1Supplementary data
2
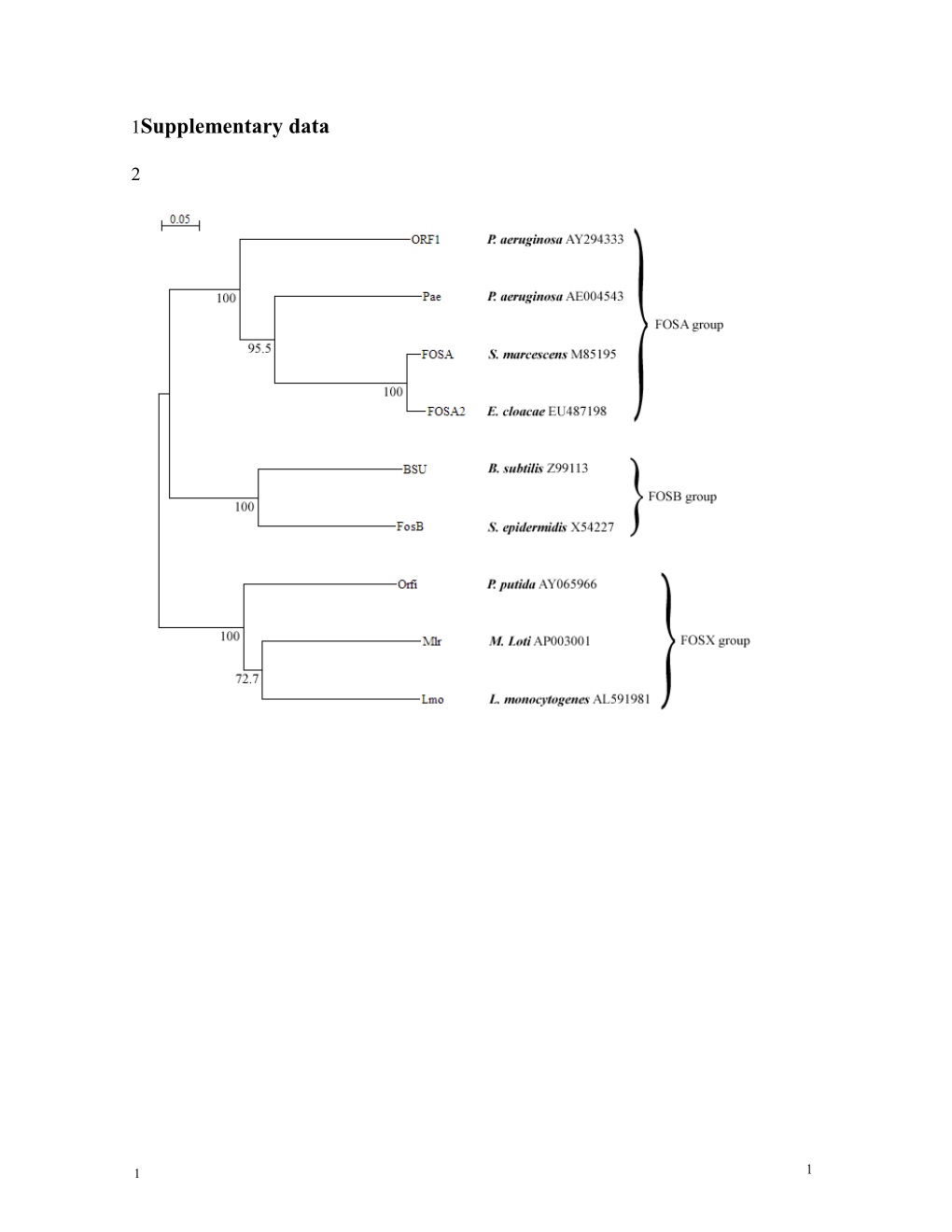
1 1 3Figure S1. Phylogenetic tree of fosfomycin resistance proteins. Sequences were aligned
4by ClustalW, and a dendrogram was generated using the neighbor-joining method.
5Bootstrap values (n=10,000) are shown for the major nodes. The bacterial source and the
6GenBank accession number are given for each FOS protein. The three classes of
7fosfomycin resistance proteins are indicated: FosA (see references in text), Fos B (Zilhao,
8R., Courvalin, P. (1990) Nucleotide sequence of the fosB gene conferring fosfomycin
9resistance in Staphylococcus epidermidis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 68, 267-272. and Cao,
10M., Bernat, B.A., Wang, Z., Armstrong R.N., Helmann, J.D. (2001) FosB, a cysteine-
11dependent fosfomycin resistance protein under the control of σw, an extracytoplasmic-
12function σ factor in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol 183, 2380-2383.) and FosX (Fillgrove,
13K.L., Pakhomova, S., Newcomer, M.E., Armstrong, R.N. (2003) Mechanistic diversity of
14fosfomycin resistance in pathogenic microorganisms. J. Am. Chem. Soc 125, 15730-
1515731.).
16
2 2 17
18 19 20Figure S2. Location of fosA2 gene identified by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Total
21genomic DNA of Sam066F1 was digested with I-CeuI nuclease (“a” lanes) or S1
22nuclease (“b” lanes) and probed with a labeled 23S rRNA gene (lanes a2, a3) or the
23712bp fosA2 fragment (lane b1, b2). Lane M contains a λ concatamer size ladder (New
24England Biolabs). Arrows indicate fosA2 hybridization. DNA was prepared and digested
25as described by the method of Barton et al. (Barton, B.M., Harding, G.P., Zuccarelli, A.J.
26(1995) General method for detecting and sizing large plasmids Anal. Biochem 226, 235-
27240.) and Liu et al. (Liu, S.L., Hessel, A., Sanderson, K.E. (1993) Genomic mapping with
28I-Ceu I, an intron-encoded endonuclease specific for genes for ribosomal RNA, in
29Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli, and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90, 6874–
306878.). The 23S RNA gene probe was synthesized by PCR using primer pair 23S-43af
3 3 31(5'-GGATGTTGGCTTAGAAGCAG-3') and 23S-62ar (5'-
32CTTAGGACCGTTATAGTTAC-3') on genomic DNA of Sam066F1. Both probes were
33synthesized using the (DIG High Prime DNA Labeling and Detection Starter KitI,
34Roche). Digested DNA was subjected electrophoresis at 5 to 120 seconds pulse time for
3548 hours in 1% agarose gel in TBE in a BIO-RAD CHEF MAPPER XA (BioRad) and
36transferred to Hybond-N+ nylon membrane (Amersham Biosicences) for hybridization
37and washing according to manufacturer’s instructions (DIG High Prime DNA Labeling
38and Detection Starter KitI, Roche).
39
40
41
4 4