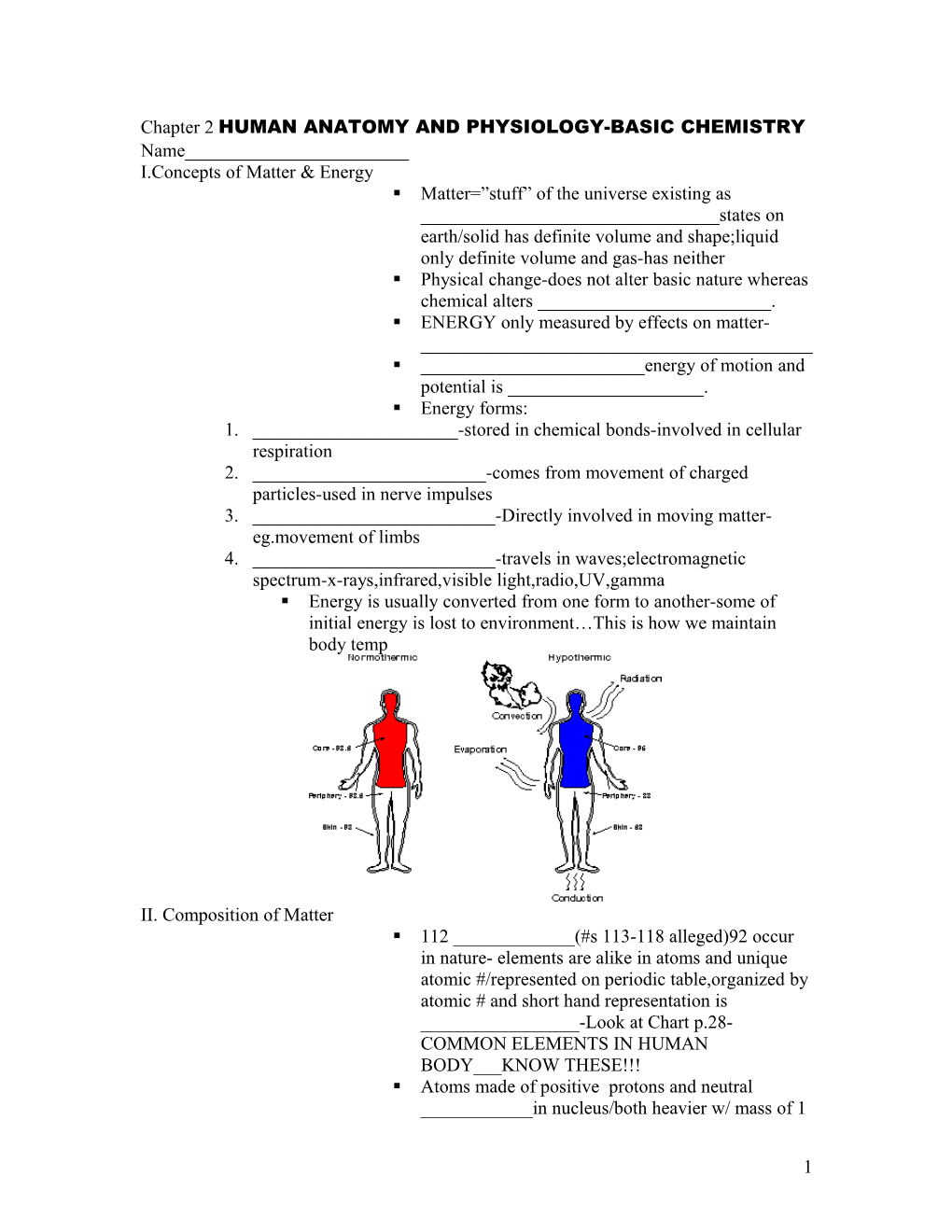
Chapter 2 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY-BASIC CHEMISTRY Name______I.Concepts of Matter & Energy . Matter=”stuff” of the universe existing as ______states on earth/solid has definite volume and shape;liquid only definite volume and gas-has neither . Physical change-does not alter basic nature whereas chemical alters ______. . ENERGY only measured by effects on matter- ______. ______energy of motion and potential is ______. . Energy forms: 1. ______-stored in chemical bonds-involved in cellular respiration 2. ______-comes from movement of charged particles-used in nerve impulses 3. ______-Directly involved in moving matter- eg.movement of limbs 4. ______-travels in waves;electromagnetic spectrum-x-rays,infrared,visible light,radio,UV,gamma . Energy is usually converted from one form to another-some of initial energy is lost to environment…This is how we maintain body temp
II. Composition of Matter . 112 ______(#s 113-118 alleged)92 occur in nature- elements are alike in atoms and unique atomic #/represented on periodic table,organized by atomic # and short hand representation is ______-Look at Chart p.28- COMMON ELEMENTS IN HUMAN BODY___KNOW THESE!!! . Atoms made of positive protons and neutral ______in nucleus/both heavier w/ mass of 1
1 AMU,surrounded by ______electrons(mass= minute fraction of an amu), in energy levels . Atomic # = # protons . Atomic mass #= # p+n . Atomic mass –average of all isotope masses for an element . p’s and e-‘s are = to make a neutral atom/losing electrons creates a + charge and gaining e’s creates a (-) charge/+ and- attract ,while likes repel . ______-e’s are arranged in energy levels w/in an electron cloud
______are atoms that differ in number of neutrons ,are identified by mass number ,and one medical use is as tracers in medical diagnosis.---see.pp. 10-11 ______=spontaneous atomic decay(alpha,beta, and the more intense gamma) ______occur whenever atoms combine with or dissociate from other atoms ______-2 or more combined chemically;more specifically a compound 2 bonds we see in living things are ______,w/a transfer of electrons and ______w/a sharing of electrons-this transfer or sharing is occurring with the electron shells(ie. Energy levels) Outer -______electrons determine bonding capacity and thus properties—These electrons have more energy ,away from the + nucleus ______-charged atom
2 Polar molecules have unequal sharing of electrons ,as seen in water
Water bonds to other water atoms by H- bonds-a weak bond/polar molecules orient themselves towards other polar molecules These combined H-bonds create a high surface tension H-bonds are also important intra-molecular bonds-creating 3-d shape 3 reaction types A) synthesis ----2H2 + O2 2H2O B) ______------H2O 2H2 +O2 C) Exchange---2HCl + Zn ZnCl2 +H2 OR HCl + NaOH HOH +NaCl
D) Most chemical reactions are reversible,indicated by a double arrow
3 A+BAB
III. Biochemistry:Chemical Composition of Living Matter ______contain carbon ,but not all are involved in living things(inorganic lack C-CO,CO2 and cyanide 3 exemptions-they are inorganic)
INORGANICS_WATER-most abundant inorganic compound in the body 1. high heat capacity(ie before a temperature-absorbs and releases large amounts of heat before a temp change change/ thus preventing us from sudden body temperature changes. 2. Polarity/solvent properties ***______-“universal solvent” . Solute dissolves in a ______to make a solution- Thus water able to transport many materials
• 3. chemical reactivity • ______reaction---water added to the bond.
4 4.______-protective as in CSF or amniotic fluid…………………………………….. INORGANIC COMPOUNDS- SALTS Salt contains cation besides H+ and an anion besides OH- …examples:NaCl,KCl,CaI2 Easily separate into ions______ Because ions are charged particles,all salts are ______-able to conduct a current ______-pH<7 and proton donor ______-pH> 7 and proton acceptor pH measures H+ concentration Acid +Base=Salt + water –all neutral---- NEUTRALIZATION REACTION
______prevents sharp pH change
5 FOUR CLASSES of MACROMOLECULES(ORGANICS) in Living Things: ______=chainlike molecules made of many similar repeating units called______.These are joined by dehydration synthesis-Here a H-atom is removed from one monomer and a hydroxyl group(OH) is removed from from the monomer it is being joined with…a water molecule is released When a polymer needs to be broken down/digested the reverse happens- ______occurs-water molecule added to each bond, releasing monomers 1. Carbohydrates(this means”hydrated C”)-FIRST SOURCE FOR ENERGY!!!!!inc. sugars ,starches/have C,H and O in a 1:2:1 ratio (w/some exceptions) Example: C6H12O6= GLUCOSE(blood sugar)
6 Sugars inc. monosaccharides(Glucose, fructose, galactose ,ribose and deoxyiribose),disaccharides-double sugars-2 monosaccharides joined by dehydration(Sucrose,lactose,maltose)---must be broken down to monosaccharides to be digested and polysaccharides---long branching chains(starch and glycogen)---ideal for storage---/but lack the sweetness of smaller sugars….Examples of starches______
2. Lipids-made of C,H and O---look at lipid table p.46
7 3. Enter body as fat –marbled meats,egg yolks,milk products,and oils ---made up of often fatty acids and glycerol 4. Most abundant in body are triglycerides,phospholipids, and steroids ______-are solid fats (@ rm Temp) with all C-C
bonds filled-no double or triple bonds…. ______-are liquids (rm temp) and they have at least 1 C-C double bond-either mono- or polyunsaturated
8 . Neutral fats_triglycerides-made of fatty acid and glycerol( 3 fatty acids attached to 1 glycerol)
. in fat deposits-in subcutaneous tissue and around organs-protect,insulate and major energy source Trans fats----(common in margarines and baked products)oils solidifies by adding H atoms---- considered bad for the cardiovascular system Omega -3 fatty acids(in cold water fish)-help your heart and immune system Phospholipids found in cell membrane
______fat soluble-inc. cholesterol and hormones,such as sex hormones-cholesterol basis of all body steroids Cholesterol is the single most important steroid-from animal products and made by the liver---found in cell membranes ,raw material of vitamin D, steroid hormones, and bile salts ______a breakdown product of cholesterol;released by liver into digestive tract-aid in fat digestion and absorption ______-cortisol;aldersterone LIPIDS ALSO Includes vitamins A(for vision)E(wound healing,fertility,antioxidant),K(for clotting,Prostaglandins-from fatty acid-membranes(used in labor, blood pressure, movement in digestive tract and in inflammation), lipoproteins(transport fatty acids and
9 cholesterol in bloodstream-HDL and LDL-bad cholesterol)
5. PROTEINS-made up of monomer of amino acids;>50% organic matter in the body, most varied functions,contain C,H,O,and N,~ 20 amino acids, polypeptide is another word for protein(containing fewer than 50 amino acids) and peptide bonds join amino acids,made of an amine(NH2) group and an acid(COOH) group,differ in R group
Fibrous(or structural ) –strandlike/Proteins are in most body structures;provide strength-eg.collagen in bones,cartilage and tendons…..also KERATIN—protein of hair , nails ,and skin- providing toughness
10 Globular proteins-mobile and mostly spherical ,compact,and DO things---FUNCTIONAL PROTEINS----examples:enzymes-regulate reactions,antibodies---H-bonds and van der waals force help them- like hemoglogin, keep their shape,less stable than fibrous structures/If that structure is compromised by heat or extremes of pH,they are______-no longer perform their physiological functions.(because their structure dictates their function)
11 Draw an enzyme- substrate complex and label active site(see p.53)
ENZYME__(biological catalyst)-increases reaction rate/controls most physiological reactions
12 Enzymes include______that add water ,OXIDASES- add O2,etc Most enzymes are produced in inactive form and must be activated/some inactivated immediately after they catalyze reaction —example in blood clotting process Enzymes usually end in –ase /(sugars in –ose)
6. NUCLEIC ACIDS-made of C,H,O,N and P-DNA provides heredity and RNA takes DNA’s info to make proteins/the monomer is a nucleotide consisting of sugar ,nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. ---Bases in DNA: Adenine bonds w/ thymine and cytosine with guanine/ Uracil replaces thymine in RNA
-
ATP is the energy storage molecule-This is what carbs are broken down into so we can get usable energy---ATP and ADP continually recycle- Without ATP,molecules cannot be made or broken down,cells cannot maintain their boundaries, and all life processes stop!
13 14