SBI3U – Assigned Work – Answer Sheet Thursday, March 3, 2011
Learning Objective: To examine the process of meiosis in eukaryotic cells, to be able to label the main phases of meiosis and to describe the different genetic components of the cell during meiosis. To describe some genetic disorders caused by chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., non-disjunction of chromosomes during meiosis) or other genetic mutations in terms of chromosomes affected, physical effects, and treatments
Success Indicators: To be able to label the genetic components of a cell during a meiosis. To be able to distinguish some standard different genetic diseases by looking at a karyotype of a human. To be able to describe the differences between the process of Mitosis vs Meiosis and the type of daughter cells produced.
Read section 5.2: Meiosis (pages 131-142)
Complete the following Table: Number of Diploid Haploid Number of Pairs Number of Chromosomes Present in Chromosomes in Number Number of Homologous Meiosis at Beginning of Each Phase Daughter Cells Chromosomes Prophase I Prophase Telophase of Mitosis II II Human 46 46 23 23 46 23 23 Chimpanzee 24 24 12 12 24 12 12 Yeast 32 32 16 16 32 16 16 Rhesus 42 42 21 21 42 21 21 Monkey Dog 78 78 39 39 78 39 39 Cat 38 38 19 19 38 19 19 Potato 48 48 24 24 48 24 24 Mosquito 6 6 3 3 6 3 3
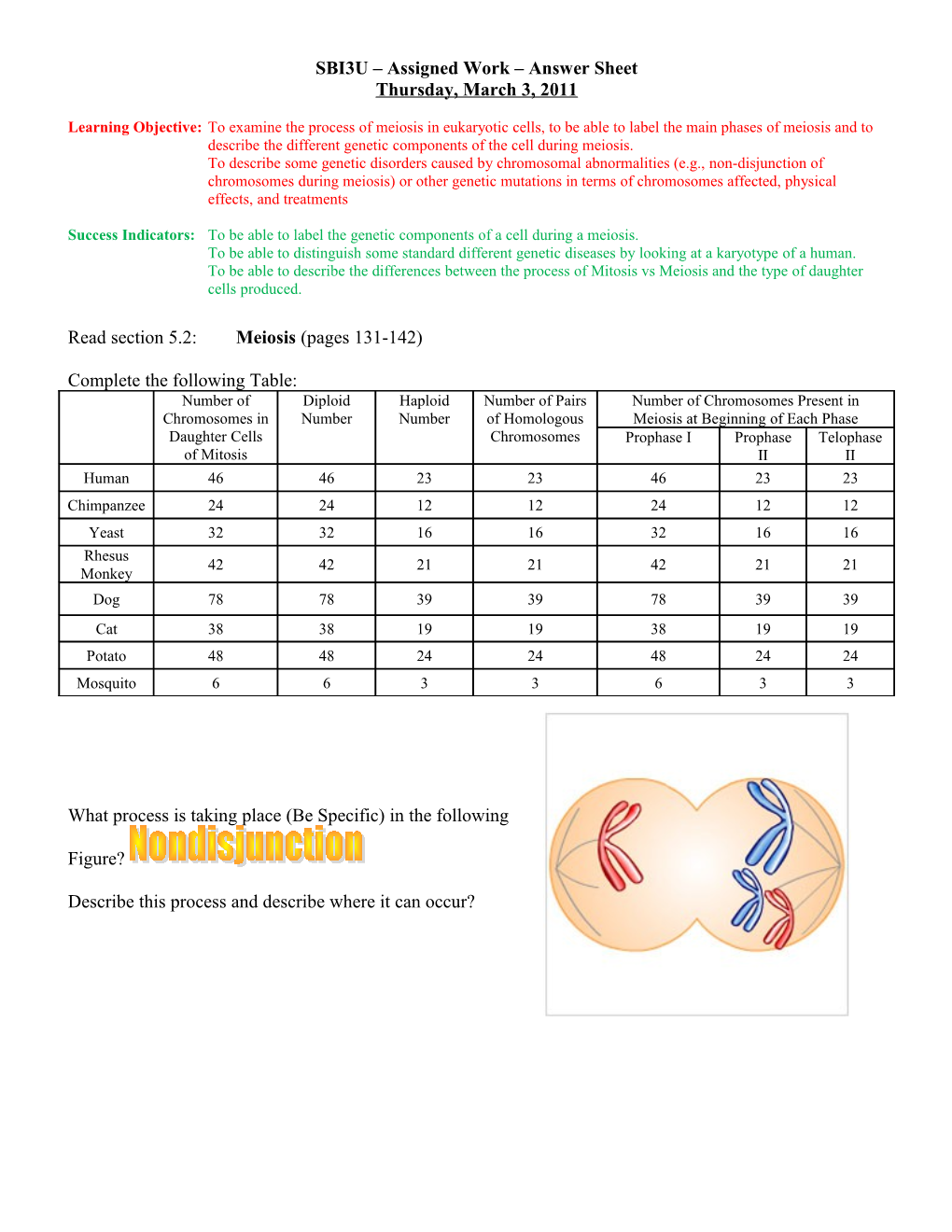
What process is taking place (Be Specific) in the following
Figure?
Describe this process and describe where it can occur? Define the Following Terms: Aneuploidy Polyploidy
The following is a Figure of a Normal Human Karyotype (page 186 of text):
Label the following Human Karyotypes as: Monosomy, Trisomy and Triploidy and give a reason why you named them the way you did:
Describe the type of Chromosomal mistakes that have taken place in the following Figures:
Duplication
Deletion
Inversion
Inversion Translocation
Deletion
Deletion
Understand Table 5.2: Mitosis and Meiosis Comparison.
Starting with a cell that is diploid (2n = 6), demonstrate using 3 alleles per chromosome (see definition of alleles page 157), how all 4 haploid cells are different genetically from their parent cell. (Use the traits below to demonstrate) – need to incorporate Random Assortment and Crossing-over.
i.e.: chromosome 1 / 2 : Blue (b) eyes vs Brown (B) eyes; Tall (T) vs Short (t); Tongue Roller (R) vs Non-tongue roller (r)
chromosome 3 / 4: Have freckles (F) vs No freckles (f) Widow’s peak (W) vs Straight hair line (w) Free-hanging earlobe (E) vs Attached earlobe (e)
chromosome 5 / 6: Cleft chin (C) vs No cleft chin (c) Hitchhiker’s thumb (H) vs straight thumb (h) Dimples (D) vs No dimples (d) Define: Cancer What is the difference between a Benign tumour and a Malignant tumour. Why is a malignant tumour more dangerous than a benign tumour?
Answer Page 142:
Understanding Concepts: 3, 4, 6, 7, 9 Applying Inquiry/Communication Skills: 11, 12
Read Section 5.3: Sexual versus Asexual Reproduction (Pages 143 – 146)
Answer Page 146:
Understanding Concepts: 1, 2, 6 Applying Inquiry/Communication Skills: 7