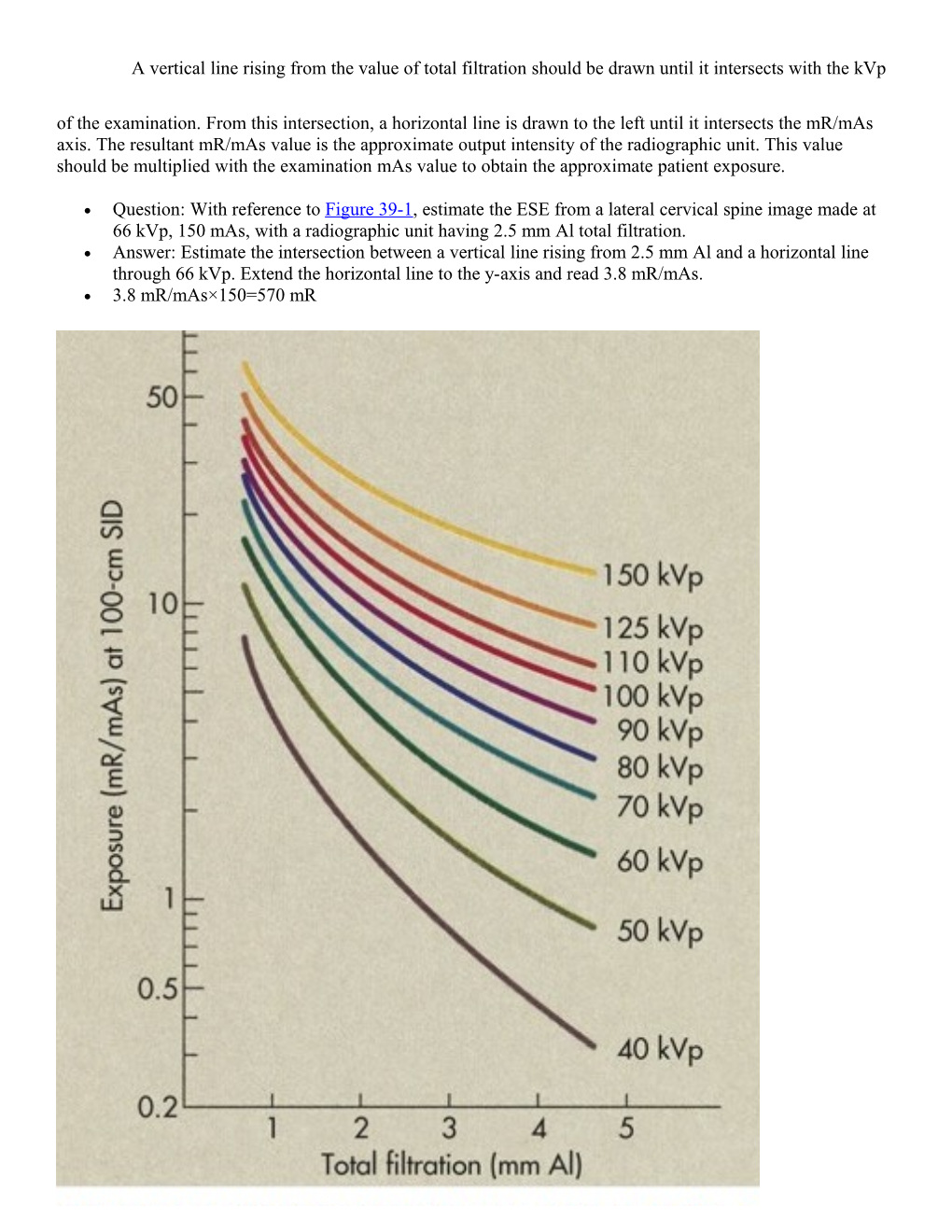
A vertical line rising from the value of total filtration should be drawn until it intersects with the kVp of the examination. From this intersection, a horizontal line is drawn to the left until it intersects the mR/mAs axis. The resultant mR/mAs value is the approximate output intensity of the radiographic unit. This value should be multiplied with the examination mAs value to obtain the approximate patient exposure.
Question: With reference to Figure 39-1, estimate the ESE from a lateral cervical spine image made at 66 kVp, 150 mAs, with a radiographic unit having 2.5 mm Al total filtration. Answer: Estimate the intersection between a vertical line rising from 2.5 mm Al and a horizontal line through 66 kVp. Extend the horizontal line to the y-axis and read 3.8 mR/mAs. 3.8 mR/mAs×150=570 mR Question: Using the nomogram in Figure 39-2, identify the ESE when a radiographic exposure is made at 66 kVp, 150 mAs. Answer: The line is drawn as shown and crosses the ESE scale at 1000 mR.
A third method for estimating ESE requires that one know the output intensity for at least one operating condition. During the annual or special radiation control survey and calibration of an x-ray imaging system, the medical physicist measures this output intensity, usually in units of mR/mAs at 80 cm—the approximate source-to-skin distance (SSD)—or at 100 cm—the source-to-image receptor distance (SID).