2005 ICP Regional Summary: Sub-Saharan Africa
Overview Forty-eight countries participated in the Africa regional ICP coordinated by the African Development Bank. Forty-five countries were from Sub-Saharan Africa along with Egypt, Morocco, and Tunisia. The program was beneficial not only in terms of providing PPPs but also in improving the national accounts data. Country statistical offices benefited from training and information sharing in a number of workshops held throughout the program and a regional plan to extend these efforts in improving statistics are currently being planned. All regional values shown below include only the countries that participated in the 2005 International Comparison Program.
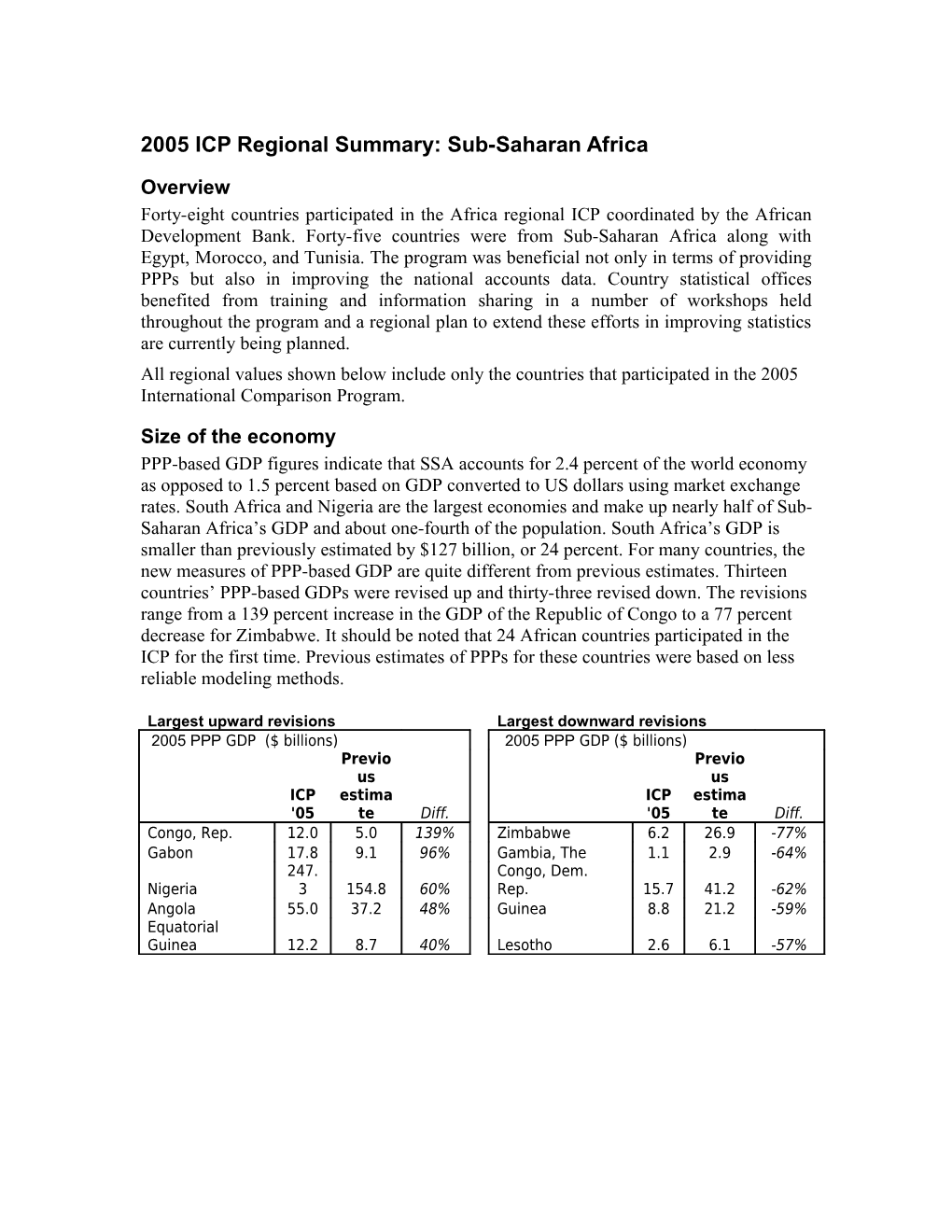
Size of the economy PPP-based GDP figures indicate that SSA accounts for 2.4 percent of the world economy as opposed to 1.5 percent based on GDP converted to US dollars using market exchange rates. South Africa and Nigeria are the largest economies and make up nearly half of Sub- Saharan Africa’s GDP and about one-fourth of the population. South Africa’s GDP is smaller than previously estimated by $127 billion, or 24 percent. For many countries, the new measures of PPP-based GDP are quite different from previous estimates. Thirteen countries’ PPP-based GDPs were revised up and thirty-three revised down. The revisions range from a 139 percent increase in the GDP of the Republic of Congo to a 77 percent decrease for Zimbabwe. It should be noted that 24 African countries participated in the ICP for the first time. Previous estimates of PPPs for these countries were based on less reliable modeling methods.
Largest upward revisions Largest downward revisions 2005 PPP GDP ($ billions) 2005 PPP GDP ($ billions) Previo Previo us us ICP estima ICP estima '05 te Diff. '05 te Diff. Congo, Rep. 12.0 5.0 139% Zimbabwe 6.2 26.9 -77% Gabon 17.8 9.1 96% Gambia, The 1.1 2.9 -64% 247. Congo, Dem. Nigeria 3 154.8 60% Rep. 15.7 41.2 -62% Angola 55.0 37.2 48% Guinea 8.8 21.2 -59% Equatorial Guinea 12.2 8.7 40% Lesotho 2.6 6.1 -57% Living Standards There are five countries with GDP per capita above $5,000, seven countries with GDP per capita between $5,000 and $2,000, and thirty-four countries with GDP per capita below $2000, and half of those countries are below $1,000.
GDP per capita (World=100%)
400%
300%
200%
100%
0% East Asia Europe and High-income Latin Middle-East South Asia Sub- and Pacific Central Asia America and and North Saharan Caribbean Africa Africa
Distribution of GDP per capita
14000
12000
10000
8000
6000
4000
2000
0
Countries with highest GDP per capita GDP per capita Gabon 12,742 Botswana 12,057 Equatorial Guinea 11,999 Mauritius 10,155 South Africa 8,477
Countries with the lowest GDP per capita GDP per capita Congo, Dem. Rep. 264 Liberia 383 Burundi 410 Zimbabwe 538 Guinea-Bissau 569
Actual Individual Consumption Actual individual consumption is measured by the total value of household final consumption expenditure, expenditures by non-profit institutions (such as NGOs and charities) serving households, and government expenditure on individual consumption goods and services (such as education or health). Sub-Saharan Africa is the region with the lowest actual individual consumption per capita at about one-fifth of the world average. Consumption per capita is below the regional average for more than three- fourths of the countries.
Actual Individual Consumption per capita (World=100%)
400%
300%
200%
100%
0% East Asia Europe and High-income Latin Middle-East South Asia Sub- and Pacific Central Asia America and and North Saharan Caribbean Africa Africa Actual Individual Consumption per capita
140.0%
120.0%
100.0%
80.0%
60.0%
40.0%
20.0%
0.0%
PPP-based measures of collective government consumption Collective government consumption expenditures consist of expenditures incurred by general and local governments for collective consumption services such as defense, justice, general administration, and the protection of the environment. Lower prices for such services in developing countries tend to reduce the dispersion of collective government consumption per capita across regions compared to that observed for per capita GDPs.
Collective Government Consumption per capita (World=100%)
400%
300%
200%
100%
0% East Asia Europe and High-income Latin Middle-East South Asia Sub- and Pacific Central Asia America and and North Saharan Caribbean Africa Africa
Collective Government Consumption per capita
400.0%
350.0%
300.0%
250.0%
200.0%
150.0%
100.0%
50.0%
0.0%
PPP-based measures of gross fixed capital formation Gross fixed capital formation measures countries’ investment expenditures, which are mostly comprised of purchases of equipment and construction services. Compared with the regional dispersion of GDP per capita, investment expenditures per capita appear to be less unequally distributed across regions. In particular, differences between the Asia- Pacific, CIS, South America, and West Asia regions narrow. Differences between these regions and the OECD/Eurostat grouping also narrows in comparison with differences in GDPs per capita. On the other hand, Africa lags far behind, reflecting low investment efforts from nationals and foreign investors, and high investment prices. Some countries have higher investment rates such as Gabon, Botswana, and Equatorial Guinea. GFCF per capita (World=100%)
400%
300%
200%
100%
0% East Asia Europe and High-income Latin Middle-East South Asia Sub- and Pacific Central Asia America and and North Saharan Caribbean Africa Africa
Gross Fixed Capital Formation
140.0%
120.0%
100.0%
80.0%
60.0%
40.0%
20.0%
0.0%
Price level indexes
A price level index (PLI) is the ratio of a PPP to the market exchange rate of the numeraire currency. PLIs are used to compare price levels between countries. The PLI indicates the relative price of GDP (or its components) in a country, as if it were “purchased” after acquiring local currency at the prevailing exchange rate. PLIs are generally low in poorest countries. This reflects the common experience of travelers who find many (but not all) of the goods and services in the poorest countries relatively cheap compared to similar products in their home country. Price levels generally increase with GDP per capita. In Sub-Saharan Africa, Zimbabwe, Cape Verde, Namibia, and South Africa have the highest prices and Ethiopia, The Gambia, and Burundi the lowest. Zimbabwe is a noticeable outlier. Its price level index may be affected by high inflation and the disparity between its official exchange rate and the rate at which international transactions actually take place.
GDP Price Level Indexes, World = 100
100% Cape Verde Zimbabwe (180%) 90%
Namibia 80%
South Africa
70%
60%
50%
40% Burundi
The Gambia 30% Ethiopia
20% GDP per capita