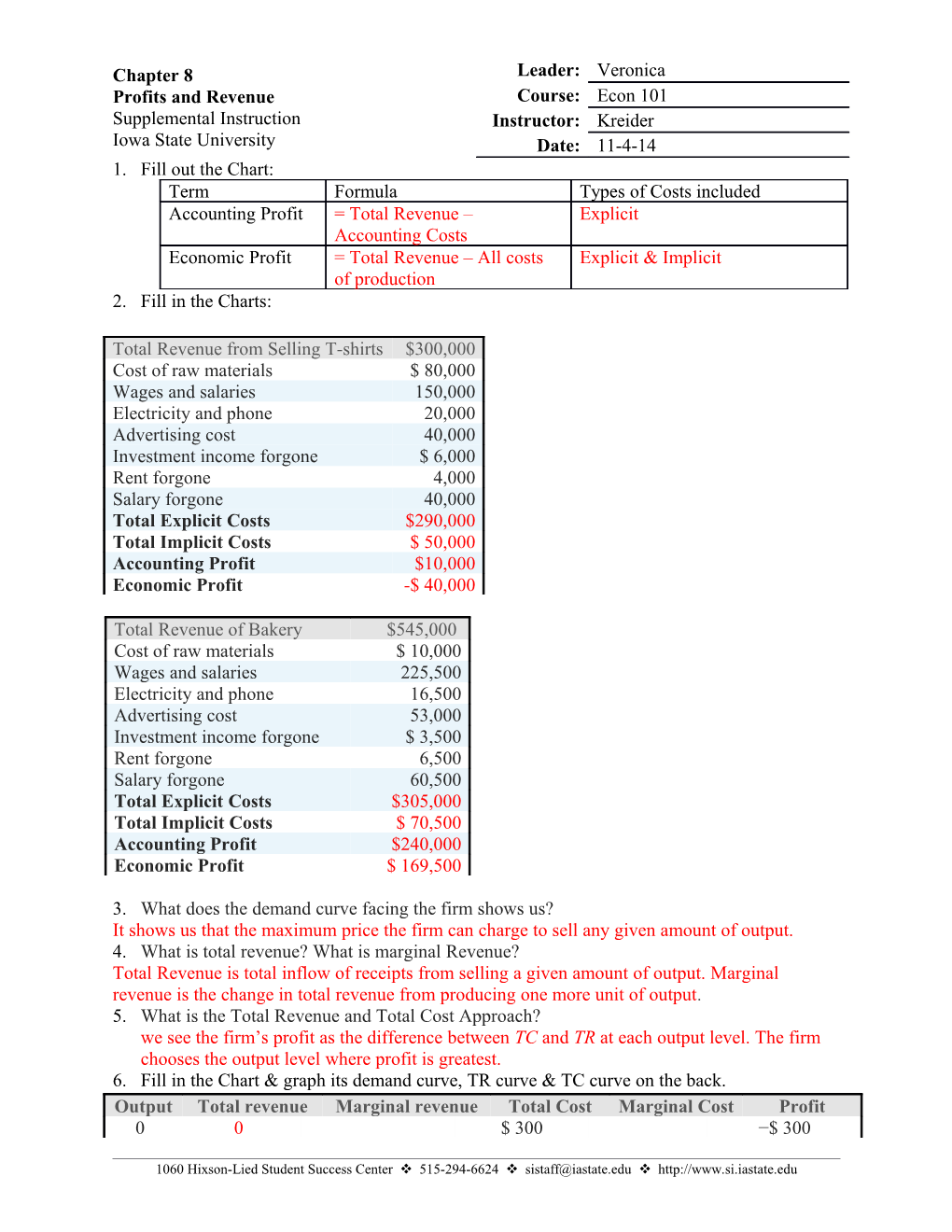
Chapter 8 Leader: Veronica Profits and Revenue Course: Econ 101 Supplemental Instruction Instructor: Kreider Iowa State University Date: 11-4-14 1. Fill out the Chart: Term Formula Types of Costs included Accounting Profit = Total Revenue – Explicit Accounting Costs Economic Profit = Total Revenue – All costs Explicit & Implicit of production 2. Fill in the Charts:
Total Revenue from Selling T-shirts $300,000 Cost of raw materials $ 80,000 Wages and salaries 150,000 Electricity and phone 20,000 Advertising cost 40,000 Investment income forgone $ 6,000 Rent forgone 4,000 Salary forgone 40,000 Total Explicit Costs $290,000 Total Implicit Costs $ 50,000 Accounting Profit $10,000 Economic Profit -$ 40,000
Total Revenue of Bakery $545,000 Cost of raw materials $ 10,000 Wages and salaries 225,500 Electricity and phone 16,500 Advertising cost 53,000 Investment income forgone $ 3,500 Rent forgone 6,500 Salary forgone 60,500 Total Explicit Costs $305,000 Total Implicit Costs $ 70,500 Accounting Profit $240,000 Economic Profit $ 169,500
3. What does the demand curve facing the firm shows us? It shows us that the maximum price the firm can charge to sell any given amount of output. 4. What is total revenue? What is marginal Revenue? Total Revenue is total inflow of receipts from selling a given amount of output. Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue from producing one more unit of output. 5. What is the Total Revenue and Total Cost Approach? we see the firm’s profit as the difference between TC and TR at each output level. The firm chooses the output level where profit is greatest. 6. Fill in the Chart & graph its demand curve, TR curve & TC curve on the back. Output Total revenue Marginal revenue Total Cost Marginal Cost Profit 0 0 $ 300 −$ 300
1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center v 515-294-6624 v [email protected] v http://www.si.iastate.edu $650 $400 1 $ 650 $ 700 −$ 50 $550 $200 2 $1,200 $ 900 $ 300 $450 $100 3 $1,650 $1,000 $ 650 $350 $150 4 $2,000 $1,150 $ 850 $250 $200 5 $2,250 $1,350 $ 900 $150 $250 6 $2,400 $1,600 $ 800 7. Facts on MR and MC: a. When a firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve, each increase in output causes a revenue gain, from selling additional output at the new price, and a revenue loss, from having to lower the price on all previous units of output. Marginal revenue is therefore less than the price of the last unit of output. b. An increase in output will always raise profit as long as marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost (MR > MC). c. An increase in output will always lower profit whenever marginal revenue is less than marginal cost (MR < MC). d. To find the profit-maximizing output level, the firm should increase output whenever MR > MC, but not increase output when MR < MC. 8. What is the profit-maximizing output from question 6? Answer 5.