Lab Assignment Ch.1
1.4 Occupational deaths. In 2004 there were 5703 job-related deaths in the United States. Among these were 659 deaths in agriculture-related jobs (including forestry, fishing, and hunting), 152 in mining, 1224 in construction, 459 in manufacturing, 880 in transportation and public utilities, 203 in wholesale trade, 372 in retail trade, 115 in finance-related jobs (including insurance and real estate), 1054 in service-related jobs, and 526 in government jobs. (a) Find the percent of occupational deaths for each of these job categories, rounded to the nearest whole percent. What percent of job-related deaths were in categories not listed above? (b) Make a well-labeled bar graph of the distribution of occupational deaths. Be sure to include an “other occupations” bar. (c) Make a well-labeled Pareto chart of these data. What percent of all occupational deaths are accounted for by the first three categories in your Pareto chart? (d) Would it also be correct to use a pie chart to display these data? Explain your answer.
1.8 Baseball salaries. How would you describe the center and spread of the distribution of average salaries in Figure 1.3? Of the distribution of Cincinnati Reds’ salaries in Figure 1.4?
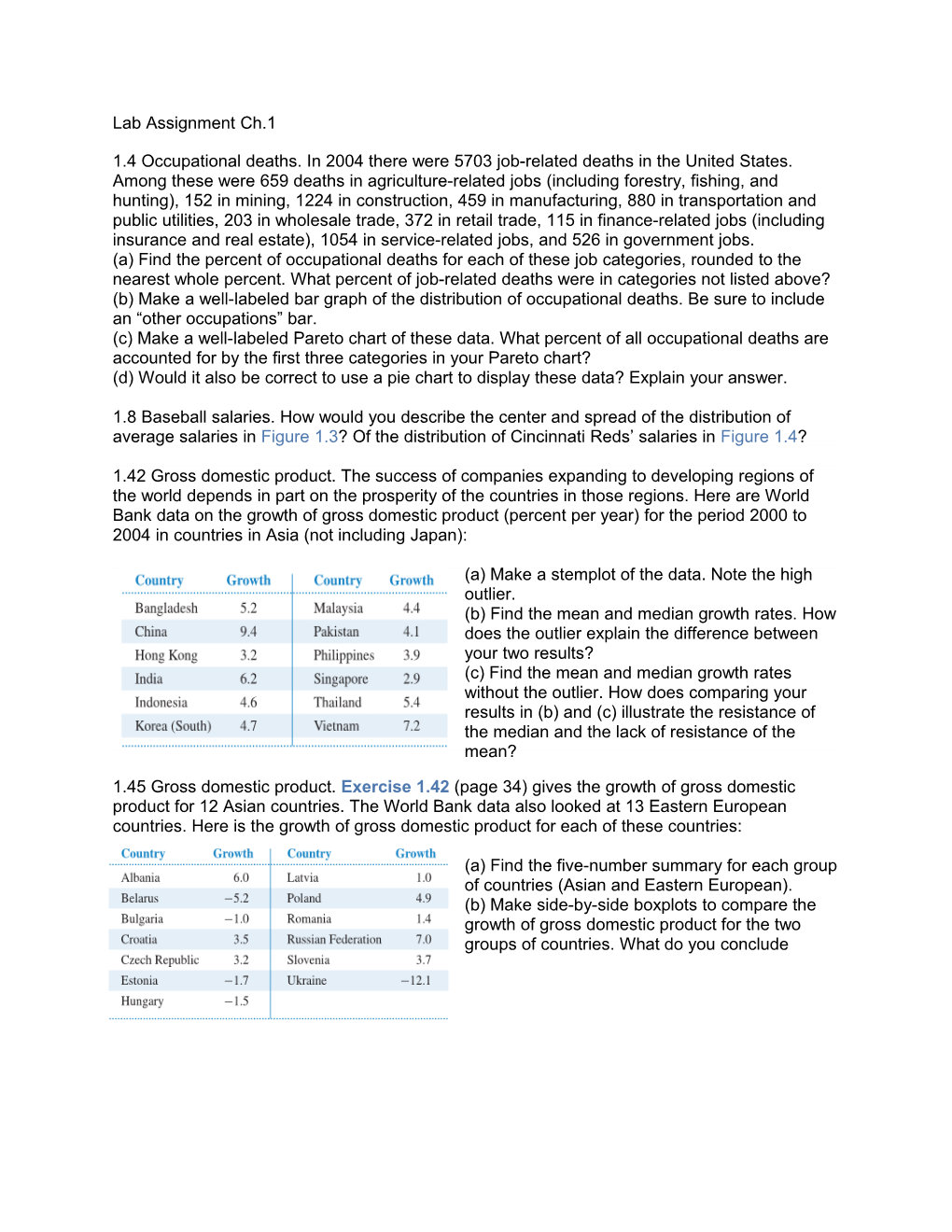
1.42 Gross domestic product. The success of companies expanding to developing regions of the world depends in part on the prosperity of the countries in those regions. Here are World Bank data on the growth of gross domestic product (percent per year) for the period 2000 to 2004 in countries in Asia (not including Japan):
(a) Make a stemplot of the data. Note the high outlier. (b) Find the mean and median growth rates. How does the outlier explain the difference between your two results? (c) Find the mean and median growth rates without the outlier. How does comparing your results in (b) and (c) illustrate the resistance of the median and the lack of resistance of the mean?
1.45 Gross domestic product. Exercise 1.42 (page 34) gives the growth of gross domestic product for 12 Asian countries. The World Bank data also looked at 13 Eastern European countries. Here is the growth of gross domestic product for each of these countries:
(a) Find the five-number summary for each group of countries (Asian and Eastern European). (b) Make side-by-side boxplots to compare the growth of gross domestic product for the two groups of countries. What do you conclude 1.84 IQ test scores. Employers may ask job applicants to take an IQ test if the test has been shown to predict performance on the job. One such test is the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS). Scores on the WAIS for the 20 to 34 age group are approximately Normally distributed with μ = 110 and σ = 25. Use the 68–95–99.7 rule to answer these questions. (a) About what percent of people in this age group have scores above 110? (b) About what percent have scores above 160? (c) In what range do the middle 95% of all scores?
1.87 Gas mileage. The miles per gallon ratings for 2001 model vehicles vary according to an approximately Normal distribution with mean μ = 21.22 miles per gallon and standard deviation σ = 5.36 miles per gallon. (a) What percent of vehicles have miles per gallon ratings greater than 30? (b) What percent of vehicles have miles per gallon ratings between 30 and 35? (c) What percent of vehicles have miles per gallon ratings less than 12?
1.89 GMAT scores. Most graduate schools of business require applicants for admission to take the Graduate Management Admission Council’s GMAT examination. Total scores on the GMAT for the more than 500,000 people who took the exam between April 1997 and March 2000 are roughly Normally distributed with mean μ = 527 and standard deviation σ = 112. (a) What percent of test takers have scores above 500? (b) What GMAT scores fall in the lowest 25% of the distribution? (c) How high a GMAT score is needed to be in the highest 5%?