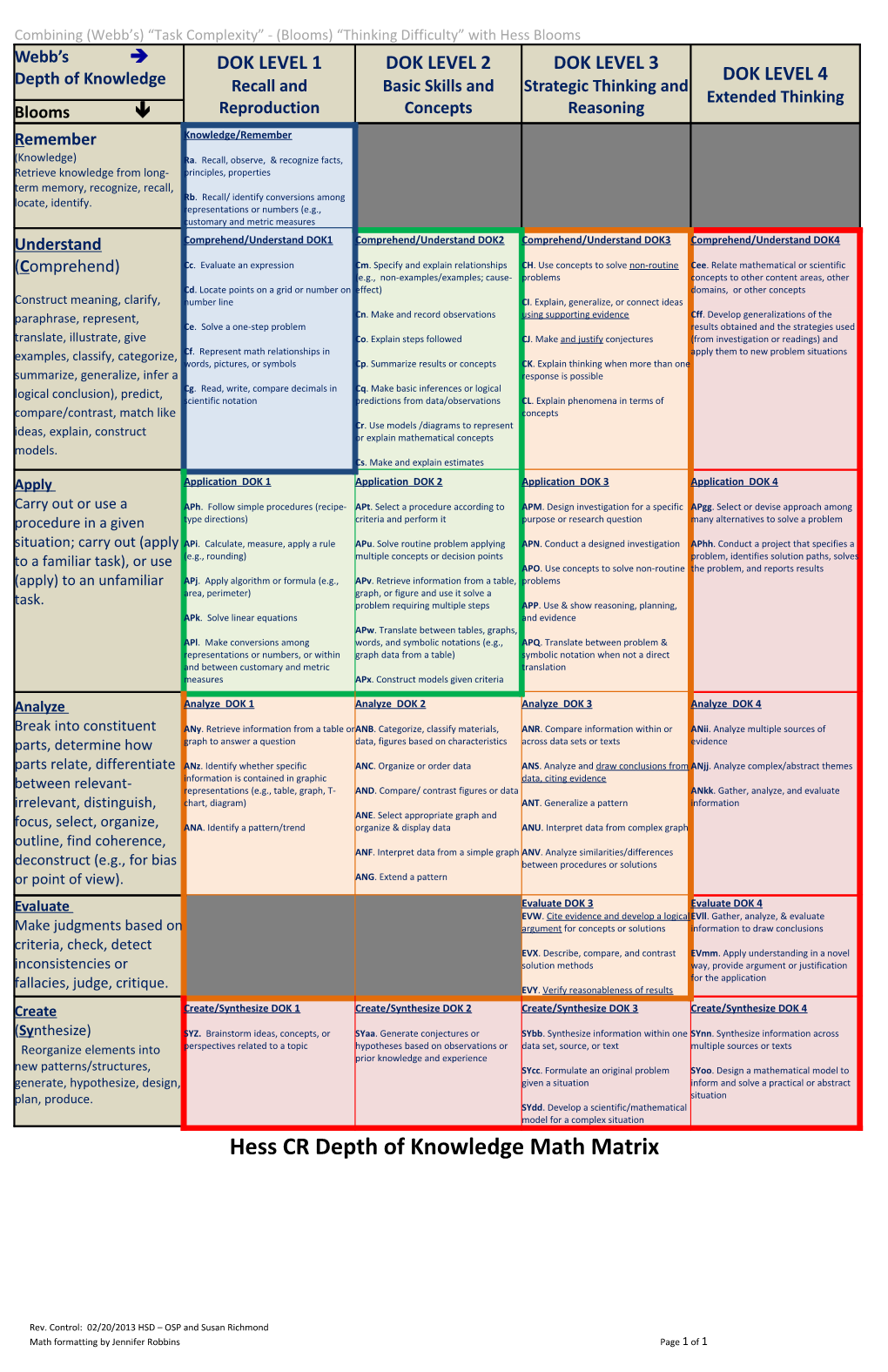
Combining (Webb’s) “Task Complexity” - (Blooms) “Thinking Difficulty” with Hess Blooms Webb’s DOK LEVEL 1 DOK LEVEL 2 DOK LEVEL 3 DOK LEVEL 4 Depth of Knowledge Recall and Basic Skills and Strategic Thinking and Extended Thinking Blooms Reproduction Concepts Reasoning Remember Knowledge/Remember (Knowledge) Ra. Recall, observe, & recognize facts, Retrieve knowledge from long- principles, properties term memory, recognize, recall, locate, identify. Rb. Recall/ identify conversions among representations or numbers (e.g., customary and metric measures Understand Comprehend/Understand DOK1 Comprehend/Understand DOK2 Comprehend/Understand DOK3 Comprehend/Understand DOK4 (Comprehend) Cc. Evaluate an expression Cm. Specify and explain relationships CH. Use concepts to solve non-routine Cee. Relate mathematical or scientific (e.g., non-examples/examples; cause- problems concepts to other content areas, other Cd. Locate points on a grid or number on effect) domains, or other concepts Construct meaning, clarify, number line CI. Explain, generalize, or connect ideas paraphrase, represent, Cn. Make and record observations using supporting evidence Cff. Develop generalizations of the Ce. Solve a one-step problem results obtained and the strategies used translate, illustrate, give Co. Explain steps followed CJ. Make and justify conjectures (from investigation or readings) and examples, classify, categorize, Cf. Represent math relationships in apply them to new problem situations words, pictures, or symbols Cp. Summarize results or concepts CK. Explain thinking when more than one summarize, generalize, infer a response is possible Cg. Read, write, compare decimals in Cq. Make basic inferences or logical logical conclusion), predict, scientific notation predictions from data/observations CL. Explain phenomena in terms of compare/contrast, match like concepts Cr. Use models /diagrams to represent ideas, explain, construct or explain mathematical concepts models. Cs. Make and explain estimates Apply Application DOK 1 Application DOK 2 Application DOK 3 Application DOK 4 Carry out or use a APh. Follow simple procedures (recipe- APt. Select a procedure according to APM. Design investigation for a specific APgg. Select or devise approach among procedure in a given type directions) criteria and perform it purpose or research question many alternatives to solve a problem situation; carry out (apply APi. Calculate, measure, apply a rule APu. Solve routine problem applying APN. Conduct a designed investigation APhh. Conduct a project that specifies a (e.g., rounding) multiple concepts or decision points problem, identifies solution paths, solves to a familiar task), or use APO. Use concepts to solve non-routine the problem, and reports results (apply) to an unfamiliar APj. Apply algorithm or formula (e.g., APv. Retrieve information from a table, problems area, perimeter) graph, or figure and use it solve a task. problem requiring multiple steps APP. Use & show reasoning, planning, APk. Solve linear equations and evidence APw. Translate between tables, graphs, APl. Make conversions among words, and symbolic notations (e.g., APQ. Translate between problem & representations or numbers, or within graph data from a table) symbolic notation when not a direct and between customary and metric translation measures APx. Construct models given criteria Analyze Analyze DOK 1 Analyze DOK 2 Analyze DOK 3 Analyze DOK 4 Break into constituent ANy. Retrieve information from a table orANB. Categorize, classify materials, ANR. Compare information within or ANii. Analyze multiple sources of parts, determine how graph to answer a question data, figures based on characteristics across data sets or texts evidence parts relate, differentiate ANz. Identify whether specific ANC. Organize or order data ANS. Analyze and draw conclusions from ANjj. Analyze complex/abstract themes information is contained in graphic data, citing evidence between relevant- representations (e.g., table, graph, T- AND. Compare/ contrast figures or data ANkk. Gather, analyze, and evaluate irrelevant, distinguish, chart, diagram) ANT. Generalize a pattern information ANE. Select appropriate graph and focus, select, organize, ANA. Identify a pattern/trend organize & display data ANU. Interpret data from complex graph outline, find coherence, ANF. Interpret data from a simple graph ANV. Analyze similarities/differences deconstruct (e.g., for bias between procedures or solutions or point of view). ANG. Extend a pattern Evaluate Evaluate DOK 3 Evaluate DOK 4 EVW. Cite evidence and develop a logicalEVll. Gather, analyze, & evaluate Make judgments based on argument for concepts or solutions information to draw conclusions criteria, check, detect EVX. Describe, compare, and contrast EVmm. Apply understanding in a novel inconsistencies or solution methods way, provide argument or justification for the application fallacies, judge, critique. EVY. Verify reasonableness of results Create Create/Synthesize DOK 1 Create/Synthesize DOK 2 Create/Synthesize DOK 3 Create/Synthesize DOK 4 (Synthesize) SYZ. Brainstorm ideas, concepts, or SYaa. Generate conjectures or SYbb. Synthesize information within one SYnn. Synthesize information across Reorganize elements into perspectives related to a topic hypotheses based on observations or data set, source, or text multiple sources or texts prior knowledge and experience new patterns/structures, SYcc. Formulate an original problem SYoo. Design a mathematical model to generate, hypothesize, design, given a situation inform and solve a practical or abstract plan, produce. situation SYdd. Develop a scientific/mathematical model for a complex situation Hess CR Depth of Knowledge Math Matrix
Rev. Control: 02/20/2013 HSD – OSP and Susan Richmond Math formatting by Jennifer Robbins Page 1 of 1