Endocrinology 6a – Menopause & its Treatment Anil Chopra 1. Definitions: Menopause and climacteric 2. Symptoms of menopause 3. Complications of menopause 4. Treatment of menopause 5. Related drugs
Menopause: - cessation of menstruation resulting from the loss of ovarian follicular cells resulting in amenorrhoea for 12 months. Average age of onset = 51 years (range 45-55) - Premature menopause is the onset of menopause before the age of 40 and occurs in 1% of women. Can occur because of surgery or as an autoimmune condition (check family history). - Climacteric: the period of transition from predictable ovarian function through the post menopausal years. Ovarian function is erratic and oestrogen levels decline. - Primary Amenorrhoea: never had a period - Secondary Amenorrhoea: periods stop (can be caused by pregnancy, pituitary problems e.g. prolactinoma)
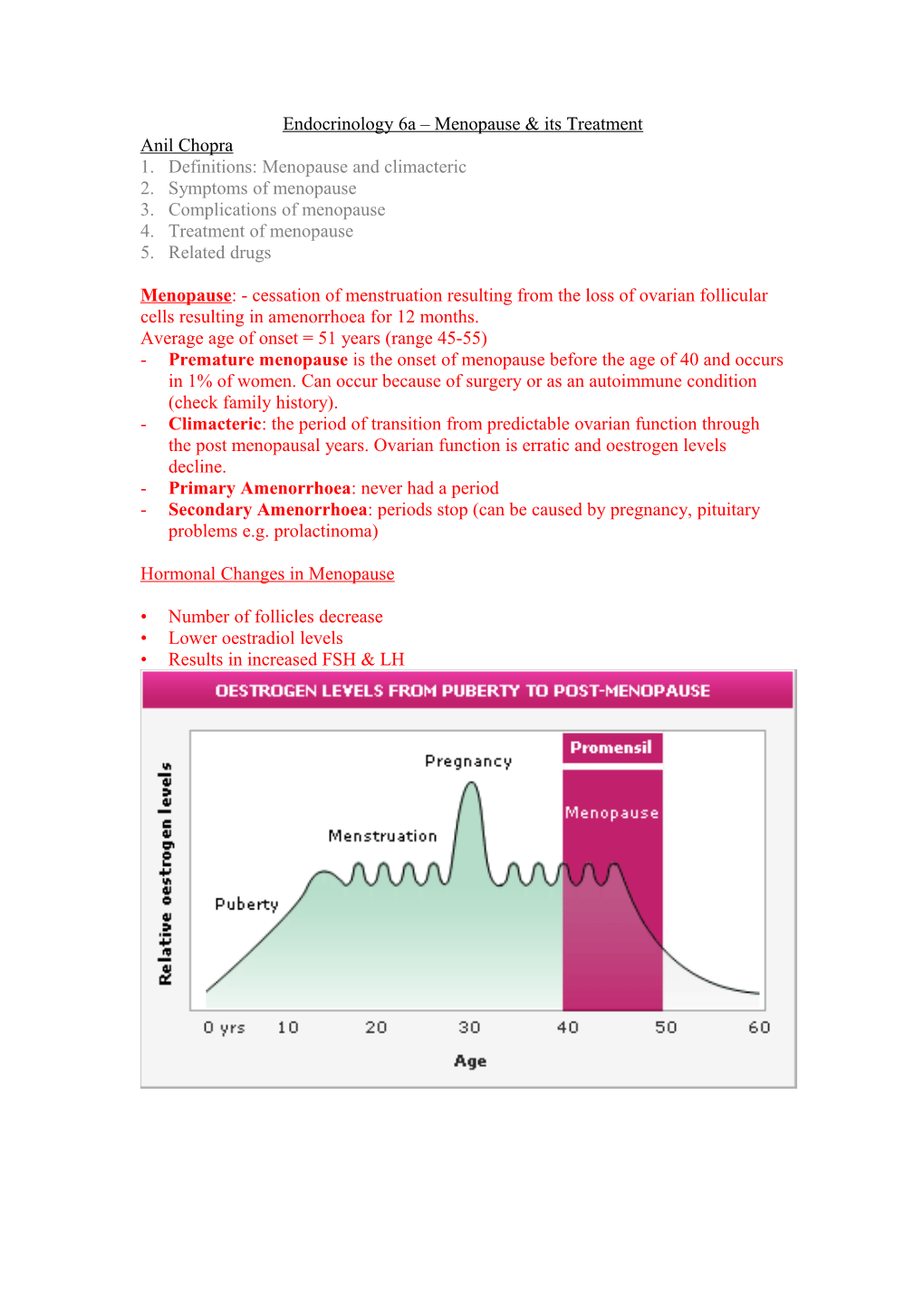
Hormonal Changes in Menopause
• Number of follicles decrease • Lower oestradiol levels • Results in increased FSH & LH Symptoms of Menopause
- Irregular menstrual cycles - Hot flushes that last around 4 minutes, anything from 1 to 20 times per day. o 80% of women affected o Resolve within 1 year. o Increased pulse rate o Sweating o Causes insomnia - Psycho-social symptoms o Depression o Mood swings o Loss of energy - Low oestrogen levels o Loss of collagen - Decreased libido - Urogenital atrophy o Urgency, nocturia (passing urine at night), incontinence, increase risk of UT infections o Dryness of vagina (atrophic vaginitis), o Discomfort with intercourse (dyspareunia)
Complications of Menopause - Osteoporosis – 70 year old women may lose 50% of bone mass o Oestrogen deficiency cause loss of bone matrix o Lose 1-3% of bone mass per year. (10x increase of fracture) - Cardiovascular disease o Women are protected against CV disease if given HRT Treatment of Menopause
HRT – Hormone Replacement Therapy
For women who have had a hysterectomy, only oestrogen is given.
All other women are given combined oestrogen & progesterone (in order to prevent hyperplasia of endometrium)
Administration - Oral - Transdermal HRT (patch / gel) - Percutaneous slow release implant - Intranasal spray - Intravaginal oestrogens
Advantages » Controls vasomotor symptoms (flushing) in 90% » Controls vaginitis » Can delay osteoporosis but not unless it also controls vasomotor symptoms (bisphosphonate or raloxifen also used to delay osteoporosis) » Including progesterones in formulation reduces risk of endometrial cancer » Possibly reduces risk of ischaemic heart disease – although should not be given to prevent it or for those with high risk » Small reduction in risk of colon cancer
Disadvantages - Slight increase in ischaemic heart disease risk. - Increases risk of endometrial carcinoma as oestrogen induces endometrial hyperplasia. - Increases risk of breast cancer after 5 years of use. - Increases risk of gallstones. - Increases risk of thromboembolism - Increases risk of Cerebrovascular accident
Patients can decide whether to take the treatment after they have education and counselling. Patients should definitely take it unless they are at high risk of any of the above conditions for 5-7 years. Premature menopausal women should be kept on treatment until normal menopausal age.
Tibolone - Synthetic prohormone. - Oestrogenic, progestogenic and weak androgenic actions - As effective at HRT for relief of vasomotor symptoms - Increases bone density - Link with cancers same as HRT. SERMs – Selective Oestrogen-Related Modulating drugs
- Selective oestrogen receptor modulating drugs - Don’t have classic steroid structure. - Their actions are tissue selective - High affinity for oestrogen receptor. - Activate oestrogen metabolic pathways (act like oestrogen).
Tamoxifen Anti-oestrogenic on breast tissue – treatment for breast cancer. Oestrogenic on o Bone – maintains density o Endometrium – increases CA risk Side effects o Endometrial changes (hyperplasia, polyps, cancer) o Bone pain with bony metastases o Hot flushes o Menstrual irregularities o Gastrointestinal disturbances
Clomiphene Anti-oestrogenic on o Hypothalamus – blocks normal negative feedback resulting in increase in GnRH and this increase in LH and FSH secretion. It is used as fertility drug. ONLY TAKEN FOR FIRST 5 DAYS OF MENSTRUAL CYCLE in order to induce ovulation in women who are infertile due to lack of ovulation. Side effects o Multiple pregnancies can occur – patients need follicle tracking by ultrasound scanning. o Abdominal discomfort o Ovarian hyperstimulation o Endometriosis o Hot flushes o Nausea, vomiting, headache.
Raloxifene Oestrogenic on bone – increases density: osteoporosis treatment, Anti-oestrogenic on breast and uterus – reduces CA risk. Has no effect on vascular symptoms i.e. does not stop hot flushes. Side effects o Increases risk of stroke and thromboembolism.