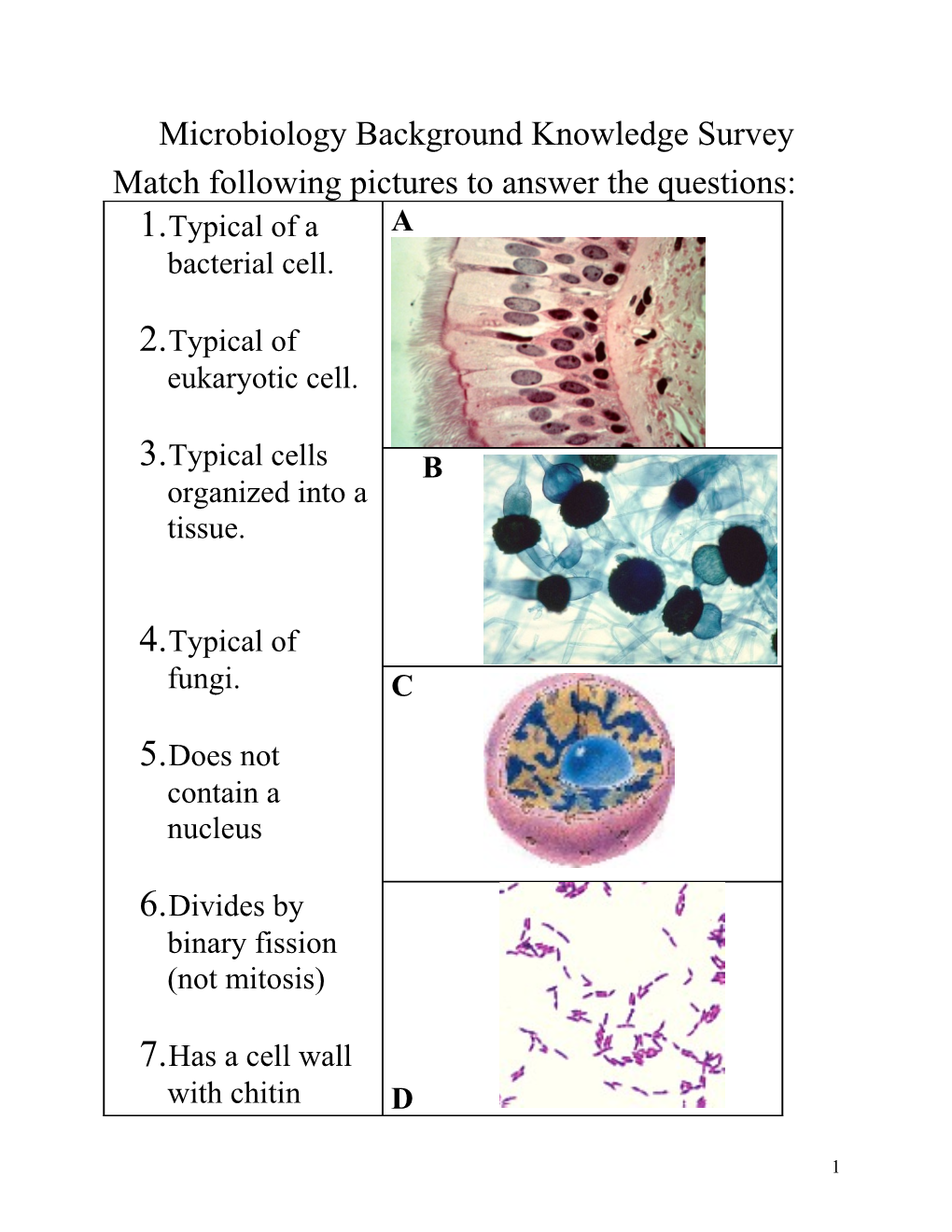
Microbiology Background Knowledge Survey Match following pictures to answer the questions: 1.Typical of a A bacterial cell.
2.Typical of eukaryotic cell.
3.Typical cells B organized into a tissue.
4.Typical of fungi. C
5.Does not contain a nucleus
6.Divides by binary fission (not mitosis)
7.Has a cell wall with chitin D
1 8.Which is usually true of Bacteria? a. They are found as rods, spheres, or spirals. b. They reproduce by binary fission. c. They have no nucleus. d. All of the above.
2 9.Water a. is a polar molecule. b. is referred to as the universal solvent. c. is often a product or reactant in chemical reactions. d. All of the above.
3 10. pH a. is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration. b. Utilizes a scale from 5 to 8. c. Is a geometric scale. d. Is an abbreviation for “power of hydrogen.”
4 11. Organic chemistry is the study of a. molecules containing carbon. b. molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. c. chemicals important to living organisms d. All of the above
5 12. The important class of chemicals that limit radical pH changes in the body, medications, food, and also bacterial media are referred to as a. enzymes. b. bases. c. buffers. d. acids.
6 13. ATP a. is an important molecule for energy storage. b. contains three high-energy phosphate bonds. c. is classified as a nucleic acid. d. All of the above.
7 14. Two atoms equally sharing electrons have formed what kind of bond? a. hydrogen bond. b. ionic bond. c. covalent bond. d. All of the above.
8 15. The negatively charged component of the atom is the a. proton. b. nucleus. c. neutron. d. electron.
9 16. Which of the following describes the differences between DNA and RNA a. DNA is the code of life; RNA replicates itself b. DNA is the recipe for proteins; RNA translates the recipe c. DNA is a small molecule; RNA is a large nucleotide d. DNA translates codes for protein; RNA
10 17. In biological systems, the most important feature, which determines the function of a protein a. the order of amino acids, primary structure b. the reactive side groups c. the shape or three dimensional, tertiary structure. d. the secondary structure, folding or twisting
11 18. Which of the following is a phagocytic cell found in the human body? a. Erythrocyte. b. Neutrophils c. B cell d. T cell
12 19. Which of the following is responsible for the majority of illness and death that occur each year worldwide? a. Infectious diseases b. Heart disease c. Cancer d. HIV
13 20. Some common diseases once considered physiological can actually be the result of infections, such as a. ulcers b. diabetes c. cervical cancer d. all of the above
14 21. Microorganisms are involved in a. the production of medicinal products. b. food production. c. pollution cleanup. d. All of the above.
15 22. The single most important measure to prevent the spread of disease is a. antibiotics. b. quarantines. c. Pasteurization. d. hand washing.
16 23. Colds a. are caused by prolonged exposure to a cold environment. b. can be cured by antibiotics. c. are caused by viruses and basically untreatable. d. all of the above.
17 24. Which of the following is true about HIV? a. There is a mutated strain of HIV that is transmitted through the air. b. HIV can be easily contracted through saliva, contact with a soiled feminine napkin, or other sources of dried blood. c. HIV infects T-lymphocytes and macrophages and requires close contact with blood or body fluid. d. All of the above.
18 25. STD’s (sexually transmitted diseases) a. are preventable through the use of birth control pills. b. are the most common infectious diseases in the United States. c. are easy to diagnose with easily identifiable symptoms in both males and females. d. All of the above.
19 26. Antibiotics help in the treatment of a. bacterial infections. b. viral infections c. allergies. d. All of the above.
20 27. Viral infections are primarily controlled by a. Antivirals b. Antibiotics c. Vaccination d. Quarantine
21 28. I would evaluate my overall laboratory skills and safety practices as: a. Excellent b. Good c. Needing improvement d. Non-existent
22 29. I would evaluate my microscope skills as a. Excellent b. Adequate and ready to go in the microbiology class c. Rusty needing practice and guidance d. Very poor to non-existent – What’s a microscope!
23