The University of Edinburgh College of Humanities and Social Science Undergraduate Learning and Teaching Committee e-CUGLAT November 2012 Paper EC2C For approval Disclosable New programmes
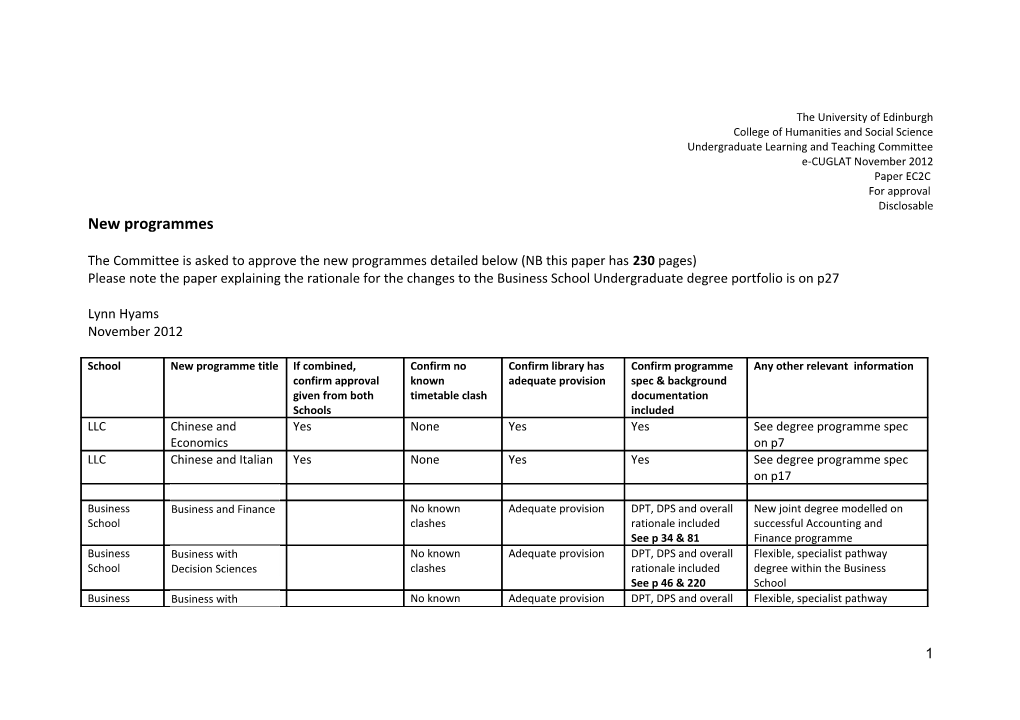
The Committee is asked to approve the new programmes detailed below (NB this paper has 230 pages) Please note the paper explaining the rationale for the changes to the Business School Undergraduate degree portfolio is on p27
Lynn Hyams November 2012
School New programme title If combined, Confirm no Confirm library has Confirm programme Any other relevant information confirm approval known adequate provision spec & background given from both timetable clash documentation Schools included LLC Chinese and Yes None Yes Yes See degree programme spec Economics on p7 LLC Chinese and Italian Yes None Yes Yes See degree programme spec on p17
Business Business and Finance No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall New joint degree modelled on School clashes rationale included successful Accounting and See p 34 & 81 Finance programme Business Business with No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Flexible, specialist pathway School Decision Sciences clashes rationale included degree within the Business See p 46 & 220 School Business Business with No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Flexible, specialist pathway
1 School Enterprise and clashes rationale included degree within the Business Innovation See p 55 & 163 School Business Business with Human No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Flexible, specialist pathway School Resource clashes rationale included degree within the Business Management See p 63 & 192 School Business Business with No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Flexible, specialist pathway School Marketing clashes rationale included degree within the Business see p 73 & 91 School Business Business with No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Flexible, specialist pathway School Strategic Economics clashes rationale included degree within the Business See p 39 & 132 School Business International Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Renamed variant on the School Business with French clashes rationale included International Business with a (MA) See p 78 & 144 Language degree to specify language of study Business International Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Renamed variant on the School Business with clashes rationale included International Business with a German (MA) See p 60 & 173 Language degree to specify language of study Business International Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Renamed variant on the School Business with Spanish clashes rationale included International Business with a (MA) See p 70 & 153 Language degree to specify language of study Business International Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Renamed variant on the School Business with Italian clashes rationale included International Business with a (MA) See p 51 & 182 Language degree to specify language of study Business International Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Renamed variant on the School Business with Russian clashes rationale included International Business with a (MA) See p 61 & 110 Language degree to specify language of study Business International Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Renamed variant on the School Business with clashes rationale included International Business with a
2 Chinese (MA) See p 68 & 101 Language degree to specify language of study Business International Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Renamed variant on the School Business with clashes rationale included International Business with a Japanese (MA) See p 53 & 211 Language degree to specify language of study Business International Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision DPT, DPS and overall Renamed variant on the School Business with Arabic clashes rationale included International Business with a (MA) See p 59 & 202 Language degree to specify language of study
Business Business No known Adequate provision No change to Renamed Business Studies School Management (MA) clashes DPT/DPS for degree it degree as title did fully reflect the replaces Business content – content remains Studies unchanged Business Business and No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School Accounting (MA) clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces Business the degree to reflect better its Studies and focus as the degree is about more Accounting than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Business and Approved by School No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School Economics (MA) of Economics clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces - Business the degree to reflect better its Studies and focus as the degree is about more Economics than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Business and Approved by School No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School Geography (MA) of Geoscience clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces - Business the degree to reflect better its Studies and focus as the degree is about more Geography than just ‘studying’ business–
3 content remains unchanged Business Business and Law Approved by School No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School (MA) of Law clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces - Business the degree to reflect better its Studies and Law focus as the degree is about more than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Arabic and Business Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School (MA clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces - Arabic and the degree to reflect better its Business Studies focus as the degree is about more than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Economic History and Approved by HCA No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School Business (MA) clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces – Economic the degree to reflect better its History and Business focus as the degree is about more Studies than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business French and Business Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School (MA) clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces – French and the degree to reflect better its Business Studies focus as the degree is about more than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business German and Business Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School (MA) clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces – German the degree to reflect better its and Business Studies focus as the degree is about more than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Italian and Business Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School (MA) clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from
4 replaces – Italian and the degree to reflect better its Business Studies focus as the degree is about more than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Law and Business Approved by Law No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School (LLB) School clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces – Law and the degree to reflect better its Business Studies focus as the degree is about more than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Mathematics and Approved by No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School Business (BSc) Mathematics clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces – the degree to reflect better its Mathematics and focus as the degree is about more Business Studies than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Portuguese and Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School Business (MA) clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces – Portuguese the degree to reflect better its and Business Studies focus as the degree is about more than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Psychology and Approved by No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School Business (MA) Psychology clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces – Psychology the degree to reflect better its and Business Studies focus as the degree is about more than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged Business Russian Studies and Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School Business (MA) clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces – Russian the degree to reflect better its Studies and Business focus as the degree is about more Studies than just ‘studying’ business–
5 content remains unchanged Business Spanish and Business Approved by LLC No known Adequate provision No change to Change of degree name to School (MA) clashes DPT/DPS for degree it remove the word ‘Studies’ from replaces – Spanish the degree to reflect better its and Business Studies focus as the degree is about more than just ‘studying’ business– content remains unchanged
6 THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION MA Honours in Chinese and Economics
1) Awarding Institution: University of Edinburgh
2) Teaching Institution: University of Edinburgh
3) Programme accredited by: The University of Edinburgh
4) Final Award: MA (Hons)
5) Programme Title: Chinese and Economics
6) UCAS Code: Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): Language and Related Studies
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Head of School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary
The University of Edinburgh is the only university in Scotland to offer an Honours degree in Chinese. The Scottish Centre for Chinese Studies offers courses in Chinese at all levels, taught by three full-time members of staff and a Chinese Language Assistant. Staff research interests cover literature, translation, film, history and culture in both modern and traditional Chinese: the expertise of the teaching staff was reflected in an excellent performance in the recent Research Assessment Exercise. For anyone thinking further ahead, this expertise has led to the development of an expanding programme of postgraduate studies. You will discover Edinburgh to be a cosmopolitan city with ever-increasing opportunities to engage with China on academic, professional and cultural terms. The Scottish Centre for Chinese Studies serves as a platform to link China related research at University of Edinburgh and at other HEI's in Scotland. The Centre organises interdisciplinary research seminar series, and hosts the interdisciplinary Master of Chinese studies programme. The Confucius Institute was established in 2006 as a partnership between the University and Fudan University in Shanghai. Within four years of operation the Institute has developed into a comprehensive cultural centre, providing non degree
7 language training as well as a large outreach and knowledge transfer programme. In 2010, it has been honoured as ‘Institute of the Year’ by Hanban, sponsor of the global network of Confucius Institutes and Classrooms, for the fourth consecutive year, a recognition of its status as a world class Institute.
From the low point of the stagnation of the 1970s, China has risen at a staggering rate, overtaking Japan in August 2010 to become the world’s second largest economy. This major success story has attracted the attention of leading international academics: it is important that the University of Edinburgh should be seen to be involved in the discussion.
During the first two years of the MA in Chinese and Economics, students attend a range of classes which provide a solid foundation in the Chinese language (Mandarin). Together with courses on modern Chinese society and culture as well as outlines on China's rich history from earliest times to the present day students are well prepared for the third year of the programme, which is spent studying at a Chinese university. In the fourth year intensify their study on primary sources in courses on key notions of classical philosophy and literature as well as courses on modern and contemporary China.
Economics at Edinburgh offers students the opportunity to develop (i) an understanding of key economic and social issues, (ii) a strong blend of qualitative and quantitative reasoning skills, (iii) the ability to abstract from less relevant issues and get to the heart of a problem, (iv) the ability to assemble and evaluate complex evidence and arguments, (v) the ability to apply core economic principles to key decision-making contexts, (vi) the ability to communicate precisely and succinctly and (vii) personal effectiveness in task-management, time-management and teamwork. The programme is taught within the Schools of Literatures, Languages and Cultures and Economics.
10) Educational aims of programme:
The programme aims to enable students with little or no previous knowledge of Chinese language and culture to acquire and develop interest in and understanding of Chinese speaking countries, including the Chinese language (Mandarin), history, literature, culture and society. It offers society the resource of intellectually trained individuals capable of acting as conduits of knowledge and understanding between Britain and Chinese-speaking countries. The programme, taught in the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures and Economics, offers society the resource of intellectually trained individuals capable of acting as conduits of knowledge and understanding between Britain and Chinese-speaking countries.
1. Modern spoken and written Chinese (Mandarin) 2. Modern and classical Chinese literature 3. Chinese history and thought
8 4. Political and social issues related to Chinese speaking countries 5. Linguistic issues related to the Chinese language (its structure, functions, registers, writing systems etc.) 6. Key methods and concepts of literary, historic and linguistic analysis 7. A broad knowledge and understanding of key economic and social issues, principles, models and associates mathematical and statistical techniques, along with applications and policy implications of those models and a deeper understanding of recent research activity in some more specialised areas 8. Research and investigative skills such as problem framing and solving and the ability to assemble and evaluate complex evidence and arguments 9. Personal and intellectual autonomy through independent learning, self evaluation and self improvement and through the application of core economic principles to key decision-making contexts 10. Communication skills in order to critique, create and communicate understanding and to collaborate with and relate to others 11. Personal effectiveness through task-management, time-management, teamwork and group interaction, dealing with uncertainty and adapting to new situations.
Teaching/learning methods and strategies Chinese language is acquired through small-group classes, tutorials and regular, assessed coursework. Additional support is provided through the self-access facilities for language learning at the Language and Humanities Centre and the Languages MicroLab. The third year abroad provides total immersion in the Chinese language and culture.
Knowledge of Chinese literature, history, thought, culture and society is acquired through a combination of lectures and tutorials or seminars including group discussion and individual or joint presentations.
Assessment Testing on the knowledge base is through unseen written examinations in all areas, combined with assessed regular language exercises and oral examinations in Chinese language; and essays, coursework assignments and a dissertation in Chinese studies.
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry
1 to reason critically and cogently 2 to apply linguistic, literary and historical concepts 3 to identify and solve problems 4 to analyse and interpret 5 to find information on and use information technology 6 To use the Internet and bibliographic resources in both Mandarin Chinese and English 7 plan, undertake and (in a scholarly and literate fashion) report on a piece of
9 self-initiated research, retrieve, sift and select information from a variety of sources and media, including those in the target language; analyse and interpret information and texts
Teaching/learning methods and strategies Intellectual skills are developed through the teaching and learning programme outlined above. Each course, whatever the format of the teaching, involves discussion of the key issues, practice in applying concepts both orally and in writing, analysis and interpretation of material and individual feedback on work produced.
Assessment The variety of assessment methods employed all place great emphasis on the learner’s ability to demonstrate the above skills through the production of cogent and coherent written and oral responses to problems and tasks set. Essays and dissertations produced in the Honours years provide an especially valuable vehicle for the training of those skills. In particular, the combination of Chinese and Economics allows for the development of a variety of skills in researching material produced not just in different languages, but with widely varying ideological content.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy
1 to work independently 2 to be self-reliant 3 to assess and respond to the ideas of others 4 demonstrate and exercise independence of mind and thought 5 distinguish relevant from irrelevant considerations in argument 6 construct clearly organised arguments
Teaching/learning methods and strategies All courses require written work, usually in the form of essays, and regular feedback is given to the learners in order to develop their understanding and power of expression. Teamwork and leadership skills are acquired through active contributions to tutorials and seminars, both as group members and discussion leaders. Time management is learned through the expectation to submit coursework by prescribed deadlines notified at the outset of each course. Teamwork and assessment and response to the ideas of others are developed in classes, seminars and tutorials, which rely on discussion and interaction, as well as presentations by individuals and groups of students. Independent work and self- reliance are developed during the year abroad. IT skills are developed through University-wide training courses and individual learning.
Assessment Effective communication of ideas is an important criterion in assessing all areas of a learner’s work, and the regular feedback and the final mark both reflect this. Additionally, penalties are levied for late submission of essays and coursework assignments. Structuring and communication of ideas, independent work, self-
10 reliance, IT skills and assessment and response to the ideas of others are all assessed through regular coursework, essays and dissertations. Although these are supervised they are nevertheless a manifestation of the independent thought and research by the learner. IT skills are assessed through the assembly of necessary information for essays, etc. and their production on PCs.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication
1 To speak, write and read Mandarin Chinese at an advance level of proficiency 2 To translate and interpret from and into Mandarin Chinese 3 To communicate effectively in English to inform and educate others about Chinese language and culture 4 to structure and communicate ideas effectively in both oral and written form 5 to be a constructive and efficient member of a team 6 The ability to further their own learning through effective use of feedback 7 The ability to communicate both qualitative and quantitative reasoning
Teaching/learning methods and strategies Classes are given on literary, historical and linguistic concepts and on approaches to translation. Throughout their studies, students take classes and receive instruction in Mandarin Chinese language. The year abroad further promotes the active learning of the Chinese language to an advanced level. Comprehensive bibliographies are provided for each course, as are guidelines for the production of essays, coursework assignments and dissertations.
Assessment All skills listed are primarily assessed through essays, coursework assignments and dissertations. Use of the Mandarin Chinese language and translating and interpreting from and into Chinese are assessed by class and home exercises, tests and degree examinations. The ability to gather information on Chinese speaking countries and to present it effectively in English is assessed through degree examinations on Chinese literature, history, thought, culture and society.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness
the confidence to rely on one’s own intellectual capacities the ability to motivate oneself, to plan one’s own work, and to set one’s own goals and deadlines ability to work autonomously time and priority management skills be sensitive to ambiguity and multiplicity of meanings to exercise leadership skills
The small classes in the final year of the degree allow space for extensive discussion involving all the students.
11 The dissertation and the year abroad work for History test the ability to sustain skills over a more extended and complex piece of work.
11f) Technical/practical skills
Students should acquire skills that can be used in a wide variety of intellectual contexts and forms of employment. These include: -
Computing skills – the ability to use computers for word-processing, information storage and for retrieving information from the world wide web High level language programming ability in STATA and/or other statistical packages Modelling skills: abstraction, logic, succinctness, quantitative analysis (mathematics and statistics) Qualitative analysis Use of libraries – the ability to use libraries for the recovery of information, and related research skills, including the ability to discriminate between different sources of information, suggested readings, and so on.
Students are given instruction in how to access material in Chinese through the use of internet resources. Students routinely use Chinese word processing software to insert Chinese characters into essays and dissertations. During the year abroad, students carry out guided reading under the supervision of a member of the School of Economics, and write an essay.
12 12 Programme structure and features
Chinese and Economics(MA)
Degree Type: Joint Honours
NYT Course CT W 1 Economics 1A 40 Chinese 1 40 Further courses 40 2 Chinese 2A or 2B 40 Economics 2 40 Issues in Global Economics 20 Further Courses 20 3* Chinese Language 80 0 Acquisition Through Residence/Study B Chinese History 3 or 20 1 Chinese Literature 3 Chinese Special 20 0 Subject 3 4 Chinese Language 4a 10 2 Chinese Language 4b 10 2 Chinese Oral 0 1 Chinese Special 20 2 Subject 4 Essentials of Econometrics 20 1 Applications of Economic 20 1 Analysis Topics in Economic 20 1 Analysis 1 Economics Option 20 1 * Entry into third year normally requires (i) 240 credits (ii) a mark of 50% or above at first sitting in Economics 2 (iii) a pass in Issues in Global Economics (iv) a mark of 50% or above at first sitting in Chinese 2A or 2B FINAL ASSESSMENT WEIGHTING: - One unit of assessment is allocated to every 20 credits and constitutes one 20-credit paper. The following are the twelve 20-credit papers on
13 which the classification of the degree is based. (Papers that for the purposes of degree classification acquire a weighting of 40 credits are, therefore, listed twice.) 1. (Chinese Language 4A). 2. (Chinese Language 4A). 3. (Chinese Language 4B). 4. (Chinese Language 4B). 5. (Oral for Chinese). 6. (Chinese Special Subject 3). 7. (Chinese Special Subject 4). 8. (Chinese History 3 or Chinese Literature 3). 9. (Essentials of Econometrics). 10. (Applications of Economic Analysis). 11. (Topics in Economics Analysis 1). 12. (Honours option for Economics).
Progression Requirements: Students are normally expected to have gained 120 credits from each year of study.
Students who do not progress into Honours may graduate after three years of full- time study, or a longer prescribed period of part-time study, with a B.A. in Humanities and Social Science.
13 Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies
Teaching and Learning strategies employed at the University of Edinburgh consist of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
Teaching and Learning Activities
In Year 1 Lectures Tutorials
In Year 2 Lectures Tutorials
In Year 3 Year Abroad Work Dissertation Independent Study
In Year 4 Seminars Lectures Presentations Group Work
Innovative Learning Week
The University of Edinburgh Innovative Learning Week is scheduled in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space
14 outwith the curriculum for staff and students to explore new learning activities. Some examples of the types of activities held in the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures were: -
The Year Abroad: the funny, the frazzling, the infuriating, Guided Visit to the East Asian Collection at the National Museum of Scotland, ‘Halal Haggis? An Introduction to Islam in Scotland’, Scots Ballard Workshop, The Hidden Lives of your Lecturers and Tutors: a one day Colloquium on research in progress.
14 Assessment Methods and Strategies
Assessment Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often takes the form of formative work which provided the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment which is submitted for assessment.
In Year 1 Written Examinations Oral Examinations Coursework Essays Coursework Exercises
In Year 2 Written Examinations Oral Examinations Coursework Essays Coursework Exercises
In Year 3 Year Abroad Work Dissertation
In Year 4 Written Examinations Coursework Essays Oral Examination Dissertation
15 Career Opportunities Graduates have a broad range of careers available to them. Chinese and Economics graduates are in demand in the media, commerce and the Civil Service, and many are recruited by companies based in East Asia.
15 Graduates in Chinese and Economics can use their language skills to work as translators, interpreters or teachers. The research and analytical skills you will develop throughout the course can be used in any research-based career. These skills can also be applied to careers including journalism, museum or heritage work, public relations, the Diplomatic Service or teaching. Previous graduates have also gone on to work in finance, law or local government or have chosen postgraduate study.
16 Other Items all students are assigned a Personal Tutor on admission to the degree programme, who oversees the course of the student’s degree programme, offers advice on academic matters (including degree-progression) and should be the student’s first port of call for course-related worries or concerns student opinion is actively sought through participation in Staff-Student Liaison Committees, through the election of class- and tutorial- representatives, and by the wide circulation and review of detailed student questionnaires each semester. LLC have a student support office, where students can go for advice on degree transfers, course changes, authorised interruption of studies, confirmation letters and general support. Information can be found at: - http://www.ed.ac.uk/schools-departments/literatures-languages- cultures/current-students/undergraduate-support further information about Asian Studies can be found at http://www.asianstudies.ed.ac.uk/ further information about Economics can be found at http://www.ed.ac.uk/schools-departments/economics
16 THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR M.A. Honours in Chinese and Italian1
7) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
8) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
9) Programme accredited by: The University of Edinburgh
10) Final Award: MA
11) Programme Title: MA Joint Honours in Chinese and Italian
12) UCAS Code: Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): Languages
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Iona Macintyre 8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary The University of Edinburgh is the only university in Scotland to offer an Honours degree in Chinese. Research interests of staff at the Scottish Centre for Chinese Studies cover literature, translation, film, history and culture: the expertise of the teaching staff was reflected in an excellent performance in the recent Research Assessment Exercise. The Scottish Centre for Chinese Studies serves as a platform to link China related research at University of Edinburgh and at other HEI's in Scotland. The Confucius Institute was established in 2006. Within six years of operation the Institute has developed into a comprehensive cultural centre.
Italy is one of Europe’s most creative and distinctive civilisations with a fascinating history and culture. You will receive a good foundation in both the language and cultural studies and will spend time teaching, working or studying in Italy. The small class sizes and vibrant Italian Society make it easy to get to know teaching staff and other students. The mixture of exchange students and Italian and UK staff creates an interesting and vibrant learning environment.
Connections between China and Italy can be traced back for hundreds of years, from the Silk Road and Marco Polo to Michelangelo Antonioni’s Chung Kuo Cina. a documentary about life in Maoist China that sparked huge controversy. The
1 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 17 combined degree in Chinese and Italian provides students with the opportunity to acquire expertise in two of the world’s most important languages.
10) Educational aims of programme:
The programme aims to develop the student’s interest in and complex knowledge and understanding of the target countries, including their language, history, literature, culture and social issues. The programme offers society the resource of intellectually trained individuals capable of acting as conduits of knowledge and understanding between British and non-British cultures, as well as using the acquired knowledge to contribute to the wealth creation of Britain and other nations. The programme is taught within the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures.
The programme aims to enable students with little or no previous knowledge of Chinese language and culture to acquire and develop interest in and understanding of Chinese speaking countries, including the Chinese language (Mandarin), history, literature, culture and society. It offers society the resource of intellectually trained individuals capable of acting as conduits of knowledge and understanding between Britain and Chinese-speaking countries. During the first two years, students attend a range of classes which provide a solid foundation in the Chinese language (Mandarin). Together with courses on modern Chinese society and culture as well as outlines on China's rich history from earliest times to the present day students are well prepared for the third year of the programme. The same pattern is repeated in Italian with language courses supplemented by courses on culture and society. For the third year of the programme students can choose whether to spend one semester in Italy and one in China or the whole of the academic year in China with a minimum of eight weeks in a Italian-speaking country. In the fourth year students intensify their study on primary sources in courses on key notions of classical philosophy and literature as well as courses on modern and contemporary China and Italy.
The programme is taught within the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures.
The main programme aims of the programme are to enable students to understand, evaluate and compare a range of theoretical and methodological frameworks. to enable students to develop and apply their knowledge and skills to the understanding and evaluation of issues and problems in the contemporary world. to enable students to develop and apply key generic skills in critical thinking, research, oral and written articulation of information and argument. to equip students for progression to a wide variety of careers or to further academic study.
18 11) Programme outcomes:
11a) Knowledge and understanding
1. Modern spoken and written Chinese (Mandarin) and Italian 2. Modern and classical Chinese and Italian literature 3. Chinese and Italian history and thought 4. Political and social issues related to Chinese and Italian speaking countries 5. Linguistic issues related to the Chinese and Italian languages (structure, functions, registers, writing systems etc.) 6. Key methods and concepts of literary, historic and linguistic analysis
Teaching/learning methods and strategies The target languages are acquired through small-group classes, tutorials and regular, assessed coursework. Additional support is provided through the self-access facilities for language learning at the Language and Humanities Centre and the Languages MicroLab. Knowledge of Chinese and Italian literature, history, thought, culture and society is acquired through a combination of lectures and tutorials or seminars including group discussion and individual or joint presentations.
Assessment Testing on the knowledge base is through unseen written examinations in all areas, combined with assessed regular language exercises and oral examinations in Chinese language; and essays, coursework assignments and exams in Chinese cultural studies. For Italian, testing on the knowledge base is through a combination of assessed regular language exercises, class presentation and unseen written examination, coursework essays, extended essays and oral examination.
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry
8 to reason critically and cogently 9 to apply linguistic, literary and historical concepts 10 to identify and solve problems 11 to analyse and interpret
Teaching/learning methods and strategies Intellectual skills are developed through the teaching and learning programme outlined above. Each course, whatever the format of the teaching, involves discussion of the key issues, practice in applying concepts both orally and in writing, analysis and interpretation of material and individual feedback on work produced Classes are given on literary, historical, social and linguistic concepts and on approaches to translation. Throughout their studies, students take classes and receive instruction in the target languages. The Year abroad further promotes the active learning of the target languages to a high level.
19 Comprehensive bibliographies are provided for each course as are the guidelines for the production of coursework essays, and extended essays.
Assessment The variety of assessment methods employed all place great emphasis on the learner’s ability to demonstrate the above skills through the production of cogent and coherent written and oral responses to problems and tasks set. Essays produced in the Honours years provide an especially valuable vehicle for the training of those skills. All the listed skills are primarily assessed through the assessed coursework essays, and extended essays, skills are manifested in degree exams on the Literature, Culture and History of the target languages and country/countries concerned.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy graduates will be able to: process, structure and communicate ideas effectively and at an advanced/near-native level of proficiency, both orally and in written form in Italian, Chinese and English; communicate clearly and accurately, constructing cogent arguments; participate constructively and efficiently in group discussions, assessing and responding effectively to the ideas of others; and communicate effectively in English to inform and educate others about Italian and Chinese language and culture. demonstrate and exercise independence of mind and thought
Teaching/learning methods and strategies All courses require written work, usually in the form of essays, and regular feedback is given to the learners in order to develop their understanding and power of expression. Teamwork and leadership skills are acquired through active contributions to tutorials and seminars, both as group members and discussion leaders. Time management is learned through the expectation to submit coursework by prescribed deadlines notified at the outset of each course. Teamwork and assessment and response to the ideas of others are developed in classes, seminars and tutorials, which rely on discussion and interaction, as well as presentations by individuals and groups of students. Independent work and self- reliance are developed during the year abroad. IT skills are developed through University-wide training courses and individual learning.
Assessment Effective communication of ideas is an important criterion in assessing all areas of a learner’s work, and the regular feedback and the final mark both reflect this. Additionally, penalties are levied for late submission of essays and coursework assignments. Structuring and communication of ideas, independent work, self-
20 reliance, IT skills and assessment and response to the ideas of others are all assessed through regular coursework essays. Although these are supervised they are nevertheless a manifestation of the independent thought and research by the learner. I
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication
8 To speak, write and read Mandarin Chinese and Italian at an advanced level of proficiency 9 To translate and interpret from and into Mandarin Chinese and Italian 10 To use the Internet and bibliographic resources in both Mandarin Chinese and Italian 11 To communicate effectively in English to inform and educate others about Chinese and Italian language and culture
Teaching/learning methods and strategies Classes are given on literary, historical and linguistic concepts and on approaches to translation. Throughout their studies, students take classes and receive instruction in Italian and Mandarin Chinese language. The year abroad further promotes the active learning of the two languages to an advanced level. Comprehensive bibliographies are provided for each course, as are guidelines for the production of essays and coursework assignments.
Assessment All skills listed are primarily assessed through essays, and coursework assignments. Use of the Mandarin Chinese and Italian languages and translating and interpreting from and into Chinese and Italian are assessed by class and home exercises, tests and degree examinations. The ability to gather information on Chinese and Italian speaking countries and to present it effectively in English is assessed through degree examinations on Chinese and Italian literature, history, thought, culture and society. Effective communication of ideas is an important criterion in assessing all areas of a learner’s work, and the regular feedback as well as the final mark reflects this. Additionally, penalties are levied for late submission of coursework essays and other assignments. Skills are also assessed through the assembly of necessary information for essays etc. and their production on PCs.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness graduates will be able to: work autonomously, setting their own goals, self-motivating and organising their own learning; manage their time and priorities and working to both self-imposed and external deadlines; collaborate effectively and productively with others in the process of learning and presenting conclusions, exercising leadership skills as appropriate;
21 confidently rely on their own intellectual capacities; exercise sensitivity to ambiguity and multiplicity of meanings; and confidently interacting with, and think about, cultural difference.
Assessment:
Skills are assessed through regular coursework, essays, and long essays, which although supervised are nevertheless a manifestation of independent thought and work/research by the learner and are further developed during the year abroad. Also through the management of time to meet the various deadlines (all notified at the outset of each course) for submission of coursework. The small classes in the final year of the degree allow space for extensive discussion involving all the students.
11f) Technical/practical skills graduates will develop: IT skills – the ability to use computers for word-processing, information storage and for retrieving information from the world wide web, including the use of foreign language symbols on the computer, or foreign-language computer keyboards; and library skills – the ability to use libraries for the recovery of information, and related research skills, including the ability to discriminate between different sources of information, suggested readings, and so on. Students are given instruction in how to access material in Chinese through the use of internet resources. Students routinely use Chinese word processing software to insert Chinese characters into essays.
Assessment:
Skills for both languages are assessed by class and home exercises, tests and degree examinations
12 Programme structure and features The section presents the structure of the programme in relation to the University’s Curriculum Framework. It must include: SQCF credit points for each constituent course and each year of the programme Entry requirements, including requirements for second-year entry where applicable Progression requirements Modes of study Exit awards available at the completion of specific stages of the programme
22 If not provided earlier in the programme specification, include information on relevant factors from the University’s Strategic Plan, e.g. embedding in the curriculum issues of social responsibility, sustainability, equality and diversity.
DEGREE PROGRAMME TABLE
Degree Programme Title: MA with Honours in Chinese and Italian
1 Chinese 1 G 8 40 Modern China in Literature and Film G 8 40 Italian 1 G 8 40
2 Chinese 2A G 8 40 Chinese 2B G 8 40 Italian Language 2 G 8 20 Italian Literature: Texts in Context 2 G 8 20
3 Chinese Year abroad (Combined Degree) G 10 60 Language Acquisition through residence/study G 10 60
4 MEL Long Essay G 10 20 Italian Language Paper 1 G 10 10 Italian Language Paper 2 G 10 10 Italian Oral G 10 0 Course in Italian G 10 20 Chinese Oral G 10 0 Chinese Language 4A G 10 10 Chinese Language 4B G 10 10 Courses in Chinese G 10 40
Requirements for Admission to Honours Passes at 50% or above at the first attempt in all second year courses.
Final Assessment:
One unit of assessment is allocated to every 20 credits and constitutes one 20-credit paper. The following are the twelve 20-credit papers on which the classification of the degree is based. (Papers that for the purposes of degree classification acquire a weighting of 40 credits are, therefore, listed twice). 1. Italian Language Paper 1
23 2. Italian Language Paper 1 3. Italian Language Paper 2 4. Italian Oral 5. Chinese Language 4A 6. Chinese Language 4A 7. Chinese Language 4B 8. Chinese Oral 9. Italian option 10. MEL Long Essay 11. Course in Chinese 12. Course in Chinese
13 Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and Learning strategies employed at the University of Edinburgh consist of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
Teaching and Learning Activities
In Year 1 Lectures Tutorials
In Year 2 Lectures Tutorials
In Year 3 Year Abroad Work Independent Study Distance Learning
In Year 4 Seminars Lectures Presentations Group Work
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh Innovative Learning Week is scheduled in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space outwith the curriculum for staff and students to explore new learning activities. Some examples of the types of activities held in the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures were: -
The Year Abroad: the funny, the frazzling, the infuriating, Guided Visit to the East Asian Collection at the National Museum of Scotland, ‘Halal Haggis? An Introduction
24 to Islam in Scotland’, Scots Ballard Workshop, The Hidden Lives of your Lecturers and Tutors: a one day Colloquium on research in progress.
14 Assessment Methods and Strategies
Assessment Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often takes the form of formative work which provided the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment which is submitted for assessment.
In Year 1 Written Examinations Oral Examinations Coursework Essays Coursework Exercises
In Year 2 Written Examinations Oral Examinations Coursework Essays Coursework Exercises
In Year 3 Year Abroad Work
In Year 4 Written Examinations Coursework Essays Oral Examination Dissertation
15 Career Opportunities
Graduates have a broad range of careers available to them. Chinese graduates are in demand in the media, commerce and the Civil Service, and many are recruited by companies based in East Asia.
Graduates in Chinese and Italian can use their language skills to work as translators, interpreters or teachers. There are also opportunities to continue studying and some scholarships are available for masters and PhD programmes in Chinese and Italian.
French graduates from the University of Edinburgh enjoy excellent career prospects. Language and analytical skills developed in analysing cultural and political documents can open careers in teaching and translating in the UK or abroad. Your skills will also be valued in worldwide business and administration.
16 Other Items
25 all students are assigned a Personal Tutor on admission to the degree programme, who oversees the course of the student’s degree programme, offers advice on academic matters (including degree-progression) and should be the student’s first port of call for course-related worries or concerns student opinion is actively sought through participation in Staff-Student Liaison Committees, through the election of class- and tutorial- representatives, and by the wide circulation and review of detailed student questionnaires each semester. LLC have a student support office, where students can go for advice on degree transfers, course changes, authorised interruption of studies, confirmation letters and general support. Information can be found at: - http://www.ed.ac.uk/schools-departments/literatures-languages- cultures/current-students/undergraduate-support further information about the Division of European Languages and Cultures can be found at http://www.delc.ed.ac.uk/
26 Changes to the Business School Undergraduate Degree Portfolio
1. Degree Programme proposal This proposal provides brief details of the outcome of a long-term review of Undergraduate (UG) Programmes in the Business School which has resulted in the development of new degree programmes and changes to the name of a large number of the School’s existing degrees and those with other Schools. A key aim of these developments is to increase the quality of applications to all degree programmes offered by the School. This document presents a brief explanation of the rationale behind: introducing six entirely new Business School degrees revising the current International Business with a Language degree to create a suite of eight International Business degrees with a specified language renaming many of the existing Business School degrees and those with other Schools
Brief context Over the last four years the School has been undertaking a wide-ranging review of its portfolio of UG degrees. The process has included engagement and consultation with a range of internal (including, staff, students, the Careers Service and Recruitment and Admissions) and external stakeholders (including employees and accrediting bodies). Introduction of the new degree in Accounting and Finance was an early output from the review process. The introduction of this degree and other significant changes in admissions patterns has led to the development of the current proposals for entirely new and ‘renamed’ degrees, representing the most significant output from the review process. During this time the Business School has experienced a number of marked changes in terms of applications and admissions to its portfolio of Undergraduate degrees, including a steady increase in student numbers; a steady increase in the number of overseas applicants and the proportion of international students admitted to some programmes; a sharp decline in the number of students admitted to the Business Studies degree; and, growth in the number of students admitted to the Accounting and Finance degree so that it now accounts for around one third of the first year intake. Whilst the Business School is pleased that it continues to recruit well-qualified students, on- going review of the UG programme has highlighted the impact of these and other changes on key aspects such as the student experience and balance of teaching provision by subject groups, with consequent implications for longer-term development within the School. The review has included the analysis of longitudinal data on applications and admissions and this has highlighted the importance of responding to market changes. This has helped to provide direction to this significant redevelopment and refocusing of the degree portfolio to reflect areas of teaching excellence and changing student demand, with the introduction of a number of new degree offerings and revision of the name of the single Honours Business Studies degree and of other joint degree programmes based upon it. Entirely new degree programmes The following new degrees will be available to new students from September 2014 (many current students will have the option to transfer depending upon courses studied): Business and Finance (MA) Business with Decision Sciences (MA) Business with Enterprise and Innovation (MA) Business with Human Resource Management (MA) Business with Marketing (MA)
27 Business with Strategic Economics (MA) The Business and Finance degree is to be introduced to complement the Accounting and Finance programme which has proved popular, particularly with students from specific geographical markets. Research and experience from other institutions indicates that the Business and Finance degree will provide an attractive alternative degree option for those seeking a named finance degree without having to follow a concentration in accounting. It is also likely to attract a more diverse group of students, helping address issues of student mix across and within programmes. The suite of five ‘Business with …’ reflects areas of teaching and research specialisation within the School. These six new degrees will use as their building blocks the current collection of more than 60 undergraduate non-honours and honours courses. Introduction of these specialist pathways will enable a student to reflect in their degree title a key area of specialisation which a sizeable number of students already follow, but within the framework of the ‘Business Studies’ degree. The addition of degrees which include areas of specialisation, such as Marketing and Human Resource Management, will help attract new applications to the Business School as school leavers are looking for degrees in areas such as Marketing and Human Resource Management and are not attracted by the offer of being able to study those subjects, but ‘hidden’ away within the Business Studies degree. These new degrees also have clearer links to potential career pathways which should make them more attractive to students thinking about their longer-term career. In keeping with the current Business School degrees, the high degree of commonality in the curriculum in years 1 and 2 present in new as well as existing degrees permits an element of flexibility for students to move between different degrees programmes, facilitating student choice. The appropriate DPTs and DPSs are presented for all of the above new programmes.
Changes to degree in International Business with a Language The School offers a degree in International Business with a Language, which includes eight language options: however, the language of study is not reflected in the title of the degree award. Students on the programme often ask whether their language of study can be reflected in their degree title when graduating, which is not possible. A single generic degree programme title causes problems for Admissions which is required to check with applicants the language they wish to study. These two factors have resulted in the creation of eight separate degrees, each with a specified language. International Business with French (MA) International Business with German (MA) International Business with Spanish (MA) International Business with Italian (MA) International Business with Russian (MA) International Business with Chinese (MA) International Business with Japanese (MA) International Business with Arabic (MA) There will be no changes to the curriculum, and current students following the generic ‘Business with a Language degree’ will have the option of transferring to the appropriate named pathway based upon their language of study. Similarities in the curriculum of the International Business degree means that a student will still to be able to switch from the language to the non-language variant. With appropriate concessions, transfer to other Business School degrees will continue as an option. The change to the name is likely to
28 attract higher calibre applicants seeking a named language degree and allow students to signal to prospective employers, at first glance, a clearer indication of the focus of their area of language knowledge and skills. The appropriate DPTs and DPSs are presented for all of the above new programmes.
Name changes to Business School-owned degrees As noted above there has been a marked decline in the number of students admitted to the Business Studies degree at the same time as the size of the in-take has risen. The degree name of ‘Business Studies’ is considered to have become somewhat ‘dated’. In order to increase the number of high quality applicants to the School’s single honours offering the decision has been taken to rename the degree. Market research has informed the decision to change the name of the single honours degree to MA Business Management. This title is seen as providing a more appropriate description for the programme and should result in the programme being received more positively within the marketplace. The content of the programme will remain unchanged. In line with the removal of the word ‘Studies’ from the single Honours degree title, the decision has been taken to amend the name of all the joint degree titles to ‘Business and ….’ or ‘…. and Business’. All of the degrees for which the names are to be changed are viewed as new degrees but, other than the change of name, the DPT and DPS for each programme remain unchanged so, with the agreement of colleagues in CHSS, new DPTs and new DPSs are not presented here for degrees where a simple change of name is being made. Consultation has been undertaken with all Schools and there is agreement for the following degree titles to be amended: Changes to the name of Business School degrees with other Schools Old name New name Business Studies (MA) Business Management (MA) Business Studies and Accounting (MA) Business and Accounting (MA) Business Studies and Economics (MA) Business and Economics (MA) Business Studies and Geography (MA) Business and Geography (MA) Business Studies and Law (MA) Business and Law (MA)
Changes to the name of degrees with the Business School owned by other Schools Old name New name Arabic and Business Studies (MA) Arabic and Business (MA Economic History and Business Studies (MA) Economic History and Business (MA) French and Business Studies (MA) French and Business (MA) German and Business Studies (MA) German and Business (MA) Italian and Business Studies (MA) Italian and Business (MA) Law and Business Studies (LLB) Law and Business (LLB) Mathematics and Business Studies (BSc) Mathematics and Business (BSc) Portuguese and Business Studies (MA) Portuguese and Business (MA) Psychology and Business Studies (MA) Psychology and Business (MA) Russian Studies and Business Studies (MA) Russian Studies and Business (MA) Spanish and Business Studies (MA) Spanish and Business (MA)
29 Withdrawal’ of degree programmes Three joint degrees with LLC will be withdrawn as a result of very low levels of recruitment. Introduction of the International Business with a Language option some years ago has resulted in decline in intakes into the following programmes which will be closed to new applicants as of September 2014. Full support for students on the programmes will continue until all have graduated. Business Studies and French (MA) Business Studies and German (MA) Business Studies and Spanish (MA
There has been consultation will LLC and approval has been given by both Schools. Technically, all of the degrees for which the names are to be changed will be withdrawn for new entrants as of September 2014, and for current students as soon as all have graduated from the ‘old’ degree or transferred to the newly named degree.
Impact on resource and staff All of the above developments are based upon use of existing courses and library and other resources are provided to support these activities. The aim is to achieve a more optimal balance across teaching areas within the School and reduce the pressure which is being experienced in some areas. Removal of programmes with very small numbers will allow concentration of administrative resources on other programmes. The new programmes will not involve any activities which lie outside those currently undertaken to support students on current programmes of study. There was a discussion of possible risks associated with launching the new programme and none were seen to be of concern; rather, there were perceived to be serious risks associated with not making changes to the Business School’s offering.
2. External Examiner’s feedback The School’s External Examiners were informed of proposed changes and none expressed any concerns.
3. Programme specification Programme specifications are provided for the following new programmes: Business and Finance (MA) Business with Decision Sciences (MA) Business with Enterprise and Innovation (MA) Business with Human Resource Management (MA) Business with Marketing (MA) Business with Strategic Economics (MA) International Business with French (MA) International Business with German (MA) International Business with Spanish (MA) International Business with Italian (MA) International Business with Russian (MA) International Business with Chinese (MA) International Business with Japanese (MA) International Business with Arabic (MA)
30 4. Degree Programme Table Programme tables are provided for the following new programmes: Business and Finance (MA) Business with Decision Sciences (MA) Business with Enterprise and Innovation (MA) Business with Human Resource Management (MA) Business with Marketing (MA) Business with Strategic Economics (MA) International Business with French (MA) International Business with German (MA) International Business with Spanish (MA) International Business with Italian (MA) International Business with Russian (MA) International Business with Chinese (MA) International Business with Japanese (MA) International Business with Arabic (MA)
5. Course details (if new courses introduced) Not applicable
6. Extract from the Minutes of the approving Board of Studies Thursday 18 October 2012, 2.00 pm, the Boardroom, 29 Buccleuch Place 9. Board of Studies
New degree pathways
A paper summarising the proposed new degree programme pathways and the re-naming of other programmes was circulated. The content of all new programmes has been discussed within subject groups and agreed. The re-naming of the joint degree programme titles has been discussed and agreed with the appropriate schools; the curriculum for these programmes remains unchanged.
It was agreed to adopt the new programme title MA Business Management for the single degree currently entitled MA Business Studies. The new ‘with’ specialised degrees and other joint programmes will drop the ‘Management’ label eg MA Business with Marketing; MA Spanish and Business. The new specialised programmes will be available from 2014/15. Students currently in 1st year 2012/13 will be able to transfer to the more specialised degree programme at the end of their 2nd year, if they wish to do so. Approval was given by the Board of Studies to accept all the new degree proposals as outlined in the paper.
7. Prospectus text The Business School has informed colleagues in Admissions of the proposed changes and is on contact with those concerned with production of the prospectus regarding making minor modifications to the entry currently included under Business.
Sarah Cooper Director of Undergraduate Programmes University of Edinburgh Business School October 2012
31 Summary of changes to Business School degrees and those with other Schools
Current Business School degrees to be renamed for students entering in September 2014 Old name New name Discussed/approved, with relevant parties Business Studies Business Management Approved by Business School BoS Business Studies and Business and Accounting Approved by Business School BoS Accounting Business Studies and Business and Economics Approved by Business School BoS and Economics Economics Business Studies and Business and Geography Approved by Business School BoS and Geography Geosciences Business Studies and Law Business and Law Approved by Business School BoS and Law
New Business School degrees to be introduced for students entering in September 2014 Degree programme name Discussed/approved, with relevant parties Business and Finance Approved by Business School BoS Business with Decision Sciences Approved by Business School BoS Business with Enterprise and Innovation Approved by Business School BoS Business with Human Resource Management Approved by Business School BoS Business with Marketing Approved by Business School BoS Business with Strategic Economics Approved by Business School BoS International Business with French Approved by Business School BoS and LLC International Business with German Approved by Business School BoS and LLC International Business with Spanish Approved by Business School BoS and LLC International Business with Italian Approved by Business School BoS and LLC International Business with Russian Approved by Business School BoS and LLC International Business with Chinese Approved by Business School BoS and LLC International Business with Japanese Approved by Business School BoS and LLC International Business with Arabic Approved by Business School BoS and LLC
Business School degrees to be withdrawn for new admissions as of September 2014 Degree programme name Discussed/approved with relevant parties Business Studies and French Approved by Business School BoS and LLC Business Studies and German Approved by Business School BoS and LLC Business Studies and Spanish Approved by Business School BoS and LLC International Business with a Language Approved by Business School BoS and LLC
32 Degrees in other Schools to be renamed for students entering in September 2014 Old name New name Discussed/approved, with relevant parties Arabic and Business Studies Arabic and Business Approved by Business School BoS and LLC Economic History and Economic History and Approved by Business School BoS and Business Studies Business HCA French and Business Studies French and Business Approved by Business School BoS and LLC German and Business Studies German and Business Approved by Business School BoS and LLC Italian and Business Studies Italian and Business Approved by Business School BoS and LLC Law and Business Studies Law and Business Approved by Business School BoS and Law Mathematics and Business Mathematics and Business Approved by Business School BoS and Studies Mathematics Portuguese and Business Portuguese and Business Approved by Business School BoS and Studies LLC Psychology and Business Psychology and Business Approved by Business School BoS and Studies Psychology Russian Studies and Business Russian Studies and Approved by Business School BoS and Studies Business LLC Spanish and Business Studies Spanish and Business Approved by Business School BoS and LLC
33 Business DPTs Business and Finance YEAR 1 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 ACCN08007 Accountancy 1A Semester 1 20 ACCN08008 Accountancy 1B Semester 2 20 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ECNM08005 Economics 1A 40 ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications 40 YEAR 2 4 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Semester 1 20 Quantitative Techniques BUST08003 Principles of Finance Semester 1 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance Semester 2 20
AND
Select exactly 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20
Notes: (BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems (20 credits) is recommended)
Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in Principles of Finance and Applications of Finance in second year, and (iii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two other Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
Students whose application to study abroad at a partner university in third year is successful must register for the 0-credited course BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad in second year.
34 YEAR 3 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE10002 Strategic Management Semester 1 20 BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 CMSE10003 Business Research Methods Semester 2 20 II: Applications and Analysis AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20
Note: Futures and Option (BUST10023) and Investment and Securities Markets (BUST10031) are recommended.
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and 20 Controversies BUST10067 International Marketing 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10036 Risk Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10118 Marketing Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10114 Services Marketing 20
Note: Students who spend their third year abroad at a partner university must complete and pass a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be in Business and Finance. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the year 3 compulsory course Strategic Management.
35 YEAR 4 2 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Full Year 40 Dissertation BUST10012 Corporate Finance Semester 2 20
AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and 20 Controversies BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
Business with Strategic Economics YEAR 1 6 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits
36 BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 ACCN08007 Accountancy 1A Semester 1 20 ACCN08008 Accountancy 1B Semester 2 20 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0 ECNM08005 Economics 1A Full Year 40 YEAR 2 4 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Semester 2 0 Planning CMSE08002 Business Research Methods Semester 1 20 I: Quantitative Techniques BUST08005 Business Economics Semester 1 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance Semester 1 20
AND
Select a minimum of 20 credits and maximum of 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits
BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
Notes: (BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems is recommended)
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 40 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Notes: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year, one of which must be in Business Economics (but not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
Students whose application to study abroad at a partner university in third year is successful must register for the 0-credited course BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad in second year.
37 YEAR 3 4 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE10002 Strategic Management Semester 1 20 BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 CMSE10003 Business Research Methods II: Semester 2 20 Applications and Analysis BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Semester 2 20 Strategy AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Period Credits Investment and Securities BUST10032 Semester 1 20 Markets BUST10023 Futures and Options Semester 2 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ACCN10026… Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10036 Risk Management 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10067 International Marketing 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10118 Marketing Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10114 Services Marketing 20
Note: Students who spend their third year abroad at a partner university must complete and pass a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be in Business and Strategic Economics. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the
38 year 3 compulsory course Strategic Management.
39 YEAR 4 2 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40 BUST10008 Market Structure, Conduct and Semester 1 20 Performance
Exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10012 Corporate Finance Semester 2 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency Semester 1 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10036 Risk management 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10011 Mathematical programming 20 BUST10013 Decisions making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH GERMAN
40 YEAR 1 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ECNM08005 Economics 1A 40 ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications 40
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ELCG08001 German 1A 40 ELCG08002 German 1B 40
YEAR 2 6 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A Semester 1 20 BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Semester 2 20 Enterprise 2B CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Semester 1 20 Techniques BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Full Year 0 Abroad ELCG08006 German 2 Full Year 40
AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
OR
Select exactly 20 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Note: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in
41 second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
YEAR 3 2 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 XXXX10008 Compulsory year abroad (full year) - level 10 Full Year 120
Note: Students must spend their third year abroad at a partner university, in the country of the language being studied, completing and passing a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be undertaken and examined in the language being studied. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management.
YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select a minimum of 20 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
Notes: Students must choose a minimum of 60 credits in International Business: EITHER an International Business oriented Management Honours Dissertation (40 credits) plus one International Business designated course (20 credits) OR three International Business designated courses (60 credits) from the courses listed above.
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20
42 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
Business with Decision Sciences YEAR 1 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 ACCN08007 Accountancy 1A Semester 1 20 ACCN08008 Accountancy 1B Semester 2 20 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from Level 7 and 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Notes:( ECNM08005 Economics 1A (40 credits) ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits) is recommended)
YEAR 2 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Semester 2 0 Planning CMSE08002 Business Research Methods Semester 1 20 I: Quantitative Techniques BUST08007 Management Science and Semester 2 20 Information Systems AND
Select a minimum of 40 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20
43 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
Notes: (BUST08005 Business Economics (20 credits) is recommended)
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 40 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Notes: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year, one of which must be in Management Science and Information Systems (but not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
Students whose application to study abroad at a partner university in third year is successful must register for the 0-credited course BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad in second year.
44 YEAR 3 4 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE10002 Strategic Management Semester 1 20 BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 CMSE10003 Business Research Methods II: Semester 2 20 Applications and Analysis BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Semester 1 20 Planning AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Semester 2 20 Strategy BUST10036 Risk Management Semester 1 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ACCN10026… Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and 20 Controversies BUST10067 International Marketing 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10118 Marketing Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10114 Services Marketing 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10036 Risk Management 20
Note: Students who spend their third year abroad at a partner university must complete and pass a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be in Business and Decision Sciences. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the year 3 compulsory course Strategic Management.
45 YEAR 4 3 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Full Year 40 Dissertation BUST10013 Decision-Making under Semester 1 20 Uncertainty BUST10011 Mathematical Semester 2 20 Programming
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon 20 World BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and 20 Controversies BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: 20 Course B BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10036 Risk Management 20 BUST10008 Market Structure, Conduct and Performance 20
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH ITALIAN
YEAR 1
46 4 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0 ELCI08001 Italian 1 Full Year 40
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ECNM08005 Economics 1A 40 ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications 40
YEAR 2 7 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Semester 1 20 Trade 2A BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Semester 2 20 Enterprise 2B CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Semester 1 20 Techniques BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Full Year 0 Abroad ELCI08004 Italian Language 2 Full Year 1 20 ELCI08005 Italian Literature: Texts in Context 2 Full Year 20
AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
OR
Select exactly 20 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Note: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
YEAR 3 2 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits
47 BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 XXXX10008 Compulsory year abroad (full year) - level 10 Full Year 120
Note: Students must spend their third year abroad at a partner university, in the country of the language being studied, completing and passing a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be undertaken and examined in the language being studied. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management.
YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select a minimum of 20 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
Notes: Students must choose a minimum of 60 credits in International Business: EITHER an International Business oriented Management Honours Dissertation (40 credits) plus one International Business designated course (20 credits) OR three International Business designated courses (60 credits) from the courses listed above.
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20
48 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH JAPANESE
YEAR 1 4 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0 ASST08002 Japanese 1 Full Year 40
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ECNM08005 Economics 1A 40 ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications 40
YEAR 2 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Semester 1 20 Trade 2A BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Semester 2 20 Enterprise 2B CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Semester 1 20 Techniques BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Full Year 0 Abroad
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ASST08006 Japanese 2A 40 ASST08007 Japanese 2B 40
AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20
49 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
OR
Select exactly 20 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Note: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
YEAR 3 2 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 XXXX10008 Compulsory year abroad (full year) - level 10 Full Year 120
Note: Students must spend their third year abroad at a partner university, in the country of the language being studied, completing and passing a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be undertaken and examined in the language being studied. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management.
YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select a minimum of 20 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
Notes: Students must choose a minimum of 60 credits in International Business: EITHER an International Business oriented Management Honours Dissertation (40 credits) plus one International Business designated course (20 credits) OR three International Business designated courses (60 credits) from the courses listed above.
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20
50 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
Business with Enterprise and Innovation YEAR 1 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 ACCN08007 Accountancy 1A Semester 1 20 ACCN08008 Accountancy 1B Semester 2 20 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from Level 7 and 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Notes:( ECNM08005 Economics 1A (40 credits) ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits) is recommended)
YEAR 2 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Semester 1 20 Quantitative Techniques BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship Semester 2 20 AND
Select a minimum of 40 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as
51 available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 40 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Notes: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year, one of which must be in Innovation and Entrepreneurship (but not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
Students whose application to study abroad at a partner university in third year is successful must register for the 0-credited course BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad in second year.
52 YEAR 3 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE10002 Strategic Management Semester 1 20 BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 CMSE10003 Business Research Methods Semester 2 20 II: Applications and Analysis The Entrepreneurial Semester 1 20 BUST10115 Manager BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Semester 2 20 Venture Creation AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and 20 Controversies BUST10067 International Marketing 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10036 Risk Management 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: 20 Course B BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10118 Marketing Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10114 Services Marketing 20
Note: Students who spend their third year abroad at a partner university must complete and pass a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be in Business, Enterprise and Innovation. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the year 3 compulsory course Strategic Management.
53 YEAR 4 3 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40 BUST10119 Green and Sustainable Semester 2 20 Entrepreneurship BUST10120 Enterprise Consultancy Project Semester 1 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon 20 World BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and 20 Controversies BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: 20 Course B BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH ARABIC
54 YEAR 1 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0 IMES08026 Arabic 1a Semester 1 20 IMES08027 Arabic 1b Semester 2 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ECNM08005 Economics 1A 40 ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications 40
YEAR 2 6 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Semester 1 20 Trade 2A BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Semester 2 20 Enterprise 2B CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Semester 1 20 Techniques BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Full Year 0 Abroad IMES08006 Arabic 2 Full Year 40
AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
OR
Select exactly 20 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Note: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
YEAR 3 2 compulsory courses
55 Code Course Name Period Credits BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 XXXX10008 Compulsory year abroad (full year) - level 10 Full Year 120
Note: Students must spend their third year abroad at a partner university, in the country of the language being studied, completing and passing a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be undertaken and examined in the language being studied. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management.
YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select a minimum of 20 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
Notes: Students must choose a minimum of 60 credits in International Business: EITHER an International Business oriented Management Honours Dissertation (40 credits) plus one International Business designated course (20 credits) OR three International Business designated courses (60 credits) from the courses listed above.
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20
56 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH RUSSIAN
YEAR 1 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ECNM08005 Economics 1A 40 ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications 40
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ELCR08005 Russian Studies 1A 40 ELCR08002 Russian 1B 40
YEAR 2 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Semester 1 20 Trade 2A BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Semester 2 20 Enterprise 2B CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Semester 1 20 Techniques BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Full Year 0 Abroad ELCR08003 Russian Language 2 Full Year 20 ELCR08006 The Golden and Silver Ages of Russian Full Year 20 Literature (1820-1920s)
AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20
57 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
OR
Select exactly 20 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Note: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
YEAR 3 2 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 XXXX10008 Compulsory year abroad (full year) - level 10 Full Year 120
Note: Students must spend their third year abroad at a partner university, in the country of the language being studied, completing and passing a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be undertaken and examined in the language being studied. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management.
YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select a minimum of 20 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
Notes: Students must choose a minimum of 60 credits in International Business: EITHER an International Business oriented Management Honours Dissertation (40 credits) plus one International Business designated course (20 credits) OR three International Business designated courses (60 credits) from the courses listed above.
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits
58 BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
Business with Human Resource Management YEAR 1 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 ACCN08007 Accountancy 1A Semester 1 20 ACCN08008 Accountancy 1B Semester 2 20 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from Level 7 and 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Notes: (ECNM08005 Economics 1A (40 credits) or ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications or SCIL08004 Sociology 1A: The Sociological Imagination: Individuals and Society (20 credits) AND SCIL08005 Sociology 1B: The Sociological Imagination: Private Troubles, Public Problems (20 credits) are recommended)
YEAR 2 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Semester 2 0 Planning CMSE08002 Business Research Methods Semester 1 20 I: Quantitative Techniques
59 BUST08011 Organisation Studies Semester 1 20
AND
Select a minimum of 40 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
Notes: (BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations (20 credits) is recommended)
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 40 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Notes: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year, one of which must be in Organisation Studies (but not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
Students whose application to study abroad at a partner university in third year is successful must register for the 0-credited course BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad in second year.
60 YEAR 3 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE10002 Strategic Management Semester 1 20 BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 CMSE10003 Business Research Methods II: Semester 2 20 Applications and Analysis BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Semester 1 20 Current Issues and Controversies BUST10107 Managing Change Semester 2 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10067 International Marketing 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10036 Risk Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course 20 B BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10118 Marketing Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10114 Services Marketing 20
Note: Students who spend their third year abroad at a partner university must complete and pass a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be in Business and Human Resource Management. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the year 3 compulsory course Strategic Management.
61 YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and 20 Controversies BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH CHINESE
62 YEAR 1 4 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0 ASST08001 Chinese 1 Full Year 40
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ECNM08005 Economics 1A 40 ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications 40
YEAR 2 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade Semester 1 20 2A BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Semester 2 20 Enterprise 2B CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Semester 1 20 Techniques BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Full Year 0 Abroad
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ASST08018 Chinese 2A 40 ASST08019 Chinese 2B 40
AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
OR
Select exactly 20 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available 63 Note: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
YEAR 3 2 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 XXXX10008 Compulsory year abroad (full year) - level 10 Full Year 120
Note: Students must spend their third year abroad at a partner university, in the country of the language being studied, completing and passing a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be undertaken and examined in the language being studied. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management.
YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select a minimum of 20 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
Notes: Students must choose a minimum of 60 credits in International Business: EITHER an International Business oriented Management Honours Dissertation (40 credits) plus one International Business designated course (20 credits) OR three International Business designated courses (60 credits) from the courses listed above.
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20
64 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH SPANISH
YEAR 1 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ECNM08005 Economics 1A 40 ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications 40
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ELCH08001 Spanish 1A 40 ELCH08002 Spanish 1B 40
YEAR 2 6 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A Semester 1 20 BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Semester 2 20 Enterprise 2B CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Semester 1 20 Techniques BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad Full Year 0 ELCH08004 Spanish 2 Full Year 40
65 AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
OR
Select exactly 20 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Note: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
YEAR 3 2 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 XXXX10008 Compulsory year abroad (full year) - level 10 Full Year 120
Note: Students must spend their third year abroad at a partner university, in the country of the language being studied, completing and passing a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be undertaken and examined in the language being studied. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management.
YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select a minimum of 20 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
Notes: Students must choose a minimum of 60 credits in International Business: EITHER an International Business oriented Management Honours Dissertation (40 credits) plus one International Business designated course (20 credits) OR three International Business designated courses (60 credits) from the courses listed above.
66 AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
Business with Marketing YEAR 1 5 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 ACCN08007 Accountancy 1A Semester 1 20 ACCN08008 Accountancy 1B Semester 2 20 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from Level 7 and 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Notes:( ECNM08005 Economics 1A (40 credits) ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits) is recommended)
YEAR 2 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Semester 2 0 Planning
67 CMSE08002 Business Research Methods Semester 1 20 I: Quantitative Techniques BUST08004 Marketing Semester 2 20
AND
Select a minimum of 40 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 40 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Notes: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year, one of which must be in Marketing (but not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
Students whose application to study abroad at a partner university in third year is successful must register for the 0-credited course BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad in second year.
68 YEAR 3 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE10002 Strategic Management Semester 1 20 BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 CMSE10003 Business Research Methods II: Semester 2 20 Applications and Analysis
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10067 International Marketing 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10118 Marketing Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10114 Services Marketing 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10036 Risk Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10067 International Marketing 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10118 Marketing Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20 BUST10114 Services Marketing 20
Note: Students who spend their third year abroad at a partner university must complete and pass a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be in Business and Marketing. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the year 3 compulsory course Strategic Management.
69 70 YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20 BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH FRENCH
71 YEAR 1 3 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST08001 Business Studies 1 Full Year 40 BUST08014 Computing for Business Full Year 0 BUST08021 Study Skills for Business Full Year 0
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ECNM08005 Economics 1A 40 ECNM08002 Economic Principles and Applications 40
AND
Select exactly 40 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits ELCF08005 French 1A 40 ELCF08006 French 1B 40
YEAR 2 6 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits CMSE08001 Career Development Planning Semester 2 0 BUST08008 International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A Semester 1 20 BUST08009 International Business and the Multinational Semester 2 20 Enterprise 2B CMSE08002 Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Semester 1 20 Techniques BUST08022 Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad Full Year 0 ELCF08001 French 2 Full Year 40
AND
Select exactly 20 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST08005 Business Economics 20 BUST08011 Organisation Studies 20 BUST08003 Principles of Finance 20 BUST08007 Management Science and Information Systems 20 BUST08010 Managing Employment Relations 20 BUST08004 Marketing 20 BUST08015 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 20 BUST08018 Applications of Finance 20
OR
Select exactly 20 credits from Level 8 courses in Schedules A to J, N to P and W, as available
Note: Entry into third year honours normally requires (i) passes in all courses (240 credits) in the first two years, and (ii) a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
72 YEAR 3 2 compulsory courses Code Course Name Period Credits BUST09001 Research in Management Semester 2 0 XXXX10008 Compulsory year abroad (full year) - level 10 Full Year 120
Note: Students must spend their third year abroad at a partner university, in the country of the language being studied, completing and passing a full year's diet of examinable subjects (equivalent to 120 credits), the majority of which must be undertaken and examined in the language being studied. All students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management.
YEAR 4 1 compulsory course Code Course Name Period Credits BUST10049 Management Honours Dissertation Full Year 40
AND
Select a minimum of 20 credits and maximum of 80 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10103 A Global Problem? Climate Change and a Low Carbon World 20 BUST10047 Theoretical Foundations of International Business: Course B 20 BUST10113 Managing Across Borders and Cultures 20 BUST10104 International Strategic Management in Practice 20 BUST10041 Advanced Topics in International Business 20
Notes: Students must choose a minimum of 60 credits in International Business: EITHER an International Business oriented Management Honours Dissertation (40 credits) plus one International Business designated course (20 credits) OR three International Business designated courses (60 credits) from the courses listed above.
AND
Select a minimum of 0 credits and maximum of 60 credits from the following list of courses, as available Code Course Name Credits BUST10014 Advertising: Theories and Practice 20 ACCN10026 Behavioural Finance and Market Efficiency 20 BUST10004 Business Ethics 20 BUST10007 Consumer Behaviour 20 BUST10012 Corporate Finance 20 BUST10117 Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation 20 BUST10033 Financial Services Marketing 20 BUST10023 Futures and Options 20 BUST10105 Human Resource Management: Current Issues and Controversies 20 BUST10032 Investment and Securities Markets 20 BUST10020 Management Science and Operations Planning 20 BUST10107 Managing Change 20 BUST10028 Managing Employment Law 20 BUST10013 Decision-Making under Uncertainty 20
73 BUST10108 Marketing and Society 20 BUST10011 Mathematical Programming 20 BUST10039 Negotiation 20 BUST10092 Operations Strategy 20 BUST10024 Quality Management 20 BUST10115 The Entrepreneurial Manager 20 BUST10034 The Management of Technology 20 BUST10021 The Economics of Corporate Strategy 20 BUST10116 Critical Thinking in Marketing 20
74 Business DPSs THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN BUSINESS AND FINANCE2
13) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
14) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
15) Programme accredited by: N/A
16) Final Award: MA Honours
17) Programme Title: Business and Finance
18) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary A degree which combines the study of business and finance provides an extremely strong platform to build a career within or outside the commercial world. Our joint Honours degree in Business and Finance encompasses the study of public, private and not-for-profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external environment in which they operate. In our four-year programme we reflect the global, dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as corporate finance, marketing, entrepreneurship and climate change, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics, sociology and mathematics.
Students are able to study a range of disciplines outside business, particularly in years one and two, allowing them to develop a broader range of knowledge and skills. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. All students have the option of studying abroad in the third year at one of our international partner institutions.
2 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 75 Students gain in-depth knowledge in a wide range of business areas with a specialist focus on finance. They also develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management, and finance more specifically, but also for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
Our programmes are accredited by a range of leading business education organisations and professional bodies, and the School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for the wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme: The educational aim of the MA Honours in Business and Finance programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, accounting, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics, with a specific focus on finance; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes: 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of business and, in particular, finance. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of:
76 the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment.
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry Business and Finance graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business, and finance in particular, and recognise the need to re- evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, in particular finance, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research in the field of finance and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy Business and Finance graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self- improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues, and those affecting the finance field in particular. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research
77 and writing process associated with undertaking the dissertation on a finance topic. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business and finance data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication Business and Finance graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business in general and in finance more specifically. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
78 11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness Business and Finance graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills Business and Finance graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12) Programme Structure and Features The MA Business with Marketing degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits), Accountancy 1A (20 credits) and Accountancy 1B (20 credits); the remaining 40 credits in either Economics 1A or Economic Principles and Applications is recommended but students can take one or two other
79 courses in other subject areas; two compulsory non-credit bearing courses, Computing for Business and Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: four compulsory courses in Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits), Principles of Finance (20 credits), Applications of Finance (20 credits) and the non-credit bearing course Career Development Planning; three courses (60 credits) from a choice of eight Business 2nd year courses (Management Science and Information Systems (20 credits) is recommended). 3rd year: compulsory courses in Strategic Management (20 credits) and Business Research Methods II: Applications and Analysis (20 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Finance (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 20 options; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management, to support preparation of the dissertation. 4th year: the Business Honours Dissertation on a research topic in the field of Finance (40 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Finance (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 30 options.
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): students are normally required to pass all their courses in the first two years (240 credits) and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in both Principles of Finance and Applications of Finance, and two other Business courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques).
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area, embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and
80 learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of option courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes Yes the Honours dissertation research
81 Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes Yes project
82 In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Yes Written business Depends on Depends on plan choice of choice of elective elective course course Dissertation Yes Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in both of the Honours years, unless the third year is spent studying at an overseas partner institution, when the degree classification is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. Business and Finance graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being finance, accountancy, marketing management consulting and human resources management.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
83 16) Other Items All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. Opportunities are available to study abroad in the third year on a Business School exchange or University exchange at a partner university Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes, including Computing for Business, which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme. All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. In addition to the School’s IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN BUSINESS WITH MARKETING3
84 19) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
20) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
21) Programme accredited by: N/A
22) Final Award: MA Honours
23) Programme Title: Business with Marketing
24) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary Our degree in Business with Marketing encompasses the study of public, private and not-for-profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external environment in which they operate. In our four-year programme we reflect the global, dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as international marketing, entrepreneurship and climate change, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics, sociology and mathematics.
Students are able to study a range of disciplines outside business, particularly in years one and two, allowing them to develop a broader range of knowledge and skills. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. The ability to follow a concentration of courses in marketing enables students to develop a specialism within the broader business degree structure. All students have the option of studying abroad in the third year at one of our international partner institutions.
Students gain general business knowledge and a deeper understanding of marketing. They also develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management, and marketing more specifically, but also for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
3 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 85 Our programmes are accredited by a range of leading business education organisations and professional bodies, and the School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for the wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme: The educational aim of the MA Honours in Business with Marketing programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, corporate finance, accounting, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; with a specific focus on marketing; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes: 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of a number of business area, and marketing in particular. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and
86 technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment.
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry Business with Marketing graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business and marketing, and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, in particular marketing, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research in the field of marketing and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy Business with Marketing graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self- improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues, and those affecting particularly the area of marketing. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with undertaking the dissertation on a marketing topic. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business and marketing data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team.
87 able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication Business with Marketing graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business in general and in marketing, more specifically. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
88 11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness Business with Marketing graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills Business with Marketing graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12) Programme Structure and Features The MA Business with Marketing degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits), Accountancy 1A (20 credits) and Accountancy 1B (20 credits); the remaining 40 credits in either Economics 1A or Economic Principles and Applications is recommended but students can take one or two other
89 courses in other subject areas; two compulsory non-credit bearing courses, Computing for Business and Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits), Marketing 2 (20 credits) and the non-credit bearing course Career Development Planning; a choice from nine Business 2nd year courses with a minimum of two courses (40 credits) and a maximum of four (80 credits); it is also possible to choose a maximum of two courses (40 credits) out with the Business subject area. 3rd year: compulsory courses in Strategic Management (20 credits) and Business Research Methods II: Applications and Analysis (20 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Marketing (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 20 options; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management, to support preparation of the dissertation. 4th year: the Business Honours Dissertation on a research topic in the field of Marketing (40 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Marketing (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 30 options.
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): students are normally required to pass all their courses in the first two years (240 credits) and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques), one of which must be in Marketing 2.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area, embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
90 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of option courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes Yes the Honours dissertation research
91 Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes Yes project
92 In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Yes Written business Depends on Depends on plan choice of choice of elective elective course course Dissertation Yes Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in both of the Honours years, unless the third year is spent studying at an overseas partner institution, when the degree classification is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. Business graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being marketing, accountancy, management, consulting, finance and human resources.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
93 16) Other Items All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. Opportunities are available to study abroad in the third year on a Business School exchange or University exchange at a partner university Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes, including Computing for Business, which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme. All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. In addition to the School’s IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH CHINESE4
94 25) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
26) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
27) Programme accredited by: N/A
28) Final Award: MA Honours
29) Programme Title: International Business with Chinese
30) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary International Business encompasses the study of public, private and not-for- profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external and increasingly global environment in which they operate. The four-year MA Honours degree programme in International Business with Chinese is a specialist degree within the MA Business Studies portfolio and is designed to address the growing internationalisation and globalisation of business. To reflect that, students are required, through the third year exchange programme, to study abroad and experience at first hand different cultures and approaches and develop their understanding of the international environment. For students with good language skills, this may include foreign language study. The Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Asia where students will spend their 3rd year.
In the degree we reflect the dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as Theoretical Perspectives on International Business, Global Strategy and Managing Across Borders and Cultures, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics and sociology. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. Students gain specific business knowledge, an understanding of the business world and develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management but for those interested in the relationships between people,
4 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 95 organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
The School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for a wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme The educational aim of the MA Honours in International Business with Chinese programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, finance, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of international business and one or more functional areas, including finance, strategy, organisational behaviour, marketing, management science and operations and quality management. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included.
96 the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations, with a particular focus on key issues in international business,. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment..
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry International Business with Chinese graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy International Business with Chinese graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self-improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with the dissertation. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way. 97 11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication International Business with Chinese graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business, in both English and Chinese. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness International Business with Chinese graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills International Business with Chinese graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations.
98 obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12 Programme Structure and Features The MA International Business with Chinese degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits) and Economics 1A (40 credits) or Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits); Chinese 1 (40 credits); a compulsory non-credit bearing class, Computing for Business; Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in business, International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A (20 credits), International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B (20 credits) and Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing courses Career Development Planning and Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad; compulsory Chinese 2A or Chinese 2B (40 credits); one further course in Business (20 credits). 3rd year: spent studying abroad at an approved overseas exchange partner institution in the country of the language being studied, credit load equivalent to 120 University of Edinburgh credits; all students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management to support the dissertation process, completed using Learn-based materials. 4th year: the Honours Dissertation on a research topic of particular interest to the student (40 credits); four Business Honours courses (80 credits) from a choice of over 30 options. If Honours dissertation is in International Business one Honours option course (20 credits) must be in International Business, otherwise three International Business designated courses (60 credits).
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
99 For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): Students are normally required to pass all of their courses in the first two years (240 credits and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Teaching and learning approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School, including lectures and tutorials.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Varies Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on depending on choice of exchange option partner courses institution Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Oral classes Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes
100 Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to
101 develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Assessment approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School such as examinations, and coursework essays and projects.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective Varies course depending on On-line class test Depends on Depends on exchange choice of choice of partner elective elective institution course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Oral tests Yes Yes Written business Depends on plan choice of elective course Dissertation Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. International Business with Chinese graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most
102 popular being accountancy, management, consulting, finance, marketing and human resources.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
16) Other Items . All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. . All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. . Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. . First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. . Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes including Computing for Business which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme). . All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. . In addition to the School’ss IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. . University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. . Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club.
103 . Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH RUSSIAN5
31) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
32) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
33) Programme accredited by: N/A
34) Final Award: MA Honours
35) Programme Title: International Business with Russian
36) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary International Business encompasses the study of public, private and not-for- profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external and increasingly global environment in which they operate. The four-year MA Honours degree programme in International Business with Russian is a specialist degree within the MA Business Studies portfolio and is designed to address the growing internationalisation and globalisation of business. To reflect that, students are required, through the third year exchange programme, to study abroad and experience at first hand different cultures and approaches and develop their understanding of the international environment. For students with good language skills, this may include foreign language study. The Business School
5 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 104 currently has a number of exchange partners for those whose langauge of study is Russian.
In the degree we reflect the dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as Theoretical Perspectives on International Business, Global Strategy and Managing Across Borders and Cultures, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics and sociology. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. Students gain specific business knowledge, an understanding of the business world and develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
The School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for a wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme The educational aim of the MA Honours in International Business with Russian programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, finance, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
105 11) Programme outcomes 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of international business and one or more functional areas, including finance, strategy, organisational behaviour, marketing, management science and operations and quality management. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations, with a particular focus on key issues in international business,. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment..
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry International Business with Russian graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy International Business with Russian graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self-improvement.
106 open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with the dissertation. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication International Business with Russian graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business, in both English and Russian. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness International Business with Russian graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management.
107 be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills International Business with Russian graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12 Programme Structure and Features The MA International Business with Russian degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits) and Economics 1A (40 credits) or Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits); Russian Studies 1A or Russian 1B (40 credits); a compulsory non- credit bearing class, Computing for Business; Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in business, International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A (20 credits), International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B (20 credits) and Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing courses Career Development Planning and Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad; compulsory Russian Language 2 (20 credits) and The Golden and Silver Ages of Russian Literature (1820-1920s) (20 credits); one further course in Business (20 credits). 3rd year: spent studying abroad at an approved overseas exchange partner institution in the country of the language being studied, credit 108 load equivalent to 120 University of Edinburgh credits; all students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management to support the dissertation process, completed using Learn-based materials. 4th year: the Honours Dissertation on a research topic of particular interest to the student (40 credits); four Business Honours courses (80 credits) from a choice of over 30 options. If Honours dissertation is in International Business one Honours option course (20 credits) must be in International Business, otherwise three International Business designated courses (60 credits).
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): Students are normally required to pass all of their courses in the first two years (240 credits and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Teaching and learning approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but
109 include many of the approaches employed within the School, including lectures and tutorials.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of option courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Oral classes Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Varies Yes activities depending on Independent study Yes Yes exchange Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes partner Yes Poster presentation Yes institution Group projects Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives
110 from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Assessment approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School such as examinations, and coursework essays and projects.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Varies Yes Examinations (seen depending on and unseen) exchange Essays Yes Yes partner Yes institution Group/individual Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Oral tests Yes Yes Written business Depends on
111 plan choice of elective course Dissertation Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. International Business with Russian graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being accountancy, management, consulting, finance, marketing and human resources.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
16) Other Items . All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. . All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. . Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. . First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources.
112 . Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes including Computing for Business which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme). . All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. . In addition to the School’ss IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. . University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. . Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. . Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN BUSINESS WITH STRATEGIC ECONOMICS6
37) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
38) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
39) Programme accredited by: N/A
40) Final Award: MA Honours
41) Programme Title: Business with Strategic Economics
42) UCAS Code: TBA
6 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 113 Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary Our degree in Business with Strategic Economics encompasses the study of public, private and not-for-profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external environment in which they operate. Strategic economics can be thought of as the application of economic principles to strategic decisions that managers make. Most business decisions involve a comparison of marginal benefits with margin cost, widely interpreted, and so implicitly or explicitly involve economic principles. In our four-year programme we reflect the global, dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as management sciences, decision making, corporate finance, entrepreneurship and climate change, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics, sociology and mathematics. The ability to follow a concentration of courses in Strategic Economics enables students to develop a specialism within the broader business degree structure.
Students are able to study a range of disciplines outside business, particularly in years one and two, allowing them to develop a broader range of knowledge and skills. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. All students have the option of studying abroad in the third year at one of our international partner institutions.
Students gain more general business knowledge and an understanding of the world of business, as well the more specialised skills and knowledge necessary to analyse the economic decisions that managers make when formulating strategy at the level of the firm. They also develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management, but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
Our programmes are accredited by a range of leading business education organisations and professional bodies, and the School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for the wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
114 10) Educational aims of programme: The MA Honours degree in Business with Strategic Economics aims to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, corporate finance, accounting, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; with a specific focus on strategic economics; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes: 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of business, and in particular strategic economics. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment.
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry
115 Business with Strategic Economics graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business, and strategic economics in particular, and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, including strategic economics in particular, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research in the field of strategic economics and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy Business with Strategic Economics graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self- improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with undertaking the dissertation on a strategic economics-related topic. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication Business with Strategic Economics graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business.
116 communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
117 11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness Business with Strategic Economics graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills Business with Strategic Economics graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. analyse the economic decisions that managers make when formulating strategy at the level of the firm. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12) Programme Structure and Features The MA Business with Strategic Economics degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10.
118 The programme gives students a knowledge of economic principles which influence most business decisions. These principles and the skills to use them are first presented in the second year Business Economics course. The skills to develop these principles when applied to the breadth of a firm’s activities and to the degree of involvement in the supply chain, as well as their application in the development of competitive advantage, are developed in the Economics of Strategy. The Market Structure course gives students a good understanding of the implications of the industrial structure in which a firm competes. The finance courses broaden the application of economic principles to decisions concerning investment appraisal, optimal capital structure and the applications of portfolio theory which is necessary to understand the constraints placed on managers by the capital market.
119 The structure for each year of the degree is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits), Accountancy 1A (20 credits) and Accountancy 1B (20 credits); the remaining 40 credits in either Economics 1A or Economic Principles and Applications is recommended but students can take one or two other courses in other subject areas; two compulsory non-credit bearing courses, Computing for Business and Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: four compulsory courses in Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits), Business Economics (20 credits), Principles of Finance (20 credits) and the non-credit bearing course Career Development Planning; a choice from eight Business 2nd year courses with a minimum of one course (20 credits) and a maximum of three (60 credits); it is also possible to choose a maximum of two courses (40 credits) out with the Business subject area. 3rd year: compulsory courses in Strategic Management (20 credits), Business Research Methods II: Applications and Analysis (20 credits) and The Economics of Corporate Strategy (20 credits); one course from a list of Honours courses in the field of Strategic Economics (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 20 options; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management, to support preparation of the dissertation. 4th year: the Business Honours Dissertation on a research topic in the field of Strategic Economics (40 credits); one compulsory course Market Structure, Conduct and Performance (20 credits); one course from a list of Honours courses in the field of Strategic Economics (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 30 options.
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): students are normally required to pass all their courses in the first two years (240 credits) and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques), one of which must be in Business Economics.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also
120 publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area, embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
121 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/ directors of studies Independent research for Yes Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of
122 transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Yes Written business Depends on Depends on plan choice of choice of elective elective course course Dissertation Yes Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in both of the Honours years, unless the third year is spent studying at an overseas partner institution, when the degree classification is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities
123 A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. Business graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being management consulting, for which this degree provides a very appropriate preparation, finance, accountancy, human resource management and marketing. Successful completion of this degree should also enable the graduate to work in an economics department or in finance or in a strategic function within an organisation.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
124 16) Other Items All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. Opportunities are available to study abroad in the third year on a Business School exchange or University exchange at a partner university Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes, including Computing for Business, which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme. All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. In addition to the School’s IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN BUSINESS WITH STRATEGIC ECONOMICS7
125 43) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
44) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
45) Programme accredited by: N/A
46) Final Award: MA Honours
47) Programme Title: Business with Strategic Economics
48) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary Our degree in Business with Strategic Economics encompasses the study of public, private and not-for-profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external environment in which they operate. Strategic economics can be thought of as the application of economic principles to strategic decisions that managers make. Most business decisions involve a comparison of marginal benefits with margin cost, widely interpreted, and so implicitly or explicitly involve economic principles. In our four-year programme we reflect the global, dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as management sciences, decision making, corporate finance, entrepreneurship and climate change, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics, sociology and mathematics. The ability to follow a concentration of courses in Strategic Economics enables students to develop a specialism within the broader business degree structure.
Students are able to study a range of disciplines outside business, particularly in years one and two, allowing them to develop a broader range of knowledge and skills. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. All students have the option of studying abroad in the third year at one of our international partner institutions.
7 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 126 Students gain more general business knowledge and an understanding of the world of business, as well the more specialised skills and knowledge necessary to analyse the economic decisions that managers make when formulating strategy at the level of the firm. They also develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management, but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
Our programmes are accredited by a range of leading business education organisations and professional bodies, and the School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for the wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme: The MA Honours degree in Business with Strategic Economics aims to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, corporate finance, accounting, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; with a specific focus on strategic economics; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes: 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of business, and in particular strategic economics. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of:
127 the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment.
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry Business with Strategic Economics graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business, and strategic economics in particular, and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, including strategic economics in particular, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research in the field of strategic economics and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy Business with Strategic Economics graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self- improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research
128 and writing process associated with undertaking the dissertation on a strategic economics-related topic. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication Business with Strategic Economics graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
129 11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness Business with Strategic Economics graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills Business with Strategic Economics graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. analyse the economic decisions that managers make when formulating strategy at the level of the firm. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12) Programme Structure and Features The MA Business with Strategic Economics degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10.
130 The programme gives students a knowledge of economic principles which influence most business decisions. These principles and the skills to use them are first presented in the second year Business Economics course. The skills to develop these principles when applied to the breadth of a firm’s activities and to the degree of involvement in the supply chain, as well as their application in the development of competitive advantage, are developed in the Economics of Strategy. The Market Structure course gives students a good understanding of the implications of the industrial structure in which a firm competes. The finance courses broaden the application of economic principles to decisions concerning investment appraisal, optimal capital structure and the applications of portfolio theory which is necessary to understand the constraints placed on managers by the capital market.
131 The structure for each year of the degree is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits), Accountancy 1A (20 credits) and Accountancy 1B (20 credits); the remaining 40 credits in either Economics 1A or Economic Principles and Applications is recommended but students can take one or two other courses in other subject areas; two compulsory non-credit bearing courses, Computing for Business and Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: four compulsory courses in Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits), Business Economics (20 credits), Principles of Finance (20 credits) and the non-credit bearing course Career Development Planning; a choice from eight Business 2nd year courses with a minimum of one course (20 credits) and a maximum of three (60 credits); it is also possible to choose a maximum of two courses (40 credits) out with the Business subject area. 3rd year: compulsory courses in Strategic Management (20 credits), Business Research Methods II: Applications and Analysis (20 credits) and The Economics of Corporate Strategy (20 credits); one course from a list of Honours courses in the field of Strategic Economics (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 20 options; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management, to support preparation of the dissertation. 4th year: the Business Honours Dissertation on a research topic in the field of Strategic Economics (40 credits); one compulsory course Market Structure, Conduct and Performance (20 credits); one course from a list of Honours courses in the field of Strategic Economics (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 30 options.
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): students are normally required to pass all their courses in the first two years (240 credits) and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques), one of which must be in Business Economics.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also
132 publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area, embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
133 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/ directors of studies Independent research for Yes Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of
134 transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Yes Written business Depends on Depends on plan choice of choice of elective elective course course Dissertation Yes Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in both of the Honours years, unless the third year is spent studying at an overseas partner institution, when the degree classification is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities
135 A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. Business graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being management consulting, for which this degree provides a very appropriate preparation, finance, accountancy, human resource management and marketing. Successful completion of this degree should also enable the graduate to work in an economics department or in finance or in a strategic function within an organisation.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
136 16) Other Items All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. Opportunities are available to study abroad in the third year on a Business School exchange or University exchange at a partner university Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes, including Computing for Business, which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme. All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. In addition to the School’s IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH FRENCH8
137 49) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
50) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
51) Programme accredited by: N/A
52) Final Award: MA Honours
53) Programme Title: International Business with French
54) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary International Business encompasses the study of public, private and not-for- profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external and increasingly global environment in which they operate. The four-year MA Honours degree programme in International Business with French is a specialist degree within the MA Business Studies portfolio and is designed to address the growing internationalisation and globalisation of business. To reflect that, students are required, through the third year exchange programme, to study abroad and experience at first hand different cultures and approaches and develop their understanding of the international environment. For students with good language skills, this may include foreign language study. The Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe for those whose langauge of study is French
In the degree we reflect the dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as Theoretical Perspectives on International Business, Global Strategy and Managing Across Borders and Cultures, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics and sociology. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. Students gain specific business knowledge, an understanding of the business world and develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management but for those interested in the relationships between people,
8 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 138 organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
The School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for a wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme The educational aim of the MA Honours in International Business with French programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, finance, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of international business and one or more functional areas, including finance, strategy, organisational behaviour, marketing, management science and operations and quality management. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included.
139 the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations, with a particular focus on key issues in international business,. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment..
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry International Business with French graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy International Business with French graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self-improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with the dissertation. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way. 140 11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication International Business with French graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business, in both English and the foreign language of study. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness International Business with French graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills International Business with French graduates will have developed skills to:
141 apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12 Programme Structure and Features The MA International Business with French degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits) and Economics 1A (40 credits) or Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits); French 1A or French 1B (40 credits); a compulsory non-credit bearing class, Computing for Business; Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in business, International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A (20 credits), International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B (20 credits) and Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing courses Career Development Planning and Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad; compulsory French 2 (40 credits); one further course in Business (20 credits). 3rd year: spent studying abroad at an approved overseas exchange partner institution in the country of the language being studied, credit load equivalent to 120 University of Edinburgh credits; all students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management to support the dissertation process, completed using Learn-based materials. 4th year: the Honours Dissertation on a research topic of particular interest to the student (40 credits); four Business Honours courses (80 credits) from a choice of over 30 options. If Honours dissertation is in International Business one Honours option course (20 credits) must be in International Business, otherwise three International Business designated courses (60 credits).
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
142 For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): Students are normally required to pass all of their courses in the first two years (240 credits and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Teaching and learning approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School, including lectures and tutorials.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Varies Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on depending on choice of exchange option partner courses institution Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Oral classes Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes
143 Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to 144 develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Assessment approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School such as examinations, and coursework essays and projects.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective Varies course depending on On-line class test Depends on Depends on exchange choice of choice of partner elective elective institution course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Oral tests Yes Yes Written business Depends on plan choice of elective course Dissertation Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. International Business with French graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most
145 popular being accountancy, management, consulting, finance, marketing and human resources.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
16) Other Items . All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. . All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. . Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. . First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. . Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes including Computing for Business which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme). . All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. . In addition to the School’ss IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. . University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. . Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club.
146 . Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH SPANISH9
55) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
56) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
57) Programme accredited by: N/A
58) Final Award: MA Honours
59) Programme Title: International Business with Spanish
60) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary International Business encompasses the study of public, private and not-for- profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external and increasingly global environment in which they operate. The four-year MA Honours degree programme in International Business with Spanish is a specialist degree within the MA Business Studies portfolio and is designed to address the growing internationalisation and globalisation of business. To reflect that, students are required, through the third year exchange programme, to study abroad and experience at first hand different cultures and approaches and develop their understanding of the international environment. For students with good
9 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 147 language skills, this may include foreign language study. The Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe for those whose language of study is Spanish.
In the degree we reflect the dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as Theoretical Perspectives on International Business, Global Strategy and Managing Across Borders and Cultures, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics and sociology. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. Students gain specific business knowledge, an understanding of the business world and develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
The School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for a wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme The educational aim of the MA Honours in International Business with Spanish programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, finance, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
148 11) Programme outcomes 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of international business and one or more functional areas, including finance, strategy, organisational behaviour, marketing, management science and operations and quality management. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations, with a particular focus on key issues in international business,. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment..
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry International Business with Spanish graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy International Business with Spanish graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside
149 business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self-improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with the dissertation. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication International Business with Spanish graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business, in both English and Spanish. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness International Business with Spanish graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities.
150 identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills International Business with Spanish graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12 Programme Structure and Features The MA International Business with Spanish degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits) and Economics 1A (40 credits) or Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits); Spanish 1A or Spanish 1B (40 credits); a compulsory non-credit bearing class, Computing for Business; Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in business, International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A (20 credits), International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B (20 credits) and Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing courses Career Development Planning and Exchange Preparation for the
151 Business Year Abroad; compulsory Spanish 2 (40 credits); one further course in Business (20 credits). 3rd year: spent studying abroad at an approved overseas exchange partner institution in the country of the language being studied, credit load equivalent to 120 University of Edinburgh credits; all students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management to support the dissertation process, completed using Learn-based materials. 4th year: the Honours Dissertation on a research topic of particular interest to the student (40 credits); four Business Honours courses (80 credits) from a choice of over 30 options. If Honours dissertation is in International Business one Honours option course (20 credits) must be in International Business, otherwise three International Business designated courses (60 credits).
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): Students are normally required to pass all of their courses in the first two years (240 credits and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
152 The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Teaching and learning approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School, including lectures and tutorials.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of option courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Oral classes Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Varies Yes activities depending on Independent study Yes Yes exchange Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes partner Yes Poster presentation Yes institution Group projects Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities
153 outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Assessment approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School such as examinations, and coursework essays and projects.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Varies Yes Examinations (seen depending on and unseen) exchange Essays Yes Yes partner Yes institution Group/individual Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course Poster Yes
154 presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Oral tests Yes Yes Written business Depends on plan choice of elective course Dissertation Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. International Business with Spanish graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being accountancy, management, consulting, finance, marketing and human resources.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
16) Other Items . All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. . All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. . Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia.
155 . First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. . Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes including Computing for Business which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme). . All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. . In addition to the School’ss IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. . University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. . Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. . Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN BUSINESS WITH ENTERPRISE AND INNOVATION10
61) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
62) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
63) Programme accredited by: N/A
64) Final Award: MA Honours
65) Programme Title: Business with Enterprise and Innovation
10 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 156 66) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary Our degree in Business with Enterprise and Innovation encompasses the study of public, private and not-for-profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external environment in which they operate. In our four-year programme we reflect the global, dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as innovation, entrepreneurship and climate change, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics, sociology and mathematics.
Students are able to study a range of disciplines outside business, particularly in years one and two, allowing them to develop a broader range of knowledge and skills. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. The ability to follow a concentration of courses in enterprise and innovation enables students to develop a specialism within the broader business degree structure. Those interested in starting their own venture will have the opportunity to take a range of courses which will help them to understand the venture creation process. All students have the option of studying abroad in the third year at one of our international partner institutions.
Students gain business knowledge and an understanding of the world of business, and more particularly the fields of enterprise and innovation. They will also develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management, but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation or start their own venture.
Our programmes are accredited by a range of leading business education organisations and professional bodies, and the School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for the wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme:
157 The educational aim of the MA Honours in Business with Enterprise and Innovation programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, corporate finance, accounting, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; with a specific focus on enterprise and innovation; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes: 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of business and, in particular, in the fields of enterprise and innovation. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment.
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry Business with Enterprise and Innovation graduates will be able to:
158 understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business, and enterprise and innovation in particular, and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, including enterprise and innovation in particular, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research in the field of enterprise/innovation and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy Business with Enterprise and Innovation graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self- improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues, and those affecting innovation and enterprise processes and actions in particular. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with undertaking the dissertation on an enterprise or innovation-related topic. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication Business with Enterprise and Innovation graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business.
159 communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
160 11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness Business with Enterprise and Innovation graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills Business with Enterprise and Innovation graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12) Programme Structure and Features The MA Business with Enterprise and Innovation degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits), Accountancy 1A (20 credits) and Accountancy 1B (20 credits); the
161 remaining 40 credits in either Economics 1A or Economic Principles and Applications is recommended but students can take one or two other courses in other subject areas; two compulsory non-credit bearing courses, Computing for Business and Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits), Innovation and Entrepreneurship (20 credits) and the non-credit bearing course Career Development Planning; a choice from nine Business 2nd year courses with a minimum of two courses (40 credits) and a maximum of four (80 credits); it is also possible to choose a maximum of two courses (40 credits) out with the Business subject area. 3rd year: compulsory courses in Strategic Management (20 credits) and Business Research Methods II: Applications and Analysis (20 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Enterprise and Innovation (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 20 options; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management, to support preparation of the dissertation. 4th year: the Business Honours Dissertation on a research topic in the field of Enterprise and Innovation (40 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Enterprise and Innovation (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 30 options.
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): students are normally required to pass all their courses in the first two years (240 credits) and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques), one of which must be in Innovation and Entrepreneurship.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
162 13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area, embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/ directors of studies Independent research for Yes Yes the Honours dissertation research
163 Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes Yes project
164 In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Yes Written business Depends on Depends on plan choice of choice of elective elective course course Dissertation Yes Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in both of the Honours years, unless the third year is spent studying at an overseas partner institution, when the degree classification is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. Business graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being marketing, accountancy, management consulting, finance, marketing and human resources, whilst others join small, growth-oriented businesses or start their own venture.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
165 16) Other Items All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. Opportunities are available to study abroad in the third year on a Business School exchange or University exchange at a partner university Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes, including Computing for Business, which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme. All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. In addition to the School’s IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
166 THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH GERMAN11
67) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
68) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
69) Programme accredited by: N/A
70) Final Award: MA Honours
71) Programme Title: International Business with German
72) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary International Business encompasses the study of public, private and not-for- profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external and increasingly global environment in which they operate. The four-year MA Honours degree programme in International Business with German is a specialist degree within the MA Business Studies portfolio and is designed to address the growing internationalisation and globalisation of business. To reflect that, students are required, through the third year exchange programme, to study abroad and experience at first hand different cultures and approaches and develop their understanding of the international environment. For students with good language skills, this may include foreign language study. The Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe for those whose langauge of study is German.
In the degree we reflect the dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as Theoretical Perspectives on International Business, Global Strategy and Managing Across Borders and Cultures, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics and sociology. A range of compulsory and optional courses
11 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 167 examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. Students gain specific business knowledge, an understanding of the business world and develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
The School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for a wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme The educational aim of the MA Honours in International Business with German programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, finance, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of international business and one or more functional areas, including finance, strategy, organisational behaviour, marketing, management science and operations and quality management.
168 On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations, with a particular focus on key issues in international business,. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment..
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry International Business with German graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy International Business with German graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self-improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views.
169 curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with the dissertation. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication International Business with German graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business, in both English and German. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness International Business with German graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation.
170 work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills International Business with German graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12 Programme Structure and Features The MA International Business with German degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits) and Economics 1A (40 credits) or Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits); German 1A or German 1B (40 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing classes, Computing for Business; Study Skills for Business 2nd year: three compulsory courses in business, International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A (20 credits), International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B (20 credits) and Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing courses Career Development Planning and Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad; compulsory German 2 (40 credits); one further course in Business (20 credits). 3rd year: spent studying abroad at an approved overseas exchange partner institution in the country of the language being studied, credit load equivalent to 120 University of Edinburgh credits; all students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management to support the dissertation process, completed using Learn-based materials.
171 4th year: the Honours Dissertation on a research topic of particular interest to the student (40 credits); four Business Honours courses (80 credits) from a choice of over 30 options. If Honours dissertation is in International Business one Honours option course (20 credits) must be in International Business, otherwise three International Business designated courses (60 credits).
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): Students are normally required to pass all of their courses in the first two years (240 credits and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Teaching and learning approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School, including lectures and tutorials.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Varies Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on depending on
172 choice of exchange option partner courses institution Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Oral classes Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
173 14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Assessment approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School such as examinations, and coursework essays and projects.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective Varies course depending on On-line class test Depends on Depends on exchange choice of choice of partner elective elective institution course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Oral tests Yes Yes Written business Depends on plan choice of elective course Dissertation Yes
174 The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. International Business with German graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being accountancy, management, consulting, finance, marketing and human resources.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
16) Other Items . All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. . All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. . Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. . First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. . Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes including Computing for Business which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme). . All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn.
175 . In addition to the School’ss IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. . University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. . Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. . Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH ITALIAN12
73) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
74) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
75) Programme accredited by: N/A
76) Final Award: MA Honours
77) Programme Title: International Business with Italian
78) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
12 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 176 9) External Summary International Business encompasses the study of public, private and not-for- profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external and increasingly global environment in which they operate. The four-year MA Honours degree programme in International Business with Italian is a specialist degree within the MA Business Studies portfolio and is designed to address the growing internationalisation and globalisation of business. To reflect that, students are required, through the third year exchange programme, to study abroad and experience at first hand different cultures and approaches and develop their understanding of the international environment. For students with good language skills, this may include foreign language study. The Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe for those whose language of study is Italian.
In the degree we reflect the dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as Theoretical Perspectives on International Business, Global Strategy and Managing Across Borders and Cultures, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics and sociology. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. Students gain specific business knowledge, an understanding of the business world and develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
The School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for a wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme The educational aim of the MA Honours in International Business with Italian programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis;
177 a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, finance, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of international business and one or more functional areas, including finance, strategy, organisational behaviour, marketing, management science and operations and quality management. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations, with a particular focus on key issues in international business,. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment..
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry International Business with Italian graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge.
178 identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy International Business with Italian graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self-improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with the dissertation. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication International Business with Italian graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business, in both English and Italian. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. 179 seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness International Business with Italian graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills International Business with Italian graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12 Programme Structure and Features The MA International Business with Italian degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240
180 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits) and Economics 1A (40 credits) or Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits); Italian 1 (40 credits); a compulsory non-credit bearing class, Computing for Business; Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in business, International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A (20 credits), International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B (20 credits) and Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing courses Career Development Planning and Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad; compulsory Italian Language 2 (20 credits) and Italian Literature: Texts in Context 2 (20 credits); one further course in Business (20 credits). 3rd year: spent studying abroad at an approved overseas exchange partner institution in the country of the language being studied, credit load equivalent to 120 University of Edinburgh credits; all students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management to support the dissertation process, completed using Learn-based materials. 4th year: the Honours Dissertation on a research topic of particular interest to the student (40 credits); four Business Honours courses (80 credits) from a choice of over 30 options. If Honours dissertation is in International Business one Honours option course (20 credits) must be in International Business, otherwise three International Business designated courses (60 credits).
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): Students are normally required to pass all of their courses in the first two years (240 credits and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also
181 publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Teaching and learning approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School, including lectures and tutorials.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of option courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Oral classes Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Varies Yes activities depending on Independent study Yes Yes exchange Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes partner Yes Poster presentation Yes institution Group projects Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an
182 extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Assessment approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School such as examinations, and coursework essays and projects.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Varies Yes Examinations (seen depending on and unseen) exchange Essays Yes Yes partner Yes
183 Group/individual Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course institution Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Oral tests Yes Yes Written business Depends on plan choice of elective course Dissertation Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. International Business with Italian graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being accountancy, management, consulting, finance, marketing and human resources.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn
184 how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
16) Other Items . All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. . All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. . Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. . First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. . Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes including Computing for Business which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme). . All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. . In addition to the School’ss IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. . University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. . Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. . Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
185 THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN BUSINESS WITH HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT13
79) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
80) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
81) Programme accredited by: N/A
82) Final Award: MA Honours
83) Programme Title: Business with Human Resource Management
84) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary Our degree in Business with Human Resource Management encompasses the study of public, private and not-for-profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external environment in which they operate. In our four-year programme we reflect the global, dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as human resource management, entrepreneurship and climate change, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics, sociology and mathematics.
Students are able to study a range of disciplines outside business, particularly in years one and two, allowing them to develop a broader range of knowledge and skills. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. The ability to follow a concentration of courses in human resource management enables students to develop a specialism within the broader business degree structure. All students have the option of studying abroad in the third year at one of our international partner institutions.
13 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 186 Students gain business knowledge and an understanding of the world of business, and more particularly the field of human resource management. They also develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management, but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
Our programmes are accredited by a range of leading business education organisations and professional bodies, and the School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for the wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme: The educational aim of the MA Honours in Business with Human Resource Management programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, corporate finance, accounting, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; with a specific focus on human resource management; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes: 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of business and, in particular, human resource management. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of:
187 the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment.
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry Business with Human Resource Management graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business, and human resource management more specifically, and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, with a focus on human resource management, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research in the field of human resource management and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy Business with Human Resource Management graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self- improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues and, in particular, those affecting human resource management. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views.
188 curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with undertaking the dissertation on a human resource management-related topic. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication Business with Human Resource Management graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
189 11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness Business with Human Resource Management graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills Business with Human Resource Management graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12) Programme Structure and Features The MA Business with Human Resource Management degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits), Accountancy 1A (20 credits) and Accountancy 1B (20 credits); the
190 remaining 40 credits in Economics 1A, Economic Principles and Applications or Sociology 1A and Sociology 1B is recommended but students can take one or two other courses in other subject areas; two compulsory non-credit bearing courses, Computing for Business and Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits), Organisation Studies (20 credits) and the non-credit bearing course Career Development Planning; a choice from nine Business 2nd year courses with a minimum of two courses (40 credits) and a maximum of four (80 credits); it is also possible to choose a maximum of two courses (40 credits) out with the Business subject area. 3rd year: compulsory courses in Strategic Management (20 credits) and Business Research Methods II: Applications and Analysis (20 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Human Resource Management (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 20 options; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management, to support preparation of the dissertation. 4th year: the Business Honours Dissertation on a research topic in the field of Human Resource Management (40 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Human Resource Management (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 30 options.
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): students are normally required to pass all their courses in the first two years (240 credits) and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques), one of which must be in Organisation Studies.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies
191 Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area, embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/ directors of studies Independent research for Yes Yes the Honours dissertation research
192 Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes Yes project
193 In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Yes Written business Depends on Depends on plan choice of choice of elective elective course course Dissertation Yes Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in both of the Honours years, unless the third year is spent studying at an overseas partner institution, when the degree classification is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. Business graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being human resource management, accountancy, management consulting, finance and marketing.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
194 16) Other Items All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. Opportunities are available to study abroad in the third year on a Business School exchange or University exchange at a partner university Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes, including Computing for Business, which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme. All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. In addition to the School’s IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS ARABIC14
195 85) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
86) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
87) Programme accredited by: N/A
88) Final Award: MA Honours
89) Programme Title: International Business with Arabic
90) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary International Business encompasses the study of public, private and not-for- profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external and increasingly global environment in which they operate. The four-year MA Honours degree programme in International Business with Arabic is a specialist degree within the MA Business Studies portfolio and is designed to address the growing internationalisation and globalisation of business. To reflect that, students are required, through the third year exchange programme, to study abroad and experience at first hand different cultures and approaches and develop their understanding of the international environment. For students with good language skills, this may include foreign language study. The Business School currently has a number of exchange partners for those whose langauge of study is Arabic.
In the degree we reflect the dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as Theoretical Perspectives on International Business, Global Strategy and Managing Across Borders and Cultures, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics and sociology. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. Students gain specific business knowledge, an understanding of the business world and develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management but for those interested in the relationships between people,
14 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 196 organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
The School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for a wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme The educational aim of the MA Honours in International Business with Arabic programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, finance, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of international business and one or more functional areas, including finance, strategy, organisational behaviour, marketing, management science and operations and quality management. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included.
197 the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations, with a particular focus on key issues in international business,. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment..
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry International Business with Arabic graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy International Business with Arabic graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self-improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with the dissertation. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way. 198 11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication International Business with Arabic graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business, in both English and the foreign language of study. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness International Business with Arabic graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills International Business with Arabic graduates will have developed skills to:
199 apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12 Programme Structure and Features The MA International Business with Arabic degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits) and Economics 1A (40 credits) or Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits); Arabic 1a and Arabic 1b (40 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing classes, Computing for Business; Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in business, International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A (20 credits), International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B (20 credits) and Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing courses Career Development Planning and Exchange Preparation for the Business Year Abroad; compulsory Arabic 2 (40 credits); one further course in Business (20 credits). 3rd year: spent studying abroad at an approved overseas exchange partner institution, institution in the country of the language being studied, credit load equivalent to 120 University of Edinburgh credits; all students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management to support the dissertation process, completed using Learn-based materials. 4th year: the Honours Dissertation on a research topic of particular interest to the student (40 credits); four Business Honours courses (80 credits) from a choice of over 30 options. If Honours dissertation is in International Business one Honours option course (20 credits) must be in International Business, otherwise three International Business designated courses (60 credits).
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
200 For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): Students are normally required to pass all of their courses in the first two years (240 credits and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Teaching and learning approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School, including lectures and tutorials.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Varies Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on depending on choice of exchange option partner courses institution Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Oral classes Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes
201 Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to 202 develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Assessment approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School such as examinations, and coursework essays and projects.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Yes Examinations (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective Varies course depending on On-line class test Depends on Depends on exchange choice of choice of partner elective elective institution course course Poster Yes presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Oral tests Yes Yes Written business Depends on plan choice of elective course Dissertation Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. International Business with Arabic graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most
203 popular being accountancy, management, consulting, finance, marketing and human resources.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
16) Other Items . All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. . All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. . Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. . First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. . Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes including Computing for Business which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme). . All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. . In addition to the School’ss IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. . University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. . Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club.
204 . Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS WITH JAPANESE15
91) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
92) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
93) Programme accredited by: N/A
94) Final Award: MA Honours
95) Programme Title: International Business with Japanese
96) UCAS Code: TBA Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary International Business encompasses the study of public, private and not-for- profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external and increasingly global environment in which they operate. The four-year MA Honours degree programme in International Business with Japanese is a specialist degree within the MA Business Studies portfolio and is designed to address the growing internationalisation and globalisation of business. To reflect that, students are required, through the third year exchange programme, to study abroad and experience at first hand different cultures and approaches and develop their understanding of the international environment. For students with good
15 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 205 language skills, this may include foreign language study. The Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Asia for those whose langauge of study is Japanese.
In the degree we reflect the dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as Theoretical Perspectives on International Business, Global Strategy and Managing Across Borders and Cultures, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics and sociology. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. Students gain specific business knowledge, an understanding of the business world and develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
The School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for a wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme The educational aim of the MA Honours in International Business with Japanese programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate: analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, finance, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
206 11) Programme outcomes 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of international business and one or more functional areas, including finance, strategy, organisational behaviour, marketing, management science and operations and quality management. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations, with a particular focus on key issues in international business,. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment..
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry International Business with Japanese graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these. assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy International Business with Japanese graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside
207 business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self-improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with the dissertation. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate business data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication International Business with Japanese graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business, in both English and Japanese. make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness International Business with Japanese graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities.
208 identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills International Business with Japanese graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12 Programme Structure and Features The MA International Business with Japanese degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits) and Economics 1A (40 credits) or Economic Principles and Applications (40 credits); Japanese 1 (40 credits); a compulsory non-credit bearing class, Computing for Business; Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in business, International Business: Globalisation and Trade 2A (20 credits), International Business and the Multinational Enterprise 2B (20 credits) and Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits); compulsory non-credit bearing courses Career Development Planning and Exchange Preparation for the
209 Business Year Abroad; compulsory Japanese 2A or Japanese 2B (40 credits); one further course in Business (20 credits). 3rd year: spent studying abroad at an approved overseas exchange partner institution in the country of the language being studied, credit load equivalent to 120 University of Edinburgh credits; all students must complete and pass an equivalent course to the third year compulsory course Strategic Management; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management to support the dissertation process, completed using Learn-based materials. 4th year: the Honours Dissertation on a research topic of particular interest to the student (40 credits); four Business Honours courses (80 credits) from a choice of over 30 options. If Honours dissertation is in International Business one Honours option course (20 credits) must be in International Business, otherwise three International Business designated courses (60 credits).
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): Students are normally required to pass all of their courses in the first two years (240 credits and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business Studies courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
210 The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Teaching and learning approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School, including lectures and tutorials.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of option courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Oral classes Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Varies Yes activities depending on Independent study Yes Yes exchange Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes partner Yes Poster presentation Yes institution Group projects Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/directors of studies Independent research for Yes the Honours dissertation research
Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities
211 outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
The third year of the degree programme is spent studying and approved range of courses at an overseas exchange partner institution, equivalent to a load of 120 University of Edinburgh credits. Assessment approaches employed at partner institutions vary between institutions but include many of the approaches employed within the School such as examinations, and coursework essays and projects.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Yes Yes Varies Yes Examinations (seen depending on and unseen) exchange Essays Yes Yes partner Yes institution Group/individual Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective elective course course Poster Yes
212 presentations Oral presentations Yes Yes Oral tests Yes Yes Written business Depends on plan choice of elective course Dissertation Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. International Business with Japanese graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being accountancy, management, consulting, finance, marketing and human resources.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
16) Other Items . All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters. . All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. . Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia.
213 . First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. . Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes including Computing for Business which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme). . All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. . In addition to the School’ss IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. . University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. . Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. . Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
THE UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA HONOURS IN BUSINESS WITH DECISION SCIENCES16
97) Awarding Institution: The University of Edinburgh
98) Teaching Institution: The University of Edinburgh
99) Programme accredited by: N/A
100) Final Award: MA Honours
101) Programme Title: Business with Decision Sciences
102) UCAS Code: TBA
16 The information contained in this Programme Specification should be used as a guide to the content of a degree programme and should not be interpreted as a contract. 214 Relevant QAA Subject Benchmarking Group(s): General Business and Management
7) Postholder with overall responsibility for QA: Dr Inger Seiferheld
8) Date of production/revision: October 2012
9) External Summary Our degree in Business with Decision Sciences encompasses the study of public, private and not-for-profit organisations, both small and large, their management practices and processes, and the changing external environment in which they operate. In our four-year programme we reflect the global, dynamic climate of contemporary business and management, offering specialist courses in areas such as management sciences, decision making, corporate finance, entrepreneurship and climate change, drawing on disciplines which include psychology, law, economics, sociology and mathematics.
Students are able to study a range of disciplines outside business, particularly in years one and two, allowing them to develop a broader range of knowledge and skills. A range of compulsory and optional courses examine topics in the context of businesses and of other types of organisation, including, charities, voluntary organisations and the public sector. The ability to follow a concentration of courses in Decision Sciences enables students to develop a specialism within the broader business degree structure. All students have the option of studying abroad in the third year at one of our international partner institutions.
Students gain business knowledge, an understanding of the world of business and importance of decision-making processes and approaches. They also develop a range of transferable, intellectual and study skills which are appropriate not only for those aspiring to a career in management, but for those interested in the relationships between people, organisations and their environment who intend to pursue career opportunities within other types of organisation.
Our programmes are accredited by a range of leading business education organisations and professional bodies, and the School has strong links to the world of practice through research, consultancy and teaching, which ensures that our programmes are attuned to needs of employers and prepare students for the wide range of career opportunities post graduation.
10) Educational aims of programme: The educational aim of the MA Honours in Business with Decision Sciences programme is to provide students with the opportunity to develop and demonstrate:
215 analytical and conceptual knowledge and knowledge of skills relevant to senior management in purposeful organisations. This knowledge includes that of the internal aspects, functions and processes of organisations, the economic, environmental, ethical, legal, political, sociological and technological context in which organisations exist and of the conceptual and analytical tools valuable in their critical analysis; the proficiency to practice integrated and multiple management skills, including computer literacy, independent action, communication, team- working and inter-personal interaction; the knowledge and skills to address problems through flexible, adaptable, innovative and judgmental approaches; a grounding in the key concepts across a range of specialist areas: business policy, marketing, corporate finance, accounting, human resource management, industrial relations, management science and operations management and business economics; with a specific focus on decision sciences; general transferable intellectual and study skills which will equip graduates to make a valuable contribution both within their chosen career path and in the wider community and to encourage a positive attitude to continuing development and lifelong learning.
11) Programme outcomes: 11a) Knowledge and understanding During the programme students will have been given opportunities to develop their knowledge in-depth of business and, in particular, decision sciences. On completion of the programme, students will have acquired a good knowledge and understanding of: the internal functions and processes of organisations which includes their purposes, how they are structured and their governance, how they are operated and managed and an appreciation of their diversity. The behaviour of individuals and of organisations as a whole and their inter- relationships with their external environments are also included. the external environment in which organisations operate including economic factors, ethical factors, political factors, sociological factors and technological factors and their inter-relationships with the strategy, behaviour and management of organisations. the processes, procedures and practices of the management of organisations. This includes theories, models, tasks and roles of management and rational analysis and other processes of decision making within organisations and in relation to the external environment.
11b) Graduate attributes: Skills and abilities in Research and Enquiry Business with Decision Sciences graduates will be able to: understand the principles, methods, standards, values and boundaries of the business discipline and have the capacity to question these.
216 assess critically existing understanding about a range of areas within the field of business, and decision sciences in particular, and recognise the need to re-evaluate such knowledge and the limitations of their own knowledge. identify, define and analyse theoretical and applied business problems and identify or develop approaches using appropriate quantitative or qualitative techniques to explore and solve them. search for, evaluate and use information to form the basis of effective knowledge assimilation and synthesis within a number of business areas, including decision sciences in particular, recognising limitations resulting from the chosen approach. use practical and theoretical knowledge to both design and undertake a piece of original research in the field of decision sciences and write this up as a dissertation.
11c) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal and Intellectual Autonomy Business with Decision Sciences graduates will be: independent learners who take responsibility for their own learning across a range of chosen areas of study, both within and outside business, and are committed to continuous reflection, self-evaluation and self- improvement. open to new ideas, methods and ways of thinking about business issues. able to make decisions on the basis of rigorous and independent thought, taking into account ethical and professional issues. able to collaborate and debate effectively to test, modify and strengthen their own views. curious intellectually and able to sustain intellectual interest, through individual and group work assignments, in particular during the research and writing process associated with undertaking the dissertation on a decision sciences-related topic. aware of, and able to select and effectively use appropriate data, information sources and research methodologies to carry out research into business and management issues for projects, dissertations and presentations, either individually or as part of a team. able to develop and work towards a personal vision and goals and being able to work independently towards these in a sustainable way.
11d) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Communication Business with Decision Sciences graduates will be able to: apply written, oral and visual presentation skills in individual or group projects as well as through presentations linked to lecture courses both within and outside business. communicate effectively, both orally and in writing, using a range of media which are widely used in business.
217 make effective use of oral, written and visual means to critique, negotiate, create and communicate understanding during individual and group activities. use communication as a tool for collaborating and relating to others in a range of settings, including lectures, workshops/tutorial and group project settings, listening to colleagues, constructing arguments, thinking on feet and convincing others. further their own learning through effective use of the full range of communication approaches. seek and value open feedback from academic and support staff, as well as peers, to inform genuine self-awareness. use effective communication to articulate positively their skills identified through self-reflection.
218 11e) Graduate Attributes: Skills and abilities in Personal Effectiveness Business with Decision Sciences graduates will be able to: reflect upon themselves to recognise their personal strengths and the situations where they can best be applied. identify opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge in key areas and recognise how and where to gain experience to build personal capabilities. identify, seek out or otherwise create and harness opportunities in a range of areas relevant to their studies within and outside business. manage tasks and skills in time-management. be confident to make decisions based upon their assimilated understandings and their personal and intellectual autonomy. transfer their knowledge, learning, skills and abilities from one context to another, using their understanding of the issues relevant and appropriate to each situation. work effectively with others, capitalising on their different thinking, contrasting experience and complementary skills. work with, manage, and lead others in ways which value difference and equality and which encourage their contribution to the organisation and the wider community.
11f) Technical/practical skills Business with Decision Sciences graduates will have developed skills to: apply theoretical and conceptual knowledge to practical situations. obtain and process information from a variety of sources. take decisions in a range of challenging situations, informed by analysis of available information. work with others in team-based settings to deliver a project to an outline brief. plan and manage the use of resources, including time and people. summarise large quantities of material to present it in report format for a management audience. make effective use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for business applications. communicate effectively using a range of oral and written methods.
12) Programme Structure and Features The MA Business with Decision Sciences degree is an Honours degree taken over four years. It consists of two years of pre-Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 8 and two years of Honours courses totalling 240 credits at SQCF level 10. The structure for each year is as follows: 1st year: compulsory courses in Business Studies 1 (40 credits), Accountancy 1A (20 credits) and Accountancy 1B (20 credits); the remaining 40 credits in either Economics 1A or Economic Principles and Applications is recommended but students can take one or two other
219 courses in other subject areas; two compulsory non-credit bearing courses, Computing for Business and Study Skills for Business. 2nd year: three compulsory courses in Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques (20 credits), Management Science and Information Systems (20 credits) and the non-credit bearing course Career Development Planning; a choice from nine Business 2nd year courses with a minimum of two courses (40 credits) and a maximum of four (80 credits); it is also possible to choose a maximum of two courses (40 credits) out with the Business subject area. 3rd year: compulsory courses in Strategic Management (20 credits) and Business Research Methods II: Applications and Analysis (20 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Decision Sciences (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 20 options; a compulsory zero-credit course, Research in Management, to support preparation of the dissertation. 4th year: the Business Honours Dissertation on a research topic in the field of Decision Sciences (40 credits); two courses from a list of Honours courses in the field of Decision Sciences (40 credits) and a further two Business Honours courses (40 credits) from a choice of over 30 options.
For full details of the degree programme and structure see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk
For details of the entry requirements see http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/undergraduate/applications- admissions/entry-requirements
Progression requirements for entry into Honours (3rd year): students are normally required to pass all their courses in the first two years (240 credits) and achieve a mark of 50% or above at the first attempt in two Business courses in second year (not including Business Research Methods I: Quantitative Techniques), one of which must be in Management Science and Information Systems.
For full details of the learning outcomes and assessment practices for each course see the Degree Regulations and Programmes of Study http://www.drps.ed.ac.uk. More detailed information on course content is provided in course handbooks which are distributed at the start of each course. In addition to the individual course handbooks, the School also publishes details of 2nd year courses and Honours to assist students in their course choices. A Dissertation handbook is also published each year.
13) Teaching and Learning Methods and Strategies Teaching and learning strategies employed within the Business School and in other Schools where students take courses outside the business area, embrace of a variety of different methods appropriate to the programme
220 aims. The graduate attributes listed above are met through a teaching and learning framework (detailed below) which is appropriate to the level and content of the course.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Lectures Yes Yes Yes Yes Computer laboratories Yes Depends on choice of courses Workshops Yes Tutorials Yes Yes Problem-based learning Yes Yes Yes Yes activities Independent study Yes Yes Yes Yes Peer group learning Yes Yes Yes Yes Poster presentation Yes Group projects Yes Yes Yes Yes One-to-one meetings Yes Yes Yes Yes with course lecturers/tutors/ directors of studies Independent research for Yes Yes the Honours dissertation research
221 Facilities within the School Information technology and other computer-based sessions are delivered in the Business School’s IT Teaching Lab at 29 Buccleuch Place. The lab is equipped with 60 networked PCs which provide access to an extensive range of software packages and applications to support learning through teaching and independent study. Honours students have exclusive use of the UG Resource Centre which is located in a suite of rooms in 16 Buccleuch Place, opposite the main Business School building. The Centre houses two computer labs with a total of 20 work stations and printing facilities, group study space for six groups, and a group presentation room with full audio visual facilities.
Innovative Learning Week The University of Edinburgh’s Innovative Learning Week takes place in Week 6 of Semester 2. During this week ‘normal’ teaching is suspended which provides space for staff and students to explore new learning activities outwith and complementary to the regular curriculum. More than 30 events were included in the School’s programme for 2011-12, led by members of staff from the School, the University Careers Service and a large number of guest speakers representing a wide range of sectors and career perspectives from public and private commercial organisations, to the voluntary and public sectors Examples of the types of activities includes sessions on subject and careers related themes, such as life on the accounting front line and building an entrepreneurial career, whilst others focus on the development of transferable skills such as making effective presentations and developing better networking skills.
14) Assessment Methods and Strategies Courses can be assessed by a diverse range of methods and often take the form of formative work which provides the student with on-going feedback as well as summative assessment. The most common methods of assessment are identified in the table below. A very small number of courses are assessed using only a single, written examination or coursework assignment: most courses employ two or more different forms of assessment, and a growing number combine both individual and group-based activities to develop both subject-specific knowledge and subject-specific and transferable skills.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Written Examinations Yes Yes Yes Yes (seen and unseen) Essays Yes Yes Yes Yes
Group/individual Yes Yes Yes Yes project In-class Tests Depends on
222 choice of elective course On-line class test Depends on Depends on choice of choice of elective course elective course Poster presentations Yes Oral presentations Yes Yes Yes Written business Depends on Depends on plan choice of choice of elective course elective course Dissertation Yes Yes
The classification of the Honours degree is based on performance in both of the Honours years, unless the third year is spent studying at an overseas partner institution, when the degree classification is based on performance in the final Honours year.
15) Career Opportunities A key aim of our degrees is to combine academic knowledge with transferable skills in order to enhance employability. Business graduates are highly valued by employers across the world and the employment record of graduates of the School is evidence that graduates from our programmes are highly sought after by a wide range of employers. Our graduates secure employment in a diverse range of fields, the most popular being management consulting, for which this degree provides very appropriate preparation, accountancy, human resource management, finance and marketing.
During the second year of the programme all students take the Career Development Planning course which encourages early thinking about possible career paths ensuring there is ample time to reflect on how best to develop appropriate knowledge, skills and experience to maximise the likelihood of securing employment in the chosen field. Working in collaboration with the University Careers Service, the School offers the ‘Insight into Management Course’ for students in the Honours Years. The course provides a valuable opportunity to work with managers from a range of employer organisations in challenging and interactive activities, to build and enhance key skills. Innovative Learning Week also provides numerous opportunities to learn more about a range of career paths, to attend CV workshops and to learn how to approach Assessment Centres which are an increasingly common element in many large employers’ recruitment processes.
16) Other Items All students on the programme are allocated to a Personal Tutor, whose role is to provide advice and guidance on academic and personal matters.
223 All students have e-mail, which facilitates easy communication with academic and administrative staff. Generous office-hour provision allows easy personal contact with teaching staff outside formal classes. Opportunities are available to study abroad in the third year on a Business School exchange or University exchange at a partner university Business School; the Business School currently has a number of exchange partners in Europe, North America, Australia and Asia. First year students participate in an induction programme in Freshers’ week for general orientation and introduction to study skills and learning resources. Library, IT, computing and study-skills information packs, backed up by extensive advice and guidance on-line and in general; School-linked classes, including Computing for Business, which is a compulsory course in Year 1 of the programme. All students are provided with e-learning and course materials via Learn. In addition to the School’s IT Teaching Lab there are extensive library and related IT and data resources in the nearby University Library. Additional computing resources are available in extensive open access labs run by the University Computing Service, located in the Central Area as well as at the Pollock Halls of Residence. University support services include the Advice Place (run by the Students’ Association), the Student Counselling Service, Chaplaincy Centre, the Student Disability Service, Accommodation Services, International Office, Student Employment Service. Active student societies including: the Business Society; AIESEC (an international business society); the Student Industrial Society; the Trading and Investment Club (EUTIC) and the Entrepreneurship Club. Careers advice is provided by the University Careers Service; the School runs a compulsory course Career Development Planning in Year 2 of the programme, and the Insight into Management course for 3rd and 4th Year students.
Sarah Cooper October 2012
224