before identifying a child as in need of special education, and is not a program Research-based interventions need to be the core of what we do Each child is different, and one size will not fit all Unit II: Instructional Planning, Collaboration, and Assessment
Each child is different; Why can’t we put the same How to adapt lesson plans Compare and contrast therefore, one must plan at goals into each for all learners in the three developmentally the bottom level to How does one manage the Tiers of RTI using appropriate practice with differentiate instruction for demands of teaching the research-based practice age-appropriate practices all learners. demands of the individual Align adaptations to IEP Use the lesson planning To work within a team learner? goals and objectives as well matrix to adapt lessons takes planning, How can a para or 1:1 as academic content being taught in the general cooperation, and actually impede learning, Adapt materials to align educational environment compromise and how can I keep that with IEP goals and Assess the lesson and its Families are never wrong from happening? objectives that are age- demands for differentiation Transitions must be How is teacher manager? appropriate and and adaptation planned for with the entire Why empirical assessment developmentally Assess each lesson and its team and how often? appropriate demands for differentiation IEP goals must be targeted How can I better involve Planning, management and and adaptation in instruction every day, families in the planning and cooperation in the Create a weekly plan for and can be targeted in non delivery of instruction? collaborative classroom data collection for all IEP “teaching” situations How can I plan for daily as Communication and goals Strategies must match the well as programmatic contact with families - Create a weekly plan for goals and the learner and transitions with the family? management communication with must be individualized What are the best methods Setting up and managing a families All students with for communication and data collection system Identify acceptable sources disabilities are required to collaboration? The roles of each of the of research-based practice take high-stakes tests; members of the IEP team: for use in lesson plans some will participate in teacher, administrators, Compare and contrast the alternate assessment related service providers roles and responsibilities of All children have a right to such as PT, OT, Speech each member of the IEP access the general Pathologist team education curriculum in the Create a training and way that best fits them management system for Data-based decision working with making is more precise and paraprofessionals and other leads to better outcomes related service providers than anecdotal evidence? using planning tools and a plan book Unit III: Tier III – Instructional Strategies and Ethical Practice
Families must be involved What are low-tech and Selecting appropriate Create an IEP based upon a in the instructional process high tech ways to support communication support hypothetical vignette that as well as the planning communication? procedures to assist with takes into account IDEA process Why is communication the communication, speech, or requirements as well as Instruction must be single most important thing articulation. evidence-based practices in meaningful and linked to to teach? Implement a PECS the field of special “real world” knowledge Why community-based curriculum education and skill instruction as opposed to Select appropriate AAC In an IEP, select Communication and simulation? devices appropriate AAC and AT language delays are the How can I support children Accommodations for Select appropriate single most important areas with sensory impairments children who are blind, accommodations based to target (deafness, blindness)? have low vision, who are upon IEP goals and needs Social support can be tied How can I make sure that deaf/hard of hearing of a child in all areas of to academic success children with motor skill Collaboration with related development Motor development can difficulties are included in service professionals to Demonstrate a social skill affect social, my classroom? implement appropriate and communication lesson communication, and What is the difference interventions for children plan based upon evidence- academic success between Tier I and Tier with motor disabilities based practices Tier II and Tier III refers to II/III intervention? Select curriculum and specific academic What types of social skill accommodations to instructional strategies that curricula are out there? increase social skill benefit all learners. What specific interventions development for young Advocacy is possible in the are considered to be children early stages of a career evidence-based? Communication and A teacher must respect and How can families be collaboration with families balance the requirement of involved in the support in the support process privacy with the needs of process? Select appropriate the child How can disabilities affect academic interventions in social development, even if the areas of reading, the disability does not writing, and mathematics involve socialization? Select appropriate evidence-based strategies for intervention Assessment Evidence
Unit I Performance Tasks Other Evidence Given print resources, students will create a timeline of the Attendance question of the day (formative) first 100 years of special education identifying at least 4 Textbook question of the day (formative) seminal events in each decade (ungraded) Students will complete goals and objectives for students with Given a question of the day, students will identify threats to disabilities only and not ELLs typical development in the five developmental domains, play IEP assignment (summative, at the end of the semester and and temperament (ungraded) revisable) Given a game, students will answer questions related to the Multimedia assignments of the history of special education, legal requirements of IDEA as well as the three tiers of RTI IDEA (in groups, graded, summative) (ungraded) Written assignments will use person-first language at all times (formative, graded) Unit II Performance Tasks Other Evidence Given a lesson plan and guided practice, students will Attendance question of the day (formative) analyze at least three activities for prerequisite knowledge and Textbook question of the day (formative) use the adapt, augment, and alter methods for accommodating Multimedia assignment on evidence-based practice, inclusion, the needs of students with disabilities (ungraded, formative, collaboration with related service providers, or part of lesson plans) paraprofessionals in the classroom (formative) Given a lesson plan and guided practice, students will Article reviews of evidence-based practice (formative, 4 per complete an activity matrix for each lesson plan that semester) delineates IEP accommodations for students with disabilities and differentiation for students at risk for failure that are both developmentally appropriate and age-appropriate (graded, summative, part of lesson plans) Given a hypothetical classroom plan that mirrors that seen in placement, students will create a daily planning matrix that allows the student to both plan for delivery of instruction and schedule professionals in the classroom to target skills throughout the day (graded, summative) Given a hypothetical situation, students will create a data collection plan that allows for empirical monitoring of progress for all students in the classroom (ungraded) Given a hypothetical situation, students will create a family communication system that takes into account family preferences, and participate in problem-solving situations with family members Unit III Performance Tasks Other Evidence Attendance question of the day (formative) on functional assessment, functional analysis, and the legal implications of these Textbook question of the day (formative)