Supplementary Data
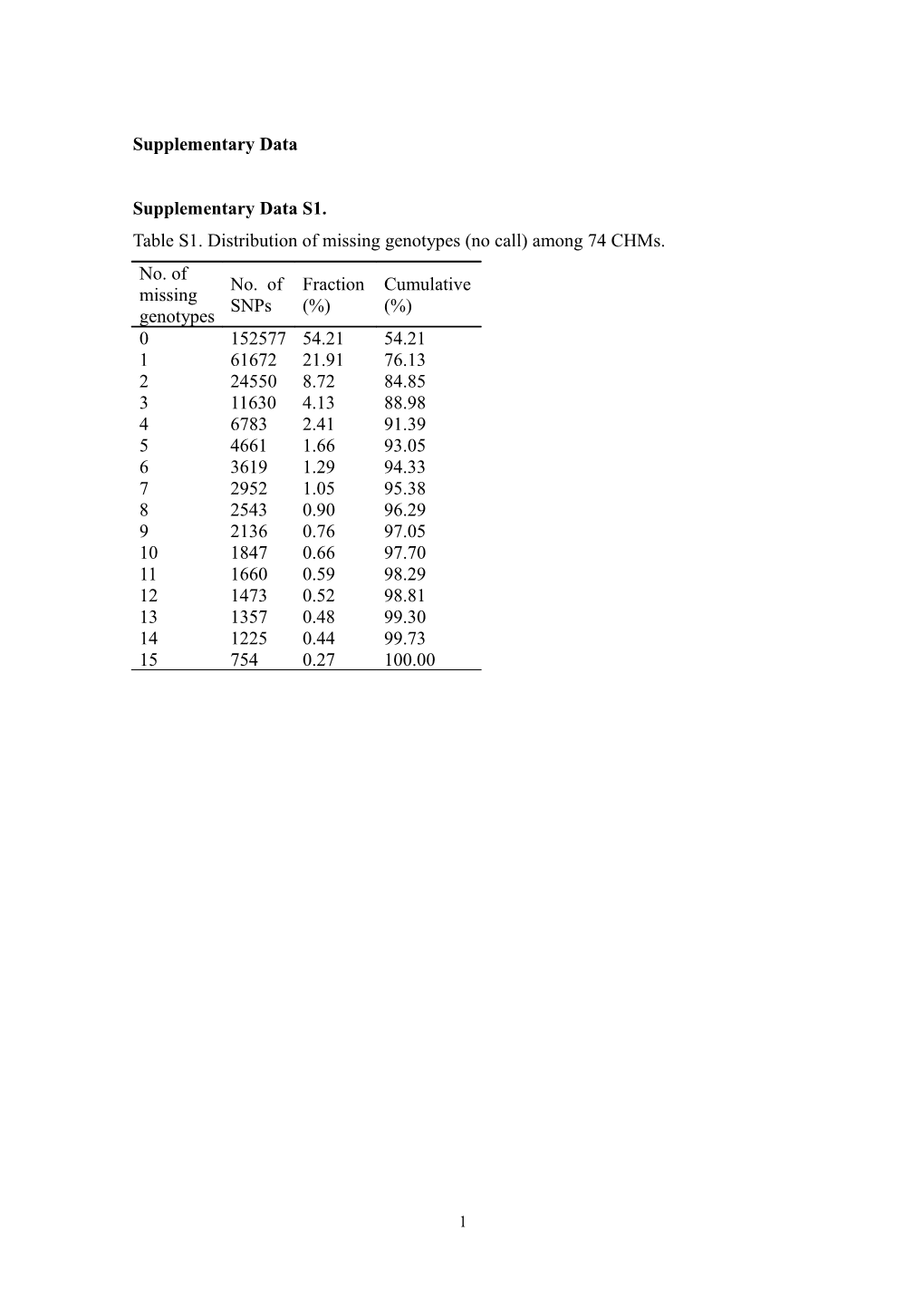
Supplementary Data S1. Table S1. Distribution of missing genotypes (no call) among 74 CHMs. No. of No. of Fraction Cumulative missing SNPs (%) (%) genotypes 0 152577 54.21 54.21 1 61672 21.91 76.13 2 24550 8.72 84.85 3 11630 4.13 88.98 4 6783 2.41 91.39 5 4661 1.66 93.05 6 3619 1.29 94.33 7 2952 1.05 95.38 8 2543 0.90 96.29 9 2136 0.76 97.05 10 1847 0.66 97.70 11 1660 0.59 98.29 12 1473 0.52 98.81 13 1357 0.48 99.30 14 1225 0.44 99.73 15 754 0.27 100.00
1 Supplementary Data S2.
Linkage disequilibrium of SNPs used in this study
Figure S1. The distribution of r2 values in the CHM data, for SNPs having r2 > 0.8 in the Han Chinese data.
2 Supplementary Data S3. Haplotype blocks defined from 74 CHMs Table S2. Properties of haplotype blocks. No. of Avg. no. of Average SNPs No. of Fraction No. of Fraction Avg. no. of common Genome size of per block of block SNPs of SNPs tag SNPs haplotypes coverage block (kb) block (≥5%) 1 6444 14.34% 0.0 6444 2.29% 0.0 2.0 0.00% 2 4668 10.39% 9.9 9336 3.32% 0.6 2.9 1.58% 3 4324 9.62% 21.5 12972 4.61% 1.1 3.6 3.18% 4 4074 9.07% 29.1 16296 5.79% 1.6 4.1 4.05% 5 3972 8.84% 36.4 19860 7.06% 1.9 4.5 4.94% 6 3687 8.20% 50.7 22122 7.86% 2.1 4.7 6.38% 7 3250 7.23% 53.1 22750 8.08% 2.2 4.8 5.89% 8 2891 6.43% 60.5 23128 8.22% 2.4 4.9 5.97% 9 2298 5.11% 71.7 20682 7.35% 2.5 5.0 5.62% 10 1909 4.25% 77.2 19090 6.78% 2.5 5.1 5.03% 11 1518 3.38% 86.3 16698 5.93% 2.6 5.2 4.47% 12 1252 2.79% 104.2 15024 5.34% 2.6 5.2 4.45% 13 1010 2.25% 110.9 13130 4.67% 2.6 5.2 3.82% 14 801 1.78% 119.0 11214 3.98% 2.7 5.3 3.25% 15 594 1.32% 135.7 8910 3.17% 2.8 5.4 2.75% 16 512 1.14% 162.4 8192 2.91% 2.8 5.5 2.84% 17 403 0.90% 163.7 6851 2.43% 2.9 5.5 2.25% 18 303 0.67% 181.7 5454 1.94% 2.9 5.5 1.88% 19 236 0.53% 214.5 4484 1.59% 3.0 5.6 1.73% ≥20 793 1.76% 305.1 18802 6.68% 3.0 5.8 8.26% Total 44939 100.00% 51.1 281439 100.00% 1.7 4.1 78.35%
Coverage values indicate the fraction of analyzed regions between SNPs in both ends of all chromosomes (2.93 Gb), including centromeres. Average number of SNPs per block is 6.3. Total tag SNPs are 74,402.
3 Supplementary Data S4. Blocks of HapMap Japanese in the following regions were placed on Build 35. Regions not included in the list contained SNPs whose locations were not assigned on Build 35 by dbSNP build 124, or whose locations were changed so that the neighboring SNPs were non-contiguous between the dbSNP build 122 and build124.
Chr Position on Build35 1 27966066-28999540 1 31697505-32731647 2 5903769-8952090 2 21521387-22759046 2 40878501-41993507 2 47229282-48273503 2 55851364-57426051 2 70936561-72006809 2 98973189-100001579 2 104587242-105704210 2 114668047-116105155 2 117904128-121140917 2 142415995-143430634 2 148370678-149422424 2 167469397-168769335 2 170602953-171973788 2 176421622-177812084 2 193193507-194575893 2 197619672-198792295 2 205326843-206917540 2 215402654-216454880 2 217329618-218708417 2 234773650-236250798 2 237698645-239007204 3 387925-1975594 3 14937952-15972853 3 18181169-20054882 3 24305287-25324418 3 59329572-60593207 3 60855949-62029636 3 70382325-71432717 3 78193644-79720968 3 81305242-82704389 3 100752611-102399472 3 108408588-109563907 3 114637538-116282114 3 116630816-118383109 3 133907478-134909922 3 157167795-158515993 3 165753114-166913783 3 171066948-172093018 3 175578180-176706268 3 181531452-182767327
4 3 182807196-183915346 4 15785365-17112227 4 21315785-22508716 4 22540820-23986345 4 29593707-30889076 4 31900044-33463430 4 39412930-41370265 4 61735975-63212013 4 73629403-74672756 4 77438265-79774965 4 81565142-83044454 4 86936888-87993230 4 88926163-90136876 4 90247962-91481052 4 93415699-94936771 4 109111441-110626869 4 112651381-113709125 4 127111750-128348024 4 133591143-134701485 4 136134437-137283515 4 155437935-156548963 4 162965535-164758999 4 171420800-173042326 4 180499221-182865951 4 184312814-185801002 4 189470389-190665806 5 5715031-6752224 5 8451016-10698871 5 11184057-12213489 5 13793976-15645415 5 18825733-20525638 5 50536385-52167072 5 73546408-74597785 5 76259121-77328470 5 106128977-107440214 5 110237481-111588276 5 131358360-132695568 5 133763745-134803516 5 138800490-139921412 5 153477241-154544610 5 155307146-157599162 7 1327915-3925330 7 3953694-5097444 7 6650556-8559297 7 9364908-10374686 7 11451486-12698016 7 13311941-14340292 7 14707195-16715722 7 16719339-18005408 7 18837260-20460421 7 22416547-24373919 7 28029480-29864911
5 7 29926791-34497160 7 36398541-37799330 7 38204721-39229892 7 39698709-41189474 7 44088781-45466602 7 50403973-51636963 7 51721181-53704713 7 53783479-55129657 7 68405987-69719408 7 76457949-77998532 7 78552200-79742227 7 79809699-82475351 7 86812678-87824070 7 88356188-89455178 7 97442617-98775526 7 98992979-100090886 7 106173648-107245066 7 107957838-108968985 7 116171075-117310336 7 120411070-123659647 7 123749921-124795525 7 131228591-132384325 7 138595806-140050085 7 154452644-156232661 7 157027277-158140725 8 1439699-2618255 8 24100246-25135419 8 31153537-33581626 8 36375984-37493810 8 37524287-38691579 8 65155016-66784346 8 81465988-82831316 8 91967607-93039329 9 6199697-7227331 9 12387700-14364275 9 21037733-22381184 9 27286595-28366865 9 36905178-37941176 9 85229006-86533479 9 100237070-101320309 9 115953056-117108502 9 118549756-120430675 9 133696037-134728940 9 136962084-138066102 10 3123648-4428977 10 8338970-9415982 10 22447662-23753917 10 54330335-55476322 10 59496055-60509229 10 66978052-68585518 10 116805438-117833005 10 121816833-122940109
6 10 133667732-135123274 11 8660517-9895121 11 12330374-13841440 11 23911655-25118820 11 27451835-29320292 11 39560586-41514305 11 46232648-47375529 11 69652959-70744872 11 79267654-80406301 11 81493252-82602006 11 82860653-84519221 11 96936342-98228838 11 104044290-105046953 11 109841392-111502973 11 114362453-115444187 11 116286128-117691515 11 131200086-133085636 11 133110660-134317533 12 40877196-42084540 12 42315568-43433403 12 57037008-58186937 12 66571409-67661472 12 69251746-70339572 12 73565116-74570616 12 90333308-91886703 12 94170905-95212919 12 109889192-110991792 13 29314962-30477567 13 59062224-60783801 13 75235781-76895414 13 90250158-91398074 13 95614377-96896525 13 101047626-102461765 13 103405911-104424613 13 110625168-111751180 14 24244559-25470394 14 26510999-27775679 14 38876703-40319704 14 40739852-41787701 14 46634902-48066956 14 50214410-51548065 14 53742324-54854490 14 61073336-62361548 14 70887439-72312898 14 73167794-74207417 14 76406956-78996355 14 79082777-80554902 14 85901674-88004455 14 91636556-93865245 14 95737634-97448273 14 97519673-99118270 14 104225150-106141273
7 15 32658588-33827340 15 43333670-44693201 15 57550746-58719074 15 60350247-61635858 15 62995280-64363284 15 64612743-66724495 15 66806636-68285062 15 87944571-88996043 15 89366490-90527706 15 90609797-92032720 15 93625941-95062362 15 96781427-98233264 16 640645-1785191 16 1817699-2851321 16 9143169-10262426 16 16786230-17787489 16 29779862-30807736 16 31765207-34464860 16 49272480-50277798 16 54274051-55504776 16 58226450-59303828 16 59822127-61014506 16 64887069-66109796 16 74735204-75839129 16 82785700-84124156 16 84148287-85827345 17 1551193-2627793 17 5282598-6599827 17 7760908-8835774 17 40483636-41706086 17 50881678-51961162 17 54486363-56141407 17 71465452-72729661 18 1193660-2262498 18 4747894-5752705 18 10556581-11586076 18 13173504-14261127 18 20145321-21375873 18 29684165-30863716 18 51053883-52882841 18 63445739-64559407 18 64661900-66024763 18 70200060-71655868 19 4070012-5946450 19 8304975-9407351 19 16468233-17802143 19 36512333-38378538 19 41159434-42180037 19 47192213-50227876 19 53381205-54634244 19 55880333-56897422 20 54379190-55582999
8 21 22119957-23230700 21 30896336-32052953 21 37811845-38823371 22 15459163-16495404 22 34558261-35893170
9 Supplementary Data S5. Blocking of simulated regions We evaluated the similarity of blocking patterns of CHM and pseudoindividual sets using several criteria. 1) The first measure was the concordance rate of SNP pairs falling into the same blocks (Liu et al. 2004). For the two partition data (i.e., one from true and the other from one of the pseudo sets), we evaluated every SNP pair if they are assigned to a single block or not. Then, the fraction of concordant pairs between the two partitions (the fraction of the pairs assigned to a same block or not in both partitions) are determined. In this analysis, the results of 100 comparisons between true and pseudo sets were averaged. Similarity was high, 95% as an average, and approximately 5% of SNP pairs were discordant due to incorrect inferring of haplotypes. However, in some cases, the discordant rate can be as high as 12%, although such cases seem to be rare (Fig. 6). 2) The second measure focused on block boundaries. Fraction of only concordant boundaries between true and pseudo sets is calculated. Concordance between SNPs those construct single SNP/block and concordance between SNPs those are contained within blocks, but are not boundaries, are not considered (Fig. S2A and B). By this measure, we focused similarities of boundary structures. Because shared regions of blocks were ignored, differences of boundaries were evaluated more accurately than first measure. So, the range of averaged block similarity was 27-95%. 3) In the third measure, sizes and positions of blocks are simply compared between two partitions, and fraction of exactly matched blocks is calculated. Results of 100 comparisons between true and pseudo sets were averaged (Fig. S2C and D). This measure evaluates difference of blocks accurately. Averaged similarity was 18-95%. 4) Fourth measure: Concordance between partitions of true and pseudo sets is evaluated (Fig. S2E and F). In other words, fraction of block partition sets of pseudoindividuals where all blocks are exactly the same as those of CHMs is calculated. This measure may be too stringent, but stresses the difference of block partitions. In most of regions, similarity is less than 20%.
10 (A) (B)
s 1.00 50 e i s r n a 0.80 40 o d i n g u 0.60 e 30 r o
f b
o 20
f 0.40
. o
o
y 0.20 10 t N i r
a 0
l 0.00 i 3 4 8 9 5 6 7 0 m i 0.00 0.10 0.20 ...... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 S Switch-error rate Similarity of boundaries
(C) (D)
1.0 50 y s t i n
r 0.8 40 o a i l i g
0.6 e 30 m r i
f s
0.4 o 20
k . c o
o 10
l 0.2 N B 0.0 0 1 4 5 6 8 0 2 3 7 9
0.00 0.10 0.20 ...... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 Switch-error rate Block similarity
(E) (F)
y 1.0 80 t i s r n a
l 0.8 o i 60 i g m i
0.6 e r s
40 f n
0.4 o o i . t i
o 20 t
r 0.2 N a
P 0.0 0 2 3 4 6 7 1 5 8 9
0.00 0.10 0.20 ...... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Switch-error rate Partition similarity
Figure S2. Evaluation of block similarity. Using HapBlock, we obtained block- partitions of pseudoindividual sets and CHM sets for haplotype-inferred regions. (A) Fraction of concordant boundaries between block partitions of CHM and pseudo sets, was calculated. Averaged fraction of 100 sets was plotted. (C) Sizes and positions of blocks are simply compared between two partitions, and fraction of concordant blocks
11 is calculated. Results of 100 comparisons between true and pseudo sets were averaged, and plotted. (E) Concordance between partitions of true and pseudo sets is evaluated. In other words, fraction of block partition sets of pseudoindividuals where all blocks are exactly the same as those of CHMs is calculated, and plotted. The histograms for (B) the similarity of boundary, (D) the block similarity, (F) the partition similarity.
12 Supplementary Data S6. Extended shared haplotype analysis
Several types of errors can be made when identifying extended shared haplotypes (ESH). A false positive happens when, due to incomplete informativeness of the assayed SNPs, two haplotypes appear to be identical across an extended interval, but additional genotyping would reveal that they are different. False negatives can happen when the assayed SNPs do not adequately cover the full extent of the shared region, or where one or more large gaps in SNP coverage cause the effective length of coverage to be reduced. Genotyping errors and phasing errors can also lead to false negatives by introducing inconsistent genotypes into regions of genuine sharing. It seems less likely, but conceivable, that phasing errors could also produce false positives, if a phasing algorithm is biased towards finding solutions having longer shared haplotypes.
We used the CHM data to evaluate false positive and false negative rates at different SNP sampling densities in the absence of phasing errors. The following table shows results of comparing the extended haplotypes identified using a 2 Mb cutoff with either all CHM SNPs, or the subset that overlaps with the HapMap data.
Extended haplotypes Haplotype coverage SNPs Total Both % Both Total, Both, Gb % Both Gb All > 2 Mb 274957 6801 5157 75.8 29.8 21.8 73.2 Subset > 2 Mb 93531 8492 5147 60.6 34.7 21.8 62.7 Using the sparse SNP subset, we can identify about 75% of the extended haplotypes seen using the dense SNP map, suggesting a false negative rate of about 25% relative to that SNP set. On the other hand, only about 60% of the intervals identified with the sparse subset are confirmed at the higher density, suggesting a false positive rate of about 40%. The following table shows the overlap between extended haplotypes with a 1 Mb cutoff in the dense SNP set, versus a 2 Mb cutoff in the sparse SNP set.
Extended haplotypes Haplotype coverage SNPs Total Both % Both Total, Both, Gb % Both
13 Gb All > 1 Mb 274957 84843 8526 10.0 158.4 28.4 18.0 Subset > 2 Mb 93531 8492 7980 94.0 34.7 28.4 81.7 Here, nearly all of the 2 Mb intervals identified with the sparse SNP set overlap an interval spanning at least 1 Mb with the dense SNP set, and more than 80% of the total distance spanned by the sparse intervals is covered by dense intervals. So it seems that most of the false positives come from moderately overestimating the extent of a genuine shared haplotype. Our gap penalty was selected to balance the false negative rate compared to the 2 Mb dense map, against the false positive rate compared to the 1 Mb dense map.
The following table shows similar results for the HapMap JPT data, first using a 2 Mb cutoff for all available SNPs and for the shared subset. The false negative rates for the sparse SNP set are much higher here than in the CHM data. This partly reflects the larger difference in SNP density between dense and sparse sets here.
Extended haplotypes Haplotype coverage SNPs Total Both % Both Total, Both, Gb % Both Gb All > 2 Mb 698909 2799 1634 58.4 15.6 6.5 41.6 Subset > 2 Mb 93531 5417 1575 29.1 22.8 6.5 28.4 With a 1 Mb cutoff for all available SNPs and a 2 Mb cutoff for the shared subset:
Extended haplotypes Haplotype coverage SNPs Total Both % Both Total, Both, Gb % Both Gb All > 1 Mb 698909 50207 4988 9.9 112.5 12.6 11.2 Subset > 2 Mb 93531 5417 4104 75.8 22.8 12.6 55.4 As in the CHM data, most of the extended haplotypes in the subset analysis do overlap with an extended haplotype of at least 1 Mb in the dense analysis, though the false positive rates are higher here. The results for the CEU samples are generally similar. The following table shows results for the CEU data, with a 2 Mb cutoff for all available SNPs and for the shared subset:
Extended haplotypes Haplotype coverage SNPs Total Both % Both Total, Both, Gb % Both Gb All > 2 Mb 772839 3064 2061 67.3 15.4 7.2 46.9
14 Subset > 2 Mb 89164 6669 1969 29.5 25.0 7.2 28.9 With a 1 Mb cutoff for all available SNPs and a 2 Mb cutoff for the shared subset:
Extended haplotypes Haplotype coverage SNPs Total Both % Both Total, Both, Gb % Both Gb All > 1 Mb 772839 44017 6361 14.5 95.6 14.7 15.4 Subset > 2 Mb 89164 6669 5292 79.4 25.0 14.7 58.8
15 References
Liu, N., Sawyer, S.L., Mukherjee, N., Pakstis, A.J., Kidd, J.R., Kidd, K.K., Brookes,
A.J., and Zhao, H. 2004. Haplotype block structures show significant variation
among populations. Genet. Epidemiol. 27: 385-400.
16