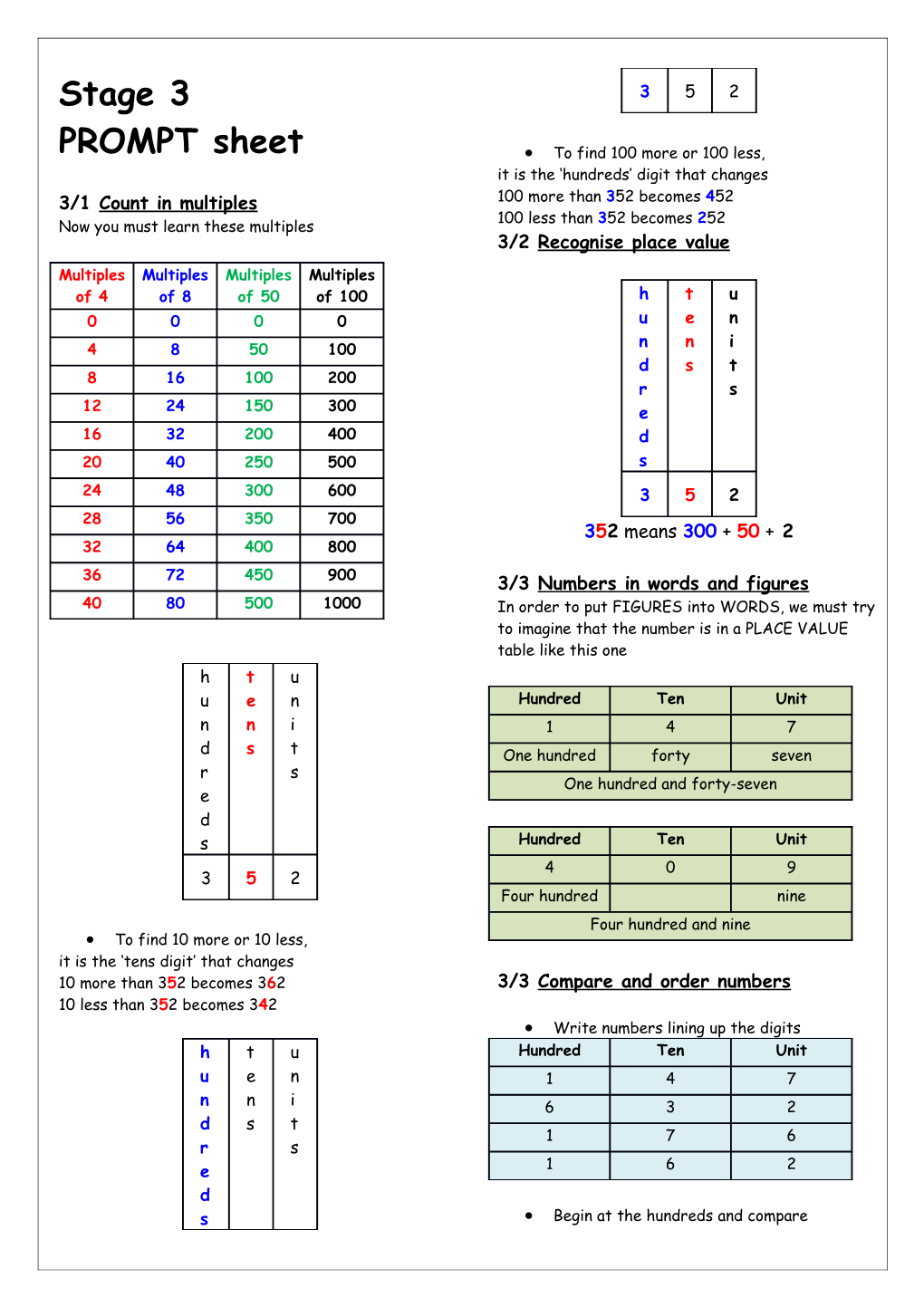
Stage 3 3 5 2
PROMPT sheet To find 100 more or 100 less, it is the ‘hundreds’ digit that changes 3/1 Count in multiples 100 more than 352 becomes 452 100 less than 352 becomes 252 Now you must learn these multiples 3/2 Recognise place value
Multiples Multiples Multiples Multiples of 4 of 8 of 50 of 100 h t u 0 0 0 0 u e n 4 8 50 100 n n i d s t 8 16 100 200 r s 12 24 150 300 e 16 32 200 400 d 20 40 250 500 s 24 48 300 600 3 5 2 28 56 350 700 352 means 300 + 50 + 2 32 64 400 800
36 72 450 900 3/3 Numbers in words and figures 40 80 500 1000 In order to put FIGURES into WORDS, we must try to imagine that the number is in a PLACE VALUE table like this one h t u u e n Hundred Ten Unit n n i 1 4 7 d s t One hundred forty seven r s One hundred and forty-seven e d s Hundred Ten Unit 4 0 9 3 5 2 Four hundred nine Four hundred and nine To find 10 more or 10 less, it is the ‘tens digit’ that changes 10 more than 352 becomes 362 3/3 Compare and order numbers 10 less than 352 becomes 342 Write numbers lining up the digits h t u Hundred Ten Unit u e n 1 4 7 n n i 6 3 2 d s t 1 7 6 r s e 1 6 2 d s Begin at the hundreds and compare 632 is the biggest Answer: It is about 5 x £2 = £10 Hundred Ten Unit 1 4 7 Example: When full this bottle holds 400ml. Estimate how much water is left in this bottle. 6 3 2 1 7 6 1 6 2
Answer: about 150ml Move to the tens and compare Order is: 632, 176, 162, 147 3/4 Estimating 3/6 Add 3 digit numbers mentally
Eyeball estimate Partitioning 236 + 319
Use this to estimate larger quantities 200 + 30 + 6 + 300 + 10 + 9 = 500 + 40 + 15 = 555
Subtract 3 digit numbers mentally Estimate by sampling Count your pulse over 15seconds Multiply the number of pulses by 4 to get the 363 - 126 pulse rate over 1 minute (15 x 4 = 60seconds) Partitioning Counting on from 126 Estimate on a number line Fill in the half way number first 363 – 100 – 20 – 6 (126) + 4 Then split up the half with the arrow =263 – 20 – 6 130 + 3 17 =243-6 133 + 230 10 20 =237 =363
15 16 17 18 19 Answer = 237
73 0 100 3/7 Written method for addition
50 60 70 80 90 Line up the digits in the correct columns Estimate by rounding off a number To make a sum easier and give a rough answer e.g. 132 + 239 H T U 1 3 2
Example: 28 could be rounded to 30 2 31 9 + £1.95 could be rounded to £2 3 7 1
3/5 Solve problems by estimating Written method for subtraction
Example: Estimate the cost of 5 magazines at £1.95 each Line up the digits in the correct columns e.g. 327 - 119 H T U 3 12 17 1 x 4 = 4 1 1 9 - 2 x 4 = 8 2 0 8 1 3 x 4 = 2 1 4 x 4 = 6 2 5 x 4 = 0 2 6 x 4 = 4 2 7 x 4 = 8 3/8 Estimate answers to calculations 3 8 x 4 = 2 Round off each number 3 9 x 4 = 6 Then do the calculation 1 4 Check using the inverse 0 x 4 = 0 1 4 Example: Estimate 83 – 28 1 x 4 = 4 1 4 80 – 30 = 50 2 x 4 = 8 Inverse: 50 + 30 = 80 1 x 8 = 8 1 2 x 8 = 6 2 3/9 Missing number problems 3 x 8 = 4 3 Fact family for +/- 4 x 8 = 2 4 5 x 8 = 0 4 34 + 23 = 57 57 - 23 = 34 6 x 8 = 8 5 23 + 34 = 57 57 – 34 = 23 7 x 8 = 6 6 8 x 8 = 4 7 9 x 8 = 2 1 8 3/10 Know the 3, 4 and 8 times tables 0 x 8 = 0 1 x 3 = 3 1 8 2 x 3 = 6 1 x 8 = 8 3 x 3 = 9 1 9 4 x 3 = 12 2 x 8 = 6 5 x 3 = 15 6 x 3 = 18 Fact family for x/÷ 7 x 3 = 21 8 x 3 = 24 9 x 8 = 72 72 ÷ 9 = 8 9 x 3 = 27 10 x 3 = 30 1 8 x 9 = 72 72 ÷ 8 = 9 1 x 3 = 33 12 x 3 = 36 This represents 6 tenths =
3/11 Multiply & divide Counting in tenths (continued) A 2-digit number by a single digit A whole one divided into 10 equal parts 1 ÷ 10 = 1 tenth or 0r 0.1 Column method 3 8 3 x 1 1 4
2
Grid method 30 8 3 90 24
90 + 24 = 114
Partitioning method A – 0.8 38 x 3 B – 1.9 = 30 x3 + 8 x 3 C – 2.6 = 90 + 24 To find a tenth of an object or quantity = 114 you divide by 10
3/12 Multiply & divide 3/14 Write a fraction of a number of object Look for connections between two sums Remember the fact family for x/÷
Example: 6 x 4 = 24 So 60 x 4 = 240 are blue and are red So 240 ÷ 4 = 60
Example: 9 x 8 = 72 So 18 x 8 = 144 3/15 Use fractions as numbers So 144 ÷ 8 = 18 To find of 20 we do 20 ÷ 5 = 4
To find of 20 we do 4 x 2 = 8 To find of 20 we do 4 x 3 = 12
3/13 Tenths
t u t Example: of 20 = 20 ÷ line e n e 10 = 2 Divide the n i n line into 5 s t . t equal parts s h s 3/14 Fraction of line or objects 8 2 6 To find of a Each part is When the denominators are the To find of a same set of + = objects Divide objects into 5 equal - = parts
3/18 Compare 3cm + 7mm fractions = 30mm + 7mm = 37mm Fractions with or 3cm 7mm or the same 3.7cm Each part is denominator The bigger the 3cm
3/16 Equivalent denominator, the 0.7cm fractions smaller the fraction
The same fraction can be expressed in different ways ALL THESE ARE
= = = 3/19 Add & subtract measures ALL THESE ARE The units Mass – Example must be the same Length – Example
= = = 3kg – 450g = 3000g – 450g = 2550g or 2kg 550g or 2.55kg The bigger the 3/17 Add & numerator, the bigger 3/19 Add & subtract the fraction subtract measures fractions (continued) Unit Fractions To add and Volume – Example subtract fractions Perimeter of this 12.00 12.00 shape = 6 + 4 + 6 + 4 = midnight noon 20cm 1.00 am 1.00 pm 2.00 am 2.00 pm 3.00 am 3.00 pm 3/21 Bills and 3/23 Time 4.00 am 4.00 pm change Reading the time 5.00 am 5.00 pm To work out a bill 6.00 am 6.00 pm 1 chocolate bar - 7.00 am 7.00 pm £1.10 8.00 am 8.00 pm 800ml + 720ml 1 pen – 10p 9.00 am 9.00 pm = 1520ml 1 pencil – 8p 10.00 am 10.00 pm Total = £1.28 = 1 litre and 520ml 11.00 am 11.00 pm = 1.52 litres 12.00 12.00 noon midnight To find change by the ‘add-on’ method 3/24 Time – hours +2p minutes, seconds 3/20 Perimeter +20p +50p = 72p PERIMETER is the distance round the £1.28 £1.30 outside of a shape £1.50 £2.00 On a centimetre square grid – count round 3/22 Time Analogue clock
Roman Months of the Hindu-Arabic
Perimeter of this year shape = 12cm A rhyme to remember the Measurements days in each 12- and 24-hour given - add up month all round clock 30 days has September, 6cm April, June and November. All the rest have 31 4cm Except February alone, 4cm Times of the day Which has 28 days clear in 12-hour clock And 29 in each leap year. the "knuckle 6cm Morning Afternoon method" A knuckle is "31 days", - Nets and in between each knuckle it isn't. And where your hands meet, the two knuckles are "July, August", which both have 31 days. 365 days in a year 366 days in a leap February has 28 days year 3/26 Angle RIGHT angles are & 29 days in a leap exactly 900 year (every 4 years) An angle is an amount of turn A 0 Days in a year square for 90 angle
OBTUSE angles are 3/25 – 2D Shapes bigger than 900 With 3 sides (Triangles)
right-angled isosceles equilateral scalene
Angles in With 4 sides (Quadrilaterals) shapes
square rectangle parallelogram Triangle - 3 angles trapezium rhombus 3/27 Right angles ONE right angle measures exactly 900 With 5 sides (Pentagons) With 6 sides (Hexagons) Quadrilateral - 4 angles
TWO right angles Pentagon – 5 angles measure exactly 1800 regular irregular This is called a half- regular irregular turn
3/25 – 3D Shapes
Names of angles
ACUTE angles are THREE right angles less than 900 measure exactly 2700 This is called three Cube cuboid triangular prism quarters of a turn cylinder sphere cone square-based
Pyramid Rabbit llll (i) How many Fish llll lll more Hamster ll children own a rabbit than a hamster? FOUR right angles 0 Answer: 4-2 = 2 measure exactly 360 (ii) What is This is called a full or the complete turn difference A bar graph to show between pets owned by Year 3 the number of This cliff face is a Type of pet children vertical line who own a Pictogram to show the dog and colours in a tube of the Smarties number of children who own a cat? To check if an angle is bigger or Answer: 5 – 3 = 2 (iii) How many smaller than a pets are right angle, use a owned square corner altogether The running track by the is parallel lines children (never meet) Year 3? Answer: 5 + 3 + 4 + 8 + 2 = 22
Pictogram in This angle is greater 3/29 This angle is less than a right angle (i) How many than a right angle fewer blue 3/28 Types of smarties Lines are there than yellow The rise & tread ones? are perpendicular Answer: 11 0 lines (meet at 90 ) – 5 = 6 3/29 Bar charts Frequency table to (ii) Work out show pets owned by 3/30 Solve answers the total Year 3 to questions number of Type of pet Tally Bar chart in smarties The Horizon is a Dog llll 3/29 in the tube horizontal line Cat lll Answer: 55