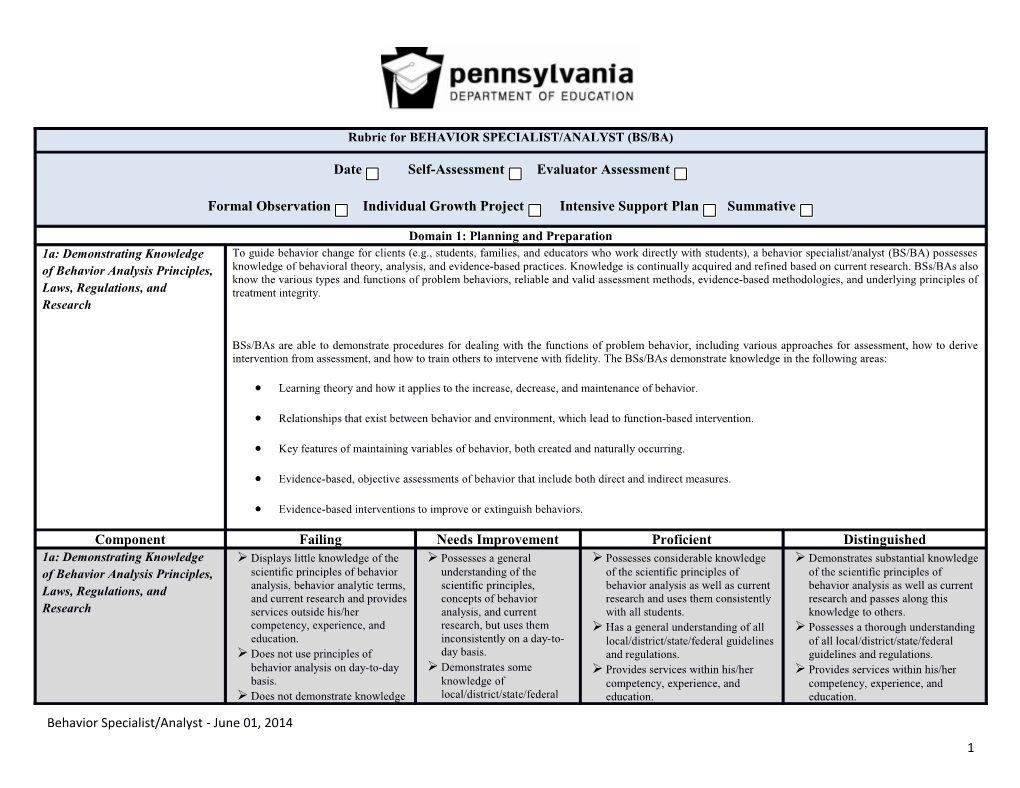
Rubric for BEHAVIOR SPECIALIST/ANALYST (BS/BA)
Date Self-Assessment Evaluator Assessment
Formal Observation Individual Growth Project Intensive Support Plan Summative
Domain 1: Planning and Preparation 1a: Demonstrating Knowledge To guide behavior change for clients (e.g., students, families, and educators who work directly with students), a behavior specialist/analyst (BS/BA) possesses of Behavior Analysis Principles, knowledge of behavioral theory, analysis, and evidence-based practices. Knowledge is continually acquired and refined based on current research. BSs/BAs also know the various types and functions of problem behaviors, reliable and valid assessment methods, evidence-based methodologies, and underlying principles of Laws, Regulations, and treatment integrity. Research
BSs/BAs are able to demonstrate procedures for dealing with the functions of problem behavior, including various approaches for assessment, how to derive intervention from assessment, and how to train others to intervene with fidelity. The BSs/BAs demonstrate knowledge in the following areas:
Learning theory and how it applies to the increase, decrease, and maintenance of behavior.
Relationships that exist between behavior and environment, which lead to function-based intervention.
Key features of maintaining variables of behavior, both created and naturally occurring.
Evidence-based, objective assessments of behavior that include both direct and indirect measures.
Evidence-based interventions to improve or extinguish behaviors.
Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 1a: Demonstrating Knowledge Displays little knowledge of the Possesses a general Possesses considerable knowledge Demonstrates substantial knowledge of Behavior Analysis Principles, scientific principles of behavior understanding of the of the scientific principles of of the scientific principles of Laws, Regulations, and analysis, behavior analytic terms, scientific principles, behavior analysis as well as current behavior analysis as well as current and current research and provides concepts of behavior research and uses them consistently research and passes along this Research services outside his/her analysis, and current with all students. knowledge to others. competency, experience, and research, but uses them Has a general understanding of all Possesses a thorough understanding education. inconsistently on a day-to- local/district/state/federal guidelines of all local/district/state/federal Does not use principles of day basis. and regulations. guidelines and regulations. behavior analysis on day-to-day Demonstrates some Provides services within his/her Provides services within his/her basis. knowledge of competency, experience, and competency, experience, and Does not demonstrate knowledge local/district/state/federal education. education. Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 1 of local/district/state/federal guidelines and regulations. guidelines and regulations. Provides services within his/her competency, experience, and education. Evidence/examples Unable to discuss or answer Can answer general Can answer specific questions about Is prepared to consult and offer questions adequately when questions about behavior behavior management programs and expertise and training on a variety of questioned about behavior management programs and principles. behavior management management programs and/or principles. Facilitates the development of a programs/principles. behavioral principles. Due to partial behavior plan for a student who is Provides clarification for Communicates that strategies that understanding of the exhibiting non-compliance, and predictable, as well as currently have been shown to be effective components of a student’s educates staff about the principles evident, misconceptions of in the majority of cases would behavior plan, simply that are used to guide the programs/principles with an only be effective for a certain recommends that other development of the plan. interdisciplinary team of educators. problem. stakeholders do the best they can. 1b: Demonstrating Knowledge BS/BA demonstrates knowledge of students through historical review and analysis of current behavior that include review of student data, observation of the of Students environment (most importantly, immediate antecedents and consequences of the behavior of concern), assessment of student’s individual preferences, assessment of current skill sets, and determination of skill sets that need to be taught to meet the individual student needs. BS/BA demonstrates knowledge of student history and individual preferences as well as other factors that may impact assessment or intervention such as special needs (including medical factors that may influence behavior), cultural and familial variables, and intervention history. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 1b: Demonstrating Knowledge Does not complete a record Does not always do a Uses language that the student, Conducts a thorough review of the of Students review before communicating thorough review of available family, or staff fully understands. student’s records and all available with the student, family, or staff. records before Always does a cursory review of all data before communicating with the Does not always check to see that communicating with the records and available data before student, family, or staff. a permission to evaluate has been student, family, or staff. communicating with the student or Uses concrete, observable, and completed. Often uses figurative other recipients, and uses clear, measureable terms when describing language, such as “happy,” descriptive, and meaningful the student’s behavior, and “sad,” or “non-compliant” terminology when describing the describes to the student or other when describing behaviors, student’s behaviors. recipients why he/she refrains from which leads to circular Makes sure that a permission to using mentalist terms that are reasoning. evaluate is signed and in the unobservable and lend themselves Makes sure that a student’s file before any work to circular reasoning. permission to evaluate is begins. Makes sure that a permission to signed and in the student’s evaluate is signed and in the file before any work begins. student’s file before any work begins. Evidence/examples: Does not complete a record Proceeds to make Makes recommendations only after Makes recommendations only after review prior to meeting with a recommendations based on a conducting a review of all available conducting a thorough review of all student and his family. 5-minute observation. clear, objective, and measurable available clear, objective, and Offers intervention Does a brief review of data as well as observation of measurable data as well as recommendations without records and only some of the student. Recommendations are observation of student. providing evidence of assessment recommendations are made written in a clear descriptive Recommendations are written in a or observation data. based on data reviewed, manner that makes it explicit for clear, descriptive manner. observation, and information student or staff to follow. Verifies understanding of gathered. Recommendations recommendations and puts data are written in a general systems in place to monitor manner that are not explicit progress and verify fidelity of enough to be carried out or implementation. understood. Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 3 1c: Setting Service Delivery Setting service delivery outcomes that are predicated upon the ability to clearly define, operationalize, and measure behavior. A good definition of behavior is Outcomes one that is free of subjective terminology and is able to be utilized by a novel observer to identify whether a behavior has or has not occurred. A good measurement system is able to capture the critical dimensions of the behavior of concern. These dimensions can include, for example, frequency, rate, intensity, duration, latency, and percentage correct. With few exceptions (such as with dangerous behaviors that may require an immediate response), BSs/BAs collect baseline data as part of their assessment prior to developing or implementing intervention. Additionally, the profession of behavior analysis is self-correcting; that is, when new and better procedures are evident, BSs/BAs utilize these new procedures rather than procedures that no longer have as much support in the prevailing literature. To set up successful programs, the BS/BA must have knowledge of scientifically supported, socially validated, and most effective treatment procedures. The BS/BA must be able to individualize and adapt principles of behavior analysis to meet the needs of an individual student, including task analysis of composite behaviors to simple components when necessary. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 1c: Setting Service Delivery Establishes service delivery Establishes service delivery Consistently establishes service Chooses a measurement system Outcomes outcomes based on poorly outcomes that may or may not be delivery outcomes that are that is evidenced based. defined behaviors that are not consistently based upon the use of evidence-based and derived from Always defines behaviors in measurable. a reliable and valid measurement the use of a reliable and valid measureable and observable Uses data that is not observable system. measurement system. terms, taking into account or measurable. Tends to make recommendations Accurately identifies behavior antecedent, consequence, and Uses data that is anecdotal and that are more general in nature that needs to be established, environmental factors. subjective. because the behaviors that have increased, decreased, or Always uses baseline data to Sets outcomes that are not clearly been targeted for establishing, maintained, which allows for determine which behaviors need stated. increasing, decreasing, or service delivery outcomes to be to be maintained, decreased, or maintaining are not accurately established and measured. Sets outcomes that are not based increased. identified and/or measured. on individual needs. Uses data that is observable and Always consults current research Uses data that is observable and measurable. Sets outcomes that do not on new and innovative measurable. correlate with other goals and Sets outcomes that are suitable interventions. disciplines. Sets outcomes that are suitable and specific to the individual Uses data that is observable and for most individuals but not student’s data and needs. measurable. necessarily specific to the Sets outcomes that are described Sets outcomes that are suitable individual student’s data and in a descriptive manner. and specific to the individual needs. Sets outcomes that do not student’s data and needs. Sets outcomes that are described correlate with other goals and Sets outcomes that are described in a general manner. disciplines. in a descriptive manner. Sets outcomes that do not Sets outcomes that correlate with correlate with other goals and other goals and disciplines disciplines. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished (1c continued) Determines that a student is having Determines that crying and verbal Creates observable and measurable Creates observable and measurable Evidence/examples meltdowns because of frustration. disruptions are related to definitions for crying and verbal definitions for crying and verbal Frequent breaks are recommended. presentation of non-preferred tasks disruptions. Interviews staff and disruptions. Interviews staff and There is no further monitoring of after one visit to the classroom. makes several observations of parents, reviews records, and makes outcomes. Recommends teaching better learner to establish baseline and multiple observations of learner to Identifies intense anger is result of a communication skills. Suggests data determines behaviors are maintained establish baseline and determines drop in adult attention, based upon monitoring but recommends a data by escape. Establishes evidence- behaviors are maintained by escape. discussions with staff. Teaching system that is not user friendly and based training protocol(s) for Establishes evidence-based training identification of emotions is fails to provide accurate replacement behavior(s) and protocol(s) for replacement suggested. No observation of student measurement of the behavior of function-based reduction behavior(s) and function-based or data collection is recommended. concern. procedures. Data collection and reduction procedures. Makes Identifies serious physical monitoring are ongoing. frequent contact with team to review aggression is related to low Clearly defines aggression (hitting, data and adjust plans accordingly. attention, based on staff interviews biting, pinching, and kicking others) Data collection and monitoring are and one observation of student. after staff interviews and several ongoing. Suggests teaching how to request observations of student. Develops Clearly defines aggression (hitting, attention. Fails to provide specific teaching plan for requesting biting, pinching and kicking others) strategies to teach requesting or how attention, as well as recommends after parent and staff interviews, to respond during aggression. function-based intervention. record review, and multiple Requests data collected once per Establishes ongoing data collection observations of student. Develops month. and monitoring system. teaching plan for requesting attention as well as recommends function-based intervention. Establishes ongoing data collection and monitoring system, continues to visit classroom to ensure treatment fidelity. Trains staff to allow self- monitoring of treatment fidelity. Makes adjustments to plans based upon data.
Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 5 1d: Demonstrating Resource knowledge results in provision of comprehensive and high-quality services. BS/BA also uses knowledge of resources to facilitate individual and collective Knowledge of understanding of behavioral principles, evidence-based methodologies, and best practices, including familiarity and application of professional ethical guidelines. Resource knowledge is applied in an effective, efficient, and equitable manner that allows them to keep up to date in current standards as well as current evidence-based research in the Resources field of behavior analysis. BSs/BAs should ensure that resources provided are appropriate for the recipients (e.g., ensures language used in resources is understood and interpreted appropriately). Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 1d: Demonstrating Fails to demonstrate a basic knowledge of Demonstrates general Demonstrates adequate knowledge of Has extensive knowledge of Knowledge of professional guidelines and does not keep up knowledge of professional professional guidelines and keeps up to evidence-based, community, and Resources to date with current research. guidelines but does not keep date with current research. other related resources. Is not aware of conferences, events, up to date with current Is aware of conferences, events, Routinely seeks information from websites, or journals that allow professional research. websites, or journals that allow organizations, journals, growth opportunities and provide resources Is aware of conferences, professional growth opportunities and professional networking, and/or on current research. events, websites, or journals provide resources on current research other sources of reliable and valid that allow professional and is able to utilize the resource to information to update knowledge growth opportunities and inform the work. of resources. provide resources on current Is viewed by colleagues as being research; however, fails to an expert in the area of resources. utilize the resources. Demonstrates extensive knowledge of professional guidelines and keeps up to date with current research. Is aware of conferences, events, websites, or journals that offer professional growth opportunities and provide resources on current research and is able to utilize the resource to inform the work. Is able to transfer the knowledge and information from the resources to the students, family, or staff they serve. Evidence/examples Is not able to identify peer-reviewed Offers recommendations for Makes recommendations based on Makes recommendations based on research-based references or resources when an evidence-based function and research. function and research. asked to provide information related to intervention to increase Ensures that staff is able to access effective interventions. prosocial behavior but is available resources that allow for Uses self-developed or agency-developed unable to provide any more independent selection of resources that are not evidence-based. specifics other than the interventions and decision Often uses phrases such as “I feel that____,” name. making. “I think that____,” and “In my opinion___” Makes statements such as to explain his/her choice of interventions or “this is what I was told I perceptions of functions of behavior. should do.” 1e: Designing Coherent Coherent design of behavioral services is dependent upon a BS/BA who has a clear understanding of expectations and that all decisions (to increase or decrease behaviors) Service Delivery need to be made based on an analysis of the antecedents and consequences in the individual’s environment. This requires the BS/BA to understand how antecedents and consequences affect behavior, have the skills to analyze these variables, and translate the analysis into a coherent plan. The BS/BA must determine how best to select goals, task analyze skills when necessary, and systematically sequence targeted behavior in a way that will result in students achieving the intended outcomes. The BS/BA provides clear procedural descriptions that allow for interpretation and application by students, families, or staff and develops positive behavior support plans that are evidence-based and include all three components of an effective behavior plan: 1. Reducing student’s motivation to engage in problem behavior by manipulating environmental antecedents. 2. Teaching a functional equivalent or appropriate replacement behavior that will allow students to contact reinforcement (in place of the problem behavior). 3. Extinction: not allowing the problem behavior to contact reinforcement. Exceptions include cases in which extinction cannot be used due to safety concerns, such as when there is severe aggression and/or self-injurious behavior. In such cases, alternative interventions to minimize reinforcing the significant problem behavior (such as reinforcing earlier in the chain of behaviors prior to escalation) should be considered. In cases where multiple functions are identified, the BS/BA clearly addresses all three components for each function. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 1e: Designing Coherent Designs instruction and intervention Makes an effort to design instruction and Demonstrates consistent effort to Designs instruction and Service Delivery that is not based on data or the intervention using reliable and valid data design instruction and intervention service delivery that function of the behavior. Designs sources, including functional behavioral intervention service delivery is comprehensive and services that are offered in isolation assessment. using reliable and valid data collaborative in nature as well as and are not based upon reliable and Designs intervention plans that include sources and functional behavioral based on reliable and valid data valid data sources. one of the following components: assessment. sources and functional behavioral Designs intervention plans for reduction of motivation to engage in the Designs intervention plans that assessment. reducing problem behavior that do behavior, teaching a functional equivalent include all of the following Is a member of a team who not address all effective components or replacement behavior, and putting the components: reduction of monitors the quality of service for all identified functions (reduction behavior on extinction. motivation to engage in the delivery design relative to of motivation to engage in the Accounts for student’s motivation to behavior, teaching a functional individual and systems level behavior, teaching a functional some extent. equivalent or replacement outcomes. equivalent or replacement behavior, Has plans in place to ensure student behavior, and putting the behavior Designs intervention plans that and putting the behavior on practices skills in more than one on extinction. include all of the following extinction). environment but fails to account for Accounts for student’s components: reduction of Does not take into account student’s generalization and independence. motivation. motivation to engage in the motivation. Has plans in place to ensure behavior, teaching a functional Does not account for the bigger student is able to perform skills in equivalent or replacement picture of everyday activities and a variety of settings, including the behavior, and putting the behavior environments in which the student natural environment. on extinction. will need to demonstrate behaviors. Uses resources for plan Ensures that student learns self- development that are based on management of behavior when current research within the field. applicable. Accounts for student’s motivation. Has plans in place to ensure student is able to perform skills in a variety of settings, including natural environment. Evidence/examples Uses anecdotal data exclusively to Works in isolation with a student to Identifies more than one function Identifies more than one function inform the development of a design a plan that includes time to learn of problem behavior and designs a of problem behavior and develops behavior plan. and practice a desirable behavior across comprehensive treatment plan to a plan that addresses all three Recommends that all students settings. address each function. effective components for all receive the same reinforcement to Designs a behavior plan that does not Provides a clear data system that identified functions. Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 7 increase a desirable behavior include monitoring the implementation will be used to monitor a Ensures that staff is able to without regard to students’ fidelity of an evidence-based intervention. student’s response to treatment. independently implement individual needs or data. Identifies more than one function of interventions with fidelity. problem behavior; however, designs a plan that only includes antecedent manipulation and teaching replacement behavior for one of the identified functions, but not extinction. 1f: Designing Outcome Skilled BSs/BAs are able to design and use assessments for all relevant and necessary data and that are consistent with current research. Purposes of assessments Evaluation include determining current baseline levels of skills/functioning, determining skills/behaviors to be targeted that are objective and measurable, determining function of behaviors, determining procedures/interventions to implement, monitoring progress of behaviors targeted, monitoring fidelity of implementation of interventions, and making data-based decisions. In addition, BSs/BAs should be able to conduct formative assessments that involve a moment-to-moment analysis of antecedents, behavior(s), and consequences. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 1f: Designing Outcome Uses inappropriate data collection Occasionally uses appropriate Uses appropriate data collection Uses appropriate data collection Evaluation techniques or performance data collection techniques and techniques and performance techniques and performance monitoring systems. performance monitoring systems. monitoring systems. monitoring systems. Does not collect ongoing data nor Reviews the data sporadically but Always uses systems to ensure Always uses systems to ensure periodically review the data, does not always make adjustments procedural integrity. procedural integrity. interprets the data incorrectly, and to the behavior program in a Conducts on-going data review Provides on-going training in data does not adjust the behavioral timely fashion. and makes adjustments to the collection and procedural programs accordingly. Does not always consider the role behavior program when indicated integrity. Does not consider the role of the of the persons implementing the by the data. Always conducts persons implementing the behavior program or plan Considers the role of the persons preference/reinforcement behavior program nor plan appropriate training procedures to implementing the behavior assessments and other appropriate training procedures to improve implementation. program and plans appropriate assessments before implementing improve implementation. Occasionally abandons the training procedures. any behavior procedures. Abandons the student and student or terminates the Never abandons the student or Makes decisions based on terminates the relationship before relationship before it is reasonably terminates the relationship before objective, concrete data. it is reasonably clear that the clear that the student no longer it is reasonably clear that the Never abandons the student or student no longer needs the needs the service. student no longer needs the terminates the relationship before service. Reviews the plan when the service. it is reasonably clear that the Discontinues service if the student student is not making adequate Refines or adjusts the plan if the student no longer needs the is not making any significant gains but does not necessarily data show that the student is not service. gains. make any changes. making adequate progress. Refines or adjusts service if the Terminates service if the student Transfers service to another Reviews all pertinent data, data show that the student is not is being harmed by the procedures provider if he/she feels that the records, and behavior programs making adequate progress. being used without re-evaluating student can be better served. with the new provider before Consults and seeks out other the behavior plan. transferring the service. BSs/BAs if the student is not Does not communicate with the making significant progress any new service providers. toward his/her goals. Always provides all documentation and records when transferring the student to another provider. When applicable, ensures students actively participate in ongoing monitoring and assessment of their own behavior. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished (1f continued) Relies upon data sources that are subjective Conducts an assessment that After developing an intervention plan After developing an intervention Evidence/examples and/or exclusively qualitative in nature measures whether “some” of to decrease problem behavior, provides plan to decrease screaming, helps when evaluating goal achievement. the behavioral goals have staff with a data system that requires educators and parents use a data Is unable to help the staff operationalize been attained. them to measure three specific tracking system that requires the “misbehaving” and develop a reliable Requests that staff assist behaviors targeted for reduction, which daily monitoring of three specific system for measuring improvement. with monitoring a targeted are defined in clear and measurable behaviors related to screaming for Uses assessments that do not match behavior but does not terms. one month. behavioral expectations/targets. clearly define how to assess Verifies that all staff is able to reliably Verifies all staff is able to collect Uses assessments that have no clear whether the intervention is collect the data and then has staff accurate data. measurable criteria. working or not. submit data daily for review and to Provides staff with data-analysis make plan adjustments as needed. Does not design formative assessments. Creates an assessment plan and intervention-implementation in which only some of the Ensures that all the behavioral assistance. Uses assessment results that do not affect behavioral expectations/targets have a method for future plans or changes in intervention. Builds capacity by helping staff expectations/targets are assessment. apply learning to future addressed. Ensures that assessment types match cases/scenarios. Uses assessment criteria that the selected targeted behaviors. are vague and not clearly Ensures that assessment criteria are measurable. clearly written in objective and Uses plans that refer to the measurable terms. use of formative Uses plans that include formative assessments, but they are not assessments during implementation of fully developed. interventions. Uses assessment results that Uses behavior plans that indicate are used to design possible adjustments based on intervention plans for groups formative assessment data. of students, not individual students.
Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 9 Domain 2: The Environment 2a: Creating an The BS/BA establishes and maintains relationships that are positive and supportive in order to create an environment conducive to the student, staff, and behavioral Environment of Respect change program. The BS/BA contributes meaningfully to establishing an environment that is safe, positive, supportive, and respectful in nature. Rapport is easily and Rapport established and maintained. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 2a: Creating an Miscommunicates and causes Inconsistently attempts to explain Explains the behavioral Explains the behavioral Environment of Respect misconceptions by inaccurately the behavioral programming or programming and expectations to programming and expectations to and Rapport explaining in common terms the expectations to the students in the students clearly, effectively, and the students clearly, effectively, and behavioral programming or understandable terms by indicating efficiently. efficiently. expectations to the students by the possible risks, adverse effects, Reviews and plans for possible Reviews and plans for possible indicating possible risks, adverse discomforts, and limitations. risks, adverse effects, discomforts, risks, adverse effects, discomforts, effects, discomforts, and limitations. Sometimes answers questions and and limitations. and limitations. In addition, ensures Does not answer questions or concerns of the student with respect Answers questions and concerns students are able to demonstrate a concerns exhibited by the student and sensitivity and occasionally exhibited by the student with clear understanding of the and treats the student in a does not disclose confidential politeness, respect, and warmth. programming and expectations. demeaning manner. information to others without Does not disclose confidential Answers questions and concerns Discusses factors concerning the consent. information to others without prior exhibited by the student with student in front of the student and consent according to regulations. politeness, respect, and warmth. disinterested third parties in an Does not disclose confidential insensitive manner. information to others without prior Discloses confidential information consent according to regulations. concerning students to others without consent or in disregard to the codes and regulations. Evidence/examples Tells staff “I don’t understand why Reports researching the background Often checks for understanding and Is viewed by colleagues and peers you are not following through with and culture of a family who is from provides staff with necessary as a highly effective recommendations. The procedures another country but does not explanations, modeling, and listener/communicator. are simple and everyone should incorporate information about procedural training. Evidences effectiveness such that know how to do this without culture and related factors within Demonstrates rapport such that colleagues report that the BS/BA requiring specific training.” treatment plan. student and/or staff follow through has been instrumental in Uses disrespectful language toward Reports that they know safety with treatment recommendations empowering them to make positive students and staff. procedures and de-escalation and seek ongoing feedback and changes to the environment. Fails to provide staff with sufficient strategies but have not shared this support from the BS/BA. Uses mutually respectful language explanation of procedures. information with the staff. Uses mutually respectful language with student and/or staff. Displays no concern about Does not always use respectful with student and/or staff. Always provides staff with individual students’ motivation or language toward students and staff. Generally provides staff with sufficient explanation of procedures; needs. Fails to provide staff with sufficient sufficient explanation of demonstrates rapport such that Speaks to staff in a demeaning tone explanation of procedures. procedures; demonstrates rapport students and/or staff members and without regard to their history Displays general concern about such that staff requests the actively seek out further information of learning and area of expertise. students but not about individual information when needed. when needed. students’ motivation or needs. Displays concern about individual Displays concern about individual Sometimes speaks to staff in a students’ motivation or needs. students’ motivation or needs. demeaning tone and without regard Generally takes into consideration Always speaks to staff in a to their history of learning and area staff history of learning and area of respectful tone and takes into of expertise. expertise. consideration their history of learning and area of expertise. 2b: Establishing a The BS/BA contributes to the development of a culture with high behavioral expectations and related achievement goals. Students and staff are empowered to establish, Culture for Goal monitor, and attain goals within the context of positive relational support and mutual accountability, modeling, skill development, and increasing levels of independence Achievement and self-regulation as it relates to goal achievement. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 2b: Establishing a Does not manage and train staff Inconsistently manages and trains Manages and trains staff responsible Manages and trains staff responsible Culture for Goal responsible for carrying out staff responsible for carrying out for carrying out behavior change for carrying out behavior change Achievement behavior change procedures and behavior change procedures. procedures, with consideration of procedures, with consideration of does not design interventions with Provides supervision and support the staff and environment and in a the staff and environment and in a staff consideration accordingly. for the behavior change agents that timely manner. timely manner. Does not provide supervision or are involved with the services. Provides ongoing supervision and Provides ongoing supervision and support for the behavior change support for the behavior change support for the behavior change agents that are directly and/or agents. agents as well as the third parties indirectly involved with the involved in the student’s natural services. settings. Acknowledges staff efforts and establishes an environment where staff is self-motivated to set high expectations and put in extra efforts because they have learned the value of the work and its result on student achievement. Evidence/examples Is unable to provide documentation Provides some training on Provides positive feedback to staff Clients share that they have made of staff development. recommended procedures but does relative to engaging a small group substantial progress and sustained it Provides general recommendations not always model or check for of students as well as specific over time with the assistance of the but fails to provide staff with any implementation fidelity. feedback on refined implementation BS/BA. modeling/training of procedures. Provides feedback to staff but the strategies based upon specific Staff tells BS/BA that in addition to Does not check for implementation feedback is not specific and does needs. following recommendations they fidelity. not result in staff changing their Provides specific training on also did further research on the Does not provide feedback to staff behavior. recommended procedures. procedures and practiced at home (positive or corrective). Staff states, “She did train us, but Models procedures and checks for because they want to make sure to do it right so students can be more Has no documentation of training. we are still not clear on what we are implementation fidelity. supposed to be doing.” successful. Staff states “he just tells us we are Provides feedback to staff that is Staff communicates with doing things wrong but doesn’t Tells staff, “You are doing a great specific and objective as well as administration to share their show us what to do.” job.” corrective feedback that allows staff to improve their performance. students’ achievements and how the Leaves staff with written Tells staff, “You did an excellent procedures they have learned and recommendations that are not implemented have influenced that clearly written and tells staff “don’t job at providing better reinforcement when your students achievement. worry too much about this, they are Staff actively shares and encourages just recommendations and things responded better”; provides specific other staff outside their classroom aren’t so bad here so it’s okay if you feedback on the need to increase and/or school to learn more about can’t implement all of this.” student engagement and responding; and provides procedures for doing effective evidence-based procedures so. and attend trainings and explains to colleagues how it will impact their students’ achievement.
Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 11 2c: Managing Effective procedural management contributes to high-quality instruction and meaningful student engagement. The BS/BA is skilled in procedural management as it relates Procedures to organization of materials, data systems, time management, and transitions/routines. The BS/BA should train and guide staff on specific procedures and protocols that allow implementation of effective classroom organization and management that will result in the smooth operation of the classroom and the efficient use of time. Training components should include: 1. Organization of materials to optimize student and staff performance. 2. Organization of data systems to monitor student progress. 3. Organization of data systems to monitor staff fidelity of implementation. 4. Time management that ensures active student engagement and learning. 5. Clearly established routines and planned activities that meet individual students’ behavioral and instructional needs. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 2c: Managing Demonstrates limited ability to Demonstrates some ability to Demonstrates adequate ability to Provides clear and easy-to-use Procedures implement and/or assist others in implement and/or assist others in implement and/or assist others in documentation of behavior services the area of procedural management the area of procedural management the area of procedural management and provides feedback in an (e.g., organization of materials, data (e.g., organization of materials, data (e.g., organization of materials, data efficient and timely manner. systems, time management, systems, time management, systems, time management, Designs and uses performance transitions, instructional routines). transitions, instructional routines). transitions, instructional routines). monitoring and reinforcement These limitations result in less These limitations result in Effective procedural management systems that are also efficient and effective service delivery for inconsistent quality of services and skills contribute to consistent effective and provide individual individuals and the system. outcomes for individuals and the quality of services and outcomes for feedback regarding the Does not implement or designate system. individuals and the system. implementation of behavior change behavior programs to staff in a Provides ongoing documentation of procedures. timely manner or with regard to behavior services in an efficient and Procedural integrity keeps the daily schedules and routines timely manner. Designs and uses behavior change agents consistent balanced with the needs of the effective performance monitoring with the procedures with ease of students. and reinforcement systems, and uses implementation. procedural integrity to provide Termination of services is written feedback and supervision for into the behavior plan, with plans behavior change agents. and training from the beginning of Uses the data systems and is able to services, utilizing the ongoing data arrange for the orderly termination systems to determine when the of services once the data indicates services are no longer required. that they are no longer required. Evidence/examples Does not use a reliable and valid Provides procedures for staff to Assists a colleague with the Assists team members, including the data system to track the monitoring follow but the procedures are not development of a time-management student, with the development of a of behavioral objectives and well defined. intervention and implementation time-management intervention and outcomes. Instructs staff that they need to run a checklist to monitor treatment implementation checklist to monitor Is ineffective in teaching and program for a student and tells them integrity. treatment integrity. holding students accountable for to just do it as often as they can. Provides staff with specific Discusses and monitors procedures transitioning smoothly from one Provides occasional documentation instructions on development of regularly to ensure that timely and class to another. or procedures for staff to follow. classroom schedule and time necessary changes are made to Instructs staff that they need to run a management and uses a fidelity improve implementation skills and program for a student and tells them checklist to verify that staff positive outcomes. to just do it as often as they can. followed through with Provides documentation of Leaves no documentation or recommendations during follow-up implementation fidelity checklists procedures for staff to follow. visit. that staff have developed or Staff cannot find materials needed Provides consistent documentation completed. for a specific activity that is and procedures for staff to follow. Provides clear and consistent scheduled. documentation as well as follow-up communication on all recommendations. 2d: Managing Student For effective management of student behavior that results in increased appropriate behaviors, decreased or ceasing of inappropriate/problem behavior, and independent Behavior student performance across environments, the BS/BA must be able to clearly identify expectations of behavior, make decisions regarding behaviors to be targeted for increasing and/or decreasing, and design interventions that will successfully accomplish the goal. Managing student behavior requires that the BS/BA is able to determine the function of behavior (using evidence-based assessment methods) and develop plans that account for all components of effective behavior management. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 2d: Managing Student Uses items as potential reinforcers Uses items as reinforcers that are Uses items as reinforcers based on Uses items as reinforcers utilizing Behavior without regard to the long-term based on student preferences. student preferences, and plans to preference assessment, and plans to health of the student. Collects data but the data is not condition reinforcers, as needed. condition reinforcers, as needed. Uses deprivation procedures as sufficient to allow for a clear Effectively plans for extinction Effectively plans for extinction motivating operations without analysis or decision making. effects if necessary. The effects before implementation. The regard to the students’ rights and Insufficiently trains others to collect consideration of generalization is consideration of generalization is needs. data.. planned and implemented. planned and implemented from the Does not state or plan for possible Collects data and trains others to beginning. unwanted effects of reinforcement, collect data. Interprets the data in Collects data and trains others to punishment, or extinction. order to make data-based decisions. collect data, and trains others to Recommends punishment rather interpret the data in order to make than reinforcement procedures and data-based decisions. reinforcement procedures for alternative behavior are disregarded in programming and implementation. Does not collect data or designate others to collect the data needed to assess progress within the program. Does not organize, analyze, or interpret observed data and make decisions and/or program changes as determined by the data. Evidence/examples When teacher asks for assistance Models how to manage disruptive Models and provides training for Provides training in evidence-based with a student who screams when he behavior but does not provide managing the behavior of a student behavioral management procedures. is asked to complete an assignment, follow-up assistance. who is hitting other students and the Implementation is monitored recommends putting the student in Does not establish a formal system teacher. Establishes a data tracking relative to consistency and fidelity “time out” without collecting for monitoring student behavior and reinforcement system after a across personnel and settings. assessment data in regard to because he/she believes staff will thorough assessment. Works with a team to assess function. follow through with recommended Develops plans based on function. response to treatment and the Does not effectively manage student procedures and be able to report Trains and monitors staff on all treatment is adjusted accordingly. behavior as evidenced by high rates their observations of progress. components of behavior plan and as Has trained staff to conduct of problem behavior. Develops non-specific plans that a result staff is able to follow functional assessments, develop Implements inconsistent and result in inconsistent behavior through and implement procedures. effective plans, and develop, different procedures among and patterns as well as inconsistent use Provides data systems to monitor implement, and analyze data across staff. of procedures. student behavior as well as fidelity systems to monitor the students’ Does not address high rates of Puts into place general plans for all of implementation of procedures. behavior and implementation “down time.” students without regard to function fidelity as well as make decisions Does not establish reinforcement of behavior. and changes based on data. systems. Though some data are available to monitor behavior, does not employ systems that ensure accurate data collection. Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 13 Provides data systems that do not allow analysis or data-based decision making. 2e: Organizing Physical Physical space is organized to maximize safety, organization, and accessibility to resources and materials. In addition, organization system should result in maximizing Space instruction and active student engagement. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 2e: Organizing Physical Does not consider organization of Makes some considerations Consistently monitors and ensures Is consistently effective in Space physical space. Safety and access to regarding the physical arrangement that organization of physical space organizing physical space to resources and materials is when planning behavior programs. results in adequate levels of safety, maintain and sustain the highest inadequate. Attempts to eliminate the organization, and access to levels of safety, organization, and Does not consider the physical environmental constraints such as resources and materials. access to resources and materials. arrangement when planning management of the materials in Provides adequate professional Empowers other educators to behavior programs. order to deliver instruction fluently. development in this area that is develop the same level of expertise. Does not eliminate the Provides training/supervision with based upon state codes and Is an expert in this area and serves environmental constraints in a regard to safety. regulations. as a continual resource for parsimonious manner. Assesses environment with only a Is able to assess environment. professional development. Does not provide proper training or few students in mind. Provides training to staff on Eliminates the environmental supervision in regard to safety Provides limited training to staff on classroom management strategies. constraints easily and efficiently and within the environment. classroom management strategies. Guides staff on materials and data is able to train staff on how to Is unable to assess the environment. Does not provide clear procedures systems set-up. manage procedures and materials in Fails to provide training to staff on on materials and data systems set- Guides staff to set up classroom order to deliver instruction in a classroom management strategies. up. environment to maximize student fluent, effective, and efficient manner. Does not provide procedures on Encourages staff to set up classroom success and prevent problem materials and data systems set-up. environment to maximize student behavior while maintaining student Provides proper training/supervision success and prevent problem safety. with regard to safety and the behavior but fails to provide Models organizational strategies. environment and according to state training or procedures on how to do codes and regulations. so. Ensures staff are able to apply learned information to make their own changes to the environment and effectively manage the classroom independent of the BS/BA. Evidence/examples Does not post rules related to safe Guides staff to set up classroom in Trains and guides staff on setting up Teacher has a new group of students behaviors and expectations. order to maintain a particular a classroom schedule that meets all with unique needs and is able to Has barriers that prevent access to student’s safety; however, does not students’ behavioral and adjust the environment and the resources when they are needed. take into consideration other instructional needs and then checks schedule based on strategies Has no indication or documentation students needs or instructional to ensure that staff are previously taught by BS/BA. on guidance regarding classroom needs. implementing and following the management. schedule and that it is resulting in the desired outcomes for the staff Does not address a problem with a and students. teacher who has an inconsistent schedule through which students spend much of their day in non- learning activities, which results in high rates of non-compliance and problem behavior.
Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 15 Domain 3: Service Delivery 3a: Communicating Clearly and The BS/BA understands how behavior analytic theory relates to applied practice and is able to communicate and teach these principles and procedures to Accurately others. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 3a: Communicating Clearly and Uses language that is Uses communication strategies Provides reinforcement of Uses communication strategies Accurately inappropriate and confusing to the and techniques that result in appropriate behavior and and techniques that result in staff. inconsistent service delivery modeling to assist staff. positive service delivery Uses prompting that is ineffective outcomes. Uses clear and effective language outcomes. with the student and does not Uses directions and explanations with staff. Provides reinforcement of reinforce appropriate behaviors of content that are clarified after Uses prompts with the student appropriate behavior and but instead inadvertently initial confusion. that ensures the response and is modeling to assist staff. reinforces inappropriate Uses language that is correct but able to fade the prompts Clients independently apply behaviors. may not be completely successfully. effective communication Tells staff how to implement understandable. Uses language that is techniques and monitor their procedures. Uses prompts with the student understandable and prompts that effectiveness with the assistance that ensures the correct response are consistent. of the BS/BA to enhance but then doesn’t fade the prompt Reinforces appropriate behaviors individual and collective effectively. on an appropriate schedule of outcomes. Reinforces appropriate behaviors reinforcement and does not Uses directions and prompts but not on an appropriate schedule reinforce inappropriate behaviors. accurately and precisely with (the reinforcement is not frequent Guides the staff by modeling how complete understanding, and enough). to implement the procedures with anticipates possible errors. Shows staff how to implement fidelity and then observing the Uses prompts that are consistent procedures but doesn’t then guide staff practice the implementation and faded appropriately when the staff in following the while giving feedback (positive dealing with appropriate procedures. and negative). behaviors and inappropriate behaviors. Uses errorless teaching with the appropriate instruction. Guides the staff in the procedures with fidelity of implementation (models, and then observes while delivering feedback until staff can independently perform the procedures). Teaches students (staff and/or students) to engage in independent responses and utilize self-management techniques and the level of instruction that he/she has received. Evidence/examples Criticizes a staff member for Explains to the staff how to Explains the prompts and Explains procedures, models the using a strategy that was prompt students and implement procedures to the staff and also procedures, and then has staff ineffective with a student. the procedures with initial shows them how to prompt and practice until they are able to Tells staff what to do without confusion, and then is able to re- implement the procedures. perform the procedures without showing them and expects the explain the procedures. Observes the staff trying to errors. staff to understand and implement Written feedback exists and implement the procedures and Shows the staff how to prompt the procedures. verbal feedback is given, however gives oral feedback. and fade prompts effectively. Written guidelines and verbal staff members report that they are Written and oral feedback are Provides written and oral not sure what they are doing. guidelines for the procedures given to the staff, and staff procedure guidelines to a team. merely exist. members are able to observe the Treatment fidelity checklists are Is not comfortable working with BS/BA implement the procedures. completed and effective feedback the student for which the behavior The staff members are able to is provided to increase skills and change program is written. perform the procedures as well. outcomes. Staff can also discuss the behavior change procedures and describe the procedures implemented. 3b: Using Data and The BS/BA uses reliable and valid data sources as well as appropriate and effective data systems. Uses functional behavioral assessment (FBAs) to inform the design, Functional Behavioral implementation, refinement, and/or evaluation of behavioral services. Effective interpretation of data is based upon knowledge of experimental design and measurement Assessment concepts and procedures. The BS/BA can discuss and demonstrate the independent and dependent variables based on data and assessment involved in the behavior change program for the individual student.
Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 3b: Using Data and Is unable to use measurement Is able to use some measurement Consistently uses reliable and valid data Consistently uses reliable and valid Functional Behavioral techniques to develop, techniques to develop, implement, sources, including FBAs, to inform the data sources, including FBAs, to Assessment implement, and/or evaluate the and/or evaluate the effectiveness of design, implementation, refinement, inform the design, implementation, effectiveness of an intervention. an intervention. Does not use the and/or evaluation of behavioral refinement, and/or evaluation of Is unable to set up or to data consistently to make services. behavioral services. maintain various measurement necessary adjustments. Effectively interprets data upon Effectively interprets data based techniques accurately and Is able to set up and use various knowledge of experimental design and upon knowledge of experimental reliably and is not able to measurement techniques that are measurement concepts and procedures. design and measurement concepts design, plot, and interpret data partially successful and is able to Is able to set up and use measurement and procedures. on a graph. design, plot, and interpret data on a techniques accurately and is able to Is able to set up and use various Is not able to design and graph with guidance. design, plot, and interpret data on a measurement techniques accurately implement a behavior change Is able to implement behavior graph. and reliably and is able to design, program according to the change programs that are partially Is able to design and implement plot, and interpret data on a graph. function of the behavior that is effective and sometimes behavior change programs that are Is able to design and implement effective with an experimental appropriate for the setting, staff, effective and appropriate for the behavior change programs that are design appropriate for the program, and student. program, student, and staff involved. effective, demonstrating an program, student, and the staff Sets up a behavior change program Sets up a behavior change program and experimental design appropriate for involved. and uses a graph to display the collects data on an ongoing basis. the program, student, and the staff Does not specify independent intervention. Creates a graph that displays the data involved. variables/dependent variables. and shows that the behavior change Trains others to develop behavioral Sets up a behavior change plan program is effective (either increasing analysis and evaluation skills. but not appropriately and it does or decreasing). Adequately trains staff in the not accurately display what is behavior change programs and actually going on with the collects and reviews treatment student. integrity data on a regular basis. Evidence/examples Develops a behavioral plan but Is able to describe the function of Is able to describe the function of the Is able to describe the function of the it does not reflect the behaviors the behavior. It is not clear, behavior, develop a system for behavior, the behavior change the student is exhibiting. however, whether the intervention measuring the impact of the program that is in place, the Is vague when explaining the is having the desired impact and intervention, and make necessary timely replacement behaviors that are being function of the behavior and staff is not sure if the change changes based upon progress- taught, and how staff has been either describes them all or program is effective. monitoring data. trained. Staff are able to show states the function unclearly. An evidenced-based behavioral Ensures that staff are able to discuss treatment fidelity checklists that strategy is implemented and the function of the behavior, describe the indicate the behavior change Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 17 outcome is graphed. behavior change program, as well as program is being implemented show the graph that indicates the consistently and accurately. progress. Models how to analyze phase change lines on the graph and relative progress, and staff carry out the analysis and graphing of the behavior change program. Teams are learning to function more independently as a result of the BS/BA’s assistance and expertise. 3c: Engaging Students in The BS/BA is able to model and show the staff how to use the applied behavior analysis (ABA) techniques. The BS/BA can put ABA into practice and work with Learning the students.
Specific ABA Techniques: Prompt procedures: how to prompt and fade prompts with students. Use of errorless learning procedures and error correction procedures. Principles of reinforcement: how to use various schedules of reinforcement with both staff (as a staff management tool) and students. Examples include use of differential reinforcement (DRH, DRA, DRI, DRL, DRO), the matching law, and pairing procedures to establish new conditioned reinforcers.
Self-management strategies: how to use token economy procedures and other conditioned reinforcement systems such as TAG teach, direct instruction methods, precision teaching methods, incidental teaching techniques, as well as discrete trial instruction and manding sessions.
Augmentative communication systems (sign language, PECS, devices)
Task analysis
Verbal operants: how to use verbal operants as a basis for language assessment. Examples include echoic stimulus control, mand training, tact training, intraverbal training, listener training, and basic matching-to-sample procedures.
Behavior change procedures: interventions based on antecedents (Motivating operations [MO]; Discriminative stimulus [SD]; Use of discrimination training, instructions and rules; contingency contracting [behavioral contracts]), use of independent, interdependent and dependent group contingencies. Use of stimulus equivalence procedures. Arrange high and low probability request sequences to increase and decrease behavior. Use of the Premack principle (if- then). Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 3c: Engaging Students in Is not able to show staff how to use Is occasionally able to show staff Is able to show staff how to use Is able to use behavior change Learning behavior change systems as how to use behavior change systems behavior change systems as relevant systems as relevant to the student, relevant to the student, as relevant to the student. to the student and environment. environment, and staff. environment, or staff. Is inconsistently able to show staff Is able to show staff how to use the Is able to use the fundamental Is not able to use the fundamental how to use the fundamental elements fundamental elements of behavior elements of behavior change such as elements of behavior change such of behavior change such as positive change such as positive and negative positive and negative reinforcement, as positive and negative and negative reinforcement, reinforcement, appropriate appropriate parameters and reinforcement, appropriate appropriate parameters and parameters and schedules of schedules of reinforcement, prompts parameters and schedules of schedules of reinforcement, prompts reinforcement, prompts and prompt and prompt fading, modeling and reinforcement, prompts and prompt and prompt fading, modeling and fading, modeling and imitation, imitation, shaping, chaining, positive fading, modeling and imitation, imitation, shaping, chaining, positive shaping, chaining, positive and and negative punishment, and shaping, chaining, positive and and negative punishment, and negative punishment, and extinction. extinction with fidelity. negative punishment, and extinction. Is able to use behavior change Is able to use behavior change extinction. Is infrequently able to show staff procedures. procedures. Is not able to use behavior change how to use behavior change procedures. procedures. Evidence/examples Is not able to answer questions Is able to talk about behavior Is able to talk about behavior Is able to talk about behavior about behavior principles, behavior principles, behavior change systems, principles, behavior change systems, principles, behavior change systems, change systems, or the use of and the use of prompts and prompt and the use of prompts and prompt and the use of prompts and prompt prompts and prompt fading fading systems. fading systems as well as model and fading systems as well as model and systems. Explains principles and then states show staff how to use these systems. show staff how to use these systems Talks about principles but does not “do the best you can” and leaves Explains principles, models how to accurately. Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 19 explain them well. Staff are left staff to fend for themselves with apply the principles, and then Explains principles, models how to confused with various terms. limited knowledge. verifies that the staff understands apply the principles, and then how to implement these systems. verifies that the staff understands how to implement these systems accurately and with fidelity. 3d: Using Assessment in The BS/BA knows how to complete various assessments. Specifically, the most important involves functional assessments which represent operant analysis (antecedent Service Delivery behavior consequence) and involve analysis of problem behaviors and/or environment with regard to instruction and analysis of the operants in regard to language.
The functional assessments include the following: Use of assessment tools, such as functional analysis, to determine an operant analysis dealing with problem behaviors. Examples include descriptive analysis (ABC data), functional manipulations, latency functional assessment, and basic functional assessments.
Use of assessment tools to determine an operant analysis dealing with language. Examples include Verbal Behavior Milestones placement program (VB MAPP) ABLLS.
Use of preference assessments (choice procedures).
Assessments relating to other skills such as task analysis, direct instruction programs, and high and low probability task sequences. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 3d: Using Assessment in Is not able to use any of the various Conducts a functional assessment Conducts a functional assessment Conducts and trains others to Service Delivery assessments to conduct an analysis utilizing data interviews and indirect utilizing data interviews and indirect conduct functional assessment, of the behavior that requires methods of assessment. methods of assessment. utilizing data interviews and indirect intervention procedures. Is able to interpret the results and Is able to conduct systematic methods of assessment. Does not conduct a functional data but explains with some manipulations/observations as Is able to conduct systematic assessment utilizing data, inconsistencies and difficulties the needed. manipulations/observations as interviews, or indirect methods of nature of the relationship and results. Is able to interpret the results and needed. assessment. Is able to use assessment tools to explain the nature of the relationship Is able to explain the nature of the Does not conduct systematic conduct an analysis of behavior that and results clearly after a functional relationship and results clearly and manipulations or observations or requires intervention procedures assessment is completed. precisely after a functional directly assess the student. with guidance. Is able to use various assessment assessment is completed. Is unable to explain clearly the tools in an appropriate manner, Is able to use various assessment nature of the relationship and demonstrating how to do so for tools in an appropriate manner and results after a functional assessment students (staff) to conduct an with fidelity, demonstrating how to is completed. analysis of behavior that requires do so for students (staff) to conduct intervention procedures. an analysis of behavior that requires intervention procedures. Evidence/examples Bases functional assessments only Bases functional assessments on Bases functional assessments on Bases functional assessments on on reports rather than on data and reports, but reporting is data and reports, and is able to data and reports, and is able to observations or data collection. inaccurate or unclear. work with the student and work with the student and Is not able to determine a function Is able to discuss and determine a determine a function based on determine a function based on or to base interventions on any function of the behavior but, when systematic manipulations (testing systematic manipulations (testing assessments. the student is observed, the function conditions). The function of the conditions). The function of the is not always accurate and clear. behavior is determined. behavior is determined and clear to Is able to discuss and determine a all staff. function of the behavior and also Is able to discuss and determine a discuss or show staff how that function of the behavior, and staff determination occurred. The are also able to discuss and function appears to be clear and determine the function based on accurate. instruction and observations of the
Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 21 BS/BA. 3e: Demonstrating Flexibility and Responsiveness Adjustments to service delivery are made flexibly and responsibly as a function of changing conditions, data, treatment response, needs, and objectives/goals. changes during the course of the interventions until the desired outcome is achieved. Selecting interventions based on function allows a BS/BA to predict behavior change, which often results in changes being unnecessary. However, because behavior is subject to a wide variety of environmental variables, there are times when the outcome of intervention may not go as planned. In such cases, the BS/BA will be ready to make in-the-moment and long-term analysis to make necessary adjustments to intervention. Component Failing Needs Improvement 3e: Demonstrating Flexibility and Responsiveness Does not demonstrate flexibility and responsiveness in service delivery Demonstrates some flexibility and responsiveness in service delivery as a as a function of changing conditions, data, response, needs, and/or function of changing conditions, data, response, needs, and/or objectives/goals. objectives/goals. Occasionally attempts to modify the service delivery according to the data and observations using appropriate data information-gathering techniques, with moderate success. Accepts responsibility for student success, but has only a limited repertoire of strategies to draw upon.
Evidence/examples Does not provide a graph and cannot find a graph or data to show the Is able to show data. effectiveness of the intervention. The student does not show progress Is able to gather data and discuss the data to determine if the plan in place is and the staff discusses how the student is not improving or that they do effective. not feel that the student is improving. Is rigid and does not change a plan even after data determines or observations determine that the plan is not effective.
Domain 4: Specialist/Analyst Responsibilities 4a: Reflecting on Practice Behavioral services are based on evidence-based practice and/or empirically-validated research. If there is weak evidence to support the behavior change program, the BS/BA should be able to supply data and evidence that the program is effective and valid.
Component Failing Needs Improvement 4a: Reflecting on Practice Does not reflect on practices. Engages in some reflective practice. Does not base behavioral services upon evidence-based methodologies Inconsistently bases behavioral services upon evidence-based and/or customize to individual or systemic needs. methodologies and/or customizes to individual or systemic needs. Does not evaluate behavioral services relative to effectiveness. Inconsistently evaluates behavioral services relative to effectiveness. In those instances where more than one scientifically supported treatment Recommends the least restrictive procedures that occasionally are effective has been established, does not make any other considerations in regard to in dealing with a behavior problem. least restrictive procedures.
Evidence/examples Does not put into place a measurement system to indicate if the treatment Collects data that is anecdotal and from which reliable and valid plan was effective. conclusions about effectiveness cannot be made.
Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 23
4b: Maintaining Accurate The BS/BA maintains accurate records through adherence to principles of applied behavior analysis (knowledge of various experimental designs, measurement, Records graphs, and state codes and regulations). The BS/BA sets up the data in a way to determine the effectiveness of the behavior change program.
Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 4b: Maintaining Accurate Does not maintain appropriate Maintains appropriate yet Maintains appropriate Maintains appropriate Records confidentiality in creating, minimal confidentiality in confidentiality in creating, confidentiality in creating, storing, accessing, transferring, creating, storing, accessing, storing, accessing, transferring, storing, accessing, transferring, and disposing of records under transferring, and disposing of and disposing of records under and disposing of records under his/her control, in accordance records under his/her control in his/her control in accordance with his/her control in accordance with with state and federal codes and accordance with state codes and state codes and regulations. state codes and regulations regulations. regulations. Presents and maintains records Presents and maintains records Has the data system in disarray Presents and maintains records and data collection with accuracy. and data collection in an and unorganized. and data collection, but requires Takes reasonable steps as soon as organized manner and with Fabricates data or falsifies results. frequent monitoring for accuracy. possible to correct errors when accuracy. Does not correct significant errors Takes steps, with guidance, to discovered. Takes reasonable steps to correct in the data when discovered. correct errors when discovered. Cites the work and research of errors immediately and Presents portions or elements of Cites the work and research of others and does not present independently when discovered. another’s work or data as his/her others accurately. another’s work or data as his/her Cites the work and research of own, without any proper citations, own. others accurately with fidelity, and omits findings that might and never presents portions or alter others’ interpretations of the elements of another’s work or work or behavior analysis in data as his/her own. general. Evidence/examples Is unable to show evidence of Has anecdotal data only. Shows graphs that are current and Empowers others to design, accuracy in record keeping and indicative of frequent progress display, and interpret data that data tracking. monitoring. reflect the effectiveness of the interventions and where changes occurred.
Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 25 4c: Communicating with Communication is characterized by professionalism, collaboration, and capacity building via clear information dissemination of data review as well as of the Stakeholders principles of behavior analysis. Communication reflects content expertise relative to behavior analytic theory, science, and application. Communication is delivered in a way that is easily understood by others and allows clarification of any misconceptions of behavior analysis. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 4c: Communicating with Uses communication that does not Uses communication that does not Uses communication that Uses communication that Stakeholders reflect content expertise and consistently reflect content consistently reflects content consistently reflects content experience relative to behavioral expertise and experience relative expertise and experience relative expertise and experience relative theory, science, and application. to behavioral theory, science, and to behavioral theory, science, and to behavioral theory, science, and Provides little/no information application. application. application. Communication about the behavior change Provides minimal and/or Provides culturally appropriate results in capacity building at the program to persons involved; occasionally insensitive information about the behavior individual and systems level. communication with behavior communication or response to change to family members and Provides frequent, culturally change agents and/or family is family concerns; occasionally other persons involved, with appropriate information about the insensitive or inappropriate to the attempts to engage third parties in consideration of issues related to behavior change programs or culture of the persons involved the service delivery program. confidentiality. student progress to family and/or makes no attempt to Does not consistently take into members and other persons engage third parties or families in consideration issues related to involved, and responds to family the service delivery program. confidentiality. member’s concerns with Does not take into consideration consideration of issues related to issues related to confidentiality. confidentiality. Collaborates successfully with third parties in the service delivery program to enhance student goal achievement when needed. Evidence/examples Uses patterns of communication Establishes a positive relationship Is viewed as an effective Through effective communication that often result in mistrust, with stakeholders but lacks communicator and problem- and interdisciplinary relational difficulties, and limited experience and knowledge to help solver. Stakeholders report that collaboration, is viewed as a collaborative problem-solving. others solve problems effectively communication skills are well- leader in facilitating problem- Sets up the behavior change and efficiently. developed and that they trust the solving, building trust, and program but staff and family do Sets up the behavior change BS/BA. Positive relationships and advancing teaming toward not have any indication of program and reviews current data results are frequently achieved. positive outcomes for individuals progress. but only meets with the family Sets up the behavior change and the system. one time. program and frequently checks Sets up the behavior change data. program, frequently checks data, and updates all the persons involved as well as the family regarding the progress. Has documentation such as signed forms or a log that documents the frequent exchange of information. 4d: Participating in a BS/BA The BS/BA is a BCBaBA, BCBA, or BCBA-D and/or is working in the role of behavior specialist/analyst or specialist/analyst without certification and adheres to Community BACB ethical principles and code. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 4d: Participating in a BS/BA Does not uphold or advance the Makes some attempts to uphold or Makes attempts to uphold or Demonstrates the highest Community values, ethics, principles, and advance the values, ethics, advance the values, ethics, standards relative to upholding mission of the field of behavior principles, and mission of the principles, and mission of the and advancing the values, ethics, analysis. field of behavior analysis. field of behavior analysis. principles, and mission of the Does not participate in local, Participates in a limited way in If there is an ethical violation, field of behavior analysis. state, or national organizations. the larger BS/BA community. attempts to resolve the issue If there is an ethical violation, according to guidelines. attempts to resolve the issue according to guidelines. Evidence/ examples Is not aware of the BACB code of Is aware of the BACB code of Has a copy of the BACB code of Has a copy of the BACB code of ethics. ethics and has a copy somewhere ethics and seeks to follow these ethics and reads them regularly. in his/her records. ethics in the daily application of Applies this code in the applied behavior analysis. interventions and discussions that occur with staff or colleagues on a regular basis.
Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 27 4e: Growing and Developing The BS/BA is knowledgeable of current peer-reviewed research in the field of behavior analysis and seeks efforts to grow professionally through multiple Professionally sources. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 4e: Growing and Developing Does not seek opportunities to Engages in some activities that Engages in assessment, therapy, Engages in assessment, therapy, Professionally grow and develop. facilitate professional growth and teaching, research, systems-level teaching, research, organizational development. consultation, and/or other consultation, or other BS/BA activities and experiences that activities. promote professional learning and Actively seeks and maintains an growth. expert level of awareness of current scientific information in his/her field of activity, and undertakes ongoing efforts to maintain competence in the skills he/she will use by reading the appropriate literature, attending conferences and conventions, participating in workshops, and contributing to the field. Evidence/examples Does not design Designs treatment based on Reviews current research, attends Reads current research and programs/interventions based on current research and is able to workshops, and applies research applies the research with students research, instead all the plans/ provide references and citations. to practice, and can design a case using case study format. The case programs are similar and are not study based on the research. study and research is presented as individualized. a poster or in a workshop, and the BS/BA is open to feedback from other professionals in the field. The research could also be published in a journal such as behavior analysis in practice. 4f: Showing Professionalism in Professionalism is demonstrated via knowledge and application of principles of behavior analysis across situations and stakeholders. The BS/BA recognizes Behavior Analysis his/her lack of expertise when applicable and actively collaborates with other professionals and colleagues to seek out the information necessary to refer services to another professional/colleague in order to ensure high quality service delivery. Component Failing Needs Improvement Proficient Distinguished 4f: Showing Professionalism in Is not able to demonstrate Shows growth relative to his/her Provides services commensurate Provides services commensurate Behavior Analysis professionalism via adequate ability to demonstrate with education, training, and with education, training, and levels of knowledge and professionalism via adequate experience. experience. application relative to behavior levels of knowledge and Collaborates with others who Collaborates with others who analysis. application relative to behavior support and provide services to support and provide services to analysis. the student. the student. Has interactions and makes Has interactions and makes decisions that are characterized by decisions that are characterized by honesty, integrity, confidentiality, honesty, integrity, confidentiality, and equity in services. and equity in services. Complies with regulations. Complies with regulations. Actively attempts to continually improve upon professionalism and formal methods for monitoring development in this area. Evidence/examples Makes recommendations for a Makes recommendations for Makes recommendations for Is able to explain the current student/staff without prior student/staff based on review of student/staff based on reviewing research literature and apply it to experience. The recommendations one research article. current literature, attempting to a new situation while admitting to are based on observations alone apply it to the current situation, not having experience with the and without reviewing the current and collaborating with other current situation. Attempts to literature or consulting with experts regarding the situation. apply the current research to the another professional in the field. situation and individualizes it to the student, while seeking collaboration and cooperation with others on the team.
Behavior Specialist/Analyst - June 01, 2014 29