Chemistry 30A Test 2 Sept. 16, 2005
Show all work. Include units and correct sig. figs. A mole is 6.022 x 1023 of something. The molar mass of a particular kind of atom, molecule, or formula unit is the mass in grams of a mole of those atoms, molecules, or formula units. So units of molar mass are g/mol (grams per mole).
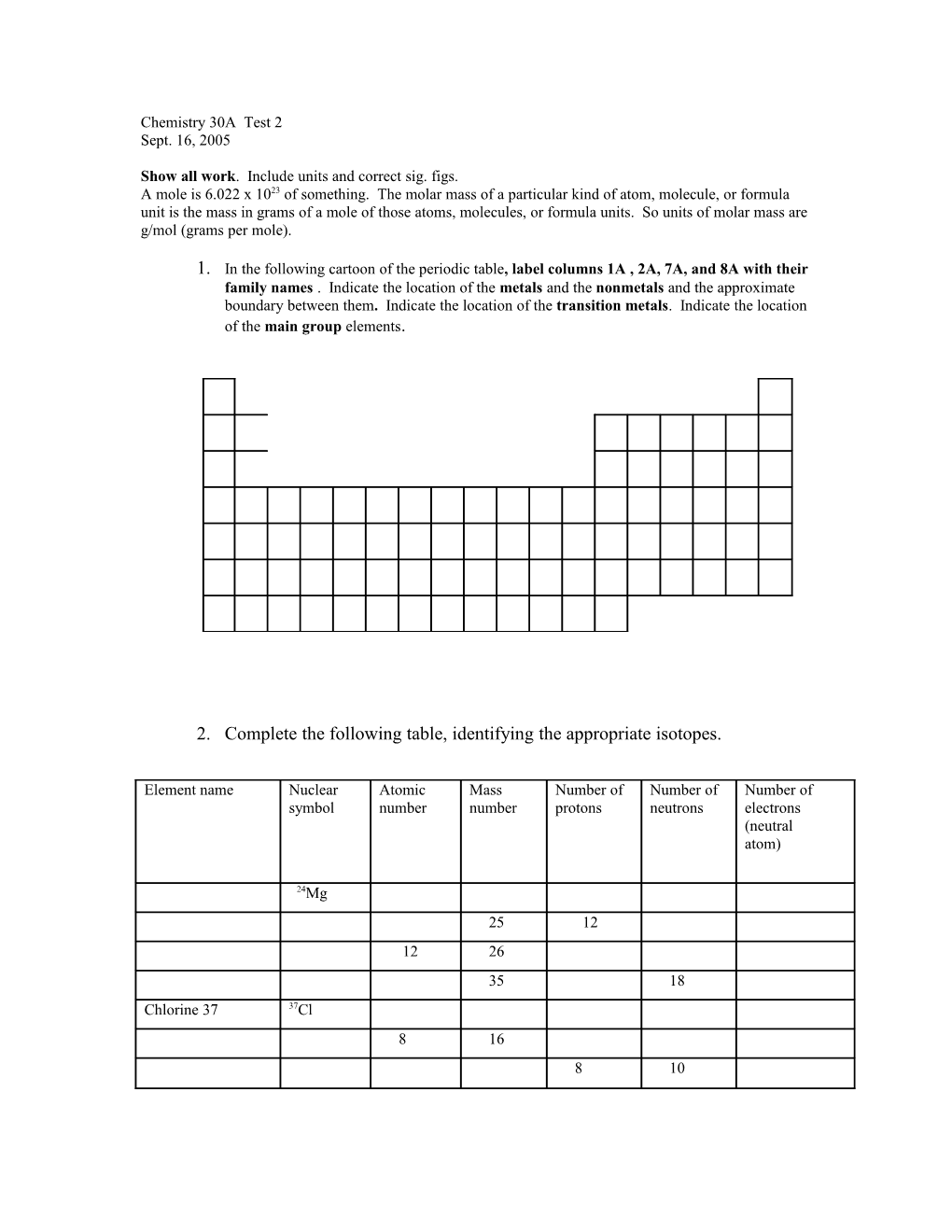
1. In the following cartoon of the periodic table, label columns 1A , 2A, 7A, and 8A with their family names . Indicate the location of the metals and the nonmetals and the approximate boundary between them. Indicate the location of the transition metals. Indicate the location of the main group elements.
2. Complete the following table, identifying the appropriate isotopes.
Element name Nuclear Atomic Mass Number of Number of Number of symbol number number protons neutrons electrons (neutral atom)
24Mg 25 12 12 26 35 18 Chlorine 37 37Cl 8 16 8 10 3. Pure silicon has density 2.329 g/mL, and from the periodic table, an atomic mass of 28.09 amu or a molar mass of 28.09 g/mol. Hint: Just like density is a conversion factor between mass and volume, molar mass is a conversion factor between mass and number of moles.
a. What is the volume of 0.500 kg of silicon?
b. How many moles (of atoms) in 0.500 kg of silicon?
4. Pure iron metal has density 7.874 g/mL, and from the periodic table, an atomic mass of 55.85 amu or a molar mass of 55.85 g/mol.
a. What is the mass of a piece of iron with volume 0.350 L.
b. What is the mass of a piece of iron containing 0.350 moles (of Fe atoms)?
5. The molar mass of a molecular compound is just the sum of the molar masses of all the atoms in the molecule. Using your periodic table determine the molar mass of each of the following molecular compounds. Then calculate the mass in grams of each of the following samples Be careful about sig. figs.!
a. Example: the molar mass of C2H4O2 (acetic acid) = 2 x 12.01 + 4 x 1.008 + 2 x 16.00 = 60.05 g/mol
-3 b. What is the mass of 3.5 x 10 moles of C2H4O2 (or H3CCOOH)?
c. What is the molar mass of ethanol or C2H6O?
d. What is the mass of 0.500 moles of ethanol, C2H6O (also C2H5OH)? 4. In a similar fashion, the molar mass of an ionic compound is just the sum of all the molar masses of all the atoms in one formula unit. The formula unit for sodium nitrate is just NaNO3. Use your periodic table to determine the molar mass and then calculate the number of moles present for each of the following samples of ionic compounds: Be careful with sig. figs. here!
a. Example: the molar mass of NaNO3 = 22.99 + 14.01 + 3 x 16.00 = 85.00 g/mol
b. How many moles (of formula units) are in 3.0 g of sodium nitrate, NaNO3?
c. What is the molar mass of FeCl2?
d. How many moles (of formula units) are in 2.2 g of iron II chloride or FeCl2?
5. Ions versus neutral atoms.
a. What are ions?
b. What is the difference between a sodium atom and a sodium ion?
c. What kinds of ions are typically formed by metals? Give specific examples.
d. What kinds of ions are typically formed by nonmetals? Give specific examples.
e. What is the difference between an ionic compound and a molecular compound? Give a specific example of an ionic compound and a molecular compound. In the first case say what ions are involved. (Do not use compound already seen in this test!) 6. Extra: Give correct names for the following compounds:
a. MnO2
b. MnO
c. NO
d. NO2
e. N2O4
f. NH4Cl
7. Extra: Give formulas for the following compounds: a. iron III chloride
b. iron III oxide
c. iron II chloride
d. iron II nitride
e. dinitrogen monoxide
f. nitrogen dioxide
g. calcium oxide
h. calcium chloride
i. calcium nitride
j. calcium carbonate
8. Extra: Write a balanced chemical reaction equation for the complete burning of decane, C10H22, in oxygen.
9. Extra: Ammonia, NH3, is produced industrially from the gases hydrogen and nitrogen at high temperature.
a. Write a balanced equation for the chemical reaction.
b. Give the microscopic (molecular scale) meaning of the equation in words.
c. Give the macroscopic (large scale) meaning of the equation in words.
10. Extra: The molecular formula and the empirical formula of a compound may or may not be the same. The molecular
formula for decane, a component of gasoline, is C10H22.
a. What is the molecular mass?
b. What is the empirical formula for decane?
c. What is the empirical formula mass?
Note: For molecular compounds we generally use the molecular formula and the molecular mass unless otherwise instructed. On the other hand, for ionic compounds we always use the empirical formula and the empirical formula mass (also called the formula unit and formula unit mass respectively).