Chapter Thirteen Handout: MC/Soc From the PowerPoint Presentation:
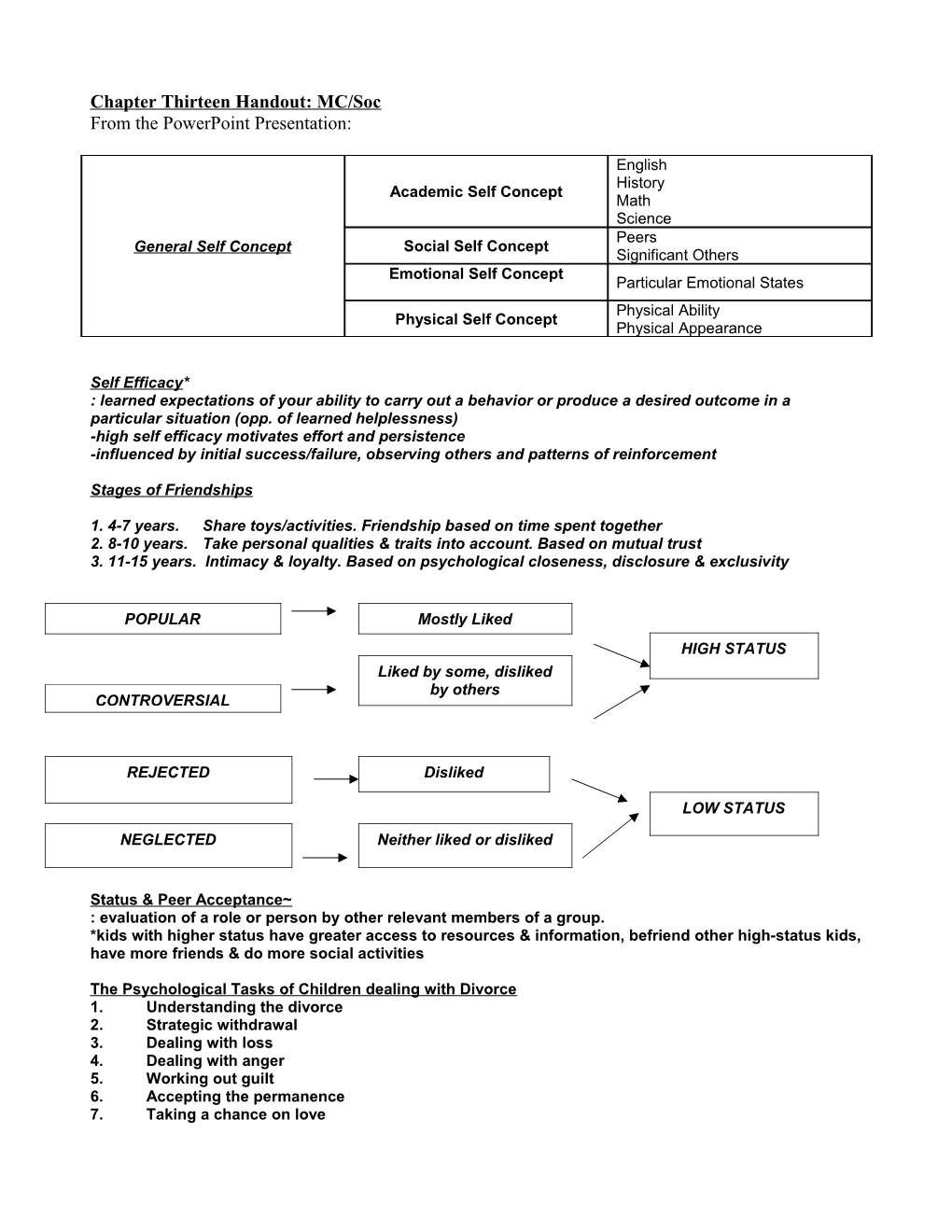
English History Academic Self Concept Math Science Peers General Self Concept Social Self Concept Significant Others Emotional Self Concept Particular Emotional States Physical Ability Physical Self Concept Physical Appearance
Self Efficacy* : learned expectations of your ability to carry out a behavior or produce a desired outcome in a particular situation (opp. of learned helplessness) -high self efficacy motivates effort and persistence -influenced by initial success/failure, observing others and patterns of reinforcement
Stages of Friendships
1. 4-7 years. Share toys/activities. Friendship based on time spent together 2. 8-10 years. Take personal qualities & traits into account. Based on mutual trust 3. 11-15 years. Intimacy & loyalty. Based on psychological closeness, disclosure & exclusivity
POPULAR Mostly Liked HIGH STATUS Liked by some, disliked by others CONTROVERSIAL
REJECTED Disliked
LOW STATUS
NEGLECTED Neither liked or disliked
Status & Peer Acceptance~ : evaluation of a role or person by other relevant members of a group. *kids with higher status have greater access to resources & information, befriend other high-status kids, have more friends & do more social activities
The Psychological Tasks of Children dealing with Divorce 1. Understanding the divorce 2. Strategic withdrawal 3. Dealing with loss 4. Dealing with anger 5. Working out guilt 6. Accepting the permanence 7. Taking a chance on love Term Definition Peer group A. The largest subgroup of rejected children Peer culture B. Children who show both academic and social competence Relational aggression C. Children who get a large number of positive and negative votes on sociometric measures of peer acceptance Overt aggression D. Children who get many positive votes on sociometric measures of peer acceptance Trust E. Verbal insults and pranks are an example of this Popular children F. Specialized vocabulary and a dress code are part of this Rejected children G. A subgroup of rejected children who are passive and socially awkward Controversial children H. A social unit that is formed by generating unique values and standards for behavior and a social structure of leaders and followers Neglected children I. Gossip, rumor spreading, and exclusion Popular-prosocial J. The defining feature of school-age children’s friendships children Popular-antisocial K. Children who are actively disliked and get many negative votes on children sociometric measures of peer acceptance Rejected-aggressive L. Children who do not receive either positive or negative votes on children sociometric measures of peer acceptance Rejected-withdrawn M. Aggressive children who are liked because they are seen as “cool” and children have athletic skills