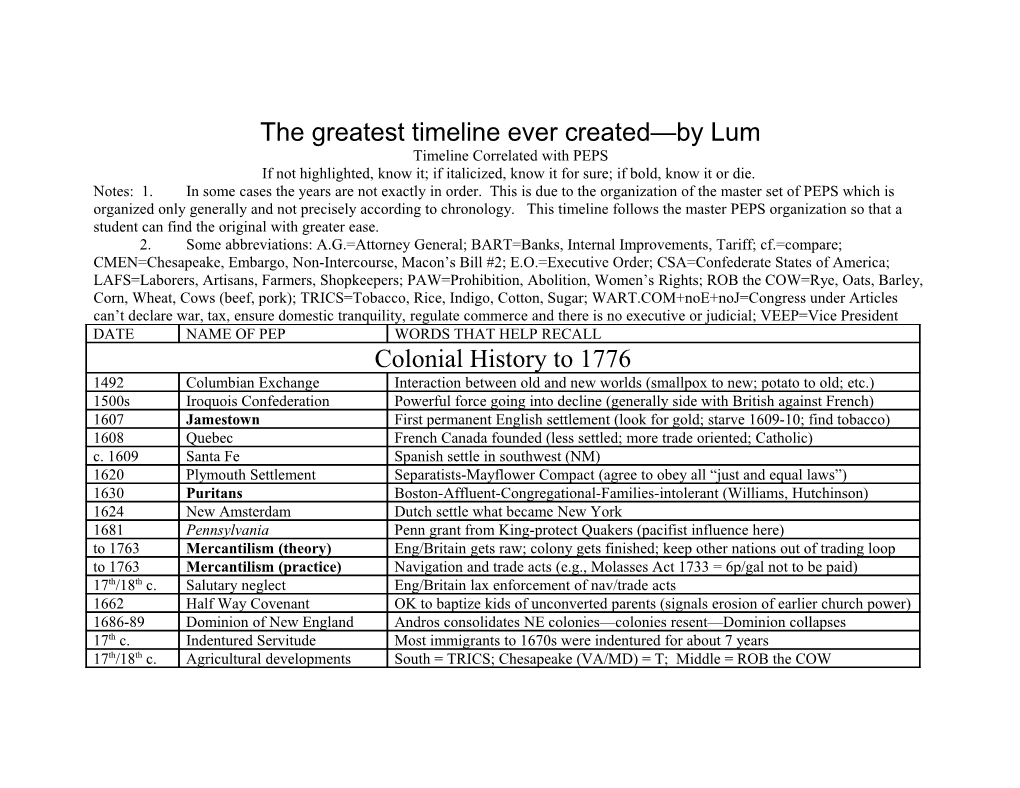
The greatest timeline ever created—by Lum Timeline Correlated with PEPS If not highlighted, know it; if italicized, know it for sure; if bold, know it or die. Notes: 1. In some cases the years are not exactly in order. This is due to the organization of the master set of PEPS which is organized only generally and not precisely according to chronology. This timeline follows the master PEPS organization so that a student can find the original with greater ease. 2. Some abbreviations: A.G.=Attorney General; BART=Banks, Internal Improvements, Tariff; cf.=compare; CMEN=Chesapeake, Embargo, Non-Intercourse, Macon’s Bill #2; E.O.=Executive Order; CSA=Confederate States of America; LAFS=Laborers, Artisans, Farmers, Shopkeepers; PAW=Prohibition, Abolition, Women’s Rights; ROB the COW=Rye, Oats, Barley, Corn, Wheat, Cows (beef, pork); TRICS=Tobacco, Rice, Indigo, Cotton, Sugar; WART.COM+noE+noJ=Congress under Articles can’t declare war, tax, ensure domestic tranquility, regulate commerce and there is no executive or judicial; VEEP=Vice President DATE NAME OF PEP WORDS THAT HELP RECALL Colonial History to 1776 1492 Columbian Exchange Interaction between old and new worlds (smallpox to new; potato to old; etc.) 1500s Iroquois Confederation Powerful force going into decline (generally side with British against French) 1607 Jamestown First permanent English settlement (look for gold; starve 1609-10; find tobacco) 1608 Quebec French Canada founded (less settled; more trade oriented; Catholic) c. 1609 Santa Fe Spanish settle in southwest (NM) 1620 Plymouth Settlement Separatists-Mayflower Compact (agree to obey all “just and equal laws”) 1630 Puritans Boston-Affluent-Congregational-Families-intolerant (Williams, Hutchinson) 1624 New Amsterdam Dutch settle what became New York 1681 Pennsylvania Penn grant from King-protect Quakers (pacifist influence here) to 1763 Mercantilism (theory) Eng/Britain gets raw; colony gets finished; keep other nations out of trading loop to 1763 Mercantilism (practice) Navigation and trade acts (e.g., Molasses Act 1733 = 6p/gal not to be paid) 17th/18th c. Salutary neglect Eng/Britain lax enforcement of nav/trade acts 1662 Half Way Covenant OK to baptize kids of unconverted parents (signals erosion of earlier church power) 1686-89 Dominion of New England Andros consolidates NE colonies—colonies resent—Dominion collapses 17th c. Indentured Servitude Most immigrants to 1670s were indentured for about 7 years 17th/18th c. Agricultural developments South = TRICS; Chesapeake (VA/MD) = T; Middle = ROB the COW 17th/18th c. Northern Merchants Northern colonies = merchants, traders, shipbuilding, fishing, finance, slave trade 1624, 1691 VA and Mass become royal Crown takes VA in 1624; Crown takes Mass in 1691 1660s on Emergence of Slavery VA leads way with 1662 law saying child retains condition of mother 17th/18th c. Role of cities Colonial cities = centers of essentially agrarian society 17th/18th c. Role of women Fully ½ of marriage partnership; raise kids; farm as needed; make candles, soap 17th/18th c. Married women’s rights Fully subordinate to husband; no property rights in marriage 1676 Bacon’s Rebellion Frontier poor protest Berkeley policies; Gov. Berkeley crushes rebellion 1680 Pueblo Revolt Popé successfully leads revolt against Spanish in Santa Fe. 1739 Stono Rebellion 50 SC slaves rebel; crushed; harsher slave codes enacted (no meetings; no read) 1689-91 Leisler’s Rebellion Leisler overthrows Andros in NY; resists new British govt.; is hanged 18th c. Scots-Irish Independent, tough, anti-king, anti-Anglican, frontier/backwoods people 17th/18th c. Triangular Trade Goods from Europe to Africa; Slaves to colonies; rum/raw materials to Europe 17th/18th c. Religious diversity Congregationalist = North; Quaker, Catholic, Meth, Pres = Middle; Anglican = So. 1730s/40s Great Awakening 1st mass movement causes decline in authority of existing church as people convert 18th c. Deism God is nothing but cosmic watchmaker who does not actively intervene in world 1734-35 John Peter Zenger Free speech case; Zenger is acquitted (not guilty) on libel charge 1754-63 French and Indian War War for empire between Britain and France; French lose; Brits need to raise money 1763 Treaty of Paris Ends Fr. and Indian War; Britain gets all to Mississippi (Spain west of Mississippi) 1763-64 Imperial Reorganization Acts of Britain to manage empire and pay war debts 1763 Proclamation Line Indian threat (Pontiac-1763) causes king to say no settlers beyond Appalachians 1764 Currency Act Colonists can’t use paper money to pay debts; colonists don’t have gold; big pain 1764 Sugar Act Brit needs money; reduces tariff on foreign molasses from 6p to 3p/gallon = TAX 1765 Stamp Act Direct tax on some colonial paper; colonies = no tax w/o rep; and can’t be rep!!! 1766 Declaratory Act Stamp Act repealed but this act says Parliament can bind colonies in all cases 1760s on Virtual Representation Members of Parliament represent all British citizens, even those who can’t vote 1767 Townshend Acts Tariffs for revenue on glass, lead, paint, paper, tea opposed by colonies 1773 Boston Tea Party Sons of Liberty toss tea into Boston Harbor 1772-74 Committees of Sam Adams organizes first; communications fostered among towns, and then Correspondence among colonies; used to promote opposition to British policies 1774 Quebec Act Extends Quebec down to Ohio; colonists resented 1774 Coercive Acts (CA) 4 acts described below designed to bring colonies into compliance after tea party 1774 Massachusetts Govt. Act CA1 Must get governor’s approval to have meetings; governor’s council now appointive 1774 Boston Port Act CA2 Closes port of Boston until tea paid for; cripples Boston trade 1774 Admin. of Justice Act CA3 Royal officials can be tried in England for crimes committed in Massachusetts 1774 Quartering Act CA4 Troops can now be housed in occupied houses, including homes The American Revolution 1776-1783 The three PEPS in bold below are the “philosophy of the American Revolution”—know these three well 1690 John Locke Life, liberty, property = natural rights; abolish govt. that is destructive of these 18th c. Popular sovereignty Hobbes, Locke, Rousseau = people are source of all government power 18th c. Small, limited government Government does only what sovereign people tell it to do 1774 1st Continental Congress Called to respond to Coercive Acts 1775-81 2nd Continental Congress Fights war; calls for Articles 1781-88 Congress under Art of Confed Congress under Articles wins war/passes land ordinances;WART.COM noE/no J 7-4-76 Declaration of Independence Colonies declare independence from Great Britain over year after war starts 1777 Saratoga-battle Great U.S. victory—leads to Franco-American alliance in 1778 1775-83 Revolutionary War diplomacy French ally with U.S.; provide troops, supplies, ships; French aid essential 1775-83 Loyalists (“Tories” in U.S.) Mistreated within colonies; U.S. breaks ’83 treaty promise to restore property 1783 Treaty of Paris Britain recognizes U.S. sovereignty; war over; U.S. wins The Articles of Confederation and Constitution-Making 1776-1788 1776-1781 State Constitution making Former colonies draft constitutions republican in form, with bills of rights 1781-88 Articles of Confederation U.S. organizing document; WART.COM + no E = no J 1785 Land Ordinance Survey western lands; 36 sq. mile townships; one section for education; great law 1787 Northwest Ordinance Up to five state to come out of northwest territory; no slavery; fug. slave provision 1786-87 Shays Rebellion Farmers west. Mass rebel; put down by Mass. Militia; shows weakness of Articles 1787 Great Compromise Senate = 2/state; House representation based on population of state 1787 3/5 compromise For taxes and house representation, 3/5ths of slaves can be counted 1787 “Electoral College” States choose electors who vote for president and vice president 1787-88 Federalists v. Anti-Federalists Feds support ratification; anti-feds oppose ratification (too strong govt/no bill of r.) 1787-88 The Federalist 85 essays; Hamilton, Madison, Jay; support ratification of Constitution 1791 Bill of Rights 1st ten amendments protects freedoms of speech, religion, life, liberty, property Early National History 1789-1824 1790 Ham: Public Credit #1 Fund national debt at par; assume state debts; good for speculators and rich 1790 Ham: Public Credit #2 Calls for BUS the BA in BART (Congress accepts); 1st BUS runs from 1791-1811 1791 Ham: Report on Manufact. Calls for the R and T in BART (Congress doesn’t accept) 1790s Jefferson v. Hamilton Strict v. Loose construction = origins of first party system 1776 Republican motherhood Educated moms must teach civic virtue to sons in a republic based on pop. sov. 1793 Washington’s neutrality procl. Wash. wants to stay out of French Revolutionary war; isolationism 1793 Cotton Gin Eli Whitney invents; revolutionizes cotton processing; demand for slaves increases 1798 Interchangeable parts Eli Whitney invents process with muskets; begins mass production capability 1794 Whiskey Rebellion Washington crushes western Penn. rebels opposed to tax on whiskey 1794/95 Jay Treaty Avoids war with Britain; Britain finally gets out of west. forts; Brit. pays damages 1795 Pinckney Treaty Spain grants free navigation of Mississippi; good deal that follows Jay treaty 1795 Treaty of Greenville After Fallen Timbers (Gen. Wayne), Miamis cede vast tract in Ohio valley to U.S. 1798 XYZ Affair U.S. refuses to pay bribe to talk with French; ignites war fever in U.S. 1798-1800 Undeclared war with France U.S.-France seizing ships; near to full war; Convention of 1800 defuses issue 1798 Alien & Sedition Acts Sedition act punishes Jeffersonians for speaking out against Adams; bad law 1798-1799 VA & KY Resolutions Responding to Sedition act, Mad/Jeff assert right of a state to nullify federal law 1792-1831 Slave revolts Fears cause states to adopt laws restricting communications, learning, travel 1800 Convention of 1800 U.S.-France cancel 1778 alliance; peace not war here 1800 Election of 1800 “Revolution” of 1800 causes peaceful transfer of power from Feds to Jefferson 1801-09 Significance of Jeff Presidency Strict in theory, loose in practice (e.g., Louisiana); did not attack Hamilton’s BUS 1803 Louisiana Purchase by Jeff U.S. doubles in size for $15 million; New Orleans belongs to U.S. 1804-06 Lewis and Clark Expedition Great exploration of Louisiana; promotes nationalism and pride 1803 Marbury vs. Madison Principle of judicial review established (articulated by Hamilton in Federalist #78) early 1800s Aaron Burr Jeff’s VEEP kills Hamilton; organizes conspiracy in southwest; tried for treason 1801-05 War with Tripoli A reluctant Jefferson beats Tripoli who wanted tribute to allow U.S. ships to sail 1807 U.S.S. Chesapeake British, looking for deserters, attack U.S. warship; almost leads to war 1807-09 Jefferson’s neutrality Following Chesapeake affair, Jefferson approves embargo then nonintercourse early 1800s Impressment British seize men (including U.S. citizens) to serve in Royal navy; U.S. hates this 1807 Embargo Congress/Jeff order no trade whatsoever with Europe; cripples U.S. commerce 1809 Non-Intercourse Act Embargo repealed in favor of no trade with Britain and France 1810 Macon’s Bill #2 Trade OK with Brit/Fr; if one stop offenses, embargo will be put on the other 1812-15 War of 1812 causes CMEN + warhawks = cause early 1800s Tecumseh Shawnee chief; forces defeated at Tippecanoe/1811; killed at Thames/1813 1794-1823 U.S. foreign policy European distresses = American successes, from ’95 Greenville to ’23 Monroe Doc 1-8-15 Battle of New Orleans After Treaty of Ghent, Jackson beats British and becomes national hero 1814-15 Hartford Convention Anti-war Federalists oppose Madison; Federalist Party dies at Hartford 1815 War of 1812 consequences BART called for; era of good feelings and one-party rule; Clay’s Amer. System 1800 on Nationalism emerges Judicial (Marshall decisions); economic (BART); cultural (BIC and HR School) 1816 Tariff 1st tariff for protective purposes (infant manufacturing spawned by War of 1812) c. 1824 American System/Henry Clay supported BART; the So and West benefit too with R carrying stuff to market Clay 1817-25 Era of Good Feelings Monroe’s terms; one-party; but Panic of 1819 and conflicts over BART occurred 1817 American Colonization Let’s free the slaves and move them to Africa; Liberia created on African coast Society 1818 Convention of 1818 Joint occupation of Oregon; sets Louisiana boundary from Lake of Woods to Rock. 1819 Panic of 1819 Speculation in western lands sparks unemployment, bank failures, debtors’ prison 1819 McCulloch v. Maryland MD tax law struck down; federal supremacy here; necessary and proper here too 1819 Adams-Onis Treaty Spain cedes Florida and gives up vague Oregon claim; So. border Louisiana fixed 1820 Missouri Compromise MO slave; ME free; no slavery in LA territory above 36°30' north latitude 1823 Monroe Doctrine Europe/American continents different, so nonintervention/noncolonization needed Age of Jackson, 1824-48 1820s Texas Austin gets Mexican land grant; Americans settle; conflicts arise 1820s-30s Lowell System NE farmgirls work in company factories and live in company housing 1832 Anti-Masonic Party 1st 3rd party; anti-Mason, anti-Jackson early 1800s Expansion of Suffrage States drop property quals to vote; contributes to Jackson “Era of Common Man” 1828-48 Jacksonian Democracy Expand votes/ appeal to LAFS; hate monopoly; start spoils; hurt Indians 1832-35 Bank War Jackson attacks 2nd BUS as monopolistic monster; success creates $ instability 1836 Specie Circular Jackson says you must use gold/silver to buy western lands; paper can’t be used 1830-39 Indian Removal Jackson OKs Indian Removal in ’30; tribes move; Cherokee Trail of Tears ’38-‘39 1828 on Spoils system Jackson thinks govt work easy; gives govt jobs to friends and cronies; bad system 1840 on Second Party System Democrats and Whigs form second party system; Whigs strongly pro-BART + 1830 Maysville Road veto Jackson vetoes funds for highway in KY because it’s only in KY (blow to BART) 1830 Webster-Hayne debate Webster: constitution=supreme law of land; Hayne: U.S.= compact among states 1828-33 Nullification Crisis SC nullifies tariff of ’32; nullification theory = states are sovereign 1832 Worcester v. Georgia USSC says only feds, not states, can regulate Indian affairs; federal supremacy 1835 Democracy in America Tocqueville: Africans and Indians lose in U.S.; women do better than in Europe 1837 Panic of 1837 Speculation led to panic; Jacksonians call for independent treasury 1840 Independent Treasury Put fed. $ in independent vaults, not state banks; will stop speculation 1832-52 Whigs Elected 2 pres (Harrison ’40; Taylor ’48); BART + moral reforms, public educ. 1828-48 Jacksonian Democracy 1830s: Good: expands vote, handles tariff controversy well; Bad: attack on BUS, (Jackson ‘29-‘37; Van Buren Specie circular, Panic of ’37, treatment of Indians ‘37-‘41; Polk ‘45-‘49) 1840s: Good: establishes Independent treasury, gains from Mexican War, settles Oregon; Bad: imperialistic war with Mexico Transportation Developments in the Early Nineteenth Century 1811-52 National Road Public road from MD to IL helps transportation and movement of goods 1825 Erie Canal NY builds canal from Buffalo to Albany; west can get goods to market now 1828 on Railroads Railroads contribute to national market; major industry in later 1800s Immigration and Nativism 1840-1850s 1830-1900 Irish Immigration Cheap labor; keep Catholicism; prompts nativist reaction; stayed on east coast 1840s on German Immigration Wealthier, moved inland, cultural diversity (kindergarten, beer), reformers 1840s-1850s American (Know-Nothing) Political party reacts against immigrants; anti-German, anti-Irish, anti-Catholic Party Religion, Reform, and Renaissance in Antebellum American 1840s on Cult of Domesticity A woman’s place=home (artistic, moral are good), but too sensitive for labor 1848 on Women’s Rights Denied econ./polit. opportunity and freedom (married/property), women object; women fight for abolition and reforms; Wyoming Terr. grants vote 1869 1845 Margaret Fuller Women in the Nineteenth Century is manifesto of women’s rights movement 1848 Seneca Falls Convention Stanton, Mott, Declaration of Sentiments modeled on Dec of Ind; demands rights 1820-60 Education Reform Horace Mann fights for longer hours, better teachers, improved curriculum 1820s-40s Second Great Awakening Finney leads revivals; reforms gain ground (PAW); Meth/Bapt gains are huge 1830s-40s Mormons Joseph Smith starts; Brigham Young leads them to Utah 1848-1880 Oneida Community Bible communism; complex marriage/selective breeding marginalizes sect 1841-46 Brook Farm Transcendentalists lead communitarian lifestyle on 200 acre farm that fails but demonstrates utopian fervor of mid-century idealists 1830s-50s Transcendentalists Emerson, Thoreau elevate individual dignity; reformers; self-reliance 1820s on Hudson River School Thomas Cole; romantic landscapes; break from Europe; cultural nationalism 1820s on Knickerbocker School Bryant, Irving, Cooper=BIC=cultural nationalism 1830s-60s Abolition Douglass, Garrison, Truth promote abolition 1850s Temperance and Prohibition Neil Dow=prohibition; women fight for temperance 1840s Criminals and the insane Dorothea Dix fights for humane treatment of mentally ill Territorial Expansion and Manifest Destiny 1840s-50s Manifest Destiny God ordained U.S. to take all to Pacific, then in ‘50s reach into Latin America 1836-45 Texas Alamo (’36) leads to independence; slavery issue keeps TX out of U.S. until 1845 1846 Oregon Polk/Britain agree to 49th parallel to divide Oregon—good deal for both 1846-48 Mexican War and Treaty Polk prompts war; gets all from TX to Pacific; Treaty of Guad.-Hidalgo (2-2-48) 1846 Wilmot Proviso PA rep. proposes no slavery in lands taken from Mexico in upcoming war; fails (2) The Crisis of the Union 1820 Missouri Compromise MO slave; ME free; no slavery in LA territory above 36°30' north latitude 1831 on William Lloyd Garrison Radical abolitionist; Liberator (1st=1-1-31); Southerners start to defend slavery 1833 Amer. Anti-Slavery Society Supports immediate abolition; later for Liberty, Free-Soil, and Republican parties 1800-1860 Slavery in general Read the PEP on this one; there is too much info to put here 1837 Calhoun’s defense of slavery S.C. Senator Calhoun argues that slavery is a positive good; blasts North. bosses 1817?-95 Frederick Douglass Brilliant orator and writer; most prominent of the black abolitionists 1840s-1850s Popular Sovereignty Right of the people in territories to vote to have slavery or no slavery 1850 Compromise of 1850 CA=free; no slave trade in D.C.; NM/UT terr.=pop.sov.; strong fug. slave act 1850 Fugitive Slave Act Part of Comp. of ’50; NO=personal liberty laws ; resentment in NO and SO 1852 Uncle Tom’s Cabin Enflamed passions in both NO and SO; written in response to Fug. Slave Act 1853 Gadsden Purchase Part of Mexico (now AZ/NM) for $10 mill.; to build southern railroad 1854 Kansas-Nebraska Act Remainder of LA terr.=pop.sov.; KS and NE terr. formed; free-soilers enraged 1854 on Republican Party NO based party; for BART and no slavery in territories; higher educ; homesteads 1857 Dred Scott decision Slaves can’t sue; MO Comp.=unconst.; free blacks can’t be citizens; bad decison 1857 Lecompton Crisis 1857 KS constitution is pro-slave; Douglas opposes and loses SO Dem. support 1858 Lincoln-Douglas debates IL senate race debate; Douglas=Freeport Doctrine=people can vote vs. slavery 1793-1860 King Cotton Cotton is King; no one dare make war on cotton; SO arrogance here is misplaced 1859 John Brown's Raid Abolitionist radical=violent assault on Harper’s Ferry; becomes martyr for North 1860 Republican Party platform No slavery in territories; BART; public education; homesteads Civil War 1861-1865 4-12-61 Fort Sumter Fort at Charleston, SC: Confederates open fire, starting Civil War 1861-65 North v. South 20 million in NO vs. 9 in SO; 5Xas many mfg. plants in NO.; SO needs quick war 1861-1865 Lincoln and Border States Lincoln could not alienate four slave states still in Union (DEL, MD, KY, MO) 1861-65 Union war goals Preserve Union at start, later add emancipation 1861-1865 African-American Soldiers 180,000 served; 38,000 killed; 54th Mass.=1st regiment in ’63; full pay by 1864 1862-1864 C.S.S. Alabama C.S.A. commerce raider; points to delicate diplomatic issue with Britain 1862 Homestead Act Law grants 160 acres for small fee to settlers (previous: land sales=revenue) 9-17-62 Antietam Union “victory” shows Br/Fr Union power; Emancipation Proclamation follows 1-1-63 Emancipation Proclamation All slaves in land still in rebellion are free as of 1-1-63; turns War into crusade 1862 Morrill Act Rep. education act for land-grant colleges (Texas A&M, e.g.); far-sighted Reconstruction 1865 to 1877 1865 Freedmen’s Bureau To provide food, clothing shelter, education for freed slaves; education a big ++++ 1865 13th Amendment Frees slaves 1865 on Sharecropping/Tenant Freed slaves share crop proceeds (50/50) or become tenants on farms and forever Farming indebted to owners and stores; this reconfigures SO agriculture after the Civil War 1865-67 Black Codes SO states pass laws restricting freedmen to stabilize workforce and keep them down 1863, 1865 Presidential Reconstruction 10% of voters in 1860 election can start gov’t; Johnson adds pardons required 1867-1877 Congressional Reconstruction Cong. Radicals divide S) into 5 military districts; SO states must ratify 14th Amend. 1865, 68, 70 Civil War Amendments 13th=free slave; 14th=citizenship to Africans; 15th=vote for Africans-but no women 1867 Alaska purchase Sec. of State Seward gets Alaska for $7.2 million; Russia off No. Amer. now 1868 Impeachment of Johnson Johnson opposes Congress; House impeaches; one vote short of removal in Sen. 1877 Compromise of 1877 Hayes promises to pull troops out of South; ends Reconstruction; begin Jim Crow 1870s on Southern “Redeemers” Redeemers installed Jim Crow/tenant farming/sharecropping/crop liens 1877 on Jim Crow Systematic legal separation of whites and blacks to keep blacks “in their place” Plains Indian Wars 1866-1890 1866-1890 Plains Indian Wars U.S. Army v. Plains Indians for control of land; Indians lose; cattle in, buffalo out 1868 Washita River U.S. 7th Cavalry annihilates Cheyenne encampment (in present day Oklahoma) 1868 Treaty of Fort Laramie Red Cloud forces U.S. to close Bozeman Road and respect sacred Powder Riv land 1876 Little Bighorn Crazy Horse annihilates U.S. 7th Cavalry under Lt. Col. George Armstrong Custer 1870s Sitting Bull and Crazy Horse Great Sioux leaders at Little Big Horn; both killed by Army (CH=’77;SB=’90) 1866-1890 U.S. 7th Cavalry At Washita (’68); Little Big Horn (’76); and reconstituted at Wounded Knee (’90) 1877 Chief Joseph of the Nez Percé Chief runs with people toward Canada; fails; “I will fight no more forever” quote 1890 Ghost Dance Army fears Indian uprising; Sitting Bull killed; leads to Wounded Knee 1890 Wounded Knee U.S. 7th wipes out Sioux under Bigfoot; ends Plains Indian wars National Politics, 1877-96: The Gilded Age 1877-1896 Corruption during Gilded Age Boss Tweed=Tammany; Credit Mobilier; Whiskey Ring; Sec. War Belnap=bribes 1880s Nativism Chinese Exclusion (’82); American Protective Assoc. (’87)vs. Catholics/foreigners 1881 A Century of Dishonor Helen Hunt Jackson writes about mistreatment of Indians; starts reform movement 1883 Pendleton Act Ends spoils system; begins civil service (what, not who, you know to get a job) 1886 Wabash v. Illinois (1886) Case States can’t regulate railroads; leads to Interstate Commerce Act of 1887 1887 Dawes Severalty Act Civilize Indians; give them 160 acres; end reservation system; reform plan fails 1869 on Women’s Suffrage in West Wyoming Terr. grants women vote in ’69; other West states follow; SE U.S. lags 1840s-1940s Environmental impacts of Plains Indian way of life destroyed; Buffalo grass removed for crops makes land western settlement ripe for “dust bowl” in times of drought; contaminated H2O sources 1893 Turner thesis “Significance of Frontier” = practical/inventive/restless/individualistic/free=Amer. 1880s on Trusts Companies join to create monopolistic combines to control trade/commerce 1873, 84, 93 Panics or recessions Business failures every decade; unemployment; strikes; labor strife 1880s, 90s Farmers’ problems More crops=lower prices; farmers want inflation and railroad regulation 1890 Sherman Antitrust Act To prevent combinations in restraint of trade; 1st used against striking workers 1890s, 1892 Populism “free silver”, initiative, referendum, direct elec. of sen., rr ownership, income tax 1896 Free Silver Democrats ’96; Bryan, Cross of Gold; inflation to help farmers; lost this one to Rep 1896 Plessy v. Ferguson “Separate but equal” is OK says USSC; sanctions Jim Crow; Brown(1954) reverses 1896 Election of 1896 McKinley for gold standard and high tariff beats Bryan; farmers lose 1890 A good year No frontier; Mahan; Sherman AT Act; Riis book; see PEP on this one Industrialization and Corporate Consolidation 1850s on Bessemer process Process to make steel; U.S. becomes industrial giant; Masabi Iron Ore range 1880s on Horizontal integration Rockefeller buys out competition, controls oil industry; robber baron; trust 1880s on Vertical Integration Carnegie controls all phases of production, from mine to finished steel 1886 on American Federation of Labor Strong craft unions; more conservative; Samuel Gompers = leader 1886-1924 1869-1890s Knights of Labor Early labor union; blamed for Haymarket Riot of 1886—declines thereafter 1886 Haymarket Riot Chicago; anarchist bomb; Knights of Labor blamed; labor loses 1892 Homestead Strike Carnegie Steel Works; governor crushes strike with many troops; labor loses 1894 Pullman Strike American Railway Workers/Eugene V. Debs; U.S. troops used; labor loses 1830s on Technological improvements sew mach, lights, typewriter, telephone, elevator, assembly line = rise in business Urban Society 1889 Gospel of Wealth Andrew Carnegie; wealthy must share money to help society 1900s Social Gospel Walter Rauschenbusch; Hell’s Kitchen (NY); must help the poor; Sheldon=WWJD 1880s Social Darwinism Survival of fittest applied to society; poor deserve it; savage defense of wealth 1900s Social critics and dissenters African Americans, unions, socialists, progressives, feminists, writers want change 1890-1920 Immigration Jews, Italians, Croats, Greeks, Poles, Slovaks; cheap labor; nativist reaction 1890 How the Other Half Lives Jacob Riis; book on dirt, disease, vice, and misery of the rat-infested slums in NYC Early 1900s City problems Slums; machine politics/corruption(Tweed); water/sewer problems; gangs/crime 1890s on Hull House = Jane Addams Settlement house; kids day care; English classes; cultural activities; reformist 1900 or so Culture and entertainment Socialism, progressivism, pragmatism; baseball, football, circus, vaudeville Foreign Policy 1890 to 1914 1890-1914 Jingoism Fanatical patriotism; big-navy advocates; support Sp-Amer War and expansion 1890s Jos. Pulitzer/Will. Rand Yellow journalism=lurid headlines/little regard for truth/circulation war/NYC Hearst 1890 Capt. Alfred Thayer Mahan Influence of Sea Power Upon History prompts desire for big navy; jingoism 1898 Spanish-American War Maine; Hearst/Pulitzer; free Cuba; keep Philippines, Guam, Puerto Rico; empire 1898-1902 Aguinaldo and War vs. U.S. Filipino leader vs. U.S. occupation; savage war for few years; Aguinaldo captured 1898 Anti-Imperialist League Formed to oppose keeping Philippines; M. Twain, Sam. Gompers, And. Carnegie 1899-1900 Open Door Policy John Hay: nations in China to respect Chinese terr. integrity and allow fair trade 1904-1914 Panama Canal TR takes Panama strip and builds Canal to facilitate U.S. ship movement 1904-1905 Russo- Japanese War TR brokers peace, wins Nobel Peace Prize 1904-1905 Roosevelt Corollary TR will collect customs in Carib; keep Brit/Ger out; corollary to Monroe Doctrine 1909-1913 Dollar Diplomacy Pres. Taft promotes business investment in Latin America/Asia in lieu of force 1913-1921 Moral diplomacy Pres. Wilson wants to promote human rights/democracy; reflects his idealism Progressive Era 1900-1920 1900-1920 Progressivism Urban middle-class for reforms: TR’s 3Cs; clean govt; welfare; democratic reforms 1880s on Pragmatism John Dewey Kids learn by doing; philosophy=truth of idea=does it work in practice 1900-1916 Good Government League Locals get rid of corruption in cities and install honest, capable officials 1900 on Initiative, Referendum, Recall Progressives: ini=people pass law; ref=legis. asks people; rec=get rid of officials early 1900s Muckrakers McClure’s:Steffens/corruption in cities;Tarbell/Standard Oil;Sinclair/meat-packing 1906 The Jungle Sinclair exposes Chicago meat-packing industry; leads to reform (Meat Insp. Act) 1904 The Shame of the Cities Steffens exposes corruption in cities; leads to “Good Govt. Leagues” and reform 1904 History of Standard Oil Co. Tarbell exposes Standard Oil abuses; Taft files antitrust; company broken up(1911) 1906 Pure Food and Drug Act Prevent the contamination and mislabeling or packaging of foodstuffs 1906 Meat Inspection Act Inspect and condemn bad meat; response to Sinclair’s The Jungle 1903 Elkins Act Prohibits railroad rebates 1906 Hepburn Act Free passes on railroads prohibited; ICC can set rr rates on complaint of shipper 1895 Atlanta Compromise Speech Booker T. Washington accommodationist speech= blacks should work with hands 1890-1920 Niagara Movement W.E.B. DuBois detests Washington; demands equality now; founds N.A.A.C.P. 1909 on N.A.A.C.P. Fights Jim Crow through legal action; Brown v. Board (1954) great victory 1920s Marcus Garvey Black leader (NYC); back-to-Africa; economic self-sufficiency for African Amer. 1901-1909 T.R.’s “Square Deal To help labor but expands to 3Cs: control corps, consumer prot; conservation 1910-1912 T.R.’s New Nationalism Growth of big business OK if checked by growth of big regulatory power in Wash. 1910 Pinchot-Ballinger Controversy Taft fires TR’s friend Pinchot; angers TR; splits TR from Taft; Reps lose in 1912 1909 Payne-Aldrich Tariff Taft angers Dems and Prog Reps with this 41% tariff (helps split Republicans) 1791-1913 Customs Tariffs (customs duties) = chief source of revenue to 1913; income tax takes over 1912-1914 Wilson’s New Freedom 1) Tariff (lower to 27%); 2) Federal Reserve Act; 3) Clayton Act protects unions 1914 Federal Trade Commission FTC prohibits unfair trade practices; consistent with New Freedom of Wilson 1913 Federal Reserve Act Creates 12 banks to issue paper money and regulate economy via interest rates 1913-1920 Prog Era Const Amendments 16th=income tax; 17th=direct elec. senators; 18th=prohibition; 19th=women vote 1900-1920 Women’s roles College in; settlement houses; reform movements; temperance/prohibition 1917 World War I: Causes for U.S Germans sank U.S. ships; British trade soars; German trade drops; U.S. pro-Brit. World War I 1914-1917 Neutral in thought and action Wilson wanted this; impossible due to entry immediately above 1915 Arabic Pledge Germans pledge to not attack passenger ships without giving proper warning 1916 Sussex Pledge Germans pledge to not attack passenger ships without giving proper warning-again 1915 Birth of A Nation D.W. Griffith glorifies KKK in racist movie that is popular 1917-1918 War Industries Board Federal agency to organize economy for war; largely voluntary 1917-1918 WWI on the Home Front Factories reorganized to make bombs; draft started; women go to work; farm products rise; victory gardens; blacks move to cities; food and fuel administrations promote conservation; war (savings) bonds raise money for war effort; anti- German/anti-Socialist sentiment prompts Espionage and Sedition Acts 1-8-18 Wilson’s Fourteen Points Address to Congress: No secret alliances; arms reduction; league of nations 1918-1920 Senator Henry Cabot Lodge Opposed League; opposed Treaty; beat Wilson badly (cf. with U.N. after WWII) 1919 League Article X Article X says U.S. to defend member of League if attacked; Lodge opposed 1919-1920 Red scare A.G. Palmer leads raids; anti-communist hysteria; many jailed or deported 1917 on African American Migration Blacks go to jobs in North and West, creating their own communities in new areas The Roaring 20s 1921-1922 Washington Conference Isolationist pacts; disarm navy; respect Open Door; respect possessions in Asia 1921-1923 Harding scandals Teapot Dome (oil leases for bribes); Vet. Admin. head stole millions from U.S. 1921-1929 Harding and Coolidge Pro-business; antitrust laws ignored; tax cuts for wealthy; high tariffs 1920s Jazz Age Also “Roaring ‘20s”: black music migrates North; Louis Armstrong 1920s Harlem Renaissance Langston Hughes; literary blossoming of racial pride/culture in Harlem 1919-1933 Prohibition 18th Amendment says no alcohol; crime flourishes (Capone); 21st Am ’33 repeals 1920s Modernism Conservatives/Fundamentalists struggled with modernist trends in 1920s 1840s on Nativism 1840s=anti-Irish/Ger; 1880s Chinese; 1908-1924=Japanese; 1924=Europeans 1925 Scopes Trial Scopes convicted of teaching evolution but Fundamentalists (Bryan) look bad 1920s KKK Anti-Catholic, Anti-Jew, Anti-foreign: for white Protestants; many members 1920s Women Flapper=independence; vacuum cleaner, refrig=liberation; jobs=freedom 1920s Margaret Sanger Promotes birth control as alternative to poverty and crime; she was persecuted 1920s “Lost Generation” Fitzgerald=This Side of Paradise; Hemingway=The Sun Also Rises(booze and sex) 1920-1940 Isolationism Wash. Conf. ’21-’22; KB Peace Pact ’28; Nye Report; Neutrality laws ‘35,’36,‘37 1920s-1930s Reparation Problems Dawes Plan; U.S. loan $ to Ger; Ger pays Brit/Fr: Brit/Fr pay loans to U.S.: mess 1920s Farm problems in 1920s Overproduction=lower prices; Coolidge vetoes farm price support laws 1920s Ford Motor Co Model T revolutionizes travel; cheap; reliable; freedom; Henry Ford 1921, 1924 Immigration Restriction 1924 Immigration Act = 2% of 1890 #s in U.S. from any nation; no Japanese 1920s Consumerism Buy refrigerators, cars, vacuum cleaners, radios on credit; lower hours, higher pay 1928 Kellogg-Briand Peace Pact Nations renounce war as instrument of foreign policy; hollow but nice 1920s Blacks and Women Gov does nothing to stop Jim Crow; women return to home after war, but “flapper” Great Depression and the New Deal 1929-1933 Causes of Depression Overproduction on farm and in factory; too much credit; stock speculation 1929-1933 Hoover’s Response Let states/locals fix; later he supports Reconstruction Finance Corp (build dams) 1929-1933 Hoovervilles Shacks/tents encampments for homeless; government sometimes broke them up 1932 Bonus March Vets march on Wash. to demand pay; Hoover busts up encampment and looks bad 1933-1945 F.D. Roosevelt Elected 4 times; got U.S. through Depression and WWII: Practical and tough 3/33 to 6/33 1st 100 Days of FDR’s term Relief, recovery, reform; alphabet soup (CCC, FERA, TVA, AAA) 1933 March Civilian Conservation Corps Puts young men to work in 3Fs: reforestation, firefighting, flood control; good deal 1933 May FERA Federal Emerg. Relief. Admin. provides money for immediate help; simple jobs 1933 May AAA (Agric. Adjustment Act) Price supports for farmers; USSC strikes down; new AAA in 1938 still with us 1933 June HOLC Home Owner’s Loan Corporation = $ for non-farm mortgage help 1933 CWA Civil Works Admin. provides $ for all kinds of simple jobs (part of FERA) 1933 June NRA National Indust. Recovery Act: businesses voluntarily limit hours to increase jobs 1933 June Public Works Administration PWA = $ for dams, roads, buildings = long term recovery in major public works 1933 May Tennessee Valley Authority TVA electrifies Appalachia; provides long-term employment to present 1934 SEC Securities and Exchange Commission regulates stock market 1935 Second New Deal 3 laws: Social Security; Wagner Act (unions can organize/bargain); WPA for jobs 1930s Immigration, Mexican U.S. holds back visas; deports many Mexicans; U.S. trying to protect jobs at home 1930s Radicals, crackpots Huey Long, Father Coughlin, Upton Sinclair, Francis Townsend/all crazy schemes 1934 Indian Reorganization Act John Collier gets abandonment of ’87 Dawes Act in favor of respect for tribes 1935 CIO Congress of Industrial Organizations; all workers in an industry; John L. Lewis 1937 FDR’s Supreme Court USSC strikes down AAA/NIRA; FDR upset; court-packing scheme fails; FDR bad 1937 Keynesian Economics FDR buys into Keynes idea on deficit spending to prime the economic pump 1939 Grapes of Wrath John Steinbeck writes about Dust Bowl migrants and criticizes farmers/landowners 1930s Trilogy John Dos Passos’s 3 books on struggles of Americans in early 1900s 1932 Tobacco Road, Erskine Caldwell writes about alienated poor white Georgia farmers 1938 Recession of 1938 Unemployment rises proving New Deal is not final answer to depression; WWII is The Coming of the Second World War (think isolationism) 1931 Stimson Doctrine Japan invades China; Sec. State Stimson says U.S. won’t recognize terr. gains 1933 Good Neighbor Policy FDR promotes nonintervention in Latin America; TR rolls over in his grave 1933 London Economic Conference FDR is a no-show due to not wanting to stabilize currency in world; isolationism 1934 Nye Committee report Senator Nye says arms merchants/bankers got us into WWI, not subs; isolationism 1930s Japan./Italy/Ger. aggression Japan=China/’31,’37; Italy=Ethiopia/’35; Germany=Poland/’39: U.S. avoids 1935-1937 Neutrality legislation Americans can’t travel on combatant ships, sell goods, loan money during war 1938 Appeasement of Hitler by Brit Britain OKs Hitler taking Sudetenland, but Hitler then takes all of Czech. 1941 Lend-Lease U.S. can lease, loan, sell war goods to help British 1941 Atlantic Charter In secret meeting on ship, FDR/Churchill OK what becomes U.N. World War II 12-07-41 Pearl Harbor 12-07-41 Japan sinks Pacific fleet (except carriers) at Pearl; U.S. declares war; iso’ism ends June 1942 Midway, June 3-6, 1942 Great U.S. carrier victory stops Japanese advance in Pacific (6 mo after Pearl!!!) 1943 Teheran Conference FDR, Churchill, Stalin agree to open 2nd front in 1944; leads to D-Day (6-6-44) 6-6-44 D-Day Ike leads Normandy invasion on French coast; Germany surrenders in May 1945 1941-1945 Adm. Nimitz/Gen. MacArthur Two U.S. commanders who win war in Pacific 1945 Yalta Conference Stalin OKs elections in Europe (reneges) and U.S.S.R. to enter war in Pacific 1945 Potsdam Conference Truman, Stalin, Churchill/Atlee: Japan must surrender or be destroyed 1945 United Nations U.S. creates U.N. (cf. with rejection of League after WWI) 1945 Hiroshima and Nagasaki 8/6&8/9 atomic bombs; Japan surrenders 8/15; WWII ends The Home Front during World War II 1941-1945 Wartime mobilization Must convert industry to war: no more cars but lots of tanks, planes, artillery 1941-1945 Wartime mobilization Draft begun in 1940—before war but in anticipation of war (cf. WWI/draft during) 1941-1945 Wartime mobilization Women go to work: Rosie the Riveter 1941-1945 Wartime mobilization Blacks to NO/West cities for jobs; Mexicans (braceros) brought into U.S. 1941-1945 Wartime mobilization War Production Board has power to ration critical items (gas, oil, metal, rubber) [cf. War Industries Board in WWI which was much weaker and less effective] 1941-1945 Urban migration Blacks, Mexicans, Native Amers. go to cities for jobs, creating communities 1941-1945 Regional development L.A., Detroit, Seattle flourish with wartime jobs 1941-1945 Expansion of govt. power U.S. power to regulate economy and people grows much during WWII 1941-1945 Women and work during war Women make tanks, planes, artillery’ “We Can Do It!” campaign=patriotic 1942-1943 Zoot Suit Riots Sailors attack young Mexicans in L.A., claiming self-defense; racial tensions 1942-46 Internment of Japanese 120,000 (most citizens) interned under E.O. 9066 (USSC says OK): horrible event 1941-1946 Double-V Campaign Blacks soldiers fight racism abroad and at home, thus the double-V (for victory) Truman and the Start of the Cold War 1945-1952 1945-1950s Post WWII Economic Boom Middle class=prosperity; baby boom; TV, cars, washing machines, homes 1944 G.I. Bill 10 million veterans get $ for education and homes: fuels economic boom 1946 Taft-Harley Act Anti-union law (passed over Truman veto) outlaws closed shop + more anti-union 1949 Truman’s Fair Deal [Extension of New Deal] Min. wage increased but Congress opposes health insur. 1946 Employment Act of 1946 Signals U.S. govt. intrusion into national economy (cf. Laissez Faire) 1948 Dixiecrats Truman for civil rights; Thurmond leads racist states’ rights party in election of ‘48 1948 Alger Hiss Accused of being Communist; convicted of perjury; elevates Nixon’s career 1951-1953 Julius and Ethel Rosenberg Executed as spies; some saw trial as anti-communist witch hunt gone too far 1947 Containment: Kennan George Kennan argues U.S. must vigilantly “contain” Soviet expansionism 1947 Contain.: Truman Doctrine Must get $ to Greece and Turkey to fight Commies; let’s help “free peoples” fight 1947 Contain. Marshall Plan U.S. provides billions to rebuild Europe and erode attractiveness of Communism 1948-1949 Berlin Airlift Crisis Truman airlifts supplies to Berlin (cutoff); Stalin loses and reopens roads to Berlin 1949 No. Atlantic Treaty Org. U.S. joins NATO=alliance to confront U.S.S.R.=attack on one is attack on all The 1950s 1951 Korea/MacArthur Feud MacArthur wants big war and won’t shut up: Truman fires this national hero 1950-1954 McCarthyism Wis. Senator conducts anti-commie witch hunt=hurts many; in end he loses 1950 McCarran Act Truman vetoes (Congress overrides): Pres. can detain “suspicious” people 1950s Social Impact of Cold War Fear of atomic war; let’s help blacks so commies won’t gain; must be anti-commie 1950s Science, technology, medicine Salk vaccine; transistors; NASA; NDEA ($ for educ.) 1950s Social developments Transportation: interstates go around towns; speed up transport of goods/people 1950s Social developments Housing: low-cost loans, most Americans own homes by 1960; suburbs 1950s Social developments Standard of living: many have homes, cars, TVs, washing machines: “happy days” 1950s Social developments Black migration: many escape Jim Crow and move to NO/West. cities 1946-1963 Social developments Baby boom: largest generation in U.S. history 1950s Social developments Rock and roll: Elvis merges black and country producing new genre: very popular 1950s Social developments “Happy Days”: OK for white, middle class, but blacks stuck in Jim Crow 1950s Literature of criticism 1. The Lonely Crowd (David Riesman), The Organization Man (William H. Whyte), The Man in the Gray Flannel Suit (Sloan Wilson)=U.S. society=pack of conformists 2. The Affluent Society (John Kenneth Galbraith) questions the relation between private wealth and the public good. These critics represent the conscience of America. 1950s Consensus and conformity McDonald’s; homogenization of society; same cars, same homes; same everything 1950s Beatniks Jack Kerouac (On the Road); counter-culture filled with casual drugs, booze, sex 1954 Dulles’ foreign policy “Brinksmanship”; massive retaliation; mutual assured destruction 1957 Sputnik U.S.S.R. satellite scares U.S., sparks U.S. space program and $ for scientific educ. 1961 “Military Industrial Complex” Ike warns of power, influence, cost of merger of the military with U.S. industry 1954 Brown v. Board of Education Plessy ’96 and separate but equal overturned by USSC; big victory for NAACP 1955 Rosa Parks Refuses to move; convicted; Montgomery Bus Boycott; MLK begins; buses integ. 1957 Civil Rights Commission Weak commission foreshadows CRA of ’64 and Voting Rights Act of ‘65 The 1960s: Kennedy’s New Frontier and Johnson’s Great Society 1960 "New Frontier" JFK ’60 campaign promises: improve Social Security; increase minimum wage 1960 Greensboro sit-in 4 black students NC A & T sit-in at Woolworth’s; Jim Crow attacked; blacks win 1961 Freedom Rides CORE sponsors interstate bus rides to attack Jim Crow; successful 1961 Berlin Wall Khrushchev builds wall to stop flow of East Germans to West; Cold War increases 4-17-61 Bay of Pigs CIA-backed invasion of Cuba; Castro beats; embarrassment for JFK 1962 Cuban missile crisis Khrushchev puts missiles in Cuba; JFK blockades; JFK wins; nuclear war near 1962 Silent Spring Rachel Carson’s book launches environmental protection movement 1950-60s Martin Luther King MLK early fights Jim Crow and for political rights, later for economic justice 1963 The Feminine Mystique Betty Friedan book launches modern women’s rights (feminist) movement 1950s-1960s Vietnam War U.S. must stop Communism; U.S. backs corrupt govt; antiwar protests; U.S. loses 1964 Tonkin Resolution LBJ says U.S. attacked in Tonkin Gulf; Congress gives LBJ authority to fight 1965-1972 Antiwar Movement Massive antiwar movement turned U.S. public against Vietnam war 1964 Civil Rights Act Nobody can discriminate on account of race, color, creed, national origin, sex 1965 Selma Bridge MLK marchers beaten at bridge; leads to Voting Rights Act later in year 1965 The Great Society LBJ domestic agenda: Medicare; immigration reform; Head Start; voting rights 1965 Voting Rights Act LBJ backed this law to register blacks in Southern states; changed Southern politics 1965 on Black Militancy after 1965 Frustration in cities over jobs and justice; riots; blacks promote separateness 1960s Malcolm X Black nationalist leader; for black pride and economic self-sufficiency 1960s Stokely Carmichael SNCC; Black Panthers later 1960s Roy Wilkins Head of NAACP (Brown v. Board of Education) 1960s James Farmer CORE; Freedom Rides 1960s Huey P. Newton Founder of militant Black Panthers 1968 Tet Offensive Vietnamese Communists’ attack is beaten back but discredits U.S. war effort 1968 MLK killed MLK assassinated while in Memphis supporting garbage collectors’ strike 1968 Nuclear Nonproliferation Tre. Treaty is first effort to put a stop to Cold War arms escalation 1968 Robert F. Kennedy killed JFK brother killed while running for president 1968 Washington D.C. riots After RFK killed, riots hurt Wash D.C. economy, crime rises 1968 Democratic Convention Riots Antiwar riots on TV fuel antiwar movement 1968 “Silent Majority” Nixon Nixon=president on appeal to “silent majority” who oppose 1960s protest excesses 1968 George Wallace in election Wallace=3rd party=states’ rights=racist=against civil rights, for segregation 1969-1973 Nixon’s Challenge: Vietnam Nixon gets U.S. out of Vietnam=“peace with honor” in 1973; Commies win 1975 1969-1973 Vietnamization of War Nixon idea to train Vietnamese to take over U.S. role so U.S. can withdraw troops 1972 Nixon’s Challenge: China Nixon thaws Cold War with China; eases burden in Vietnam; confronts U.S.S.R. 1972-1974 Watergate Nixon resigns after being implicated in criminal wrongdoing at Watergate hotel 1969-1989 New Federalism Give more $ and power to states; grants to states for specific programs (Nixon) 1970 Environmental Protec. Agency EPA for clean water and air; environmental protection movement 1972 Title IX No sex discrimination in federally funded education programs; women’s sports 1973 Roe v. Wade USSC legalizes abortion; controversy; court decisions over time erode 1975 on Changes in Amer. economy Higher paid industrial jobs down; lower paid service jobs up; 1990s=outsourcing The United States since 1972 1970s-1980s Détente and Glasnost Détente is “relaxation of tension”; Glasnost=U.S.S.R. openness in government 1978 Camp David Accords Carter brokers peace between Israel and Egypt 1979 Three Mile Island Nuclear plant meltdown = U.S. loses interest in nuclear power; just use more oil 1979-1981 Iranian Hostage Crisis Iran. terrorists keep U.S. hostages 444 days; U.S. can’t cope with terrorists well 1977, 1999 Carter & Panama Canal Carter treaty to turn Canal over to Panama in 1999; better relations w/ Latin Amer. Late 1970s Carter’s economic problems “Stagflation”=high inflation/high unemployment; high interest rates; Carter blamed 1981=Lum’s dog Sunshine is born in Los Angeles 1980 New Right = Reagan Conservative social agenda: vs. ‘60s; anti-porn, abortion, homo., feminism, affirm action; pro-prayer in schools, tougher penalties for crimes 1980s Reaganomics Cut taxes to stimulate economy; but mili. $ so high that debt becomes staggering 1976-1989 Reagan and Carter Washington outsiders: people like anti-Washington establishment Rea. And Car. 1972 ABM Treaty (Nixon) U.S./U.S.S.R. treaty limits anti-ballistic missile missiles; helps thaw Cold War 1979 SALT Carter fails with strategic arms limitation talks 1993 START Treaty Russia/U.S. agree to reduce long-range nuclear weapons 1983 Invasion of Grenada Reagan fears Marxists in Carib. Island; sends troops to install pro-U.S. govt. 1986 Iran-Contra Scandal Sells arms to Iran, then give profits to Contras; illegal; Reagan escapes (Teflon) 1980s Resurgent Fundamentalism Jerry Falwell=Moral Majority; polit. active conserva. Christians: see New Right 1980s on Consumerism Good life=material goods; selfish; little concern for poor, environment 1991 End of the Cold War U.S.S.R. collapses into separate republics; ends Cold War: What will U.S. do now? 1990s on Globalization Interconnectedness of global money and markets make isolationism impossible 1990s on Environmental Issues Global warming; nuclear waste disposal; oil spills vs. hybrid cars, clean air efforts 1990 Persian Gulf Crisis Iraq (Saddam Hussein) invades Kuwait and seizes its vast oil supply 1991 Operation Desert Storm U.S. led coalition forces Iraq out of Kuwait 1999 Clinton Impeachment Clinton not convicted of perjury and obstruction of justice 2001 on Terrorism 9/11/2001 Anti-terrorism becomes organizing principle of U.S. foreign policy WOW—THIS IS SOME TIMELINE—and if I’m reading this I am going to pass on 5-08-09. Smile.
Chronology Correlated with PEPS
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Recommended publications