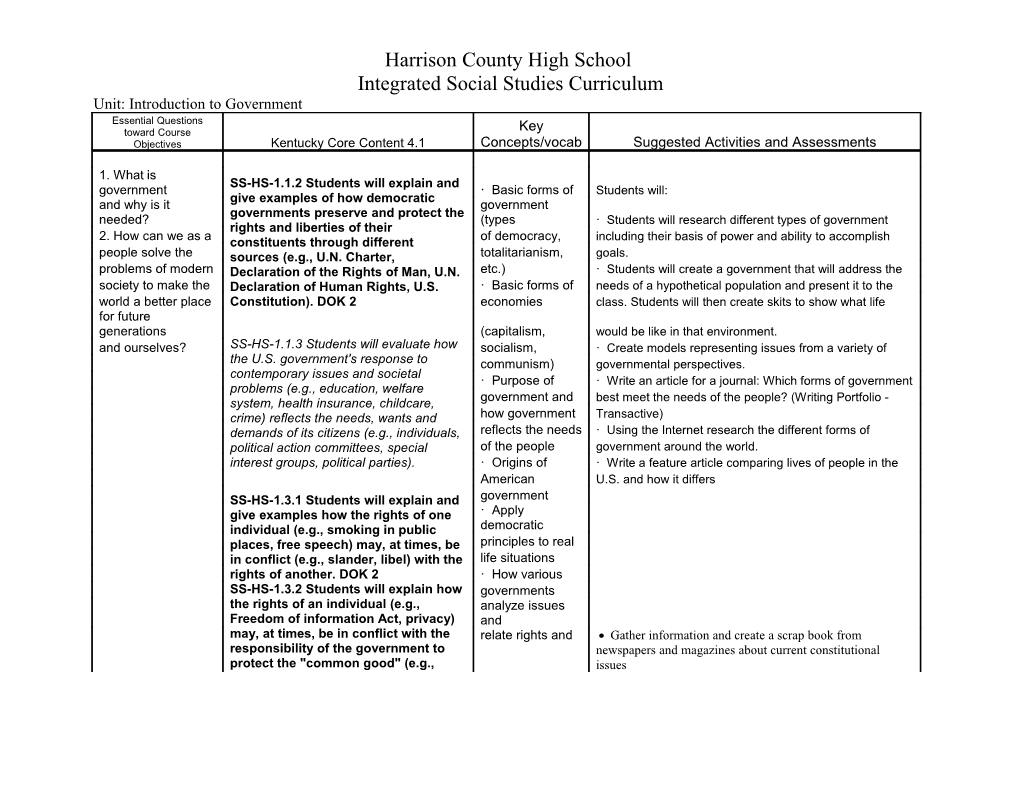
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum Unit: Introduction to Government Essential Questions toward Course Key Objectives Kentucky Core Content 4.1 Concepts/vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments
1. What is SS-HS-1.1.2 Students will explain and government · Basic forms of Students will: give examples of how democratic and why is it government governments preserve and protect the needed? (types · Students will research different types of government rights and liberties of their 2. How can we as a constituents through different of democracy, including their basis of power and ability to accomplish people solve the sources (e.g., U.N. Charter, totalitarianism, goals. problems of modern Declaration of the Rights of Man, U.N. etc.) · Students will create a government that will address the society to make the Declaration of Human Rights, U.S. · Basic forms of needs of a hypothetical population and present it to the world a better place Constitution). DOK 2 economies class. Students will then create skits to show what life for future generations (capitalism, would be like in that environment. and ourselves? SS-HS-1.1.3 Students will evaluate how socialism, · Create models representing issues from a variety of the U.S. government's response to communism) governmental perspectives. contemporary issues and societal · Purpose of · Write an article for a journal: Which forms of government problems (e.g., education, welfare
system, health insurance, childcare, government and best meet the needs of the people? (Writing Portfolio - crime) reflects the needs, wants and how government Transactive) demands of its citizens (e.g., individuals, reflects the needs · Using the Internet research the different forms of political action committees, special of the people government around the world. interest groups, political parties). · Origins of · Write a feature article comparing lives of people in the American U.S. and how it differs SS-HS-1.3.1 Students will explain and government give examples how the rights of one · Apply individual (e.g., smoking in public democratic places, free speech) may, at times, be principles to real in conflict (e.g., slander, libel) with the life situations rights of another. DOK 2 · How various SS-HS-1.3.2 Students will explain how governments the rights of an individual (e.g., analyze issues Freedom of information Act, privacy) and may, at times, be in conflict with the relate rights and Gather information and create a scrap book from responsibility of the government to newspapers and magazines about current constitutional protect the "common good" (e.g., issues Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum responsibilities to its citizens. homeland security issues, environmental regulations, censorship, search and seizure). DOK SS-HS-1.3.3 Students will evaluate the impact citizens have on the functioning of a democratic government by assuming responsibilities (e.g., seeking and assuming leadership positions, voting) and duties (e.g., serving as jurors, paying taxes, complying with local, state and federal laws, serving in the armed forces). DOK 3
SS-HS-2.2.1 Students will explain how various human needs are met through interaction in and among social institutions (e.g., family, religion, education, government, economy) in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and the United States (Reconstruction to present).
SS-HS-3.2.1 Students will compare and contrast economic systems (traditional, command, market, mixed) based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security and growth in the modern world. DOK 2
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum Unit: Basic Principles of Government
Essential Questions Key toward Course Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments sources (e.g., U.N. Charter, Declaration of the Rights of Man, U.N. Declaration of Human Rights, U.S. Constitution problems (e.g., education, welfare system, health insurance, childcare, crime) citizens (e.g., individuals, political action committees, special interest groups, political parties) 1. How do the SS-HS-1.1.2 Students will explain principles and give examples of how · Origins of Students will: democratic governments preserve · Create and participate in a mock Constitutional of the Constitution and protect the rights and liberties American convention provide for a more of their constituents through democracy · Conduct a Constitutional search to find how the effective or efficient different sources (e.g., U.N. (Declaration of Constitution addresses the weaknesses on the Articles of government? Charter, Declaration of the Rights Independence, Confederation. 2. Thinking back to of Man, U.N. Declaration of Human the Rights, U.S. Constitution). DOK 2 Articles of · Research political philosophers and write a quote original Confederation, consistent with their perspective. Present this to the class Constitutional SS-HS-1.1.3 Students will evaluate how Constitutional and the other groups will determine the principle that is principles, would the the U.S. government's response to Convention etc.) being addressed. founding fathers be contemporary issues and societal · Contributions of · Create a timeline of events effecting Constitutional surprised by the problems (e.g., education, welfare political influences system, health insurance, childcare, · Research using the Internet and newspaper articles to crime) reflects the needs, wants, and changes in their philosophers: find demands of its citizens (e.g., individuals, government over the political action committees, special Locke, information that deals with Constitutional principles. last 200 years? interest groups, political parties). Montesquieu, · Create political cartoons or editorials reflective of the 3. Was our government Rousseu, Adam development of Constitutional government. created to protect us SS-HS-1.2.2 Students will interpret Smith · Debate from Federalist/ Anti-Federalist perspective. from ourselves? the principles of limited · Limited government (e.g., rule of law, Government, federalism, checks and balances, Constitutional majority rule, protection of minority supremacy, rule government (e.g., rule of law, federalism, checks rights, separation of powers) and of and balances, majority rule, protection of minority evaluate how these principles rights, separation of powers) Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum law, popular protect individual rights and sovereignty, promote the "common good.” DOK separation of SS-HS-1.3.1 Students will explain powers, checks Rights…individual (e.g., smoking in public places, and give examples how the rights and free speech) of one individual (e.g., smoking in balances, public places, free speech) may, at federalism, times, be in conflict (e.g., slander, adaptability, civil libel) with the rights of another. conflict (e.g., slander, libel) with the rights of DOK 2 liberties, another. DOK 2 capitalism, change, basic assumptions
SS-HS-1.3.2 Students will explain how the rights of an individual
(e.g., Freedom of information Act, privacy) may, at times, be in conflict with the responsibility of the government to protect the "common good" (e.g., homeland security issues, environmental "common good" (e.g., homeland security issues, regulations, censorship, search environmental regulations, censorship, search and and seizure). DOK 2 seizure)
SS-HS-1.3.3 Students will evaluate the impact citizens have on the functioning of a democratic government by assuming responsibilities (e.g., seeking and assuming leadership positions, voting) and duties (e.g., serving as jurors, paying taxes, complying responsibilities (e.g., seeking and assuming with local, state and federal laws, leadership positions, voting)… duties (e.g., serving serving in the armed forces). DOK as jurors, paying taxes, complying with local, state 3 and federal laws, serving in the armed forces) Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
SS-HS-2.1.1 Students will explain how belief systems, knowledge, technology and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2 (1500 A.D. to present) (Reconstruction to present)
SS-HS-2.2.1 Students will explain how various human needs are met through interaction in and among social institutions (e.g., family, religion, education, government, economy) in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and the United States (Reconstruction to present). SS-HS-2.3.1 Students will explain the reasons why conflict and competition (e.g., violence, difference of opinion, stereotypes, prejudice, discrimination, genocide) may develop as cultures emerge in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and the United …conflict and competition (e.g., violence, States (Reconstruction to present). difference of opinion, stereotypes, prejudice, DOK 2 discrimination, genocide)
SS-HS-3.3.4 Students will explain how laws and government mandates (e.g., anti-trust legislation, tariff policy, regulatory (e.g., anti-trust legislation, tariff policy, policy) regulatory policy) have been adopted to maintain competition in the United States and in the global marketplace.
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum SS-HS-3.4.1 Students will analyze the changing relationships among business, labor and government (e.g., unions, anti-trust laws, tariff policy, price controls, subsidies,
tax incentives) and how each has affected production, distribution and consumption in the United (e.g., unions, anti-trust laws, tariff policy, price States or the world. DOK 3 controls, subsidies, tax incentives)
SS-HS-4.2.4 Students will explain how people from different cultures with different perspectives view regions (e.g., Middle East, (e.g., Middle East, Balkans) Balkans) in different ways, sometimes resulting (1500 A.D. to present) in conflict in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to (Reconstruction to present). present).
Unit: Court Systems Essential Question toward Course Key Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments
1. How do the courts · Article III Students will: SS-HS-1.2.2 Students will interpret · Present Supreme Court cases allowing the class to be balance the rights of the principles of limited government · Make-up of court the society v. the rights (e.g., rule of law, federalism, checks federal and state Supreme court to decide the cases and then analyzing the of the individual? and balances, majority rule, court system and resulting precedent. protection of minority rights, · Listen to guest speakers that discuss the court system 2. What impact have separation of powers) and evaluate responsibilities and judicial decisions how these principles protect had individual rights and promote the · Appointment of differences between criminal and civil law. on society? "common good.” DOK 3 justices · Conduct on-line researching for current Kentucky 3. How has the judicial · Judicial review Supreme Court cases. Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum · Important · Chart and graph the differences between state and branch adapted to SS-HS-1.1.2 Students will explain Supreme federal society? and give examples of how Court cases (Civil courts. democratic governments preserve rights etc.) · Take a field trip to watch court in action and visit the jail. and protect the rights and liberties of · Criminal and their constituents through different Civil · Watch videotapes of the Civil and Criminal trials of OJ sources (e.g., U.N. Charter, Law Simpson and make conclusions comparing civil v. Declaration of the Rights of Man, · Adversary U.N. Declaration of Human Rights, system criminal cases. U.S. Constitution). DOK 2 · Original v. · Role play the President and pick a Supreme Court appellate member. jurisdiction SS-HS-1.1.3 Students will evaluate how · Judicial restraint the U.S. government's response to v. contemporary issues and societal Judicial activism problems (e.g., education, welfare · Adaptability system, health insurance, childcare,
crime) reflects the needs, wants, and demands of its citizens (e.g., individuals, political action committees, special interest groups, political parties).
SS-HS-1.3.1 Students will explain and give examples how the rights of one individual (e.g., smoking in public places, free speech) may, at times, be in conflict (e.g., slander,
libel) with the rights of another. DOK 2
SS-HS-1.3.2 Students will explain how the rights of an individual (e.g., Freedom of information Act, privacy) may, at times, be in conflict with the responsibility of the government to
protect the "common good" (e.g.,
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
homeland security issues, environmental regulations,
SS-HS-1.3.3 Students will evaluate the impact citizens have on the functioning of a democratic government by assuming responsibilities (e.g., seeking and assuming leadership positions, voting) and duties (e.g., serving as jurors, paying taxes, complying with local, state and federal laws, serving in the armed forces). DOK 3
SS-HS-2.3.1 Students will explain the reasons why conflict and competition (e.g., violence, difference of opinion, stereotypes, prejudice, discrimination, genocide) may develop as cultures emerge in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and the United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2
SS-HS-3.2.1 Students will compare and contrast economic systems (traditional, command, market, mixed) based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security and growth in the modern world. economic systems (traditional, command, market, DOK 2 mixed)
SS-HS-3.2.3 Students will explain how, in a free enterprise system, Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
Maximize their profits…e.g., producers try to maximize resources, entrepreneurs try to maximize profits, workers try to maximize income, savers and individuals attempt to maximize their investors try to maximize return profits based on their role in the economy (e.g., producers try to maximize resources, entrepreneurs try to maximize profits, workers try to maximize income, savers and
SS-HS-3.3.4 Students will explain how laws and government mandates (e.g., anti-trust legislation, tariff policy, regulatory policy) have been adopted to maintain competition in the United States and in the global marketplace.
SS-HS-3.4.1 Students will analyze the changing relationships among business, labor and government (e.g., unions, anti-trust laws, tariff policy, price controls, subsidies, tax incentives) and how each has affected production, distribution and consumption in the United States or (e.g., unions, anti-trust laws, tariff policy, price the world. DOK 3 controls, subsidies, tax incentives)
SS-HS-3.4.3 Students will explain and give examples of how interdependence of personal, national and international economic activities often results in international issues and concerns (e.g., natural resource dependencies, economic sanctions, environmental Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
international issues and concerns (e.g., natural and humanitarian issues) in the resource dependencies, economic sanctions, modern world (1500 A.D. to present) environmental and humanitarian issues) and the United States
SS-HS-5.3.6 Students will explain how the second half of the 20th century was characterized by rapid social, political and economic changes that created new challenges (e.g., population growth, diminishing natural resources, environmental concerns, human rights issues, technological and scientific advances, shifting political alliances, new challenges (e.g., population growth, globalization of the economy) in diminishing natural resources, environmental countries around the world, and give concerns, human rights issues, technological and examples of how countries have scientific advances, shifting political alliances, addressed these challenges. DOK 2 globalization of the economy)
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum Unit: Executive Branch Essential Question toward Course Key Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments
1. Compared to the SS-HS-1.2.2 Students will interpret · Article II Students will: original goal of the the principles of limited government · Make-up of the · Perform a mock presidential election. framers, has the (e.g., rule of law, federalism, checks executive branch · Create their own hypothetical candidate, based on civic President and balances, majority rule, overstepped protection of minority rights, · Presidential virtue, background, and personality characteristics. his bounds? separation of powers) and evaluate election process · Use the Internet and other resources to analyze 2. Do Americans how these principles protect expect individual rights and promote the · Powers of the background of past presidents and present their impact on too much today from "common good.” DOK 3 president the country, presidency, or world. · Duties and roles the President? of · Write a feature article analyzing who was the most 3. How does the the president influential president, and why. (Writing Portfolio - President organize the · Checks on the Transactive) · Make presentations focusing on the roles of the executive branch in executive branch president. · Succession of · Participate in a role play activity in which they are to order to meet all the react his/her duties and presidency to historical scenarios of historical significance and then roles? · Executive analyze the actual response. · Compare/ contrast famous inauguration addresses to bureaucracy what (independent they were actually able to accomplish. agencies, cabinet) · Write a feature article about an event going on in the · Development of world today and how the U.S. is responding. (Writing foreign policy Portfolio - Transactive) · Use a world map to research ten “hot spots”, and locate them on a map. They will present to the class how the UN or U.S. government is using its structure to deal with Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum these problems.
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum Unit: Political Process Essential Question toward Course Key Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments
1. Does the current · Understanding Students will: political system allow citizenship rights · Perform a mock political conventions for the best and · Perform a mock election SS-HS-1.1.3 Students will evaluate representation how the U.S. government's response responsibilities. · Simulate the role of the electoral college to contemporary issues and societal · Rise and stance possible? problems (e.g., education, welfare of · Create charts that reflect the impact of the electoral 2. What are the system, health insurance, childcare, current political college. elements of “good crime) reflects the needs, wants, and parties as well as · Write an editorial concerning the validity of the electoral participation” in a demands of its citizens (e.g., importance of third college. (Writing Portfolio - Transactive) healthy democracy? individuals, political action committees, parties. · Research the development of political parties. 3. All things special interest groups, political · Understanding considered parties). the · Debate current issues from the perspective of the can voters make nomination final process political parties, or interest groups. decisions to do what SS-HS-1.2.2 Students will interpret (political process): · Participate in a voter registration drive. is best for society? the principles of limited government Announcement, · Write letters to political candidates addressing their (e.g., rule of law, federalism, checks conventions and stand on particular issues. (Writing Portfolio - Transactive) and balances, majority rule, primaries, national · Write an academic essay: Does the current political protection of minority rights, convention, party system allow the U.S. to achieve the best representation separation of powers) and evaluate how these principles protect ticket and platform possible? Or does your vote really count? individual rights and promote the · Understanding "common good.” DOK 3 the · View and analyze documentaries and other films election process: regarding the political process.
SS-HS-1.3.1 Students will explain general election, · Participate in the collection of exit poll data. and give examples how the rights of electoral college, one individual (e.g., smoking in inauguration public places, free speech) may, at · Influence of times, be in conflict (e.g., slander, media, libel) with the rights of another. polls, technologies DOK 2 influence on Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum political system, SS-HS-1.3.2 Students will explain and interest how the rights of an individual (e.g., groups Freedom of information Act, privacy) may, at times, be in conflict with the responsibility of the government to protect the "common good" (e.g., homeland security issues, environmental regulations, censorship, search and seizure). DOK 2 SS-HS-1.3.3 Students will evaluate the impact citizens have on the functioning of a democratic government by assuming responsibilities (e.g., seeking and assuming leadership positions, voting) and duties (e.g., serving as jurors, paying taxes, complying with local, state and federal laws, serving in the armed forces). DOK 3
SS-HS-2.1.1 Students will explain how belief systems, knowledge, technology and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2
SS-HS-3.1.1 Students will give examples of and explain how scarcity of resources necessitates choices at both the personal and societal levels in the modern world
(1500 A.D. to present) and the
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
United States (Reconstruction to present) and explain the impact of
SS-HS-3.1.2 Students will explain how governments have limited budgets, so they must compare revenues to costs and consider opportunity cost when planning public projects.
SS-HS-3.2.1 Students will compare and contrast economic systems (traditional, command, market, mixed) based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security and
SS-HS-3.2.2 Students will describe economic institutions such as corporations, labor unions, banks, stock markets, cooperatives, and partnerships.
SS-HS-3.2.3 Students will explain how, in a free enterprise system, individuals attempt to maximize their profits based on their role in the economy (e.g., producers try to maximize resources, entrepreneurs try to maximize profits, workers try to maximize income, savers and investors try to maximize return). DOK 2
SS-HS-3.3.1 Students will explain Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum and give examples of how numerous factors influence the supply and demand of products (e.g., supply— technology, cost of inputs, number of sellers: demand—income, utility, price of similar products, consumers' preferences). DOK 2
SS-HS-3.3.2 Students will explain how specific financial and non-financial incentives often influence individuals differently (e.g., discounts, sales promotions, trends, personal convictions).
SS-HS-3.3.3 Students will explain how the level of competition in a market is largely determined by the number of buyers and sellers.
SS-HS-3.3.4 Students will explain how laws and government mandates (e.g., anti-trust legislation, tariff policy, regulatory policy) have been adopted to maintain competition in the United States and in the global marketplace.
SS-HS-3.4.1 Students will analyze the changing relationships among business, labor and government (e.g., unions, anti-trust laws, tariff policy, price controls, subsidies, tax incentives) and how each has affected production, distribution and consumption in the United States or the world. DOK 3 Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
SS-HS-3.4.2 Students will describe and give examples of how factors such as technological change, investments in capital goods and human capital/resources have increased productivity in the world. DOK 2
SS-HS-3.4.3 Students will explain and give examples of how interdependence of personal, national and international economic activities often results in international issues and concerns (e.g., natural resource dependencies, economic sanctions, environmental and humanitarian issues) in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and the United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2
SS-HS-4.3.1 Students will describe the movement and settlement patterns of people in various places and analyze the causes of that movement and settlement (e.g., push factors such as famines or military conflicts; pull factors such as climate or economic opportunity) and the impacts in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 3 Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
SS-HS-4.3.2 Students will explain how technology (e.g., computers, telecommunications) has facilitated the movement of goods, services and populations, increased economic interdependence at all levels, and influenced development of centers of economic activity. DOK 2
SS-HS-4.4.1 Students will explain how humans develop strategies (e.g., transportation, communication, technology) to overcome limits of their physical environment.
SS-HS-5.2.2 Students will explain how the rise of big business, factories, mechanized farming and the labor movement impacted the lives of Americans. DOK 2
SS-HS-5.2.4 Students will explain and evaluate the impact of significant social, political and economic changes during the Progressive Movement (e.g., industrial capitalism, urbanization, political corruption, initiation of reforms), World War I (e.g., imperialism to isolationism, (e.g., industrial capitalism, urbanization, political nationalism), and the Twenties (e.g., corruption, initiation of reforms) (e.g., imperialism Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum to isolationism, nationalism) e.g., economic economic prosperity, consumerism, prosperity, consumerism, women’s suffrage)
SS-HS-5.3.6 Students will explain how the second half of the 20th century was characterized by rapid social, political and economic changes that created new challenges (e.g., population growth, diminishing natural resources, environmental concerns, human rights issues, technological and scientific advances, shifting political alliances, globalization of challenges (e.g., population growth, diminishing the economy) in countries around natural resources, environmental concerns, human the world, and give examples of rights issues, technological and scientific how countries have addressed advances, shifting political alliances, globalization these challenges. DOK 2 of the economy) Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum Unit: Individual Rights
Essential Question toward Course Key Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments
1. Even in a democracy SS-HS-1.1.2 Students will explain · What is a right? Students will: and give examples of how Law of nature, are rights relative or democratic governments preserve etc. · Divide into groups. Each group will be given an absolute? and protect the rights and liberties · Bill of Rights, amendment to research and present court cases dealing 2. What connection of their constituents through do different sources (e.g., U.N. Charter, other with that amendment. rights have to a Declaration of the Rights of Man, Constitutional · Simulate court cases that reflect conflicts between successful U.N. Declaration of Human Rights, rights individuals and government. democracy? U.S. Constitution). DOK 2 · Civic · Debate issues revolving rights and the roles of 3. How does our responsibilities: government and the protection of those rights. Constitution protect jury duty, voting · Create a cartoon or editorial reflective of these issues. rights? etc. · View documentary and films related to this unit. · Important Court · Interpret an Amendment and perform a skit displaying SS-HS-1.1.3 Students will evaluate how the U.S. government's response to contemporary cases dealing issues and societal problems (e.g., education, with what life would be like without that Amendment. welfare system, health insurance, childcare, rights · Listen to guest speakers discuss individual rights. crime) reflects the needs, wants, and · How changes in · Interpret quotes from philosophers and writers regarding demands of its citizens (e.g., individuals, political action committees, special interest society effect the responsibilities and determine if these are necessary groups, political parties). definition of responsibilities for life in a democracy. individual rights (ex. Civil rights SS-HS-1.2.2 Students will interpret movement, the principles of limited government abortion, wartime (e.g., rule of law, federalism, checks rights etc..) and balances, majority rule,
protection of minority rights, · Juvenile rights separation of powers) and evaluate how these principles protect individual rights and promote the "common good.” DOK 3 Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum SS-HS-1.3.1 Students will explain and give examples how the rights of one individual (e.g., smoking in public places, free speech) may, at times, be in conflict (e.g., slander, libel) with the rights of another. DOK 2
SS-HS-1.3.2 Students will explain how the rights of an individual (e.g., Freedom of information Act, privacy) may, at times, be in conflict with the responsibility of the government to protect the "common good" (e.g., homeland security issues, environmental regulations, censorship, search and seizure). DOK 2
SS-HS-1.3.3 Students will evaluate the impact citizens have on the functioning of a democratic government by assuming responsibilities (e.g., seeking and assuming leadership positions, voting) and duties (e.g., serving as jurors, paying taxes, complying with local, state and federal laws, serving in the armed forces). DOK 3
SS-HS-2.1.1 Students will explain how belief systems, knowledge, technology and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2 Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
SS-HS-2.2.1 Students will explain how various human needs are met through interaction in and among social institutions (e.g., family, religion, education, government, economy) in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and the United States (Reconstruction to present).
SS-HS-2.3.1 Students will explain the reasons why conflict and competition (e.g., violence, difference of opinion, stereotypes, prejudice, discrimination, genocide) may develop as cultures emerge in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and the United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2
SS-HS-3.1.2 Students will explain how governments have limited budgets, so they must compare revenues to costs and consider opportunity cost when planning public projects.
SS-HS-5.3.5 Students will explain the rise of both the United States and the Soviet Union to superpower status following World War II, the subsequent development of the
Cold War, and the formation of new nations in Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe and the Middle East, and evaluate the impact of these events on the global community. DOK 3 Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
SS-HS-5.3.6 Students will explain how the second half of the 20th century was characterized by rapid social, political and economic changes that created new challenges (e.g., population growth, diminishing natural resources, environmental concerns, human rights issues, technological and scientific advances, shifting political alliances, globalization of the new challenges (e.g., population growth, economy) in countries around the diminishing natural resources, environmental world, and give examples of how concerns, human rights issues, technological and countries have addressed these scientific advances, shifting political alliances, challenges. DOK 2 globalization of the economy) Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum Unit: State and Local Government Essential Question toward Course Key Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments
1. Why do we need state · Concept of Students will: SS-HS-1.1.2 Students will explain · Listen to guest speakers from state and local and local and give examples of how federalism government government? democratic governments preserve · Roles of state · Conduct interviews with local government officials and 2. How do they meet and protect the rights and liberties analyze the way in which this position addresses the the of their constituents through branches needs needs of the people? different sources (e.g., U.N. Charter, · Various forms of of the people. 3. What are the roles Declaration of the Rights of Man, · Research a local problem and address how state and of U.N. Declaration of Human Rights, local governments local the different levels of U.S. Constitution). DOK 2 · Levels of state government can propose solutions to this problem in the state government? government: state, form of a feature article. (Writing Portfolio - Transactive) county, local · Interview local business leaders who explain the impact SS-HS-1.1.3 Students will evaluate · Powers denied how the U.S. government's response to local laws have on their businesses. to contemporary issues and societal states and 9th and · Examine the previous year’s budget and prioritize where problems (e.g., education, welfare 10th amendments the expenditures should be made. system, health insurance, childcare,
crime) reflects the needs, wants, and · State revenues demands of its citizens (e.g., · State expenses individuals, political action · Local issues committees, special interest groups, political parties).
SS-HS-1.3.1 Students will explain and give examples how the rights of one individual (e.g., smoking in public places, free speech) may, at times, be in conflict (e.g., slander,
libel) with the rights of another. DOK 2 SS-HS-1.3.2 Students will explain how the rights of an individual (e.g., Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
Freedom of information Act, privacy) may, at times, be in conflict with the responsibility of the government to protect the SS-HS-2.1.1 Students will explain how belief systems, knowledge, technology and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2
SS-HS-2.2.1 Students will explain how various human needs are met through interaction in and among social institutions (e.g., family, religion, education, government, economy) in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and the United States (Reconstruction to present).
SS-HS-3.2.1 Students will compare and contrast economic systems (traditional, command, market, mixed) based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security and growth in the modern world. DOK 2
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum Unit: Basic of Economics Essential Questions toward Course Key Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments 1. What is SS-HS-3.1.1 Students will give economics economics? examples of and explain how scarcity scarcity of resources necessitates factors of choices at both the personal and production Have students use a four column retrieval chart to 2. What are the societal levels in the modern land identify characteristics of traditional, command, market, types of economic world (1500 A.D. to present) and and mixed economies. Brainstorm examples (specific systems? the United States (Reconstruction labor countries) of each. to present) and explain the impact goods of those choices. DOK 2 services Ask students to use a 4 point scale to rate each of the 3.Explain supply capital types of economies listed above as to: freedom, and demand. productivity effeciency, equity, security and growth. SS-HS-3.1.2 Students will explain entreperneurship 4. How does one go how governments have limited technology budgets, so they must compare about starting a consumer Tell student that the American Economic system is revenues to costs and consider business? deposable income often referred to as a "free enterprise" system. Have opportunity cost when planning students work in pairs writing down what they think the public projects. discretionary funds characteristics of a free enterprise system are. Discuss rational choices and debate as a class. competitive advertising 5. Explain the SS-HS-3.2.1 Students will compare concepts of and contrast economic systems informative advertising competition and (traditional, command, market, bait and switch Note that the government sometimes finds it necessary monopolies among mixed) based on their abilities to comparision to intervene in a free enterprise system. Brainstorm businesses. achieve broad social goals such shopping situations in which there has been a need for as freedom, efficiency, equity, warranty government intervention (e.g., monopolies, truth in security and growth in the modern brand name advertising, public safety) world. DOK 2 generic brand economic system Invite a banker as a guest speaker. Have students SS-HS-3.2.3 Students will explain traditional economy develop a set of questions for the interview prior to the how, in a free enterprise system, command economy visit. Be sure to include a question about the role of the individuals attempt to maximize market economy Federal Reserve Bank. their profits based on their role in market the economy (e.g., producers try mixed economy Have students create a flow chart to follow the route a Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum capitalism check takes from consumer to bank for payment. laissez faire to maximize resources, free enterprise Have students visit the Federal Reserve's website to entrepreneurs try to maximize system learn more about this institution. profits, workers try to maximize profit profit incentive private property SS-HS-3.3.1 Students will explain competition Invite a Labor Union leader in to discuss the role that and give examples of how Adam Smith labor unions play in the American economy. numerous factors influence the supply and demand of products Discuss the fact that in a market economy (capitalism) (e.g., supply—technology, cost of everyone tries to maximize their profits based on their inputs, number of sellers: demand role in the economy. Have students list these four —income, utility, price of similar groups: producers, workers, savers, investors. They products, consumers' should then explain how each one makes a profit. preferences). DOK 2 Discuss the give-and-take among these groups (e.g., Producers may make a lower profit if they pay their SS-HS-3.3.4 Students will explain workers more.) how laws and government mandates (e.g., anti-trust legislation, tariff policy, regulatory policy) have been adopted to maintain competition in the United States and in the global marketplace.
SS-HS-3.4.2 Students will describe and give examples of how factors such as technological change, investments in capital goods and human capital/resources have increased productivity in the world. DOK 2
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum Unit: Practical Economics
Essential Questions Key toward Course Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments 1. What is your role SS-HS-3.1.1 Students will give scarcity, want, Have students brainstorm responses to the question as a consumer? examples of and explain how need, opportunity "What is scarcity?" Each student should then make a scarcity of resources necessitates cost chart with two columns. In the left column list these 2. What does is choices at both the personal and categories: individual, family, school, local government, mean to go into societal levels in the modern world state government, national government. Entitle the debt? (1500 A.D. to present) and the second column "Wants" and have students write down United States (Reconstruction to How scarcity of the kinds of "wants" each of those in the first column 3.How do you present) and explain the impact of resources have. Discuss ways in which decisions are made at necessitates choices determine what is a those choices. DOK 2 at both the personal each level. necessity? and societal levels? Help students define the term "opportunity costs" (the SS-HS-3.1.2 Students will explain how cost of the next best alternative use of money, time, or 4. How do you save governments have limited budgets, so resources when one choice is made rather than and invest your they must compare revenues to costs another) Have students provide examples at the money? How do the federal, personal level. and consider opportunity cost when state, and local planning public projects. governments having limited budgets, Have students collect current event articles that show SS-HS-3.2.1 Students will compare compare revenues to costs when planning how the three levels of government make public and contrast economic systems public projects? choices for their constituents. (traditional, command, market, Post the articles and then have students make lists of mixed) based on their abilities to the types of spending or projects at each level. Discuss achieve broad social goals such as How does one findings. freedom, efficiency, equity, security make informed and growth in the modern world. choices, DOK 2 consumers must Discuss the kinds of "opportunity costs" that occur when analyze government decisions are made. (The terms "trade offs" advertisements, is also used when discussing this type issue.) SS-HS-3.2.3 Students will explain consider personal
how, in a free enterprise system, finances
individuals attempt to maximize (including the Have students keep a spending log. After several days their profits based on their role in importance of have the students note what choices they made. Also the economy (e.g., producers try to savings, have them note economic goods or services that they maximize resources, entrepreneurs investment, and wanted, but did not get. Discuss reasons for choices. try to maximize profits, workers try use of credit), and Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
Have students compare the advantages and to maximize income, savers and examine disadvantages of using credit cards vs. cash spending. investors try to maximize return). opportunity cost?
SS-HS-3.3.1 Students will explain and give examples of how numerous factors influence the supply and demand of products (e.g., supply— technology, cost of inputs, number of sellers: demand—income, utility, price of similar products, consumers' preferences). DOK 2
SS-HS-3.3.2 Students will explain how specific financial and non-financial incentives often influence individuals differently (e.g., discounts, sales promotions, trends, personal convictions).
SS-HS-3.4.3 Students will explain and give examples of how interdependence of personal, national and international economic activities often results in international issues and concerns (e.g., natural resource dependencies, economic sanctions, environmental and humanitarian issues) in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and the United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2
SS-HS-4.3.1 Students will describe Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum the movement and settlement patterns of people in various places and analyze the causes of that movement and settlement (e.g., push factors such as famines or military conflicts; pull factors such as climate or economic opportunity) and the impacts in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 3
SS-HS-5.2.4 Students will explain and evaluate the impact of significant social, political and economic changes during the Progressive Movement (e.g., industrial capitalism, urbanization, political corruption, initiation of reforms), World War I (e.g., imperialism to isolationism, nationalism), and the Twenties (e.g., economic prosperity, consumerism, women’s suffrage). DOK 3
SS-HS-5.3.6 Students will explain how the second half of the 20th century was characterized by rapid social, political and economic changes that created new challenges (e.g., population growth, diminishing natural resources, environmental concerns, human rights issues, technological and scientific advances, shifting political alliances, globalization of Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
the economy) in countries around the world, and give examples of
Unit: Basics of Geography
Essential Questions Key toward Course Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments What is geography? SS-HS-4.1.1 Students will use a Themes: location, Use introductory activity to become familiar with new variety of geographic tools (e.g., place, region, students. Briefly describe the Survey of the Social Analyze the maps, globes, photographs, movement, Sciences course and this semester's emphasis. Set distribution of models, satellite images, charts, human/environment classroom expectations. physical and human graphs, databases) to explain and interaction features on Earth’s analyze the reasons for the surface. distribution of physical and human Divide class into small groups (2-3) and have each features on Earth's surface. DOK 3 Direction and distance group brainstorm the question: In what ways does Use representations geography touch our everyday lives? Have groups of Earth and latitude and longitude report their responses (verbally or on chart paper databases to posted around the classroom). analyze the SS-HS-4.1.2 Students will explain distribution of map symbols and how mental maps, the mental image a legends physical and human person has of an area including features on Earth’s knowledge of features and spatial Have student groups (4-5 members) create a map of surface. relationships, become more complex the world (continents) from memory. The world is to be
as experience, study, and the media types of maps torn out rather than cut with scissors. Continents should bring new geographic information Explain how the be placed in the appropriate location and students are location and to label everything they can on the map. Maps will be displayed and judged at the end of the activity using distribution of human SS-HS-4.1.3 Students will use map projections in atlases or the classroom. features on Earth’s geographic tools (e.g., maps, globes, surface are based photographs, models, satellite on reasoning and images) to explain the reasoning Provide students with a list of key concepts and terms patterns. patterns (e.g., available used in the study of geography. Have them use transportation, location of resources concept maps or other vocabulary building activities to and markets, individual preference, define and understand each term. Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
centralization versus dispersion) on Review major concepts related to the Five Themes of which the location and distribution of Geography
SS-HS-4.2.2 Students will explain Have students create a chart with these headings: how physical (e.g., climate, local, national, and international. Give examples of mountains, rivers) and human each of the five themes of geography for each of the characteristics (e.g., interstate three levels. Use headlines/articles from daily highways, urban centers, newpapers when possible. workforce) of regions create advantages and disadvantages for human activities in a specific place. DOK 2
SS-HS-4.3.1 Students will describe the movement and settlement patterns of people in various places and analyze the causes of that movement and settlement (e.g., push factors such as famines or military conflicts; pull factors such as climate or economic opportunity) and the impacts in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 3
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum Unit: Geography Skills and Earth Look
Essential Questions Key toward Course Objectives Kentucky Core Content Version 4.1 Concepts/Vocab Suggested Activities and Assessments 1. How do you read SS-HS-4.1.1 Students will use a Review the five Have students brainstorm ways in which they use a map? variety of geographic tools (e.g., themes of geography skills in everyday life. maps, globes, photographs, geography 2. Locate countries, models, satellite images, charts, Differentiate between weather and climate. continents, rivers, graphs, databases) to explain and Nature and mountains, etc. on analyze the reasons for the structure of the maps. distribution of physical and human earth Have students discuss the influence of mountains, 3. How does features on Earth's surface. DOK 3 plains, and bodies of water on climate and vegetation. geography relates to atmosphere Have students give examples of how physical features other disciplines and SS-HS-4.2.2 Students will explain weathering may limit or promote human activities and ask students you personally? how physical (e.g., climate, erosion to give specific examples. mountains, rivers) and human characteristics (e.g., interstate highways, urban centers, distribution of natural Have students label the major landforms, and rivers resources workforce) of regions create and lakes in the US and Canada. Then ask students to
advantages and disadvantages for discuss how these physical features affect climate and human activities in a specific place. vegetation in the US and Canada, and how these DOK 2 nonrewnable resource physical features have limited or promoted human activities. SS-HS-4.4.3 Students will explain how renewable resource group and individual perspectives impact the use of natural resources imports Have student label major landforms, rivers, lakes, and (e.g., mineral extraction, land cities of Latin America. Discuss the ways in which the reclamation). physical features affect human activities in Latin exports America and speculate as to the reasons for the
SS-HS-4.4.1 Students will explain how locations of major cities. humans develop strategies (e.g., Understand the transportation, communication, physical and cultural Have students label the European countries and major technology) to overcome limits of their landforms and bodies of water. Relate landforms and physical environment. geography of North America, bodies of water to political boundaries. Discuss which
South America, physical features may have promoted human activities SS-HS-4.1.2 Students will explain how Latin America, and which may limit human activities. mental maps, the mental image a Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum
Europe, Africa, Give students a blank map of Africa. Have students
Asia, Australia develop their own maps which include color, scale, a person has of an area including legend, and label physical/topographical features. knowledge of features and spatial relationships, become more complex as experience, study, and the media
SS-HS-4.1.3 Students will use geographic tools (e.g., maps, globes, Using maps, atlases and other visual aides provide an overview of the continent of Asia. Note the regions that photographs, models, satellite images) to explain the reasoning patterns (e.g., are often used to study this area of the world and ask available transportation, location of students (think-pair-share) to speculate as to the resources and markets, individual reasons for the divisions. preference, centralization versus dispersion) on which the location and distribution of Earth's human features is based.
SS-HS-4.3.2 Students will explain how technology (e.g., computers, telecommunications) has facilitated the movement of goods, services and populations, increased economic interdependence at all levels, and influenced development of centers of economic activity. DOK 2
SS-HS-4.1.2 Students will explain how mental maps, the mental image a person has of an area including knowledge of features and spatial relationships, become more complex as experience, study, and the media
Harrison County High School Integrated Social Studies Curriculum bring new geographic information.
SS-HS-2.1.1 Students will explain how belief systems, knowledge, technology and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2
SS-HS-4.2.4 Students will explain how people from different cultures with different perspectives view regions
(e.g., Middle East, Balkans) in different ways, sometimes resulting in conflict in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present).
SS-HS-4.4.2 Students will explain how human modifications to the physical environment (e.g., deforestation, mining), perspectives on the use of natural resources
(e.g., oil, water, land), and natural disasters (e.g., earthquakes, tsunamis, floods) may have possible global effects (e.g., global warming, destruction of the rainforest, acid rain) in the modern world (1500 A.D. to present) and United States (Reconstruction to present). DOK 2