Motivating Change 2: Next Steps Trainer Outline (updated 2008)
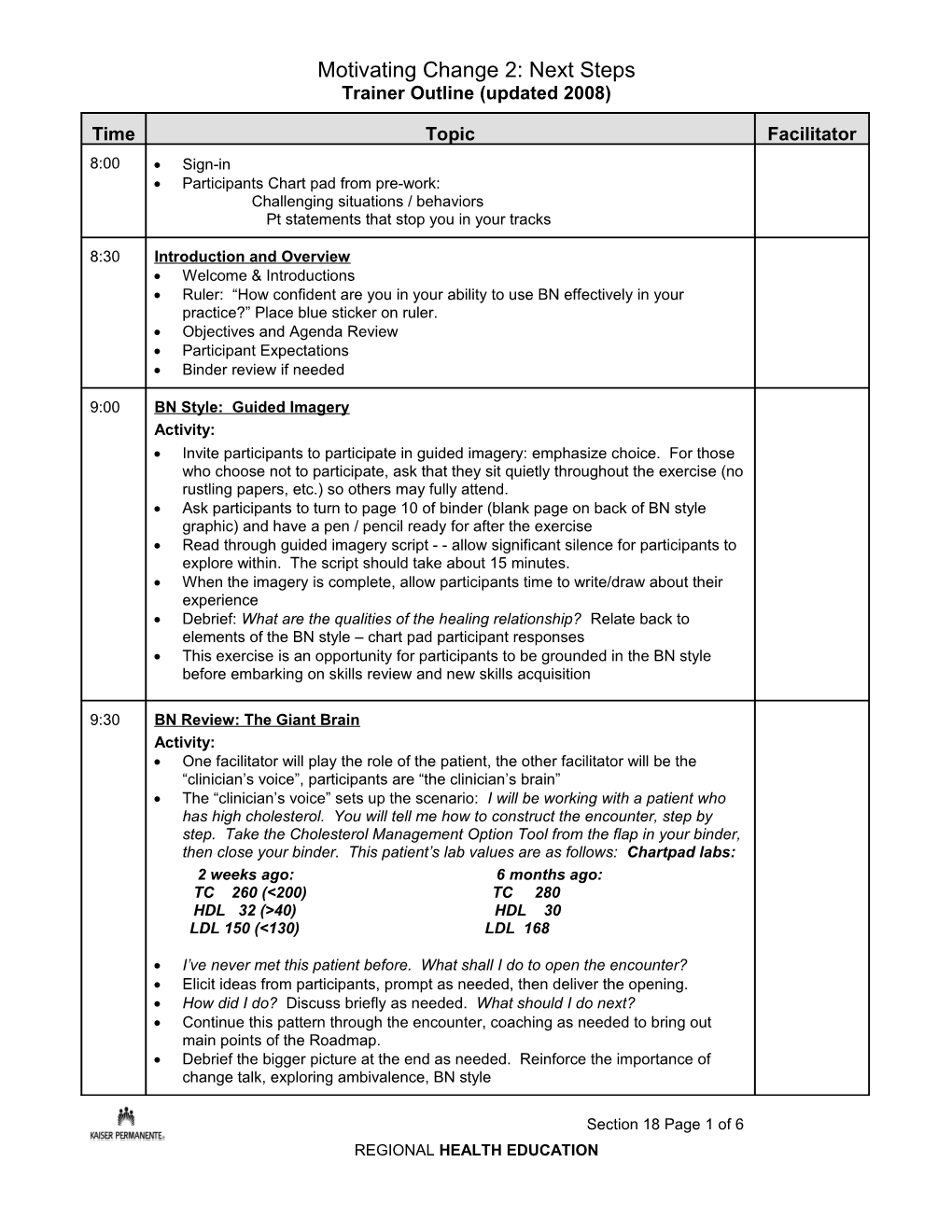
Time Topic Facilitator 8:00 Sign-in Participants Chart pad from pre-work: Challenging situations / behaviors Pt statements that stop you in your tracks
8:30 Introduction and Overview Welcome & Introductions Ruler: “How confident are you in your ability to use BN effectively in your practice?” Place blue sticker on ruler. Objectives and Agenda Review Participant Expectations Binder review if needed
9:00 BN Style: Guided Imagery Activity: Invite participants to participate in guided imagery: emphasize choice. For those who choose not to participate, ask that they sit quietly throughout the exercise (no rustling papers, etc.) so others may fully attend. Ask participants to turn to page 10 of binder (blank page on back of BN style graphic) and have a pen / pencil ready for after the exercise Read through guided imagery script - - allow significant silence for participants to explore within. The script should take about 15 minutes. When the imagery is complete, allow participants time to write/draw about their experience Debrief: What are the qualities of the healing relationship? Relate back to elements of the BN style – chart pad participant responses This exercise is an opportunity for participants to be grounded in the BN style before embarking on skills review and new skills acquisition
9:30 BN Review: The Giant Brain Activity: One facilitator will play the role of the patient, the other facilitator will be the “clinician’s voice”, participants are “the clinician’s brain” The “clinician’s voice” sets up the scenario: I will be working with a patient who has high cholesterol. You will tell me how to construct the encounter, step by step. Take the Cholesterol Management Option Tool from the flap in your binder, then close your binder. This patient’s lab values are as follows: Chartpad labs: 2 weeks ago: 6 months ago: TC 260 (<200) TC 280 HDL 32 (>40) HDL 30 LDL 150 (<130) LDL 168
I’ve never met this patient before. What shall I do to open the encounter? Elicit ideas from participants, prompt as needed, then deliver the opening. How did I do? Discuss briefly as needed. What should I do next? Continue this pattern through the encounter, coaching as needed to bring out main points of the Roadmap. Debrief the bigger picture at the end as needed. Reinforce the importance of change talk, exploring ambivalence, BN style
Section 18 Page 1 of 6 REGIONAL HEALTH EDUCATION Motivating Change 2: Next Steps Trainer Outline (updated 2008)
Time Topic Facilitator 10:15 Break 10:30 The BN Method: Clinician & Patient Instructions: Partner with someone you don’t know Each person will have an opportunity to be both patient and clinician “ Patients” Use your own personal issue from the pre-work: something you feel ambivalent about Tell your partner in a sentence or two what the issue is Offer genuine responses as the clinician guides you through the BN process “ Clinicians” Have your tools ready: Roadmap, Ruler, Option Tools Using the roadmap, assist your partner to explore ambivalence/assess readiness Remember the central skills of ask, listen and summarize You may or may not negotiate the agenda, depending on the complexity of your partner’s issue Use one of the pre-printed option tools or quickly work together to create a custom option tool based on your partner’s issue as needed.
Activity: Allow 7 -10 minutes in each role Circulate and coach as needed Debrief after both cycles complete Key Questions for Debrief: Patients: How does it feel to receive this model? What did provider do to establish rapport? What about this encounter was powerful for you personally? What have you learned that gives you insight into your patients’ experience with ambivalence and change? Providers: How was it to work through the roadmap with your partner? What were your successes? Your challenges? What did you learn about the clinician’s role in BN that you will take back to your clinical practice?
11:10 Listening for the Story Reinforce LISTENING as central to working effectively to support health behavior change How does listening build motivation? Creates environment to assist pt to explore / discover own solutions, communicates caring, builds rapport, supports collaboration, encourages self-care, etc. Activity: Introduce the book “Where’s my Teddy” Let participants know you will be reading them the book. While you read, each of
Section 18 Page 2 of 6 REGIONAL HEALTH EDUCATION Motivating Change 2: Next Steps Trainer Outline (updated 2008)
Time Topic Facilitator them will have a job Ask small groups (2-3) to listen for and count the number of words beginning with a specific letter. Group 1 listen for and count words beginning with T Group 2 listen for and count words beginning with S Group 3 listen for and count words beginning with E Group 4 listen for and count words beginning with F Group 5 listen for and count words beginning with Q Read the story start to finish (don’t stop to show pictures ) Debrief: Ask each group in sequence above: T = 49 How many words were there beginning with the letter _____? Tell them how many S = 21 there actually are. What is the story about? E = 8 Ask each subsequent group what they can add to the story line F = 4 Q = 1 Wrap up: What happens when you listen for specific words? You lose the story. Part of working effectively with patients is listening to their story and, based on who they are and the strengths and limitations they bring to the issues at hand, assisting them to build motivation for behavior change.
11:30 Reflective Listening Present Gordon’s Model of Communication Resource Introduce Reflective Listening as one way to enhance effective communication / Manual p. 22 reduce the likelihood of missing the message the patient is sending (refer back to Gordon) Introduce Reflective Listening prep step of thinking reflectively by asking “do you mean….” Emphasize that this is NOT reflective listening, but a way to learn how to think in terms of hypothesis testing
Activity 1: Preparing for Reflective Listening Introduce and demonstrate “Do you mean………” (“hypothesis testing”) Practice in 2 small groups with facilitators to coach: “ Something I like about myself is…” Each listener responds in turn – move around the circle twice (or more, time permitting) Speakers can only answer yes or no Debrief as you go
Content: Resource Stay in groups, but introduce next concepts and level of activity to whole group Manual pp. Introduce guidelines for Reflective Listening statements and Levels of Reflection 23-26
Activity 2: Reflective Listening Introduce and demonstrate “Something about myself I’d like to change is………” “You feel………” Encourage choosing something meaningful Speaker is encouraged to elaborate Practice in 2 small groups Let everyone who wants to have a turn being the speaker Debrief in small groups Back in the large group, review p.16 Chinese Symbol for listening
Section 18 Page 3 of 6 REGIONAL HEALTH EDUCATION Motivating Change 2: Next Steps Trainer Outline (updated 2008)
Time Topic Facilitator 12:30 Lunch
1:15 Video Clip: The Rounder Introduce the video Observe clinician and watch for examples of: ~ Open Ended Questions ~ Reflective listening ~ Validating / Affirming ~ Change talk Show video Quick Debrief What do you think? What are some striking examples reflective listening? What was the impact of the reflective listening? How did she roll with resistance? What was the impact of Terry’s neutral stance on the client’s willingness to process his issues? What are some examples of change talk in this encounter? What did Terry do to elicit the change talk? What was the pivotal moment in the encounter?
1:45 Batting Practice Like “The Rounder”, your patients sometimes offer challenging statements. Review "Pt statements that stop you in your tracks" add to list as needed. Activity: Distribute baseball caps and introduce activity: A chance to practice responding to “show-stoppers” with reflective listening Conduct activity with whole group – everyone has an opportunity to pitch and bat: emphasize choice: okay to sit on the bench Participants get up and form a semi-circle in front of the tables. Batter stands in front of the “U”. First pitcher faces the batter and delivers the “pitch”– then rotates to batting position when finished pitching. Batter returns to the semi-circle Pitchers can use statements from chart pad, or draw from bucket of balls Batters may ask for coaching / let it go by, etc. Debrief as you go Keep this activity moving at a fast pace - - create a climate for play/fun
2:20 Reflective Listening & The Roadmap Opportunity to practice assessing readiness and exploring ambivalence incorporating reflective listening. Aim for 2-3 reflections for each open-ended question in the yellow boxes on the map Instructions: • Invite participants to create triads. Each person will have the opportunity to be patient, provider, and observer. Consider writing instructions on chartpad: “ Clinicians”: Tell the patient who they are: consider using a typical patient from your practice. Let the patient know the diagnosis AND the specific topic for discussion, eg: Hypertension, focus on exercise
Section 18 Page 4 of 6 REGIONAL HEALTH EDUCATION Motivating Change 2: Next Steps Trainer Outline (updated 2008)
Time Topic Facilitator
Assess readiness and explore ambivalence, doing your best to offer 2-3 reflections after every open-ended question. Chart pad reminder: ASK-LISTEN- REFLECT-LISTEN-REFLECT-LISTEN-REFLECT A Trainer will stay with each group for one full cycle to provide coaching and feedback “ Patients”: Be ambivalent about making the change (4-5-6 on ruler) Verbalize the pros and cons of adopting the behavior Elaborate / offer deeper reasons when your partner offers a reflection Observers: On page 80-81, use the grid to track: OEQs, CEQs, Reflections, Change Talk. Be prepared to provide feedback to the provider Activity: Allow 10 minutes for each patient interaction, then 5 minutes for debrief - - monitor time closely Ensure that each group receives one full cycle with a trainer for extra coaching and feedback After all cycles are complete, debrief in large group: Ask each group to share one or two key learnings Before the break, invite participants to place green dots on the ruler
3:15 Break
3:30 Panel Discussion Review ruler and briefly discuss. To what do you attribute the shift? Did anyone move down the ruler? Would you be willing to tell us a bit about that? Review ppt chartpad: What are your most challenging encounters? Quickly pick a few to explore as a group – often two or more can be combined For each situation, author will provide quick summary followed by group problem solving. If feasible, briefly discuss remaining challenging situations from chart pad, eliciting problem-solving from the group
4:05 Summary, Evaluation & Close Describe online MC programs and distribute online program flyers Check expectations address gaps as needed Share key learnings / next steps for enhancing BN skills Distribute Evaluations Remind participants to sign out
4:30 Adjourn
Notes:
Section 18 Page 5 of 6 REGIONAL HEALTH EDUCATION